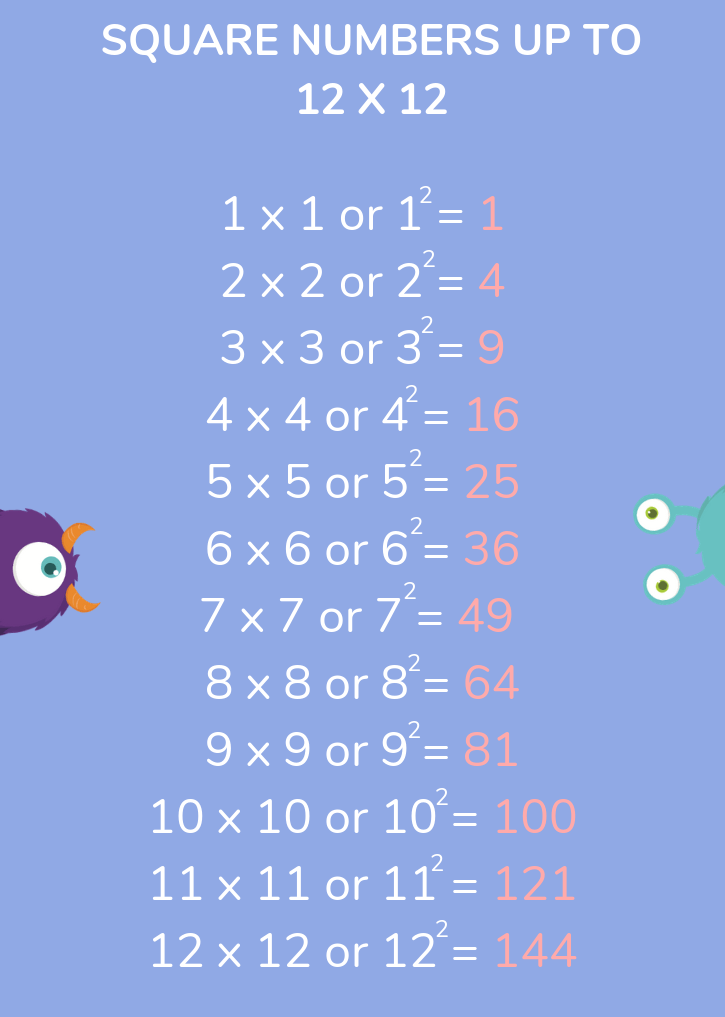
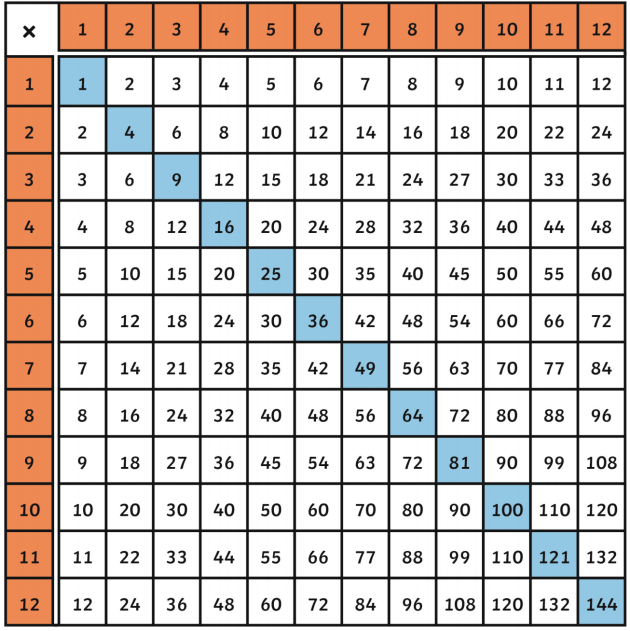
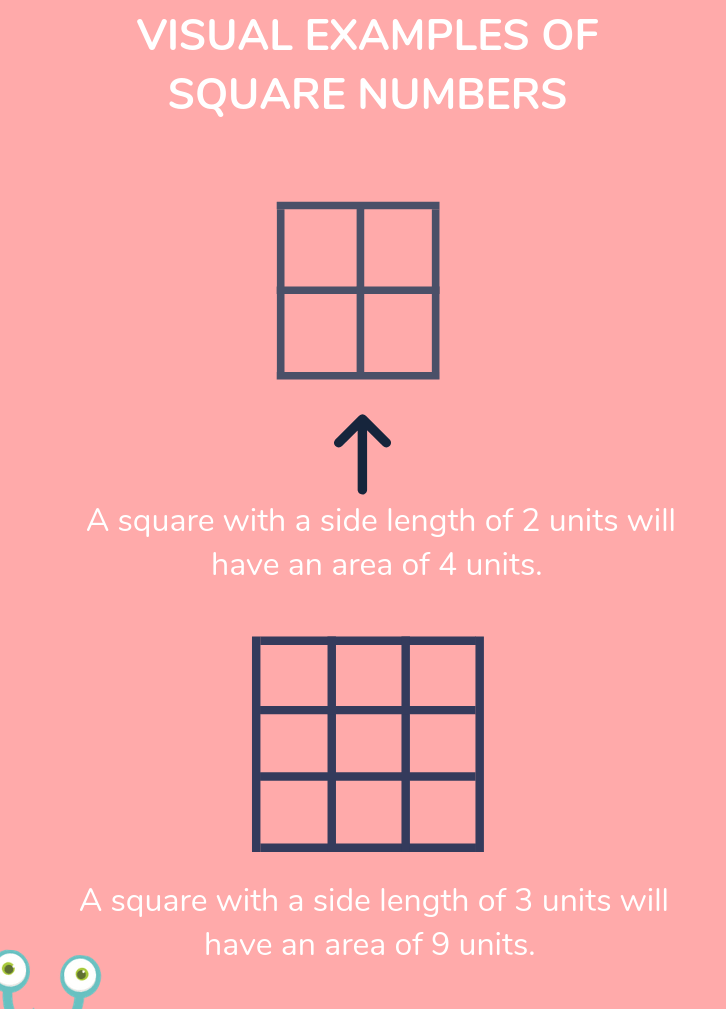Topic square root estimation worksheet: Unlock the secrets of square root estimation with our comprehensive worksheet designed for students and educators. This guide offers step-by-step instructions, practice problems, and interactive tools to help you master this essential math skill. Whether you're a beginner or looking to refine your techniques, our worksheet provides everything you need for success.
Table of Content
- Square Root Estimation Worksheet
- Basic Concepts and Definitions
- Step-by-Step Guide to Estimating Square Roots
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Worksheets and Printable Resources
- Interactive Exercises and Online Tools
- Teaching Strategies and Tips for Educators
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Techniques in Square Root Estimation
- Applications of Square Root Estimation in Real Life
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Additional Resources and References
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn ước lượng căn bậc hai nhanh chóng và chính xác, giúp bạn cải thiện kỹ năng toán học của mình.
Square Root Estimation Worksheet
Square root estimation is an essential mathematical skill that helps students approximate the square roots of non-perfect squares. Below are resources, worksheets, and examples to help in understanding and practicing square root estimation.
Introduction to Square Root Estimation
Estimating square roots involves finding which two perfect squares a number lies between and then approximating the value. This skill is useful for quick calculations and developing number sense.
Examples
- Estimate \(\sqrt{20}\):
The perfect squares closest to 20 are 16 and 25. Therefore, \(4^2 = 16\) and \(5^2 = 25\). So, \(\sqrt{20}\) is between 4 and 5. - Estimate \(\sqrt{50}\):
The perfect squares closest to 50 are 49 and 64. Therefore, \(7^2 = 49\) and \(8^2 = 64\). So, \(\sqrt{50}\) is between 7 and 8.
