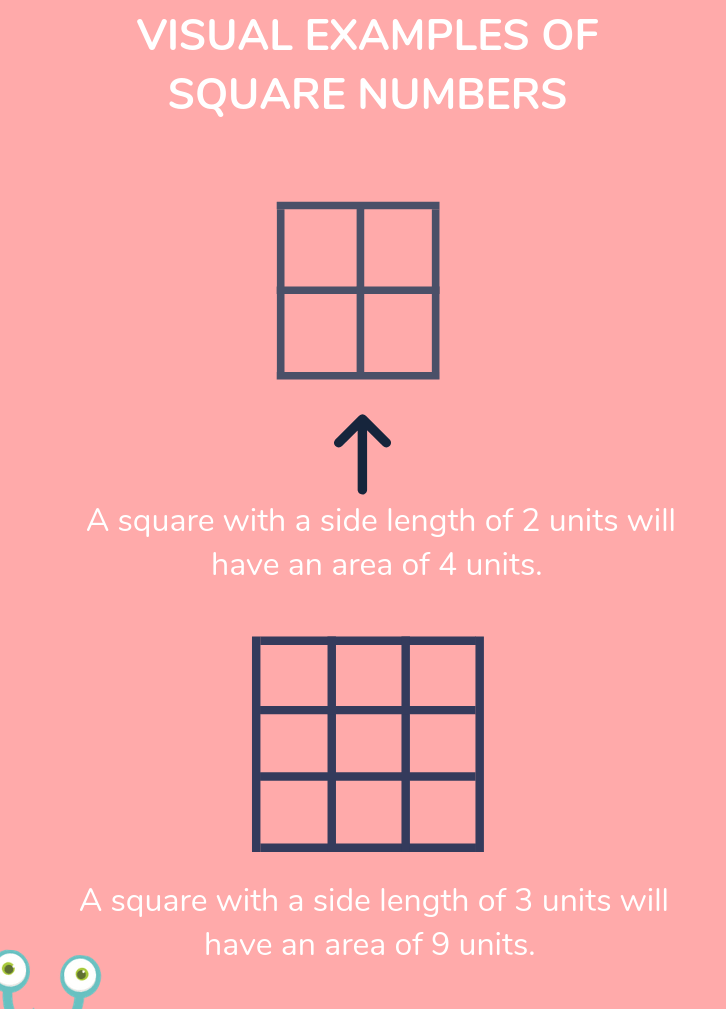Topic square and square root worksheet: Discover the essential concepts of squares and square roots with our comprehensive worksheet. Designed to enhance your mathematical skills, this resource provides clear explanations, step-by-step solutions, and engaging practice problems. Whether you're a student or an educator, our worksheet is the perfect tool to master these fundamental math topics with confidence.
Table of Content
- Square and Square Root Worksheet
- Introduction to Squares and Square Roots
- Understanding Square Numbers
- Calculating Square Roots
- Properties of Squares and Square Roots
- Real-World Applications of Squares and Square Roots
- Step-by-Step Solutions for Squaring Numbers
- Step-by-Step Solutions for Finding Square Roots
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Practice Worksheets for Squares and Square Roots
- Advanced Problems Involving Squares and Square Roots
- Visual Aids and Diagrams for Better Understanding
- Interactive Activities and Online Resources
- Summary and Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Additional Resources for Further Learning
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để hiểu về bình phương và căn bậc ba một cách dễ dàng và thú vị cùng thầy J.
Square and Square Root Worksheet
Learning about squares and square roots is essential in mathematics. Below are detailed concepts, examples, and exercises to help understand these mathematical operations.
Concepts
- Square of a number: The square of a number \( n \) is the result of multiplying the number by itself. It is denoted as \( n^2 \).
- Square root of a number: The square root of a number \( n \) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number \( n \). It is denoted as \( \sqrt{n} \).
Examples
- \( 3^2 = 9 \)
Exercises
- Calculate the square of 7.
- Find the square root of 49.
- What is \( 12^2 \) ?
- Evaluate \( \sqrt{81} \).
- Simplify \( 5^2 \) + \( \sqrt{16} \).
