Topic what is square root of 625: The square root of 625 is a fundamental concept in mathematics with various practical applications. In this article, we explore what the square root of 625 is, how to calculate it, and its relevance in different fields. Join us to uncover the significance of this intriguing mathematical figure.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 625
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding Square Roots
- Definition and Basic Concept
- Mathematical Notation of Square Roots
- Methods to Find Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method
- Estimation and Approximation Method
- Using a Calculator
- Step-by-Step Calculation of Square Root of 625
- Verification of the Result
- Applications of Square Root of 625
- Real-Life Examples and Usage
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu về căn bậc hai của 625. Video này giải thích chi tiết và ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai của 625.
Square Root of 625
The square root of 625 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 625. This number is 25. In mathematical notation, this is expressed as:
Calculation
To understand why the square root of 625 is 25, consider the following calculation:
Method
There are several methods to find the square root of a number:
- Prime Factorization
- Estimation and Approximation
- Using a Calculator
For 625, the prime factorization method is straightforward:
Therefore, the square root of 625 is:

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 625 is a number that satisfies the equation:
This means that \(25 \times 25 = 625\). Understanding square roots is essential for various mathematical calculations and real-life applications. Let's explore the concept in more detail:
- Square roots are denoted by the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \).
- The number under the radical symbol is called the radicand.
- Finding a square root is the inverse operation of squaring a number.
There are several methods to calculate square roots, including:
- Prime Factorization
- Estimation and Approximation
- Using a Calculator
In this article, we will delve deeper into these methods, starting with the square root of 625, and demonstrate their practical applications.
Understanding Square Roots
Square roots are an essential concept in mathematics, providing insight into the relationship between numbers and their factors. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number. For instance, the square root of 625 is:
This is because \(25 \times 25 = 625\). To understand square roots better, consider the following points:
- Notation: The square root is represented by the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \).
- Radicand: The number inside the radical symbol is called the radicand.
- Inverse Operation: Taking the square root is the inverse operation of squaring a number.
Properties of Square Roots
Square roots have several important properties:
- Non-negative Output: The square root of a non-negative number is also non-negative.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 625 that are the square of integers are called perfect squares.
- Multiplication: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots:
Calculating Square Roots
There are various methods to calculate square roots:
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down the number into its prime factors and pairing them.
- Estimation and Approximation: Using methods like the average of estimates to find a close value.
- Using a Calculator: The most straightforward way for most practical purposes.
Let's delve deeper into these methods by considering the square root of 625. By understanding and applying these methods, you can calculate the square root of any number efficiently.
Definition and Basic Concept
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. Mathematically, if \( x \) is the square root of \( y \), then:
For example, the square root of 625 is 25 because:
The square root symbol is \( \sqrt{} \), and the number under the symbol is called the radicand. In the case of \( \sqrt{625} \), 625 is the radicand, and the expression evaluates to 25.
Basic Properties of Square Roots
- Non-Negative Output: The square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative.
- Unique Positive Square Root: Every positive number has a unique positive square root.
- Zero: The square root of zero is zero.
Square Roots of Perfect Squares
Perfect squares are numbers that have integer square roots. For example, 625 is a perfect square because its square root is an integer (25). Other examples include:
- \( \sqrt{1} = 1 \)
- \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \)
- \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \)
- \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \)
- \( \sqrt{625} = 25 \)
Finding Square Roots
To find the square root of a number, you can use various methods:
- Prime Factorization: Decompose the number into its prime factors and pair them. For example, 625 can be factored into \( 5 \times 5 \times 5 \times 5 \), and pairing the factors gives \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \).
- Estimation and Approximation: Use trial and error or methods like averaging to approximate the square root.
- Calculator: Use a calculator for quick and accurate results.
Understanding these concepts helps in comprehending the mathematical significance of square roots and their applications in various fields.
Mathematical Notation of Square Roots
The square root of a number is denoted using the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \). The number inside the radical symbol is called the radicand. For example, in \( \sqrt{625} \), 625 is the radicand. The result is the number which, when squared, gives the radicand. For instance:
Here, \( \sqrt{625} = 25 \) because \( 25 \times 25 = 625 \).
Radical Symbol
The radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \) is used to denote the square root operation. It is essential to understand the components of this notation:
- Radicand: The number under the radical symbol. In \( \sqrt{625} \), the radicand is 625.
