Topic what does the square of a number mean: Explore the fascinating world of squaring numbers in this insightful article. Discover the meaning behind the square of a number and its significance in mathematics and beyond. From its basic definition to practical applications, delve into the properties and uses of squares with clarity and depth.
Table of Content
Understanding the Square of a Number
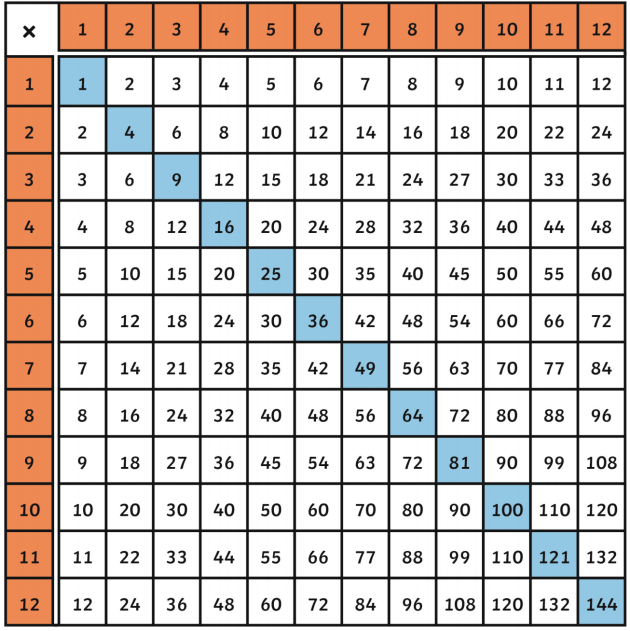
The square of a number is the result of multiplying the number by itself. It is denoted by placing the number to be squared next to itself, often with a superscript 2, indicating the operation of squaring. Mathematically, if we have a number \( x \), its square is represented as \( x^2 \).
Properties of Squares:
- Positive Outcome: Squaring any real number (positive, negative, or zero) results in a non-negative number.
- Symmetry: Squares are symmetric about the origin, meaning that the square of \( x \) is equal to the square of \( -x \).
- Geometric Interpretation: The square of a number represents the area of a square with side length equal to that number. For example, if \( x \) is the length of a side of a square, then \( x^2 \) represents the area of that square.
- Even Powers: Squares are an example of even powers, meaning that the exponent is a multiple of 2.
- Non-Negative: Regardless of the sign of the original number, the square of a real number is always non-negative.
Applications:
The concept of squaring is extensively used in various fields such as mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science. Some common applications include:
- Area Calculations: In geometry, the square of a number is used to calculate areas of squares and related shapes.
- Physical Laws: In physics, squaring is used in equations to represent phenomena such as motion, force, and energy.
- Signal Processing: In engineering and computer science, squaring is used in signal processing algorithms for tasks like noise reduction and modulation.
- Statistical Analysis: Squaring is employed in statistical analysis for calculating variances and other measures of dispersion.
READ MORE:
Table of Contents
Definition of Squaring
Meaning of Squaring in Mathematics
Understanding the Properties of Squares
Geometric Interpretation of Squares
Applications of Squaring in Real Life
Exploring the Symmetry of Squares
Practical Examples of Squaring
Importance of Squares in Algebra
How to Calculate the Square of a Number
Definition of Squaring
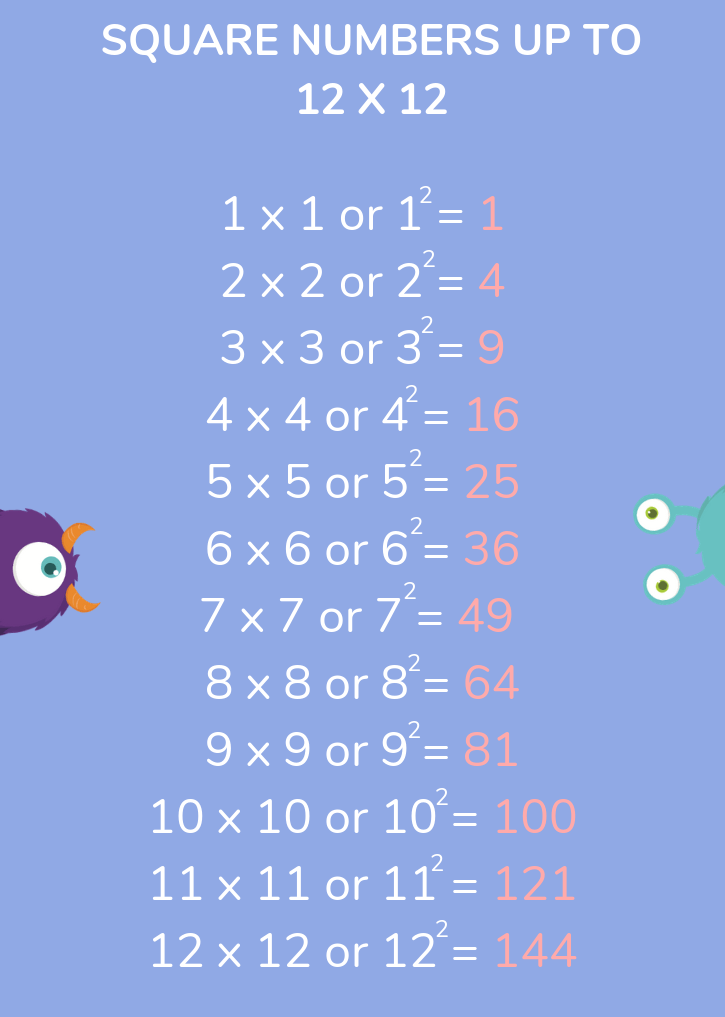
Squaring a number involves multiplying the number by itself. It is a fundamental mathematical operation used to find the area of a square with side length equal to the given number. In algebra, squaring is represented by raising a number to the power of 2. For instance, squaring the number 3 results in 9, as \(3^2 = 3 \times 3 = 9\).
Properties of Squares