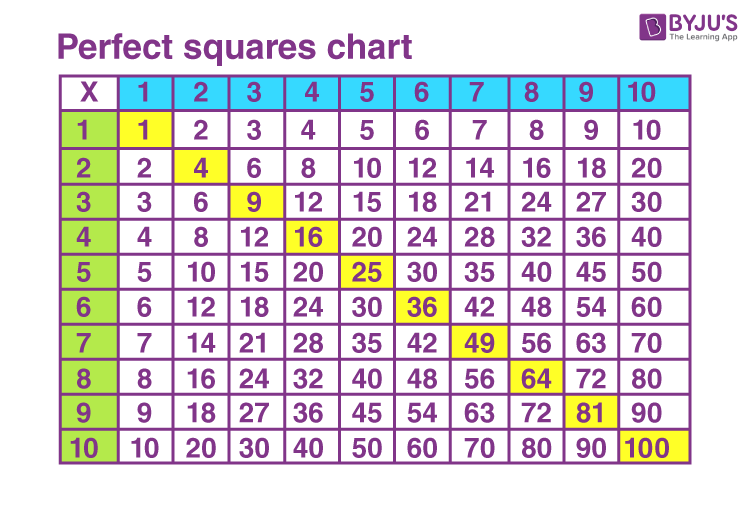
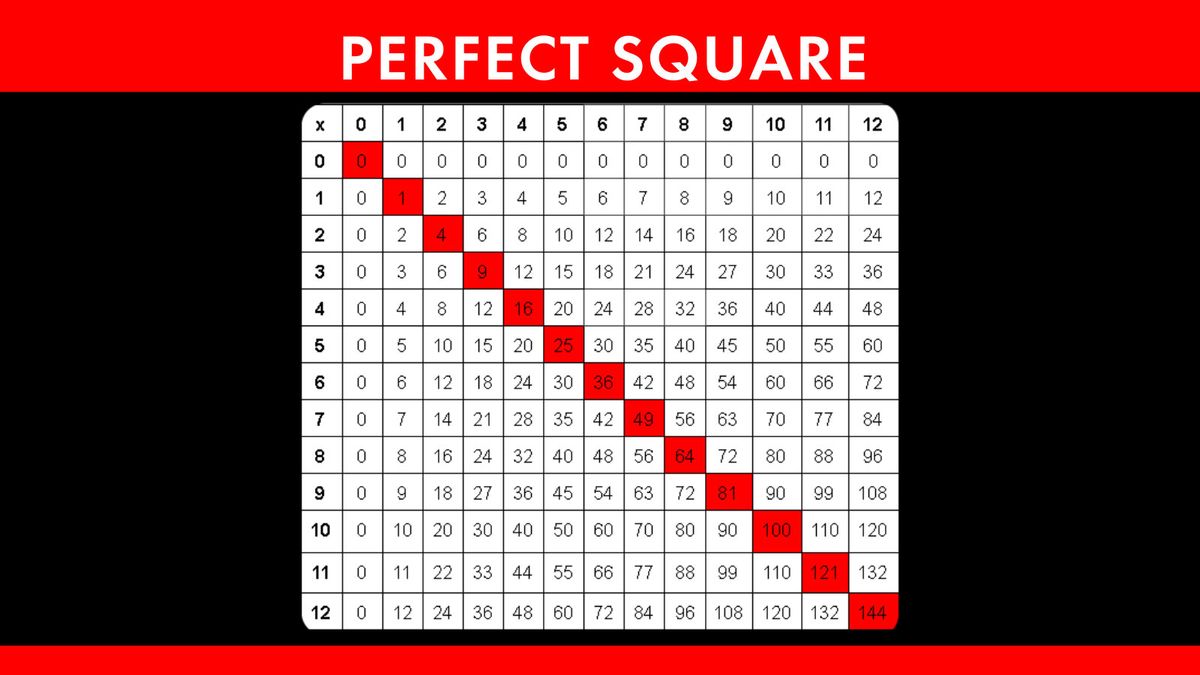
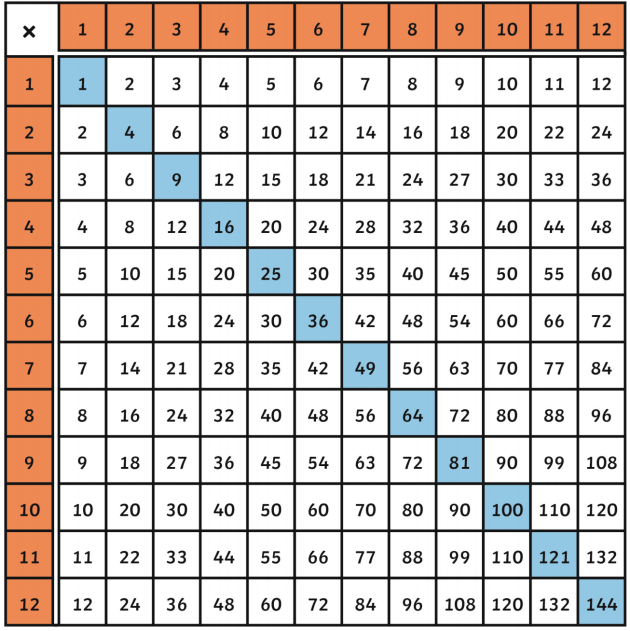
Table of Squares and Square Roots
| Number | Square | Square Root |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) |
| 3 | 9 | \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) |
| 4 | 16 | \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) |
| 5 | 25 | \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) |
Mathjax Equations
Square of \( a \): \( a^2 \)
Square root of \( b \): \( \sqrt{b} \)
Example: \( 4^2 = 16 \) and \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \)

READ MORE:
Introduction to Squares and Square Roots
Squares and square roots are fundamental concepts in mathematics that form the basis for more advanced topics. Understanding these concepts is essential for students as they progress in their mathematical education.