- Index: Although typically omitted in square roots, the index indicates the degree of the root. For square roots, the index is 2, as in \( \sqrt[2]{625} \).
Mathematical Properties
The mathematical notation of square roots follows certain properties:
- Product Property: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots:
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots:
- Power Property: The square root can be expressed as an exponent:
Examples
Consider some examples of square roots:
Understanding the notation and properties of square roots allows for a deeper comprehension of their mathematical significance and application.

Methods to Find Square Roots
Finding the square root of a number can be done using several methods, each with its own advantages. Below are some common techniques used to determine the square root:
1. Prime Factorization
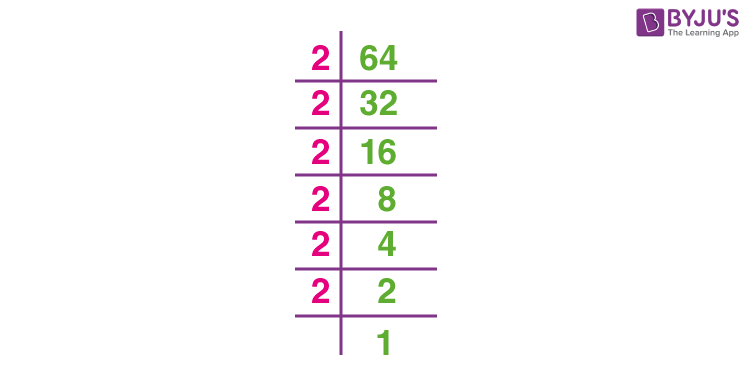
Prime factorization involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and then pairing them to find the square root. For example, to find the square root of 625:
- Factorize 625 into prime factors:
- Pair the prime factors:
- Take one factor from each pair:
So, the square root of 625 is 25.
2. Estimation and Approximation
This method involves estimating the square root by finding two close perfect squares between which the number lies and then refining the estimate. For example, for 625:
- Identify two perfect squares around 625: 400 (202) and 900 (302).
- Since 625 is closer to 676 (262), refine the estimate to 25.
This method gives an approximate value, which can be further refined if necessary.
3. Using a Calculator
Calculators provide a quick and accurate way to find square roots. Most scientific calculators have a square root function:
- Enter 625.
- Press the square root (√) button.
- The display shows 25.
This method is straightforward and reliable for practical purposes.
4. Long Division Method
The long division method is a manual way to find the square root, which is more detailed but accurate. Here's how it works for 625:
- Group the digits in pairs from right to left: (6)(25).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first group (6): 2 (since 22 = 4).
- Subtract the square of this number from the first group and bring down the next group: 6 - 4 = 2, bring down 25 to get 225.
- Double the number found in step 2 and place it as the next divisor: 2 × 2 = 4.
- Determine the next digit of the quotient, which, when added to 40 and multiplied by it, is less than or equal to 225: 45 × 5 = 225.
- The quotient is 25, which is the square root of 625.
These methods provide various ways to understand and calculate square roots, each useful in different contexts.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a straightforward way to find the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. Here is a step-by-step guide to finding the square root of 625 using this method:
- Find the prime factors of 625:
To start, divide 625 by the smallest prime number possible. Continue dividing until you cannot divide anymore, always using prime numbers.
- 625 is divisible by 5 (since the last digit is 5).
- 625 ÷ 5 = 125
- 125 is divisible by 5.
- 125 ÷ 5 = 25
- 25 is divisible by 5.
- 25 ÷ 5 = 5
- 5 is divisible by 5.
- 5 ÷ 5 = 1
So, the prime factors of 625 are 5, 5, 5, and 5.
- Express the number as a product of prime factors:
Write 625 as a product of its prime factors:
- Pair the prime factors:
Group the prime factors into pairs of the same number:
- Take one number from each pair:
Take one number from each pair and multiply them:
Therefore, the square root of 625 is 25, as illustrated by the prime factorization method.
Estimation and Approximation Method
Estimating and approximating the square root of a number is a useful skill, especially when you do not have access to a calculator. Here, we will walk through the steps to estimate and approximate the square root of 625.
-
Identify Perfect Squares: First, identify the perfect squares closest to 625. We know that:
- \(20^2 = 400\)
- \(25^2 = 625\)
- \(30^2 = 900\)
Since \(625\) is exactly \(25^2\), it is already a perfect square. However, for learning purposes, we'll proceed with estimation techniques assuming the number wasn't a perfect square.
