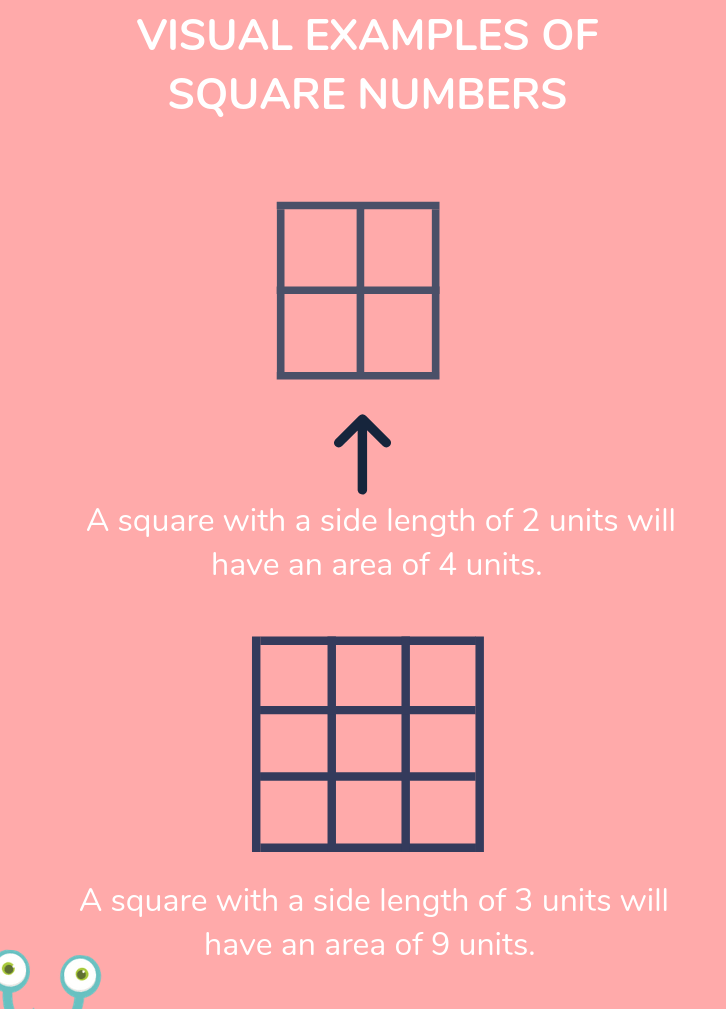Topic square root practice worksheet: Discover comprehensive square root practice worksheets designed to enhance your mathematical abilities. These worksheets cover a range of problems from basic to advanced, providing valuable practice for students of all levels. Perfect for exam preparation, homework, or extra practice, these resources are an excellent way to build confidence and proficiency in finding square roots.
Table of Content
- Square Root Practice Worksheets
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Basic Square Root Concepts
- Steps to Calculate Square Roots
- Finding Square Roots of Perfect Squares
- Square Root Practice Worksheets
- Methods to Calculate Square Roots
- Simplifying Square Roots
- Practice Problems
- Square Roots in Real Life
- Quizzes and Review Sheets
- Answer Keys and Explanations
- YOUTUBE: Video này cung cấp chìa khóa giải đáp và lời giải chi tiết cho bài tập thực hành căn bậc hai, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức một cách hiệu quả.
Square Root Practice Worksheets
Square root practice worksheets are essential tools for students to enhance their understanding of square roots. These worksheets provide a variety of problems to practice finding square roots of perfect squares, decimals, and simplifying non-perfect squares. Below are some detailed examples and types of worksheets available.
Benefits of Square Root Worksheets
- Improve understanding of square roots and their properties.
- Help students prepare for exams and competitions like Olympiads.
- Provide practice for solving square root problems both manually and with calculators.