Squares
The square of a number is obtained by multiplying the number by itself. It is denoted as \( n^2 \), where \( n \) is the number. For example:
- \( 2^2 = 2 \times 2 = 4 \)
- \( 3^2 = 3 \times 3 = 9 \)
- \( 4^2 = 4 \times 4 = 16 \)
Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is denoted as \( \sqrt{n} \). For example:
- \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) because \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \)
- \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) because \( 3 \times 3 = 9 \)
- \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) because \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \)
Understanding these basic operations helps in solving more complex mathematical problems. Here are some key properties of squares and square roots:
- The square of any real number is always non-negative.
- The square root of a positive number has two values: positive and negative (e.g., \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) and \( \sqrt{25} = -5 \)).
- The square root of zero is zero (\( \sqrt{0} = 0 \)).
- Negative numbers do not have real square roots since the square of a real number is never negative.
To solidify your understanding, let's look at a table of squares and square roots for numbers 1 through 10:
| Number | Square | Square Root |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) |
| 3 | 9 | \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) |
| 4 | 16 | \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) |
| 5 | 25 | \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) |
| 6 | 36 | \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \) |
| 7 | 49 | \( \sqrt{49} = 7 \) |
| 8 | 64 | \( \sqrt{64} = 8 \) |
| 9 | 81 | \( \sqrt{81} = 9 \) |
| 10 | 100 | \( \sqrt{100} = 10 \) |
By mastering the concepts of squares and square roots, you will be well-prepared to tackle more complex mathematical problems and applications.
Understanding Square Numbers
Square numbers, also known as perfect squares, are integers that are the product of an integer multiplied by itself. They form the foundation of many mathematical concepts and are easy to recognize with practice.
Definition and Notation
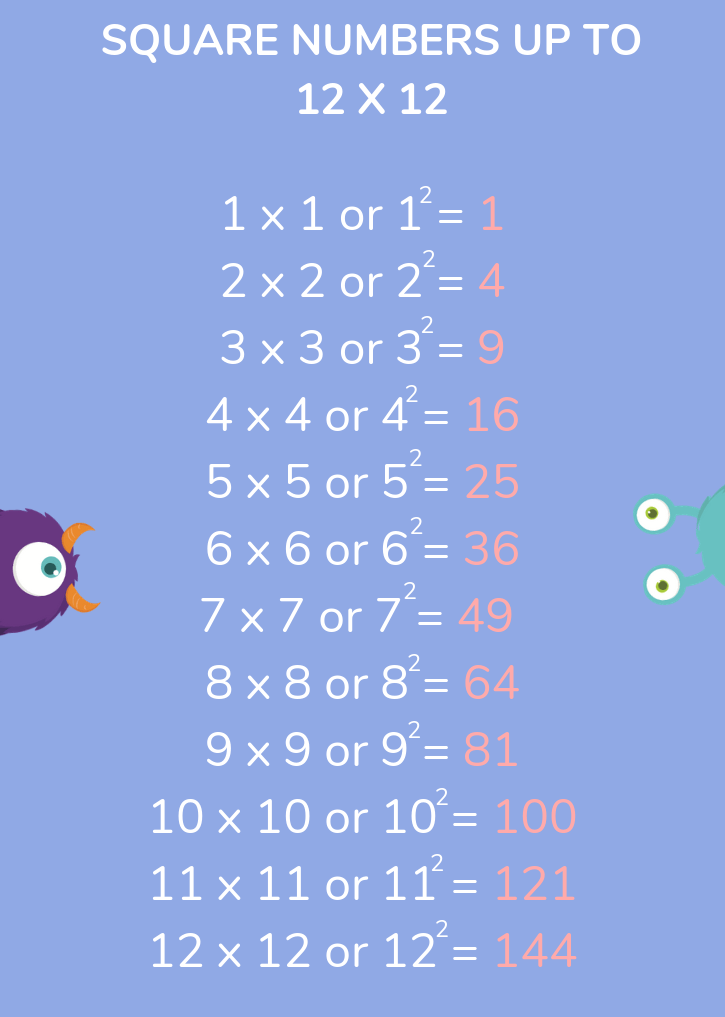
A square number is written as \( n^2 \), where \( n \) is the integer. For example:
- \( 1^2 = 1 \times 1 = 1 \)
- \( 2^2 = 2 \times 2 = 4 \)
- \( 3^2 = 3 \times 3 = 9 \)
- \( 4^2 = 4 \times 4 = 16 \)
- \( 5^2 = 5 \times 5 = 25 \)
Properties of Square Numbers
- Square numbers are always non-negative.
- The square of an even number is even, and the square of an odd number is odd.
- Square numbers increase rapidly as the base number increases.
Let's consider a few more examples to illustrate these properties:
- \( 6^2 = 36 \)
- \( 7^2 = 49 \)
- \( 8^2 = 64 \)
- \( 9^2 = 81 \)
- \( 10^2 = 100 \)
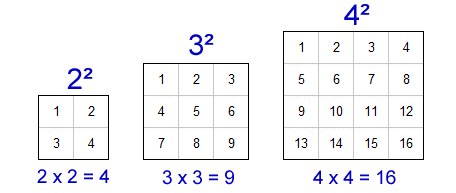
Visual Representation
Square numbers can also be represented visually. For example, \( 3^2 \) can be visualized as a 3x3 grid of squares:
