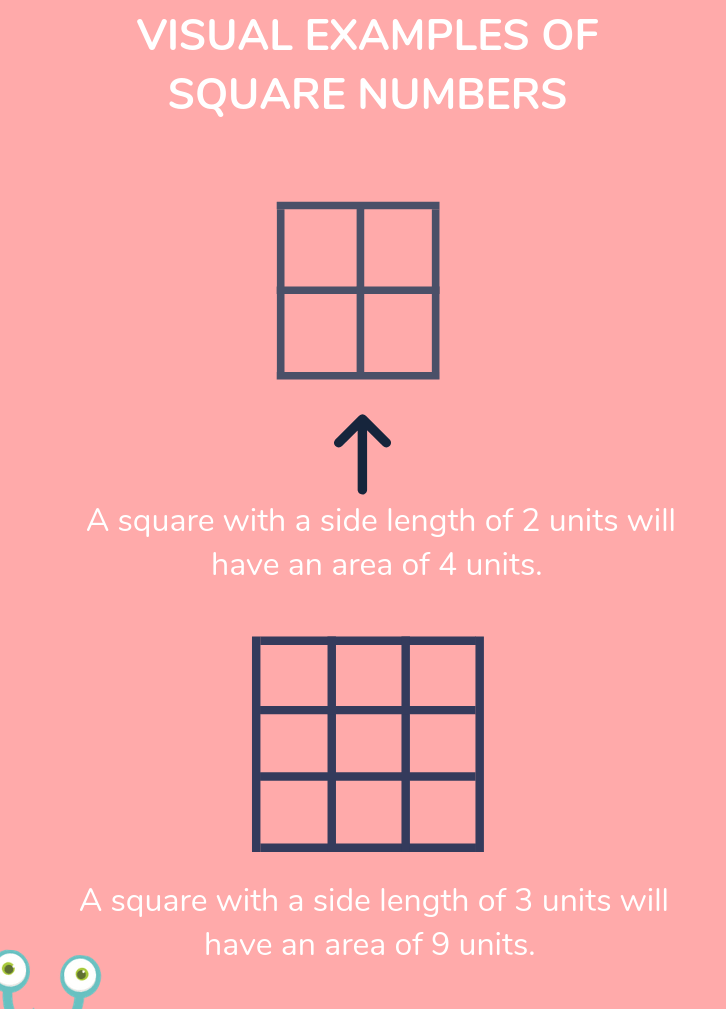Topic square root worksheet with answers: Discover the comprehensive collection of square root worksheets with answers. These worksheets are designed to help students master the concept of square roots through various exercises and practice problems. Perfect for both classroom use and homeschooling, these resources cater to different learning levels and include step-by-step solutions.
Table of Content
- Square Root Worksheets with Answers
- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Square Roots
- 2. Understanding Square Numbers
- 3. Simplifying Square Roots
- 4. Estimating Square Roots
- 5. Square Root of Fractions
- 6. Practice Problems and Worksheets
- 7. Answers and Explanations
- 8. Additional Resources and Related Topics
- 9. Interactive Tools and Calculators
- 10. Feedback and Support
- YOUTUBE: Xem cách giải bài tập căn bậc hai từ 1 đến 4 trong video này. Hãy tham gia để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này!
Square Root Worksheets with Answers
Here are some resources to help you practice finding square roots. These worksheets include various types of problems and come with answers to help you check your work.
Available Worksheets
Example Problems
- Find the square root of 144.
- Simplify the square root of 50.
- Calculate the square root of 784.
- Simplify the square root of -25.
Answer Key
| Problem | Answer |
|---|---|
| √144 | 12 |
| √50 | 5√2 |
| √784 | 28 |
| √-25 | 5i |
These worksheets and example problems should provide a comprehensive practice for mastering square roots. Happy learning!