Types of Square Root Worksheets
| Type | Description | Example Problems |
|---|---|---|
| Perfect Squares | Practice finding square roots of perfect squares. | √36, √144, √256 |
| Decimals | Finding square roots of decimal numbers. | √0.25, √1.44, √2.25 |
| Non-Perfect Squares | Simplify square roots of non-perfect squares to the simplest radical form. | √50, √75, √98 |
| Negative Numbers | Simplify square roots involving negative numbers using imaginary numbers. | √-4, √-25, √-49 |
Sample Worksheet Problems
- Find the square root of 324. (√324 = 18)
- Simplify √80. (√80 = 4√5)
- Find the square root of 2.25. (√2.25 = 1.5)
- Simplify √-144 using imaginary numbers. (√-144 = 12i)
Downloadable Worksheets
Additional Resources
For more practice and resources on square roots and other math topics, visit:

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, providing a foundation for understanding more complex algebraic and geometric principles. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 × 4 = 16.
Square roots are represented using the radical symbol (√). For instance, the square root of 25 is written as √25, which equals 5. Understanding how to calculate and simplify square roots is essential for solving various mathematical problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus.
Here are some key points to understand about square roots:
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. For example, both 3 and -3 are square roots of 9.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because their square roots are integers.
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that do not have integer square roots, such as 2 or 3, can be approximated to a decimal or left in radical form for exact representation.
- Simplifying Square Roots: To simplify a square root, factor the number into its prime components and pair the primes. For example, √72 can be simplified to 6√2 by factoring 72 into 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3.
Square roots also play a significant role in solving quadratic equations, working with Pythagorean theorem, and in various real-world applications such as physics and engineering. Regular practice with worksheets helps in mastering the calculation and application of square roots, ensuring a strong mathematical foundation.
Basic Square Root Concepts
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because \(5 \times 5 = 25\). Understanding square roots is fundamental in various areas of mathematics, including algebra and geometry. Here are some basic concepts:
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because they can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. For instance, \(16 = 4 \times 4\).
- Principal Square Root: The non-negative square root of a number. For example, the principal square root of 9 is 3, denoted as \(\sqrt{9} = 3\).
- Negative Square Roots: While the principal square root is non-negative, negative square roots also exist. For example, both 3 and -3 are square roots of 9 because \(3 \times 3 = 9\) and \((-3) \times (-3) = 9\).
- Estimating Square Roots: For non-perfect squares, square roots can be estimated. For instance, \(\sqrt{20}\) is approximately 4.47 because \(4.47 \times 4.47 \approx 20\).
Steps to Calculate Square Roots
- Identify if the number is a perfect square. If it is, determine the integer whose square gives the number.
- If the number is not a perfect square, use methods such as factorization or approximation to find the square root.
- For more precise values, use a calculator or long division method to compute the square root.
Understanding these basic concepts and steps can help in solving various mathematical problems involving square roots. Practicing with worksheets can further solidify these concepts and improve problem-solving skills.
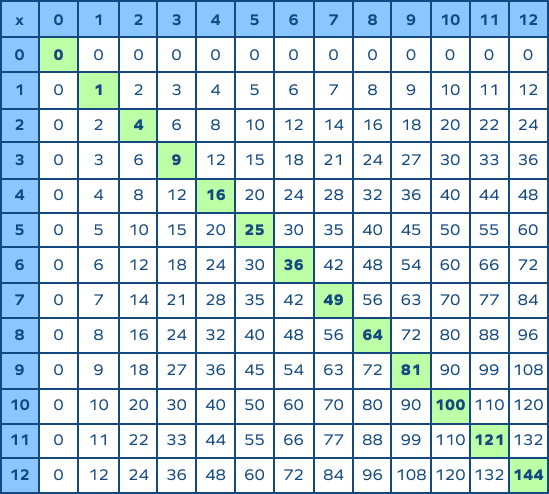
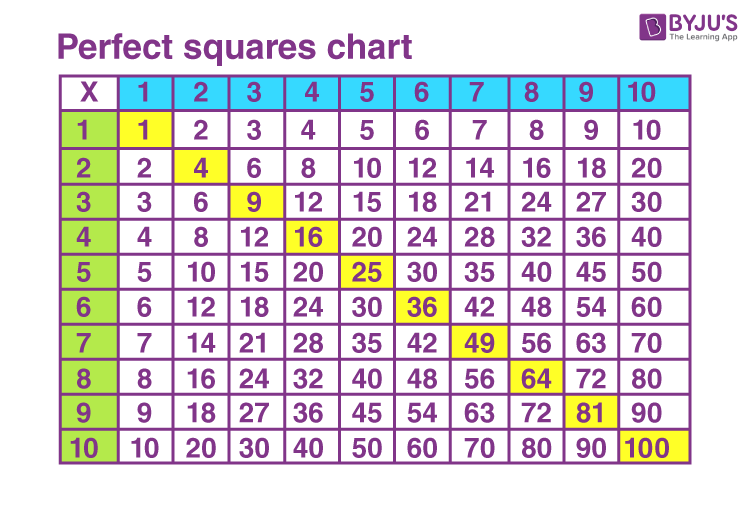
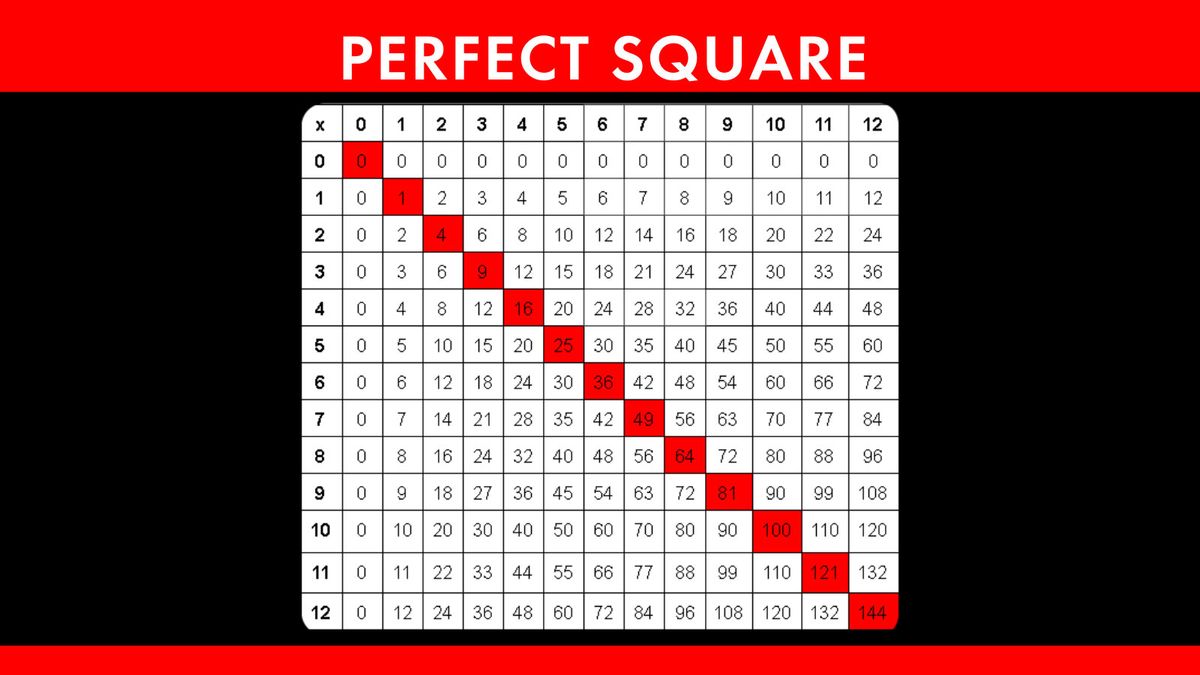
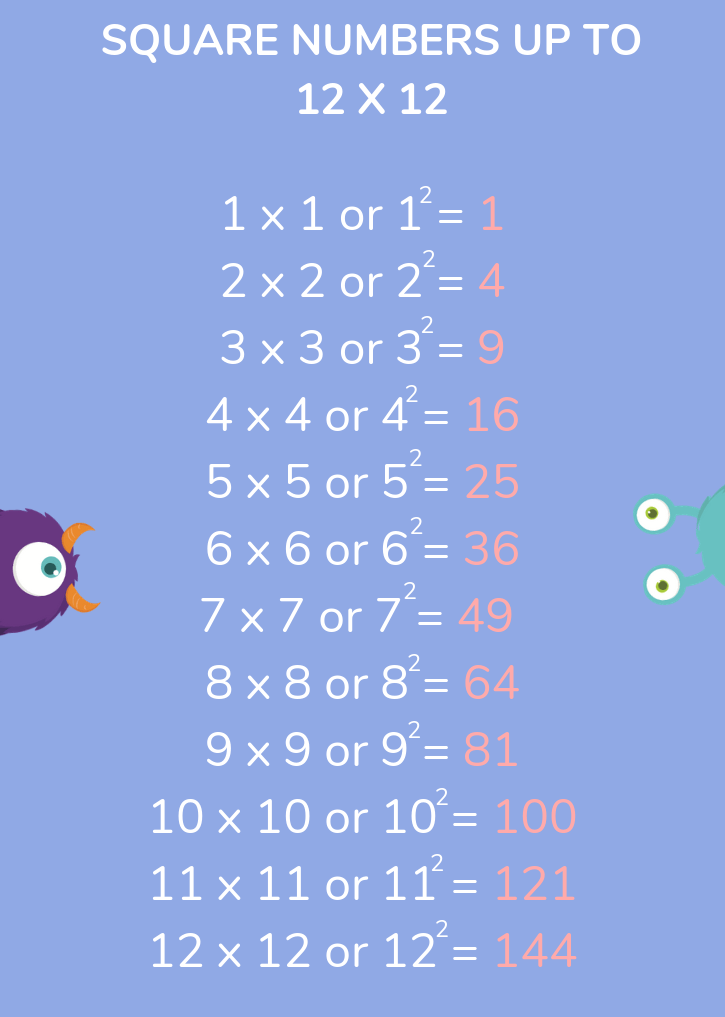
Finding Square Roots of Perfect Squares
Finding the square roots of perfect squares is a fundamental mathematical skill. A perfect square is a number that is the square of an integer. For instance, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, and so on are perfect squares because they can be expressed as \(1^2\), \(2^2\), \(3^2\), \(4^2\), \(5^2\), etc.
To find the square root of a perfect square, follow these steps:
- Identify the perfect square: Recognize if the number is a perfect square by checking if there exists an integer whose square equals the number.
- Use factorization: Factor the number into its prime factors and group the factors in pairs. For example, to find the square root of 36:
- Prime factorize 36: \(36 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\)
- Group the factors: \((2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3)\)
- Take one factor from each group: \(2 \times 3 = 6\)
- Practice with common perfect squares: Memorize the square roots of common perfect squares to speed up calculations, such as:
- \(\sqrt{1} = 1\)
- \(\sqrt{4} = 2\)
- \(\sqrt{9} = 3\)
- \(\sqrt{16} = 4\)
- \(\sqrt{25} = 5\)
- \(\sqrt{36} = 6\)
- Use a calculator for larger numbers: For very large perfect squares, using a calculator can be practical to find the square root efficiently.
Here is a table of some common perfect squares and their square roots for reference:
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
| 49 | 7 |
| 64 | 8 |
| 81 | 9 |
| 100 | 10 |
By understanding and practicing these steps, students can become proficient at finding the square roots of perfect squares and apply this knowledge to more complex mathematical problems.

Square Root Practice Worksheets
Square root practice worksheets are essential tools for students to enhance their understanding and proficiency in calculating square roots. These worksheets offer a variety of problems ranging from basic to advanced levels, helping students grasp the concept step-by-step.
- Basic Square Root Worksheets: These worksheets focus on finding the square roots of perfect squares, such as \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \). They help students practice and reinforce their basic skills.
- Intermediate Square Root Worksheets: These include problems that require finding the square roots of numbers that are not perfect squares. They challenge students to approximate square roots and understand irrational numbers.
- Advanced Square Root Worksheets: These worksheets involve more complex problems, including those that require solving equations involving square roots and applying square roots in different mathematical contexts, such as geometry and algebra.
Using a variety of square root practice worksheets can help students build a solid foundation in mathematics, making it easier for them to tackle more advanced topics in the future. Regular practice with these worksheets can significantly improve a student's problem-solving skills and confidence in math.
Methods to Calculate Square Roots
Calculating square roots can be done through various methods, each suitable for different levels of complexity and precision. Here are some common techniques:
- Prime Factorization: This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors. Group the prime factors into pairs and multiply one number from each pair to find the square root. For example, the square root of 36 is found by breaking it down into \(2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\), resulting in \(2 \times 3 = 6\).