Worksheets
Here are some worksheets to help practice estimating square roots:
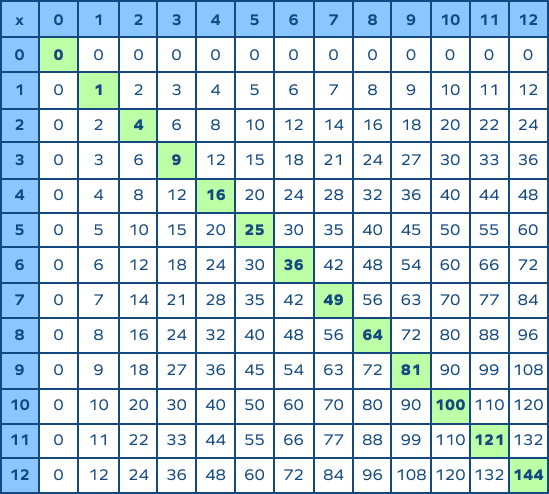
Table of Square Roots
| Number | Perfect Square Below | Perfect Square Above | Estimated Square Root |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 16 | 25 | Between 4 and 5 |
| 50 | 49 | 64 | Between 7 and 8 |
| 75 | 64 | 81 | Between 8 and 9 |
Interactive Practice
Engage with interactive practice problems and solutions to reinforce the concepts of square root estimation. These activities can help solidify understanding and improve accuracy.
Conclusion
Square root estimation is a valuable skill that aids in mental math and problem-solving. With practice, students can become proficient in quickly estimating square roots, enhancing their overall mathematical abilities.

READ MORE:
Basic Concepts and Definitions
Square root estimation is a fundamental mathematical skill that involves finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. This is particularly useful when dealing with non-perfect squares. Understanding the basic concepts and definitions related to square roots is crucial for mastering this skill.
- Square Root (\(\sqrt{}\)): A value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
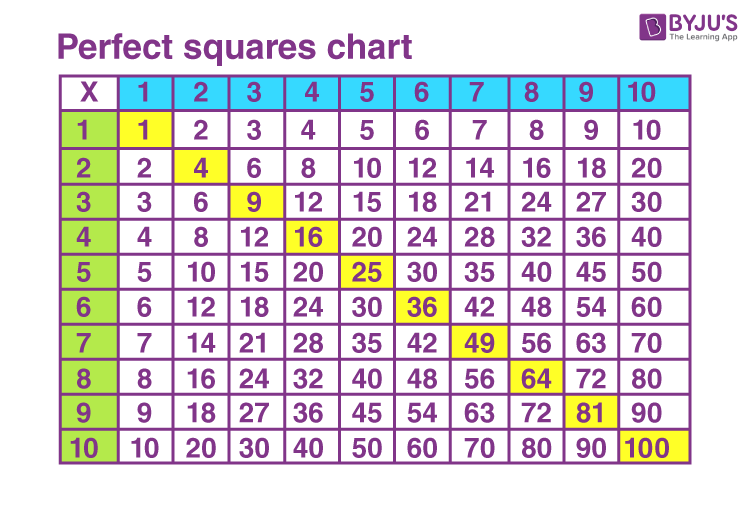
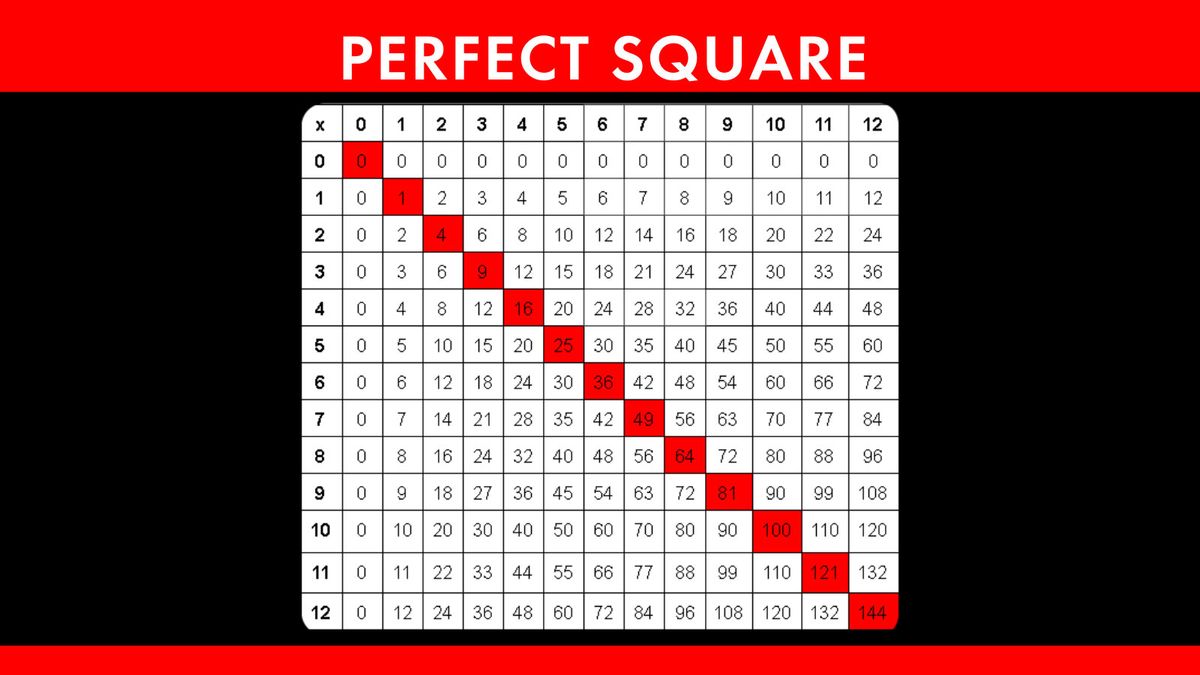
- Perfect Square: A number that has an integer as its square root. Examples include 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, and so on.
- Non-Perfect Square: A number that does not have an integer as its square root. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, and so on.
- Estimating Square Roots: The process of finding an approximate value of the square root of a non-perfect square.
The methods to estimate square roots can be divided into several steps:
-
Identify the two closest perfect squares:
For example, to estimate \(\sqrt{50}\), note that \(50\) is between \(7^2 = 49\) and \(8^2 = 64\).
-
Use these perfect squares to narrow down the estimate:
\(50\) is closer to \(49\) than \(64\), so \(\sqrt{50}\) is slightly more than 7.
-
Refine the estimate through averaging or other methods:
One can use techniques such as the average method or iterative approximation for a more precise estimate.
By understanding these concepts and following these steps, students can improve their ability to estimate square roots accurately and efficiently. Worksheets and practice problems often reinforce these skills by providing a range of examples and exercises.
Step-by-Step Guide to Estimating Square Roots
Estimating square roots can be simplified with a few systematic methods. Here, we provide a step-by-step guide to help you estimate square roots efficiently.
-
Identify the perfect squares:
Determine the two perfect squares between which your number lies. For example, to estimate \(\sqrt{20}\), note that \(16\) (which is \(4^2\)) and \(25\) (which is \(5^2\)) are the perfect squares surrounding \(20\).
-
Use the "Guess and Check" Method:
- Guess a number between the square roots of the two perfect squares. For \(\sqrt{20}\), guess between 4 and 5.
- Square your guess and compare it to the original number. Adjust your guess accordingly. For instance, if you guess 4.5: \[ 4.5^2 = 20.25 \] Since 20.25 is slightly more than 20, try a slightly smaller number.
- Continue adjusting your guess until you reach an acceptable level of accuracy. For \(\sqrt{20}\), an accurate estimate would be approximately 4.47.
-
Use the Averaging Method:
- Start with the two closest perfect squares. For \(\sqrt{20}\), these are 16 and 25.
- Average these two numbers: \[ \frac{4 + 5}{2} = 4.5 \]
- Divide the original number by this average: \[ \frac{20}{4.5} \approx 4.44 \]
- Average the result with the initial guess: \[ \frac{4.44 + 4.5}{2} \approx 4.47 \]
- Repeat the process until the desired accuracy is achieved.
-
Use a Calculator:
For the most precise result, use a calculator to find the square root. While manual methods are useful for understanding, a calculator ensures accuracy.
By following these steps, you can efficiently estimate square roots, helping with various mathematical problems and enhancing your numerical understanding.
Examples and Practice Problems
Let's work through some examples and practice problems to sharpen our skills in estimating square roots:
-
Example 1:
We want to estimate the square root of 85.