READ MORE:
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding Perfect Squares
- Methods to Find Square Roots
- Square Roots of Non-Perfect Squares
- Practice Problems
- Using Square Roots in Equations
- Real-Life Applications of Square Roots
- Advanced Square Root Concepts
- Square Roots of Fractions and Decimals
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Square Root Worksheets and Solutions
- Basic Square Root Problems
- Intermediate Level Problems
- Advanced Challenges
- Square Root Estimation
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Square Roots
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, particularly in algebra and geometry. A square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). For instance, the square root of 25 is 5 because \( 5^2 = 25 \). Square roots are used to solve quadratic equations, simplify expressions, and understand the properties of numbers.
Square roots can be both positive and negative, as both \( y \) and \( -y \) satisfy the equation \( y^2 = x \). For example, the square roots of 9 are 3 and -3. However, in many practical contexts, the principal (positive) square root is used.
Understanding square roots also involves recognizing perfect squares, such as 1, 4, 9, 16, and so on, where the square root is an integer. Non-perfect squares, like 2 or 5, result in irrational square roots, which are non-repeating and non-terminating decimals.
Square root operations can be visualized geometrically as finding the side length of a square given its area. For instance, if a square has an area of 49 square units, its side length is the square root of 49, which is 7 units.
In summary, mastering square roots is crucial for higher-level math, providing a foundation for solving more complex equations and understanding various mathematical concepts.
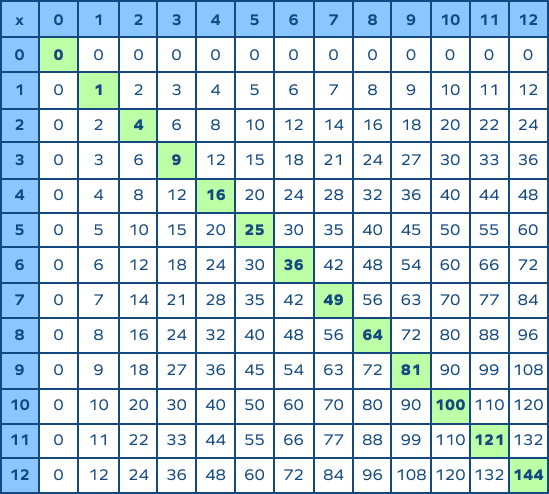
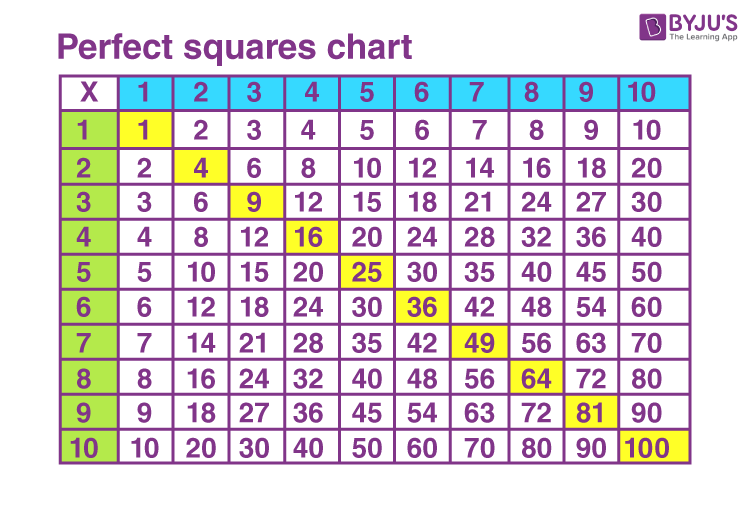
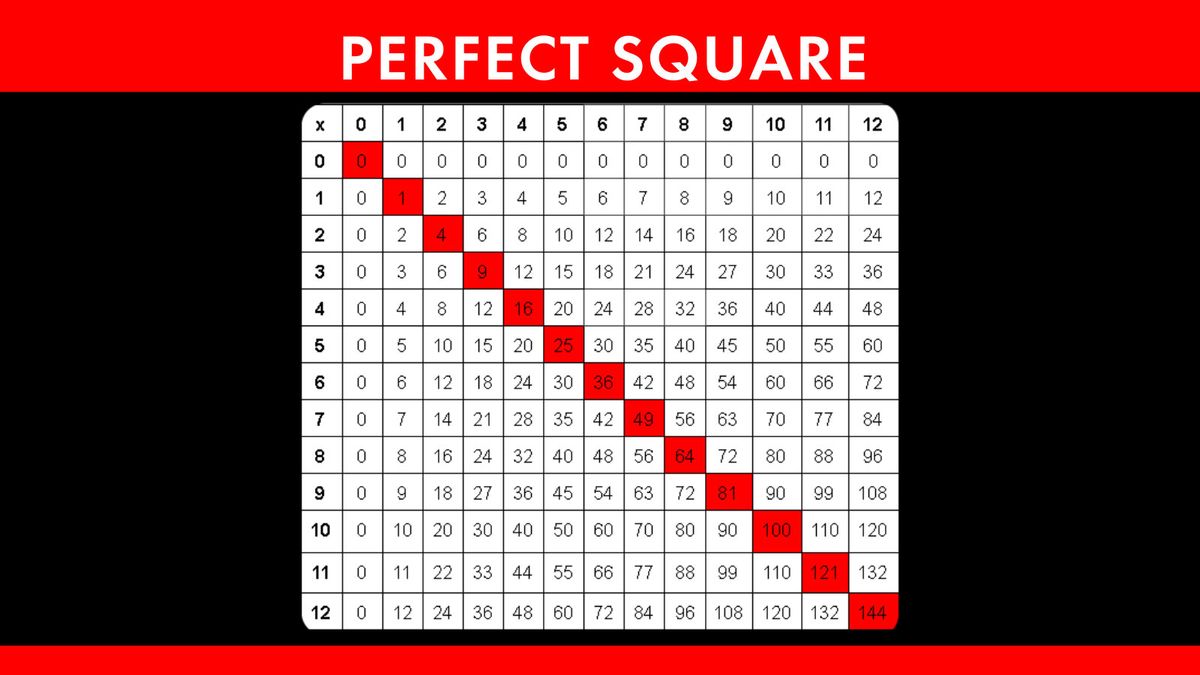
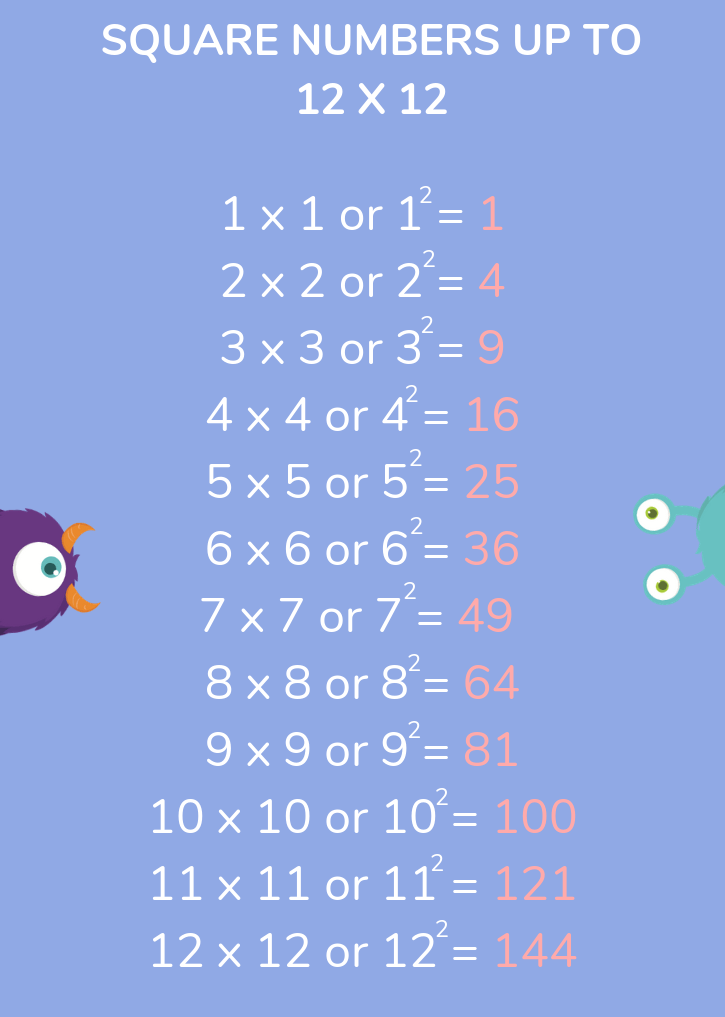
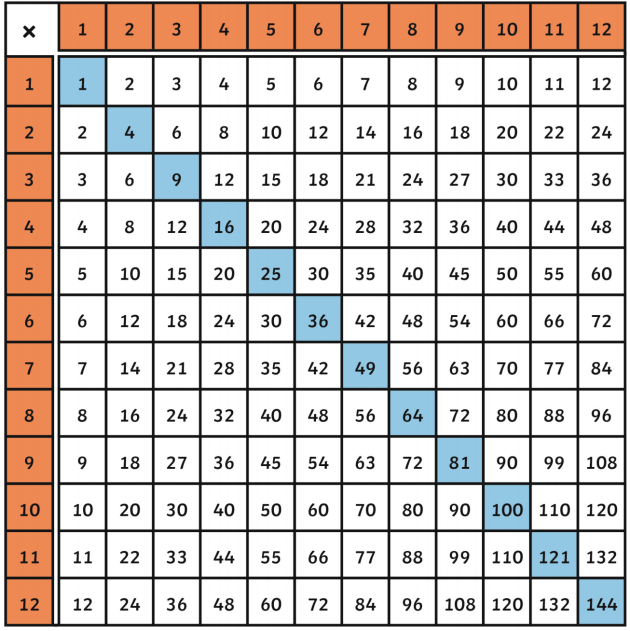
2. Understanding Square Numbers
Square numbers are the result of multiplying an integer by itself. They form the basis for understanding square roots and are fundamental in various mathematical concepts and applications. Here is a detailed explanation to enhance your understanding:
- Definition: A square number, or perfect square, is an integer that is the square of an integer. For example, \(1, 4, 9, 16,\) and \(25\) are square numbers because they can be expressed as \(1^2, 2^2, 3^2, 4^2,\) and \(5^2\) respectively.
- Properties:
- All square numbers are non-negative.
- The square of an even number is even, and the square of an odd number is odd.
- Square numbers have an odd number of total factors. For example, \(16\) has factors \(1, 2, 4, 8, 16\).
- Visualization:
Square numbers can be visually represented as a grid of dots forming a perfect square. For instance, a grid with \(3\) rows and \(3\) columns illustrates \(3^2 = 9\).
- Applications:
Understanding square numbers is crucial in various fields, including algebra, geometry, and even in real-world contexts like architecture and computer science.
- Common Examples:
Integer (n) Square Number (n^2) 1 1 2 4 3 9 4 16 5 25
By understanding these concepts, you can easily recognize and work with square numbers, paving the way for more complex mathematical problem-solving.
3. Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down the radicand into its prime factors or perfect squares. Here's a step-by-step approach to simplify square roots:
- Identify the prime factors of the radicand.
- Group the prime factors into pairs of identical factors.
- Move each pair of identical factors outside the square root as a single factor.
- Multiply the factors outside the square root.
- If any factors remain inside the square root, multiply them together.
For example, to simplify \( \sqrt{72} \):
- Find the prime factors of 72: \( 72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \).
- Group the prime factors: \( (2 \times 2) \) and \( (3 \times 3) \).
- Move each pair outside the square root: \( \sqrt{72} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Multiply the factors outside the square root: \( 2 \times 3 = 6 \).
- The simplified form is \( 6\sqrt{2} \).
Remember, not all radicands can be simplified. For instance, \( \sqrt{19} \) cannot be simplified further as 19 is a prime number.
Additionally, when simplifying the square root of fractions, handle the numerator and denominator separately before combining them:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} \) as \( \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \).
