Topic what is square root of 64: Curious about the square root of 64? Delve into the fundamental concept of square roots and uncover the straightforward calculation for this popular mathematical query. Explore its significance in mathematics and practical applications through this concise introduction.
Table of Content
Square Root of 64
The square root of 64 is:
READ MORE:
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
2. Definition of Square Root
3. Calculation of Square Root of 64
4. Properties of Square Roots
5. Applications of Square Root in Mathematics
6. Conclusion
Introduction
The square root of 64 is a fundamental mathematical concept that involves finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 64. It is represented as $\sqrt{64}$ and has a precise value of 8. Understanding square roots is essential in various fields, including mathematics, physics, and engineering, where it plays a crucial role in calculations and problem-solving.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 64, denoted as $\sqrt{64}$, is 8 because $8 \times 8 = 64$. In mathematical terms, if $a^2 = b$, then $\sqrt{b} = a$. Understanding square roots is fundamental in mathematics for solving equations and understanding geometric properties.
Calculation of Square Root of 64
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 64 is the number that, when multiplied by itself, results in 64.
To calculate the square root of 64, follow these steps:
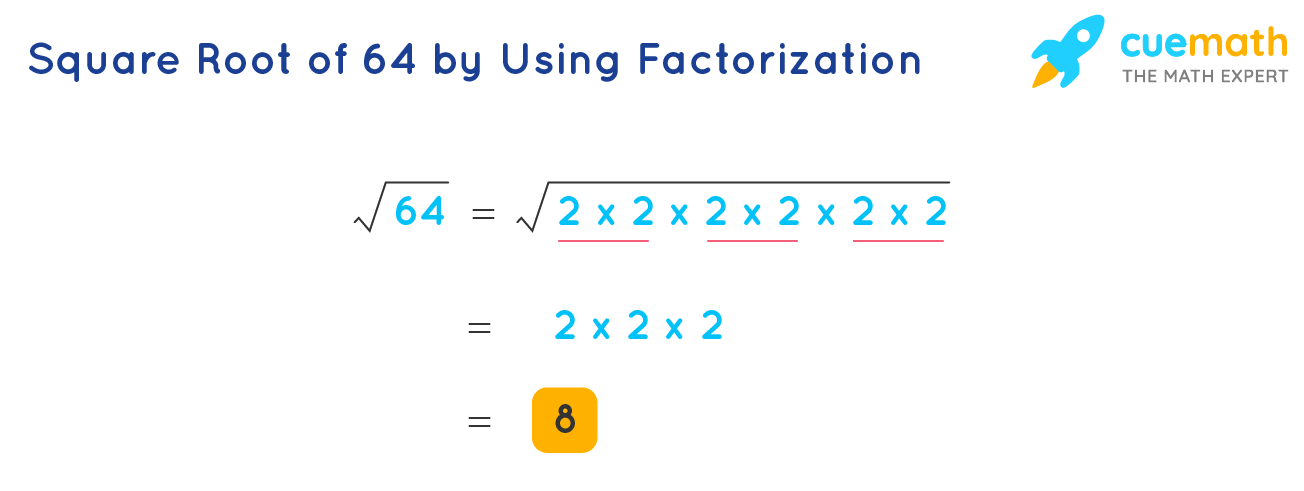
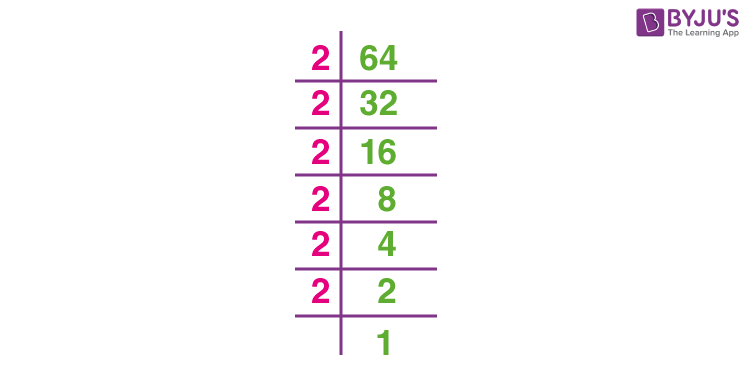
- Recognize that 64 is a perfect square. A perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer.