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Applications of Square Numbers
Square numbers are used in various mathematical and real-world applications, including:
- Geometry: Calculating the area of squares.
- Algebra: Solving quadratic equations.
- Physics: Describing certain physical properties and phenomena.
Understanding square numbers is crucial for building a strong foundation in mathematics. Practice identifying and working with these numbers to enhance your mathematical skills.
Calculating Square Roots
Calculating square roots is a fundamental skill in mathematics. The square root of a number \( n \) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals \( n \). It is denoted as \( \sqrt{n} \). Below, we explore various methods to calculate square roots effectively.
Definition and Notation
The square root of \( n \) is written as \( \sqrt{n} \). For example:
- \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \) because \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \)
- \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) because \( 3 \times 3 = 9 \)
- \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) because \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \)
Estimating Square Roots
When the number is not a perfect square, you can estimate the square root by finding the two closest perfect squares it falls between. For example, to estimate \( \sqrt{10} \):
- Find the nearest perfect squares: \( 9 \) (which is \( 3^2 \)) and \( 16 \) (which is \( 4^2 \)).
- Since \( 10 \) is closer to \( 9 \) than to \( 16 \), we estimate \( \sqrt{10} \approx 3.2 \).
Using Prime Factorization
Prime factorization can simplify the calculation of square roots. For example, to find \( \sqrt{72} \):
- Factorize \( 72 \) into prime factors: \( 72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 \).
- Pair the factors: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 3^2) \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2} \).
Long Division Method
The long division method is a step-by-step process to find square roots of larger numbers more precisely:
- Group the digits in pairs, starting from the decimal point. For example, to find \( \sqrt{529} \):
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first group. For \( 529 \), this is \( 2 \), since \( 2^2 = 4 \).
- Subtract and bring down the next pair of digits. Repeat the process until all pairs are used.
Example: Calculating \( \sqrt{529} \)
| Step | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Group digits: 5|29 | |
| 2 | Find largest square less than 5: \( 2^2 = 4 \) | 2 |
| 3 | Subtract and bring down: \( 5 - 4 = 1 \), bring down 29 | 129 |
| 4 | Double the result (2): 4x (trial and error for 4x4 = 16) | 23 |
| 5 | Subtract 129 - 96 | 33 |
With practice, you will become proficient in calculating square roots using these methods, enhancing your overall mathematical skills.