To start, we find the nearest perfect squares surrounding 85. The perfect squares nearest to 85 are 81 (9^2) and 100 (10^2).
Since 85 lies closer to 81, we'll use 9 as our initial estimate.
Next, we use the average of 9 and 85/9 (which is approximately 9.44) to refine our estimate:
Estimation = (9 + 85/9) / 2 ≈ (9 + 9.44) / 2 ≈ 9.22
Continuing this process, we iterate until we reach a satisfactory level of precision.
Through further iterations, we find that the square root of 85 is approximately 9.22.
-
Example 2:
Let's estimate the square root of 200.
Similar to the previous example, we identify the nearest perfect squares around 200, which are 196 (14^2) and 225 (15^2).
Since 200 is closer to 196, we start with an initial estimate of 14.
Refining our estimate using the average, we get:
Estimation = (14 + 200/14) / 2 ≈ (14 + 14.29) / 2 ≈ 14.145
Continuing this iterative process, we arrive at an approximate square root of 200 as 14.145.
-
Practice Problem:
Estimate the square root of 50.
Hint: Identify the nearest perfect squares, choose an initial estimate, refine using the average, and iterate until convergence.
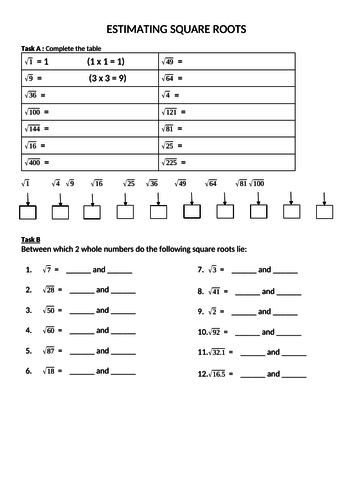
Worksheets and Printable Resources
Below are some worksheets and printable resources that can aid in practicing square root estimation:
Interactive Exercises and Online Tools
Explore these interactive exercises and online tools to enhance your understanding of square root estimation:
- : This game allows you to practice estimating square roots in a fun and engaging way.
- : IXL offers interactive exercises and problems to help you improve your square root estimation skills.
- : Use this online tool to calculate square roots and verify your estimations.
Teaching Strategies and Tips for Educators
Here are some effective teaching strategies and tips for educators to facilitate square root estimation lessons:
- Provide Real-Life Examples: Start by explaining the practical applications of square root estimation in everyday situations, such as estimating the area of a garden or the length of a cable.
- Interactive Activities: Incorporate interactive activities like estimation games, group discussions, and hands-on exercises to make learning more engaging.
- Use Visual Aids: Utilize visual aids such as charts, diagrams, and graphs to illustrate the concept of square roots and how estimation works.
- Encourage Estimation Techniques: Teach students various estimation techniques, such as using the nearest perfect squares or rounding to the nearest whole number, and encourage them to explain their reasoning.
- Provide Feedback: Offer constructive feedback and guidance to students as they practice square root estimation, highlighting both correct approaches and areas for improvement.
- Assessment and Reflection: Assess students' understanding through quizzes, worksheets, and real-world problem-solving tasks. Encourage reflection on their estimation strategies and discuss alternative methods.
- Adapt to Individual Needs: Recognize that students may have different learning styles and abilities. Provide differentiated instruction and additional support as needed to ensure all students can succeed.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Let's explore some common mistakes in square root estimation and strategies to avoid them:
- Not Identifying Nearest Perfect Squares: One of the common errors is failing to correctly identify the nearest perfect squares surrounding the given number. Ensure students understand the importance of finding these reference points.
- Incorrect Initial Estimates: Another mistake is making inaccurate initial estimates. Emphasize the significance of choosing a reasonable starting point based on the proximity of the given number to the nearest perfect squares.
- Failure to Refine Estimates: Some students may stop after making one estimation, without refining their estimate through iteration. Encourage them to continue refining their estimate until they reach an acceptable level of accuracy.
- Overreliance on Calculator: Relying too heavily on calculators for square root calculations can hinder students' ability to estimate mentally and understand the concept intuitively. Encourage mental estimation alongside calculator use.