- Simplify \( \sqrt{a} \) and \( \sqrt{b} \) individually.
With consistent practice, simplifying square roots will become an easier and more intuitive process.

4. Estimating Square Roots
Estimating square roots can be useful when you need a quick approximation without using a calculator. Here are some methods to estimate square roots:
Using Perfect Squares
To estimate the square root of a non-perfect square number, you can use the nearest perfect squares.
- Identify the two perfect squares between which the number lies. For example, to estimate
\(\sqrt{50}\), note that \(49\) and \(64\) are the nearest perfect squares. - Determine the square roots of these perfect squares. \(\sqrt{49} = 7\) and \(\sqrt{64} = 8\).
- Since \(50\) is closer to \(49\) than \(64\), \(\sqrt{50}\) is slightly more than 7. You can refine this estimate by noting how much closer \(50\) is to \(49\) compared to \(64\).
Interpolation Method
Interpolation helps get a more accurate estimate by using a linear approximation between the perfect squares.
- Calculate the differences: \(64 - 49 = 15\) and \(50 - 49 = 1\).
- Determine the fractional distance of \(50\) between \(49\) and \(64\): \(\frac{1}{15}\).
- Add this fraction to the lower square root: \(7 + \frac{1}{15} \approx 7.067\).
Average Method
The average method can provide a quick estimate by averaging values that you know are close.
- Take the number you want to find the square root of and a number you know is close. For example, for \( \sqrt{50} \), we know it is between \(7\) and \(8\).
- Average these values: \(\frac{7 + 8}{2} = 7.5\).
- Square the average to check how close it is: \(7.5^2 = 56.25\). Since \(56.25\) is higher than \(50\), we know our estimate should be lower than \(7.5\).
Using Calculators
If you need more precision, use online calculators or tools to compute square roots to several decimal places. Many educational websites provide interactive tools for this purpose.
Practice Problems
Try estimating the square roots of the following numbers using the methods above:
- \(\sqrt{18}\)
- \(\sqrt{75}\)
- \(\sqrt{120}\)
Compare your estimates with a calculator to see how close you get!
5. Square Root of Fractions
Understanding the square root of fractions involves breaking down the fraction into its numerator and denominator and taking the square root of each separately. Here is a step-by-step guide:
Steps to Find the Square Root of Fractions
- Write the fraction in the form
\(\frac{a}{b}\). - Take the square root of the numerator (a).
- Take the square root of the denominator (b).
- Express the square root of the fraction as
\(\frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\).
Let's look at a few examples:
Example 1: Square Root of \(\frac{4}{9}\)
Given the fraction \(\frac{4}{9}\):
- Take the square root of the numerator: \(\sqrt{4} = 2\).
- Take the square root of the denominator: \(\sqrt{9} = 3\).
- Combine the results: \(\frac{\sqrt{4}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{2}{3}\).
Thus, \(\sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} = \frac{2}{3}\).
Example 2: Square Root of \(\frac{1}{16}\)
Given the fraction \(\frac{1}{16}\):
- Take the square root of the numerator: \(\sqrt{1} = 1\).
- Take the square root of the denominator: \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
- Combine the results: \(\frac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{16}} = \frac{1}{4}\).
Thus, \(\sqrt{\frac{1}{16}} = \frac{1}{4}\).
Example 3: Square Root of \(\frac{25}{36}\)
Given the fraction \(\frac{25}{36}\):
- Take the square root of the numerator: \(\sqrt{25} = 5\).
- Take the square root of the denominator: \(\sqrt{36} = 6\).
- Combine the results: \(\frac{\sqrt{25}}{\sqrt{36}} = \frac{5}{6}\).
Thus, \(\sqrt{\frac{25}{36}} = \frac{5}{6}\).
More Complex Fractions
For more complex fractions, such as those involving decimals or non-perfect squares, the process remains the same. Consider converting decimals to fractions before taking square roots.
Practice Problems
- Find the square root of \(\frac{9}{25}\).