Properties of Squares and Square Roots
Squares and square roots have several important properties that are fundamental to understanding and working with these mathematical concepts. Here, we explore these properties in detail.
Properties of Squares
- Non-Negativity: The square of any real number is always non-negative. For any real number \( x \), \( x^2 \geq 0 \).
- Even and Odd Squares: The square of an even number is even, and the square of an odd number is odd. For example:
- Even: \( 4^2 = 16 \)
- Odd: \( 5^2 = 25 \)
- Monotonicity: For any two positive numbers \( a \) and \( b \), if \( a > b \), then \( a^2 > b^2 \).
- Area Representation: The square of a number can be visualized as the area of a square with side length equal to the number. For instance, \( 3^2 \) represents the area of a square with sides of length 3.
Properties of Square Roots
- Non-Negativity: The square root of a non-negative number is also non-negative. For any non-negative number \( x \), \( \sqrt{x} \geq 0 \).
- Product Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots. For any non-negative numbers \( a \) and \( b \), \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \).
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots. For any non-negative numbers \( a \) and \( b \), \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \).
- Unique Value: Every non-negative number has a unique non-negative square root. For example, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \).
To further understand these properties, let's look at a table summarizing key points:
| Property | Square | Square Root |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Negativity | \( x^2 \geq 0 \) | \( \sqrt{x} \geq 0 \) |
| Even/Odd | Even \(\rightarrow\) Even Odd \(\rightarrow\) Odd |
N/A |
| Monotonicity | If \( a > b \), then \( a^2 > b^2 \) | If \( a > b \), then \( \sqrt{a} > \sqrt{b} \) |
| Product Property | N/A | \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \) |
| Quotient Property | N/A | \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \) |
| Unique Value | N/A | Each non-negative number has a unique non-negative square root |
Understanding these properties of squares and square roots is essential for solving mathematical problems and applying these concepts in various fields such as geometry, algebra, and physics.

Real-World Applications of Squares and Square Roots
Squares and square roots are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have numerous practical applications in various fields. Understanding these real-world applications can enhance comprehension and highlight the importance of these mathematical tools.
Geometry and Area Calculation
In geometry, squares and square roots are used extensively to calculate areas. For example:
- Calculating the area of a square: The area is given by \( A = s^2 \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Finding the side length from the area: If the area \( A \) is known, the side length is \( s = \sqrt{A} \).
Physics and Engineering
In physics and engineering, square roots are often used in formulas and equations to determine various physical properties:
- Calculating the root mean square (RMS) value of alternating current (AC) voltage or current, which is essential for electrical engineering.
- Determining the speed of an object in free fall using the formula \( v = \sqrt{2gh} \), where \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity and \( h \) is the height.
Statistics and Probability
Squares and square roots are fundamental in statistics, especially in variance and standard deviation calculations:
- Variance is the average of the squared differences from the mean: \( \sigma^2 = \frac{1}{N} \sum (x_i - \mu)^2 \).
- Standard deviation is the square root of the variance: \( \sigma = \sqrt{\sigma^2} \).
Finance and Economics
In finance and economics, square roots are used in various models and calculations:
- Calculating compound interest: The formula for compound interest can involve square roots when determining the time period or interest rate.
- Risk assessment: Standard deviation, which involves square roots, is used to assess the risk associated with investments.
Architecture and Construction
Squares and square roots are crucial in architecture and construction for designing and building structures:
- Determining the dimensions of materials needed for square or rectangular areas.
- Ensuring the structural integrity of buildings by calculating load distributions and forces.
Here is a table summarizing some key real-world applications of squares and square roots:
| Field | Application | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Area Calculation | \( A = s^2 \) and \( s = \sqrt{A} \) |
| Physics | Free Fall Speed | \( v = \sqrt{2gh} \) |
| Statistics | Standard Deviation | \( \sigma = \sqrt{\sigma^2} \) |
| Finance | Compound Interest | Interest rate calculations |
| Architecture | Material Dimensions | Calculating area and load distribution |
Understanding these applications can provide a deeper appreciation for the importance of squares and square roots in both academic and practical contexts.
Step-by-Step Solutions for Squaring Numbers
Squaring a number means multiplying the number by itself. Below, we provide detailed, step-by-step solutions to help you understand and master the process of squaring numbers.