- Long Division Method: This traditional method is useful for finding square roots of large numbers. It involves dividing the number into pairs of digits starting from the decimal point and finding the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the leftmost pair. This process is repeated for subsequent pairs.
- Estimation and Approximation: This involves finding two consecutive perfect squares between which the number lies and estimating the square root. For instance, for \(\sqrt{50}\), we know it lies between \(\sqrt{49}\) and \(\sqrt{64}\), hence between 7 and 8.
- Using a Calculator: Modern calculators can quickly find the square root of any number. Simply input the number and use the square root function to get the result.
- Newton’s Method: Also known as the iterative method, it starts with an initial guess and improves the guess iteratively using the formula: \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2}\left( x_n + \frac{S}{x_n} \right) \), where \(S\) is the number whose square root is to be found.
Each method has its own advantages, and choosing the right one depends on the context and the required precision. Practice with these methods will help you become proficient in calculating square roots efficiently.
Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots is an essential skill in algebra, helping to simplify expressions and solve equations more efficiently. Here is a step-by-step guide to simplifying square roots:
-
Identify the perfect square factors:
Look for factors of the number inside the square root that are perfect squares. For example, in √72, the factors are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, and 72. Among these, 1, 4, 9, and 36 are perfect squares.
-
Rewrite the square root:
Express the square root as the product of the square root of the perfect square factor and the square root of the remaining factor. For √72, we can write it as √(36 × 2) or √36 × √2.
-
Simplify the perfect square root:
Calculate the square root of the perfect square. For √36 × √2, the square root of 36 is 6. Therefore, √72 simplifies to 6√2.
-
Combine like terms (if any):
If you have multiple square roots to simplify, combine like terms where possible. For example, 3√18 + 2√8 can be simplified to 9√2 + 4√2, which equals 13√2.
Practicing these steps with various numbers and expressions will help solidify your understanding of simplifying square roots. Using worksheets that provide numerous examples and problems can be very beneficial.
Practice Problems
Strengthen your understanding of square roots with these practice problems. Work through a variety of questions to test your skills and improve your proficiency.
Basic Problems
- Find the square root of 16.
- Calculate the square root of 81.
- Determine the square root of 144.
Intermediate Problems
- What is the square root of 169?
- Simplify the square root of 225.
- Find the square root of 256.
Advanced Problems
- Calculate the square root of 1024.
- Simplify the square root of 2025.
- Find the square root of 4096.
Mixed Problems
- Find the square root of 0.25.
- Determine the square root of 0.49.
- Simplify the square root of 3/4.
- Calculate the square root of 5/9.
- What is the square root of 2.25?
Application Problems
- If the area of a square is 49 square meters, what is the length of one side?
- A garden has an area of 121 square feet. Find the length of each side of the garden.
- The diagonal of a square is 10 meters. What is the length of each side?
Challenge Problems
- Simplify: \\(\sqrt{50} + \sqrt{75}\\).
- Find the value of \\(\sqrt{12} \times \sqrt{3}\\).
- Simplify: \\(\sqrt{200} / \sqrt{2}\\).
- Solve for x: \\(x^2 = 169\\).
- Prove that \\(\sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{8} = 4\\).
Use these problems to test your understanding and ensure you are comfortable with various types of square root calculations. Solutions can be verified using factorization or the long division method for more complex problems. For additional practice, try different sets of problems and increase the difficulty gradually to build confidence and proficiency.

Square Roots in Real Life
Square roots are not just mathematical concepts but have practical applications in various real-life scenarios. Understanding how to find and use square roots can help solve problems in fields such as construction, finance, science, and technology. Here are some common applications:
- Architecture and Construction:
In construction, square roots are used to calculate the dimensions of structures and materials. For instance, when determining the length of the diagonal of a square or the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle, the Pythagorean theorem involves finding the square root.
\[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \]
- Physics and Engineering:
Square roots are frequently used in physics equations, such as calculating the root mean square (RMS) value of alternating current (AC) or in formulas involving gravitational force and velocity.
\[ \text{RMS} = \sqrt{\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{n} x_i^2} \]
- Finance:
In finance, square roots are used in various calculations, including standard deviation and variance, which are measures of financial risk and volatility.
\[ \sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} (x_i - \mu)^2} \]
- Computer Graphics:
In computer graphics, square roots are essential for operations like calculating distances between points, magnitudes of vectors, and normalization of vectors.
\[ \| \mathbf{v} \| = \sqrt{x^2 + y^2 + z^2} \]
By understanding the practical applications of square roots, students can see the relevance of these mathematical concepts in everyday life and various professional fields.