- Ignoring Error Margin: Failing to consider the error margin in estimations can lead to inaccuracies. Teach students to assess the precision of their estimations and recognize the potential range of the actual square root.
- Lack of Practice: Insufficient practice in square root estimation can result in weak estimation skills. Encourage regular practice and provide ample opportunities for students to apply estimation techniques in various contexts.
- Not Explaining Reasoning: Lastly, students may overlook the importance of explaining their reasoning behind their estimation methods. Encourage them to articulate their thought process, fostering deeper understanding and communication skills.
Advanced Techniques in Square Root Estimation
Explore these advanced techniques to enhance your square root estimation skills:
- Newton's Method: Newton's method, also known as the Newton-Raphson method, is an iterative technique for finding the square root of a number. It involves refining an initial guess through successive iterations using the formula: \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2}(x_n + \frac{S}{x_n}) \), where \( x_n \) is the current estimate and \( S \) is the given number.
- Babylonian Method: The Babylonian method is another iterative algorithm for approximating square roots. It is similar to Newton's method and uses the formula: \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2}(x_n + \frac{S}{x_n}) \), where \( x_n \) is the current estimate and \( S \) is the given number.
- Binomial Expansion: The binomial expansion method involves using the binomial theorem to approximate square roots. It expresses \( \sqrt{S} \) as a binomial expansion and truncates the series at a certain point to obtain an approximation.
- Continued Fractions: Continued fractions are another approach to square root estimation. They involve expressing the square root as an infinite fraction and truncating it at a certain point to obtain an approximation.
- Complex Numbers: Utilizing complex numbers, particularly the imaginary unit \( i \), can provide alternative methods for estimating square roots, especially for negative numbers or complex roots.
.gif)
Applications of Square Root Estimation in Real Life
Discover the practical applications of square root estimation in various real-life scenarios:
- Area Estimation: In landscaping or construction projects, square root estimation is used to estimate the area of irregularly shaped plots of land or rooms.
- Financial Planning: When managing finances, square root estimation can help in estimating the future growth of investments or calculating compound interest.
- Engineering and Design: Engineers and designers use square root estimation to estimate dimensions, quantities, and costs of materials needed for projects.
- Healthcare: In medical imaging, such as MRI or CT scans, square root estimation is used to reconstruct images and estimate pixel intensities for diagnostic purposes.
- Statistical Analysis: Square root estimation plays a role in statistical analysis, particularly in calculating standard deviations and other measures of variability.
- Physical Sciences: In physics and chemistry, square root estimation is used to estimate physical quantities such as velocities, energies, and concentrations.
- Technology: Square root estimation is fundamental in various technological applications, including signal processing, image compression, and data encryption.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is square root estimation?
Square root estimation is the process of approximating the square root of a number without using a calculator or performing exact calculations.
-
Why is square root estimation important?
Square root estimation is important because it enhances mathematical intuition, improves problem-solving skills, and provides a practical approach to handling real-life situations where precise calculations may not be feasible.
-
What are some common techniques for square root estimation?
Common techniques for square root estimation include finding the nearest perfect squares, using iterative methods like Newton's or Babylonian methods, and employing approximation methods such as binomial expansion or continued fractions.
-
How can square root estimation be used in everyday life?
Square root estimation has numerous applications in everyday life, including estimating areas of land, managing finances, designing structures, interpreting medical imaging, analyzing data, and developing technological solutions.
-
What are some tips for improving square root estimation skills?
To improve square root estimation skills, practice regularly, understand the principles behind estimation techniques, use visual aids, and apply estimation in various contexts. Additionally, seek feedback and learn from mistakes to refine estimation strategies.
Additional Resources and References
Hướng dẫn ước lượng căn bậc hai nhanh chóng và chính xác, giúp bạn cải thiện kỹ năng toán học của mình.
Ước Lượng Căn Bậc Hai
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn ước lượng căn bậc hai một cách hiệu quả và chính xác, giúp bạn nắm vững kỹ năng toán học.
Ước Lượng Căn Bậc Hai