Example 1: Squaring a Single-Digit Number
Let's start with a simple example of squaring the number 4.
- Write down the number: \( 4 \).
- Multiply the number by itself: \( 4 \times 4 \).
- Calculate the product: \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
So, \( 4^2 = 16 \).
Example 2: Squaring a Two-Digit Number
Now, let's square the number 12.
- Write down the number: \( 12 \).
- Multiply the number by itself: \( 12 \times 12 \).
- Calculate the product using the distributive property:
- \( 12 \times 12 = (10 + 2) \times (10 + 2) \)
- Expand using FOIL (First, Outer, Inner, Last):
- First: \( 10 \times 10 = 100 \)
- Outer: \( 10 \times 2 = 20 \)
- Inner: \( 2 \times 10 = 20 \)
- Last: \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \)
- Add the results: \( 100 + 20 + 20 + 4 = 144 \).
So, \( 12^2 = 144 \).
Example 3: Squaring a Larger Number
Let's square the number 25.
- Write down the number: \( 25 \).
- Multiply the number by itself: \( 25 \times 25 \).
- Calculate the product using the distributive property:
- \( 25 \times 25 = (20 + 5) \times (20 + 5) \)
- Expand using FOIL:
- First: \( 20 \times 20 = 400 \)
- Outer: \( 20 \times 5 = 100 \)
- Inner: \( 5 \times 20 = 100 \)
- Last: \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \)
- Add the results: \( 400 + 100 + 100 + 25 = 625 \).
So, \( 25^2 = 625 \).
Example 4: Squaring a Decimal Number
Let's square the number 3.2.
- Write down the number: \( 3.2 \).
- Multiply the number by itself: \( 3.2 \times 3.2 \).
- Calculate the product:
- First, convert to fractions: \( 3.2 = \frac{32}{10} \).
- Square the fraction: \( \left( \frac{32}{10} \right)^2 = \frac{32 \times 32}{10 \times 10} = \frac{1024}{100} \).
- Convert back to a decimal: \( \frac{1024}{100} = 10.24 \).
So, \( 3.2^2 = 10.24 \).
Practice Problems
Try squaring the following numbers on your own:
- \( 7 \)
- \( 15 \)
- \( 6.5 \)
- \( 100 \)
Practicing these examples will help solidify your understanding of squaring numbers. Remember, the key is to break down the problem into manageable steps and use the distributive property for larger numbers.
Step-by-Step Solutions for Finding Square Roots
Finding square roots can seem daunting at first, but with a systematic approach, it becomes straightforward. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Understand the Concept: Before diving into calculations, ensure you understand what a square root represents. It's the number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
- Prime Factorization: If the number isn't a perfect square, break it down into its prime factors. This step simplifies the process.
- Pairing Factors: Pair up the prime factors in twos. Each pair represents a square root.
- Identify Perfect Squares: Recognize perfect squares from the pairs. They have even exponents.
- Multiplication: Multiply the prime factors to find the square root.
- Example: Let's find the square root of 144.
So, the square root of 144 is 6.Prime Factors of 144: 24 × 32 Pairing Factors: (22)2 × (31)2 Identify Perfect Squares: 22 and 31 are perfect squares. Multiplication: (22 × 31) = 2 × 3 = 6 - Verify: Always double-check your answer by squaring it to ensure correctness.
With practice, you'll master the art of finding square roots efficiently.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mastering square roots requires attention to detail. Here are some common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
- Forgetting the Order of Operations: Ensure you perform operations inside parentheses first, then exponents, followed by multiplication and division, and finally addition and subtraction.
- Incorrect Prime Factorization: Make sure to accurately break down numbers into their prime factors. Mistakes in prime factorization can lead to errors in finding square roots.
- Ignoring Negative Solutions: Remember that every positive number has both positive and negative square roots. Don't overlook negative solutions, especially in real-world problems.
- Not Verifying Answers: Always double-check your answers by squaring the calculated square root to ensure correctness. This step helps catch calculation errors.
- Relying Solely on Calculators: While calculators can be helpful, relying solely on them may hinder understanding. Practice mental math and manual calculations to reinforce concepts.
- Skipping Practice: Regular practice is crucial for mastery. Avoid skipping practice problems, as they reinforce understanding and help identify weak areas.
- Overlooking Simplification: After finding a square root, simplify the answer if possible. This step ensures clarity and may reveal patterns or relationships.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls and implementing the suggested tips, you can enhance your proficiency in dealing with square roots.