-
Choose Two Closest Perfect Squares: Select the two perfect squares that 625 lies between. In this case, we would choose \(20^2 = 400\) and \(30^2 = 900\).
-
Find the Midpoint: Calculate the midpoint between the two numbers:
\(\frac{20 + 30}{2} = 25\)
Since 625 is exactly \(25^2\), we know the square root of 625 is 25. However, if we were approximating a non-perfect square, we'd proceed by squaring the midpoint and adjusting accordingly.
-
Adjust the Estimate: For non-perfect squares, if the squared midpoint is higher than 625, adjust the midpoint downwards, and if it is lower, adjust upwards. For instance:
If our guess was 24:
- \(24^2 = 576\) which is less than 625.
So, we would try a higher number, such as 26:
- \(26^2 = 676\) which is more than 625.
-
Refine the Estimate: Continue adjusting the estimate up or down, narrowing the range until the squared value is close to 625. For example, trying 24.5:
\(24.5^2 = 600.25\)
Since \(600.25 < 625\), we would try a slightly higher value like 24.8.
\(24.8^2 = 615.04\)
And then try a higher value again, like 25.2:
\(25.2^2 = 635.04\)
This iterative process continues until the estimate is satisfactorily close to the square root of 625.
Through this method, you can estimate the square root of any number, adjusting your guesses and narrowing down to an accurate approximation. In the case of 625, since it is a perfect square, we directly find the square root to be 25.
Using a Calculator
Finding the square root of 625 using a calculator is a straightforward process. Here are the detailed steps you can follow:
- Turn on your calculator: Ensure your calculator is powered on and in working condition.
- Locate the square root button: On most calculators, this is represented by the symbol \(\sqrt{}\) or sometimes as \(x^{1/2}\).
- Enter the number: Key in the number 625 using the numerical keypad.
- Press the square root button: After entering 625, press the square root button (\(\sqrt{}\)). The calculator will process the input.
- Read the result: The display should show the result, which is 25. This is because \( \sqrt{625} = 25 \).
Using a calculator simplifies the process and ensures accuracy, especially when dealing with large numbers or more complex calculations.

Step-by-Step Calculation of Square Root of 625
Calculating the square root of 625 can be done using several methods. Here, we will use the prime factorization method and the long division method.
Prime Factorization Method
- Find the prime factors of 625:
- 625 is an odd number, so it is not divisible by 2.
- It ends in 5, so it is divisible by 5: \( 625 \div 5 = 125 \)
- 125 ends in 5, so it is divisible by 5 again: \( 125 \div 5 = 25 \)
- 25 ends in 5, so it is divisible by 5: \( 25 \div 5 = 5 \)
- Finally, 5 is a prime number: \( 5 \div 5 = 1 \)
The prime factorization of 625 is \( 5 \times 5 \times 5 \times 5 \) or \( 5^4 \).
- Pair the prime factors: Group the prime factors into pairs: \( (5 \times 5) \times (5 \times 5) \).
- Take one factor from each pair: From each pair of 5s, take one 5: \( 5 \times 5 \).
- Multiply the selected factors: \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \).
Thus, the square root of 625 is 25.
Long Division Method
- Pair the digits from right to left: 625 can be divided into pairs: (6)(25).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (6):
- The largest number is 2 because \( 2^2 = 4 \leq 6 \) and \( 3^2 = 9 > 6 \).
- Subtract the square of this number from the first pair: \( 6 - 4 = 2 \).
- Bring down the next pair of digits (25) to the right of the remainder: This gives 225.
- Double the quotient (2) and place it next to the remainder: This gives 4_.
- Find the largest digit (X) such that \( 4X \times X \leq 225 \):
- The largest digit is 5 because \( 45 \times 5 = 225 \).
- Complete the quotient: The quotient is 25.
Thus, the square root of 625 is 25.
Verification of the Result
To verify that the square root of 625 is indeed 25, we can follow these steps:
- Mathematical Verification:
Square the number 25:
\[
25 \times 25 = 625
\]Since 625 is the original number, this confirms that the square root of 625 is 25.
- Using the Prime Factorization Method:
Break down 625 into its prime factors:
\[
625 = 5 \times 5 \times 5 \times 5
\]Pair the prime factors:
\[
(5 \times 5) \times (5 \times 5) = 25 \times 25 = 625
\]Thus, the square root of 625 is 25.