Quizzes and Review Sheets
Test your understanding of square roots with these quizzes and review sheets. Each quiz is designed to challenge your knowledge and help reinforce what you've learned.
Quiz 1: Basic Square Roots
Find the square root of the following numbers:
- \(\sqrt{49}\)
- \(\sqrt{81}\)
- \(\sqrt{144}\)
- \(\sqrt{196}\)
- \(\sqrt{256}\)
Simplify the following square root expressions:
- \(\sqrt{50}\)
- \(\sqrt{75}\)
- \(\sqrt{98}\)
- \(\sqrt{147}\)
- \(\sqrt{200}\)
Quiz 2: Advanced Square Roots
Evaluate the square roots of the following decimal numbers:
- \(\sqrt{0.25}\)
- \(\sqrt{2.25}\)
- \(\sqrt{12.96}\)
- \(\sqrt{0.81}\)
- \(\sqrt{7.29}\)
Simplify the following square root expressions involving fractions:
- \(\sqrt{\frac{1}{16}}\)
- \(\sqrt{\frac{9}{25}}\)
- \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{49}}\)
- \(\sqrt{\frac{36}{100}}\)
- \(\sqrt{\frac{25}{64}}\)
Quiz 3: Mixed Practice Problems
Find the approximate value of the following square roots to two decimal places:
- \(\sqrt{20}\)
- \(\sqrt{45}\)
- \(\sqrt{72}\)
- \(\sqrt{90}\)
- \(\sqrt{150}\)
Solve the following word problems:
- Find the side length of a square with an area of 121 square units.
- A garden has an area of 64 square meters. What is the length of one side of the garden?
- If the diagonal of a square is 10 units, what is the length of each side?
- The area of a square is 225 square feet. Find the perimeter of the square.
- A square pool has an area of 169 square feet. How long is one side of the pool?
Review Sheets
Use these review sheets to reinforce your understanding and ensure you're ready for any test on square roots.
Answer Keys and Explanations
Below you will find detailed answer keys and explanations for the practice problems included in this worksheet. Each solution is broken down step-by-step to ensure comprehensive understanding.
Basic Problems
-
Problem: \( \sqrt{49} \)
Solution: The square root of 49 is 7 because \( 7 \times 7 = 49 \).
-
Problem: \( \sqrt{81} \)
Solution: The square root of 81 is 9 because \( 9 \times 9 = 81 \).
Advanced Problems
-
Problem: \( \sqrt{144} \)
Solution: The square root of 144 is 12 because \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \).
-
Problem: \( \sqrt{225} \)
Solution: The square root of 225 is 15 because \( 15 \times 15 = 225 \).
Mixed Problems
-
Problem: \( \sqrt{0.25} \)
Solution: The square root of 0.25 is 0.5 because \( 0.5 \times 0.5 = 0.25 \).
-
Problem: \( \sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \)
Solution: The square root of 2 is approximately 1.414. This is derived using methods such as long division or a calculator.
Step-by-Step Explanations
| Problem | Steps | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{36} \) |
|
6, because \( 6 \times 6 = 36 \) |
| \( \sqrt{50} \) |
|
Approximately 7.071 |
Video này cung cấp chìa khóa giải đáp và lời giải chi tiết cho bài tập thực hành căn bậc hai, giúp học sinh nắm vững kiến thức một cách hiệu quả.
Chìa Khóa Giải Đáp Bài Tập Thực Hành Căn Bậc Hai
READ MORE:
Video này giải thích khái niệm căn bậc hai và cách tính toán, giúp học sinh hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này trong toán học.
Căn Bậc Hai Là Gì? | Toán Học với Thầy J