Practice Worksheets for Squares and Square Roots
Practice makes perfect when it comes to mastering squares and square roots. Below are some practice worksheets to sharpen your skills:
- Basic Square Practice: Start with simple exercises involving perfect squares. Practice finding the square roots of numbers like 4, 9, 16, and 25.
- Advanced Square Practice: Challenge yourself with more complex square roots, such as 144, 225, and 400. These exercises will help reinforce your understanding of square roots.
- Real-World Applications: Explore real-world scenarios where knowledge of squares and square roots is essential. For example, calculate the area of a square field given its side length.
- Word Problems: Solve word problems that require the application of square roots. These problems mimic real-life situations and test your problem-solving skills.
- Mixed Practice: Mix both squares and square roots in a single worksheet to ensure comprehensive practice. This approach challenges you to switch between finding squares and square roots seamlessly.
- Online Interactive Worksheets: Utilize online platforms offering interactive worksheets. These resources provide instant feedback and additional guidance, enhancing your learning experience.
Consistent practice with these worksheets will build confidence and proficiency in dealing with squares and square roots.
Advanced Problems Involving Squares and Square Roots
Ready to tackle more challenging problems related to squares and square roots? Here are some advanced scenarios to test your understanding:
- Finding Square Roots of Large Numbers: Practice finding square roots of larger numbers, such as 10000, 100000, or even 1000000. This exercise improves your computational skills and patience.
- Decimal Square Roots: Explore square roots that result in decimal numbers. Calculate square roots like √2, √3, or √5. These exercises require a deeper understanding of irrational numbers.
- Estimation Techniques: Develop estimation techniques to approximate square roots without using calculators. This skill is valuable in situations where precise calculations aren't necessary.
- Pythagorean Theorem Applications: Apply the Pythagorean theorem in various contexts to solve complex problems involving squares and square roots. This includes scenarios like finding the length of a diagonal in a rectangle.
- Algebraic Manipulations: Solve algebraic equations involving squares and square roots. This includes equations with square roots on both sides or quadratic equations requiring manipulation to isolate the square root.
- Challenge Problems: Attempt challenging problems that combine multiple concepts, such as finding square roots in geometric series or applying square roots in calculus problems.
By engaging with these advanced problems, you'll deepen your understanding of squares and square roots and enhance your problem-solving abilities.
Visual Aids and Diagrams for Better Understanding
Visual aids and diagrams are invaluable tools for enhancing understanding of squares and square roots. Here's how they can assist:
- Geometric Figures: Use geometric figures like squares and rectangles to illustrate concepts visually. Diagrams depicting the relationship between side lengths and areas of squares aid in understanding square roots.
- Number Lines: Utilize number lines to visualize the placement of square roots on the number line. This visualization helps grasp the concept of square roots in relation to other numbers.
- Graphs: Plot graphs of quadratic functions to visualize the behavior of square roots. Observing the shape of the graph and points of intersection with the x-axis enhances comprehension.
- Pythagorean Theorem Diagrams: Diagrams illustrating the Pythagorean theorem and its applications provide insight into the relationship between squares of sides in a right triangle.
- Interactive Simulations: Engage with interactive simulations that dynamically illustrate square roots and their properties. These simulations allow for hands-on exploration and experimentation.
- Color Coding: Use color-coding techniques to differentiate between different components of square roots, such as coefficients and radicals. Colorful visuals aid in distinguishing parts and facilitate understanding.
- Step-by-Step Illustrations: Provide step-by-step illustrations of algorithms for finding square roots, accompanied by diagrams. Visualizing each step enhances clarity and reinforces the process.
By incorporating visual aids and diagrams into your learning process, you'll gain a deeper understanding of squares and square roots and improve your problem-solving skills.
Interactive Activities and Online Resources
Explore interactive activities and online resources to make learning about squares and square roots engaging and fun. Here's a curated list:
- Online Quizzes: Take interactive quizzes designed to test your knowledge of squares, square roots, and related concepts. Instant feedback helps reinforce learning.
- Virtual Manipulatives: Use virtual manipulatives to visually represent squares and square roots. These interactive tools allow for hands-on exploration and experimentation.
- Math Games: Play educational math games centered around squares and square roots. These games make learning enjoyable while reinforcing mathematical skills.