- Identify the integer that, when squared, equals 64. We know that:
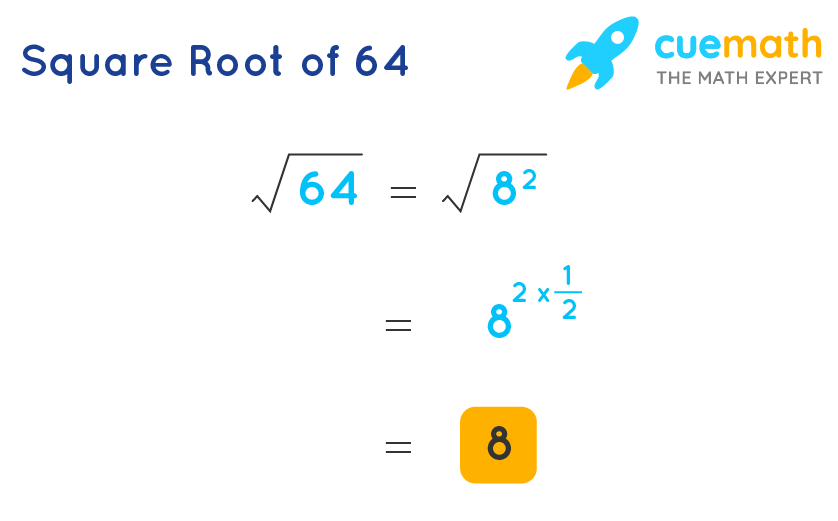
\( 8 \times 8 = 64 \) - Thus, the square root of 64 is:
\( \sqrt{64} = 8 \)
To confirm the calculation, you can use the property of exponents. The square root of a number \( x \) is the same as \( x \) raised to the power of \( \frac{1}{2} \):
| \( 64^{\frac{1}{2}} = 8 \) |
Hence, we have shown that the square root of 64 is indeed 8 through different methods of calculation.
Properties of Square Roots
The square root function has several important properties that are useful in various mathematical contexts. Here are some key properties of square roots:
- Non-negative Results: The square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative.
- \( \sqrt{x} \geq 0 \) for all \( x \geq 0 \)
- Product Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots.
- \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \)
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots.
- \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \) (for \( b \neq 0 \))
- Power Property: The square root of a number raised to an even power is the absolute value of the number raised to half that power.
- \( \sqrt{x^2} = |x| \)
- Sum of Square Roots: In general, the square root of a sum is not equal to the sum of the square roots.
- \( \sqrt{a + b} \neq \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b} \)
- Continuous and Increasing Function: The square root function is continuous and strictly increasing for all \( x \geq 0 \).
- If \( 0 \leq a < b \), then \( \sqrt{a} < \sqrt{b} \)
These properties of square roots are fundamental in algebra and are widely used in solving equations, simplifying expressions, and analyzing functions.
Applications of Square Root in Mathematics
The concept of square roots is fundamental in various areas of mathematics and has numerous practical applications. Here are some of the key applications of square roots in mathematics:
- Solving Quadratic Equations: Square roots are essential in solving quadratic equations of the form \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \).
- The quadratic formula \( x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a} \) involves the square root of the discriminant \( b^2 - 4ac \).
- Geometry: Square roots are used to calculate distances and lengths in geometry.
- The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the length of the hypotenuse \( c \) is given by \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the other two sides.
- Trigonometry: Square roots appear in trigonometric identities and formulas.
- For example, in the unit circle, the coordinates of points are often expressed using square roots, such as \( (\cos \theta, \sin \theta) = \left( \frac{1}{2}, \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right) \) for \( \theta = 30^\circ \).
- Statistics: The calculation of standard deviation, a measure of the spread of a set of values, involves square roots.
- The standard deviation \( \sigma \) is given by \( \sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^N (x_i - \mu)^2} \), where \( N \) is the number of values, \( x_i \) are the individual values, and \( \mu \) is the mean.
- Physics: Square roots are used in various physical formulas and calculations.
- For example, the formula for the period \( T \) of a simple pendulum is \( T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{L}{g}} \), where \( L \) is the length of the pendulum and \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity.
- Financial Mathematics: Square roots are used in financial calculations such as determining the volatility of asset prices.
- For example, the volatility \( \sigma \) can be estimated as the square root of the variance of the asset's returns.
These applications illustrate the wide-ranging importance of square roots in various mathematical disciplines and real-world scenarios.
Conclusion
In this article, we have explored the concept of the square root, specifically focusing on the square root of 64. We began with an introduction to the basic idea of square roots and how they are defined. The square root of 64, which is 8, was calculated and verified through different methods.
We also discussed various properties of square roots, such as the product property, quotient property, and the non-negative nature of square roots. These properties are fundamental in understanding and manipulating square roots in mathematical expressions.
Furthermore, we looked at the applications of square roots in different areas of mathematics, including solving quadratic equations, geometry, trigonometry, statistics, physics, and financial mathematics. These applications highlight the versatility and importance of square roots in both theoretical and practical contexts.
To summarize:
- The square root of 64 is 8.
- Square roots have essential properties that aid in simplifying and solving mathematical problems.
- Square roots are widely used across various mathematical fields and real-world applications.
Understanding the concept and properties of square roots enables us to solve complex problems more efficiently and appreciate the underlying principles in mathematics. The square root of 64, being a perfect square, provides a clear example to illustrate these important mathematical concepts.
Video này giải thích về căn bậc hai của 64, giúp người xem hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Căn Bậc Hai của 64
READ MORE:
Video này hướng dẫn cách tính căn bậc hai của 64, giúp người xem hiểu rõ về phương pháp tính toán này.
Cách Tính Căn Bậc Hai của 64: Sqrt(64)