- Find the square root of \(\frac{49}{64}\).
- Find the square root of \(\frac{16}{81}\).
Additional Tips
- Always simplify the fraction first if possible.
- Remember that \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\).
- Use a calculator for non-perfect squares to get approximate values.
By following these steps, you can simplify the process of finding the square root of any fraction.
6. Practice Problems and Worksheets
Practicing square roots is essential for mastering the concept. Below are a variety of problems to help reinforce your understanding.
Practice Problems
- Find the square root of the following perfect squares:
- \(\sqrt{144}\)
- \(\sqrt{169}\)
- \(\sqrt{196}\)
- \(\sqrt{225}\)
- \(\sqrt{256}\)
- Estimate the square root of non-perfect squares to the nearest tenth:
- \(\sqrt{50}\)
- \(\sqrt{75}\)
- \(\sqrt{120}\)
- \(\sqrt{200}\)
- \(\sqrt{450}\)
- Simplify the following square roots:
- \(\sqrt{18}\)
- \(\sqrt{50}\)
- \(\sqrt{98}\)
- \(\sqrt{200}\)
- \(\sqrt{500}\)
Worksheets
Download and complete the following worksheets to test your skills:
Answer Key
Check your answers below after completing the problems:
| Problem | Answer |
|---|---|
| \(\sqrt{144}\) | 12 |
| \(\sqrt{169}\) | 13 |
| \(\sqrt{196}\) | 14 |
| \(\sqrt{225}\) | 15 |
| \(\sqrt{256}\) | 16 |
| \(\sqrt{50}\) | 7.1 |
| \(\sqrt{75}\) | 8.7 |
| \(\sqrt{120}\) | 10.95 |
| \(\sqrt{200}\) | 14.14 |
| \(\sqrt{450}\) | 21.21 |
| \(\sqrt{18}\) | 3\(\sqrt{2}\) |
| \(\sqrt{50}\) | 5\(\sqrt{2}\) |
| \(\sqrt{98}\) | 7\(\sqrt{2}\) |
| \(\sqrt{200}\) | 10\(\sqrt{2}\) |
| \(\sqrt{500}\) | 10\(\sqrt{5}\) |
7. Answers and Explanations
Below are the answers and step-by-step explanations for the practice problems provided in Section 6.
Problem 1: Simplify \( \sqrt{16} \)
Answer: 4
Explanation: The number 16 is a perfect square, and \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \). Thus, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
Problem 2: Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \)
Answer: \( 5\sqrt{2} \)
Explanation:
- Factor 50 into its prime factors: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \).
- Since \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \), we get \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 25} \).
- Simplify to \( \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{25} = \sqrt{2} \times 5 = 5\sqrt{2} \).
Problem 3: Estimate \( \sqrt{10} \)
Answer: Approximately 3.16
Explanation:
- Since \( 9 < 10 < 16 \), we know \( 3 < \sqrt{10} < 4 \).
- By using a calculator, we find \( \sqrt{10} \approx 3.162 \).
Problem 4: Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} \)
Answer: \( \frac{2}{3} \)
Explanation:
- Apply the property \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \).
- Simplify \( \sqrt{\frac{4}{9}} = \frac{\sqrt{4}}{\sqrt{9}} = \frac{2}{3} \).
Problem 5: Simplify \( \sqrt{72} \)
Answer: \( 6\sqrt{2} \)
Explanation:
- Factor 72 into its prime factors: \( 72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 \).
- Since \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \), we get \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^2} \).
- Simplify to \( \sqrt{8 \times 9} = \sqrt{8} \times \sqrt{9} = 2\sqrt{2} \times 3 = 6\sqrt{2} \).
Problem 6: Solve \( x^2 = 49 \)
Answer: \( x = \pm 7 \)
Explanation:
- Take the square root of both sides: \( \sqrt{x^2} = \sqrt{49} \).
- This simplifies to \( x = \pm 7 \), since both 7 and -7 squared give 49.