- Video Tutorials: Watch video tutorials that explain concepts related to squares and square roots in a clear and engaging manner. Visual explanations enhance understanding.
- Interactive Demonstrations: Interact with online demonstrations that illustrate properties and applications of squares and square roots. Manipulate parameters to observe changes in real-time.
- Online Forums: Participate in online forums or discussion boards dedicated to mathematics. Engage with peers and instructors to ask questions, share insights, and collaborate on problem-solving.
- Math Apps: Download math apps specifically designed to teach squares and square roots. These apps often include interactive lessons, quizzes, and practice exercises.
- Webinars and Workshops: Attend webinars and workshops hosted by mathematics educators or organizations. These sessions provide in-depth insights and practical strategies for mastering squares and square roots.
By leveraging interactive activities and online resources, you can enhance your understanding of squares and square roots while enjoying the learning process.

Summary and Key Takeaways
After exploring squares and square roots through various resources, here are the key points to remember:
- Understanding: Square roots represent the inverse operation of squaring a number. They find the side length of a square with a given area.
- Properties: Square roots of perfect squares are integers, while those of non-perfect squares are irrational numbers. Every positive number has both positive and negative square roots.
- Calculation: Prime factorization and estimation techniques help in finding square roots. It's important to verify answers by squaring them.
- Applications: Squares and square roots have numerous real-world applications in geometry, physics, engineering, and finance.
- Practice: Consistent practice, including solving problems, working with interactive resources, and participating in discussions, is key to mastering squares and square roots.
- Visual Aids: Visual aids such as diagrams, graphs, and interactive simulations enhance understanding and facilitate learning.
- Online Resources: Utilize online resources such as quizzes, tutorials, math games, and webinars to supplement learning and deepen understanding.
By internalizing these key takeaways and engaging actively with the material, you'll build a solid foundation in squares and square roots, paving the way for further mathematical exploration and success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is a square number?
A square number is the product of an integer multiplied by itself. For example, 4, 9, and 16 are square numbers because they are the result of multiplying 2, 3, and 4 by themselves, respectively.
-
What is a square root?
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 × 3 = 9.
-
How do you find the square root of a number?
There are various methods to find the square root of a number, including prime factorization, estimation, and using calculators or mathematical formulas such as the Babylonian method.
-
What is the difference between a perfect square and a non-perfect square?
A perfect square is a number that has an integer square root, meaning its square root is a whole number. Non-perfect squares have square roots that are irrational numbers, meaning they cannot be expressed as simple fractions.
-
Why are square roots important?
Square roots have various applications in mathematics, science, engineering, and everyday life. They are used in calculating areas, volumes, distances, and in solving equations and problems involving quadratic functions.
-
What are some common mistakes to avoid when dealing with squares and square roots?
Common mistakes include forgetting the order of operations, incorrect prime factorization, ignoring negative solutions, not verifying answers, relying solely on calculators, skipping practice, and overlooking simplification.
Additional Resources for Further Learning
Expand your knowledge of squares and square roots with these additional resources:
- Textbooks: Explore textbooks on mathematics, algebra, and geometry that cover squares, square roots, and related topics in detail.
- Online Courses: Enroll in online courses offered by educational platforms or universities. These courses provide structured learning experiences with video lectures, assignments, and quizzes.
- Mathematical Websites: Visit websites dedicated to mathematics, where you can find articles, tutorials, practice problems, and interactive tools related to squares and square roots.
- Mathematical Software: Use mathematical software such as MATLAB, Mathematica, or GeoGebra to explore concepts visually, perform calculations, and solve problems involving squares and square roots.
- Mathematics Forums: Join online forums or communities focused on mathematics to engage with fellow learners and experts, ask questions, and participate in discussions.
- Mathematics Journals: Access academic journals in mathematics to explore research articles and papers on advanced topics related to squares, square roots, and their applications.
- Mathematics Conferences: Attend mathematics conferences and workshops to learn from leading experts, discover new trends and developments, and network with professionals in the field.
By exploring these additional resources, you can deepen your understanding of squares and square roots and further your mathematical education.
Xem video này để hiểu về bình phương và căn bậc ba một cách dễ dàng và thú vị cùng thầy J.
Bình Phương và Căn bậc ba | Toán học cùng thầy J
READ MORE:
Khám phá khái niệm căn bậc hai với thầy J trong video này. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về căn bậc hai và cách tính toán nó.
Căn bậc hai là gì? | Toán học cùng thầy J