Topic what is square of 6: Curious about the square of 6? Discover the straightforward calculation and delve into its significance across various contexts. Whether in mathematics or practical applications, understanding \( 6^2 \) illuminates its relevance and usefulness. Join us as we explore why this simple mathematical operation holds such importance.
Table of Content
Square of 6
The square of 6, denoted as \( 6^2 \), equals 36.

READ MORE:
Overview of the Square of 6
The square of 6, denoted as \( 6^2 \), is calculated by multiplying 6 by itself. This results in:
| Calculation: | \( 6 \times 6 = 36 \) |
Understanding \( 6^2 \) is fundamental in arithmetic and mathematics. It represents the area of a square with sides of length 6 units and is used extensively in algebraic equations and geometric calculations.
Calculation of 6 Squared
To calculate the square of 6, we follow these steps:
- Identify the number to be squared: 6.
- Multiply the number by itself: \(6 \times 6\).
Using basic multiplication:
\[ 6 \times 6 = 36 \]
Therefore, the square of 6 is 36.
To break this down further, we can visualize the calculation using a table:
| Step | Operation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | 6 × 6 | 36 |
Thus, the square of 6, written as \(6^2\), equals 36.
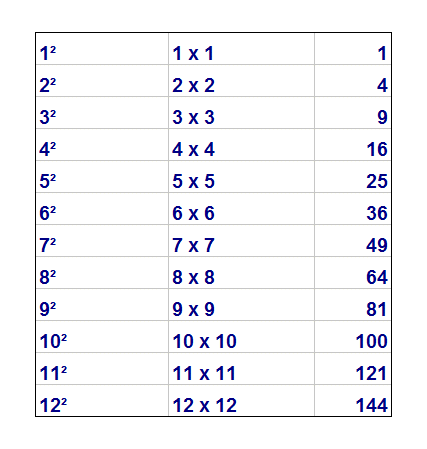
Properties of 6^2
The square of 6, denoted as \(6^2\), is a perfect square with several important properties. Below are some key properties and details of \(6^2\):
- Value: The square of 6 is \(6^2 = 36\).
- Even Number: Since 36 is an even number, it can be divided by 2 without any remainder.
- Positive Integer: \(6^2\) is a positive integer as it results from squaring a positive number.
- Multiples and Divisors:
- Multiples: 36 is a multiple of 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 36.
- Divisors: The divisors of 36 include 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 36.
- Prime Factorization: The prime factorization of 36 is \(2^2 \times 3^2\).
- Geometric Interpretation: As a square, 36 can be represented as the area of a square with each side measuring 6 units. The formula for the area of a square is: \[ \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 = 6^2 = 36 \]
- Square Root: The square root of 36 is 6: \[ \sqrt{36} = 6 \]
- Quadratic Equation: \(6^2\) can be a solution to the quadratic equation \(x^2 = 36\), where \(x = \pm 6\).
- Applications: The number 36 appears in various mathematical contexts such as geometry (area of squares), number theory (properties of integers), and can be used in real-world applications like measuring square plots of land.
Applications of the Square of 6
The square of 6, which is 36, has various practical applications in different fields. Here are some of the key applications:
- Geometry: Squares are fundamental in geometry for calculating areas and perimeters. For instance, if you have a square with each side measuring 6 units, its area is \(6^2 = 36\) square units.
- Architecture: In building design, squares are used to ensure precise measurements and create aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound buildings. The square footage calculation often involves squaring the side lengths.
- Interior Design: To determine the number of tiles required for a room, designers calculate the area by squaring the room dimensions. For a room with a side length of 6 feet, the area covered is 36 square feet.
- Science: In physics and chemistry, square calculations are used to determine properties like the intensity of sound waves or radiation absorption, which follow the inverse square law.
- Statistics: Squares are used in statistical measures such as variance and standard deviation, helping to quantify data variability. For instance, the variance is calculated as the average of squared deviations from the mean.
- Finance: In finance, square roots are used to compute stock market volatility, which helps investors assess risk. This involves taking the square root of the variance of stock returns.
- Computer Science: In algorithms, particularly in cryptography and graphics, squares and square roots are essential for tasks such as encryption and calculating distances in 2D/3D space.
- Navigation: Squares and square roots are used in navigation to compute distances and bearings between points on a map, crucial for accurate plotting of courses.
Understanding the applications of squares, like that of 6, highlights their importance in both theoretical and practical contexts, making them a fundamental concept in various disciplines.
Conclusion
The square of 6, represented as \(6^2\), is a fundamental concept in mathematics with various interesting properties and practical applications. We have seen that squaring a number involves multiplying the number by itself, leading to the result \(6 \times 6 = 36\). This operation is straightforward but forms the basis for more complex mathematical concepts and real-world applications.
Throughout this article, we explored the calculation, properties, and applications of the square of 6:
- Calculation: We detailed the simple steps to calculate \(6^2\) and highlighted its significance as a perfect square.
- Properties: We examined how the square of 6 fits into the broader context of perfect squares and its algebraic characteristics, including its behavior with negative numbers and the consistency of its positive result.
- Applications: We discussed various real-world uses, from geometry to technology, where the square of 6 plays a role in calculations, designs, and problem-solving.
Understanding squares, including \(6^2\), is crucial not only for academic purposes but also for practical applications in everyday life and advanced fields. Whether it is in constructing geometrical shapes, analyzing data, or solving equations, the principles of squaring numbers provide a foundation for further mathematical exploration and innovation.
In conclusion, the square of 6 exemplifies the beauty and utility of mathematical operations. By mastering such fundamental concepts, we equip ourselves with the tools to tackle more complex challenges and appreciate the mathematical structures that underpin much of the world around us.
Video này hướng dẫn cách bình phương một số và giải thích ý nghĩa của việc bình phương số. Theo dõi để hiểu rõ hơn về số mũ và cách áp dụng trong toán học.
Làm Thế Nào Để Bình Phương Một Số | Bình Phương Số Nghĩa Là Gì? | Số Mũ | Toán Học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Video này giải thích về số bình phương, giúp bạn hiểu rõ khái niệm và cách nhận diện các số bình phương trong toán học. Hãy theo dõi để nắm bắt kiến thức về số bình phương.
Số Bình Phương Là Gì | Các Con Số | Toán Học | FuseSchool