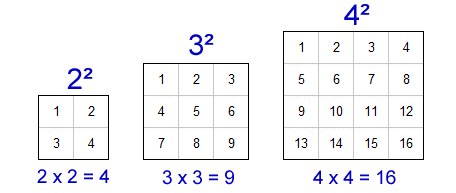
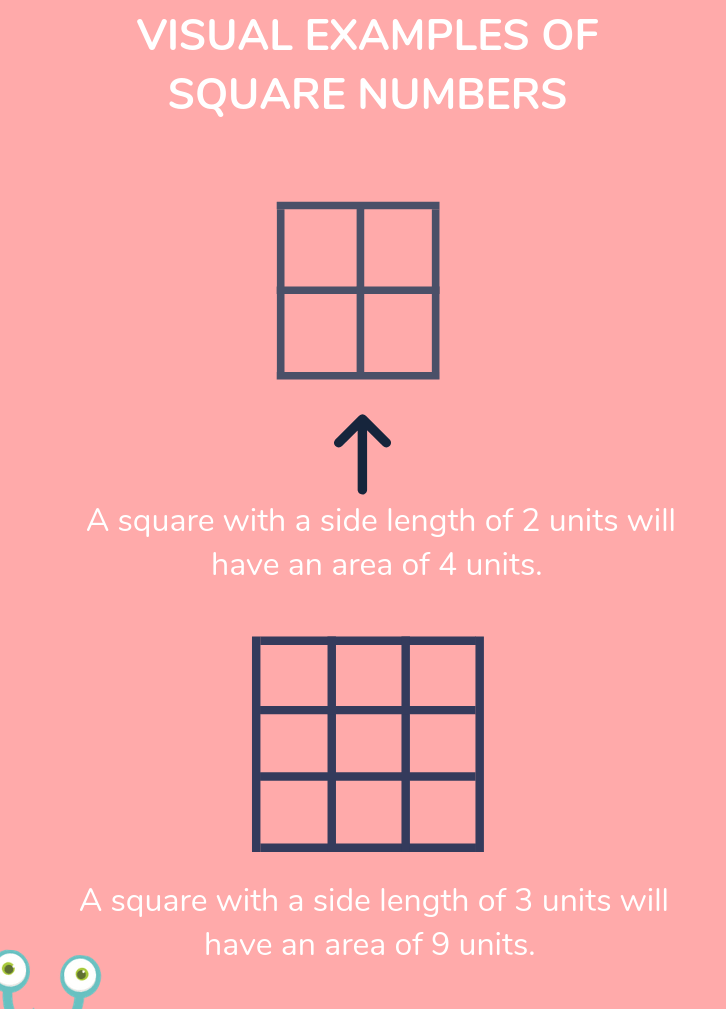Topic square root and cube root worksheet: Square root and cube root worksheets are essential tools for helping students master these fundamental mathematical concepts. These worksheets provide a variety of exercises, from basic calculations to more complex problems, ensuring comprehensive practice and skill development. Perfect for reinforcing classroom learning and boosting problem-solving abilities, these resources are ideal for students at various levels.
Table of Content
- Square Root and Cube Root Worksheets
- Introduction to Square and Cube Roots
- Finding Square Roots
- Finding Cube Roots
- Methods for Calculating Roots
- Perfect Squares and Cubes
- Interactive Exercises
- Simplifying Expressions Involving Exponents
- Advanced Problems
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Video 'Căn bậc hai và căn bậc ba' giới thiệu các khái niệm cơ bản và phương pháp tính toán với các ví dụ minh họa rõ ràng, giúp người học nắm vững kiến thức.
Square Root and Cube Root Worksheets
These worksheets are designed to help students in grades 7 and 8 understand and practice finding square roots and cube roots. They offer a variety of methods, activities, and exercises to enhance learning and mastery of these mathematical concepts.
Methods for Finding Roots
-
Using a Calculator
Enter the number and press the square root or cube root button.