Squares possess several interesting properties that make them significant in mathematics and various other fields:
Non-Negativity: The square of any real number, whether positive, negative, or zero, always results in a non-negative number.
Symmetry: Squares are symmetric about the origin, meaning that the square of \(x\) is equal to the square of \(-x\).
Even Powers: Squares represent even powers, with the exponent being a multiple of 2.
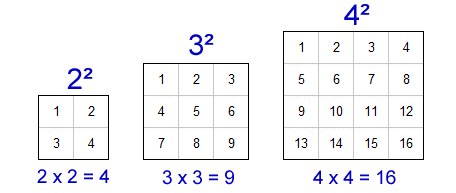
Geometric Interpretation: The square of a number corresponds to the area of a square with side length equal to the number.
Non-Negative: Regardless of the sign of the original number, the square of a real number is always non-negative.
Geometric Interpretation
The square of a number has a clear geometric interpretation, primarily in terms of area:
Area of a Square: When we square a number, we essentially find the area of a square with side length equal to that number. For example, squaring 3 gives us 9, which represents the area of a square with side length 3 units.
Visual Representation: Visualizing squaring in terms of squares helps in understanding the concept intuitively. It demonstrates how the area grows as the side length of the square increases.
Applications in Geometry: This geometric interpretation is crucial in geometry for calculating areas of squares and related shapes. It forms the basis for various geometric concepts and calculations.

Applications of Squaring
The concept of squaring numbers finds diverse applications across various fields:
Geometry: Squaring is essential in geometry for calculating areas of squares, rectangles, and other shapes. It helps in determining the size of two-dimensional objects.
Physics: In physics, squaring is used in equations related to motion, energy, and force. It plays a crucial role in understanding physical phenomena and predicting outcomes.
Engineering: Engineers use squaring in signal processing, control systems, and structural analysis. It assists in modeling and analyzing systems to design efficient solutions.
Computer Science: Squaring is utilized in algorithms for various tasks such as image processing, data compression, and cryptography. It forms the foundation of many computational operations.
Statistics: In statistics, squaring is involved in calculating variances, standard deviations, and other measures of dispersion. It helps in understanding the spread of data points in a dataset.
Học cách bình phương một số trong bài giảng này của Thầy J. Hiểu ý nghĩa của việc bình phương một số và cách sử dụng số mũ trong toán học.
Làm thế nào để bình phương một số | Ý nghĩa của việc bình phương một số | Số mũ | Toán học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu về số bình phương trong bài giảng này. Khám phá ý nghĩa của việc bình phương một số và cách áp dụng trong toán học.
Giải thích về Số Bình Phương