- Using a Calculator:
Enter 625 into a calculator and use the square root function (√). The calculator will display 25, verifying our result.
By using these methods, we can confidently verify that the square root of 625 is indeed 25.
Applications of Square Root of 625
The square root of 625, which is 25, finds applications in various fields. Here are some detailed examples:
- Mathematics and Education:
Understanding square roots, such as the square root of 625, is fundamental in mathematics. It helps students learn about perfect squares and their properties, as well as enhancing problem-solving skills.
- Geometry:
In geometry, the square root of 625 can be used to determine the side length of a square with an area of 625 square units. For example, if the area of a square is 625 square units, the side length is:
\[
\sqrt{625} = 25 \text{ units}
\] - Engineering and Construction:
Engineers and architects may use the square root of 625 in calculations involving square areas, such as determining dimensions for square plots of land or materials.
- Financial Modeling:
In finance, understanding the concept of square roots can be useful for modeling growth rates and understanding the principles of compound interest. For example, if an investment grows to 625 times its original value over a certain period, the square root can help determine the average growth rate.
- Technology and Computer Science:
Square roots are often used in algorithms for computer graphics, simulations, and optimizations. For instance, calculating distances in a 2D space often involves finding the square root of the sum of the squares of differences in coordinates.
- Everyday Life:
In practical everyday applications, such as carpentry or crafting, knowing the square root of 625 can help in creating precise measurements and ensuring accurate cuts for materials.
These examples illustrate how the square root of 625 is used in diverse fields, highlighting its importance and utility.
Real-Life Examples and Usage
The square root of 625, which is 25, can be observed in various real-life scenarios. Here are some detailed examples:
- Land Measurement:
Consider a square plot of land with an area of 625 square meters. To find the length of each side of the square, we calculate:
\[
\sqrt{625} = 25 \text{ meters}
\]This helps in determining the dimensions of the land for construction or agricultural purposes.
- Sports Fields:
In designing a square sports field with an area of 625 square yards, each side of the field will measure:
\[
\sqrt{625} = 25 \text{ yards}
\]This ensures the field is appropriately sized for the sport being played.
- Home Improvement Projects:
If a square tile has an area of 625 square centimeters, the side length of the tile can be found by:
\[
\sqrt{625} = 25 \text{ centimeters}
\]This is useful for calculating the number of tiles needed to cover a specific area.
- Art and Design:
Artists and designers often create works within specific dimensions. For example, a square canvas with an area of 625 square inches will have side lengths of:
\[
\sqrt{625} = 25 \text{ inches}
\]This helps in planning the layout and composition of the artwork.
- Gardening:
In gardening, if a square garden bed has an area of 625 square feet, each side of the garden bed will measure:
\[
\sqrt{625} = 25 \text{ feet}
\]This aids in planning the spacing and arrangement of plants.
These examples illustrate the practical applications of knowing the square root of 625, demonstrating its relevance in everyday activities and various professional fields.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the square root of 625, which is 25, is a concept that is both fundamental and widely applicable across various fields. Through our exploration, we have covered several key points:
- Understanding the Basics:
We started with the definition and basic concept of square roots, understanding that finding the square root of a number means identifying a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. In this case:
\[
\sqrt{625} = 25 \quad \text{because} \quad 25 \times 25 = 625
\] - Verification Methods:
We verified the result using different methods, including mathematical verification, prime factorization, and using a calculator. Each method confirmed that the square root of 625 is indeed 25.
- Applications:
The square root of 625 is utilized in various fields such as mathematics, geometry, engineering, financial modeling, technology, and everyday life. These applications highlight the importance and practicality of understanding square roots.
- Real-Life Examples:
Real-life examples of using the square root of 625 include measuring land areas, designing sports fields, home improvement projects, art and design, and gardening. Each example demonstrates how this mathematical concept is embedded in our daily activities.
By comprehensively understanding the square root of 625, we can appreciate its significance and utility. This knowledge not only enhances our mathematical skills but also provides practical benefits in various aspects of life.
Tìm hiểu về căn bậc hai của 625. Video này giải thích chi tiết và ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai của 625.
Căn Bậc Hai của 625
READ MORE:
Khám phá căn bậc hai của 625. Video này cung cấp giải thích chi tiết và các ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai của 625.
Căn Bậc Hai của 625