8. Additional Resources and Related Topics
For those looking to expand their understanding of square roots and related mathematical concepts, here are some valuable resources and topics to explore:
Online Tutorials and Videos
- - Comprehensive tutorials and practice exercises.
- - Video lessons on simplifying square roots.
- - Interactive explanations and examples.
Interactive Tools and Calculators
- - Powerful tool for visualizing and calculating square roots.
- - Computational engine to solve square root problems.
- - Quick calculations and step-by-step solutions.
Related Mathematical Topics
- - Understanding the relationship between exponents and square roots.
- - Application of square roots in geometry.
- - Techniques for simplifying expressions involving square roots.
Books and E-Books
- - Covers fundamentals including square roots.
- - Free resources and e-books.
Practice Problems and Worksheets
- - Printable practice problems.
- - Customizable worksheets for various difficulty levels.
- - Worksheets aligned with common core standards.
Educational Websites and Forums
- - Community and resources for math help.
- - Q&A site for math enthusiasts and students.
- - Discussion and resources for learning math.
Games and Apps
- - Fun game for practicing square roots.
- - App for solving math problems, including square roots.
- - Interactive game for mastering square roots.
9. Interactive Tools and Calculators
Enhance your understanding of square roots with these interactive tools and calculators. These resources are designed to make learning more engaging and effective, providing hands-on practice and instant feedback.
- Square Root Calculator:
Use this tool to quickly find the square root of any number. Simply enter the number and get the result instantly. This is great for checking your answers or for when you need a quick calculation.
- Square Root Simplification Tool:
This interactive tool helps you simplify square roots step-by-step. Enter the number under the square root, and the tool will guide you through the process of simplifying it to its simplest form.
- Square Root Estimation Game:
Practice estimating square roots with this fun game. It provides a number, and you have to choose the closest estimated square root. It’s a great way to improve your estimation skills.
- Practice Worksheets:
Download and print practice worksheets to solve square root problems offline. These worksheets include a variety of problems, from basic square root calculations to more complex applications.
- Interactive Quizzes:
Test your knowledge of square roots with interactive quizzes. These quizzes provide immediate feedback and explanations for each question, helping you learn from your mistakes and improve your understanding.
- Visual Learning Tools:
Utilize visual aids like number lines and graphs to better understand the concept of square roots. These tools can help you visualize how square roots work and their place on the number line.
- Math Apps:
Explore various educational apps that include square root calculators, practice problems, and games. These apps can be used on mobile devices, making it easy to practice and learn on the go.
These interactive tools and calculators are excellent resources to help you master square roots. Whether you're looking for quick calculations, detailed practice, or engaging games, these tools offer something for every learning style.
10. Feedback and Support
We value your feedback and are here to provide support as you work through these square root worksheets. Here are several ways you can reach out to us and find additional help:
Contact Us
- Email: Send your questions and feedback to .
- Phone: Call us at (123) 456-7890 for immediate assistance during business hours.
- Mail: Write to us at 123 Math Lane, Education City, ED 12345.
Online Support
- Visit our for answers to common questions.
- Join our to discuss problems and solutions with fellow learners.
- Access our to submit a support ticket for personalized help.
Additional Resources
Check out these resources for further assistance and learning opportunities:
- - Free online lessons and practice problems.
- - Easy-to-understand explanations and interactive tools.
- - Printable worksheets and detailed solutions.
Feedback Form
We would love to hear your thoughts on our worksheets and resources. Please fill out our to share your experience and suggestions.
| Support Type | Contact Details |
|---|---|
| Phone | (123) 456-7890 |
| 123 Math Lane, Education City, ED 12345 |
Xem cách giải bài tập căn bậc hai từ 1 đến 4 trong video này. Hãy tham gia để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này!
Giải Bài Tập Căn Bậc Hai 1-4
READ MORE:
Xem cách giải các bài tập về căn bậc hai và căn bậc ba trong video này do Thầy J trình bày. Hãy tham gia để tăng cường kiến thức toán học của bạn!
Căn Bậc Hai và Căn Bậc Ba | Toán cùng Thầy J