-
Prime Factorization Method
Find the prime factors of the number and group them appropriately. For square roots, group in pairs; for cube roots, group in sets of three.
-
Estimation Method
Round the number to the nearest perfect square or cube and find the root of the perfect value, then adjust the result.
Practice Activities
- Find the square roots and cube roots of given numbers.
- Count the dots and calculate squares and cubes.
- Match numbers with their square and cube values.
- Use long division method to find square roots of non-perfect squares.
Example Problems
| Method | Example | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Calculator | Find the cube root of 125. | 5 |
| Prime Factorization | Find the cube root of 216. | 2 x 3 = 6 |
| Estimation | Find the cube root of 37. | Approximately 3.3 |
Key Concepts
- Square: Multiplying a number by itself. Example: \( 5^2 = 25 \)
- Square Root: The inverse operation of squaring. Example: \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
- Cube: Multiplying a number by itself three times. Example: \( 5^3 = 125 \)
- Cube Root: The inverse operation of cubing. Example: \( \sqrt[3]{125} = 5 \)
Worksheets and Activities
Printable worksheets are available for practicing these skills, including:
- Basic root finding exercises.
- Matching square and cube values.
- Step-by-step guided lessons and independent practice.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square and Cube Roots
Understanding square and cube roots is essential in mathematics as they lay the foundation for more advanced concepts. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4, because \(4 \times 4 = 16\). This can be represented mathematically as \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
Similarly, a cube root of a number is a value that, when used three times in a multiplication, gives the original number. For example, the cube root of 27 is 3, because \(3 \times 3 \times 3 = 27\). This can be expressed as \( \sqrt[3]{27} = 3 \).
Perfect squares are integers that are the square of other integers, such as \(1, 4, 9, 16\), and perfect cubes are integers that are the cube of other integers, like \(1, 8, 27, 64\).
These concepts are fundamental in solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding various mathematical relationships. Mastery of square and cube roots enhances problem-solving skills and prepares students for higher-level math courses.
To further explore these concepts, worksheets on square and cube roots offer a variety of problems, including finding roots, solving equations, and applying these operations in real-world scenarios.
Finding Square Roots
Understanding how to find the square root of a number is a fundamental mathematical skill. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The process of finding square roots can be done using various methods, including prime factorization, estimation, and the long division method. Here is a step-by-step guide to finding square roots:
- Prime Factorization Method
- Write down the number for which you want to find the square root.
- Break the number down into its prime factors.
- Group the prime factors into pairs of the same number.
- Take one number from each pair and multiply them to get the square root.
- Example:
Find the square root of 144.
- Write 144.
- Prime factors of 144: \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\)
- Group the factors: \((2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3)\)
- Take one factor from each pair: \(2 \times 2 \times 3 = 12\)
- So, \(\sqrt{144} = 12\)
- Estimation Method
- Find the two perfect squares between which the given number lies.
- Estimate the square root to be closer to the smaller or larger perfect square based on proximity.
- Refine the estimate using averages or more precise calculations if needed.
- Long Division Method
- Group the digits of the number in pairs from right to left (for decimal numbers, start from the decimal point).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the leftmost pair. This is the first digit of the root.
- Subtract the square of this digit from the leftmost pair and bring down the next pair of digits.
- Double the current quotient and determine the next digit by trial and error to ensure the new divisor, when multiplied by this digit, fits into the current remainder.
- Repeat the process for the desired precision.
By mastering these methods, students can confidently find the square roots of various numbers, enhancing their overall mathematical proficiency.
Finding Cube Roots
Cube roots are the inverse operation of cubing a number. To find the cube root of a number \( x \), you need to determine the number \( y \) such that \( y^3 = x \). This can be represented as:
\[
\sqrt[3]{x} = y \quad \text{where} \quad y^3 = x
\]
Here are the steps to find the cube root:
- Identify the number you want to find the cube root of.
- Estimate a number that, when cubed, is close to the original number.
- Use the estimation to narrow down the possible values.
- Apply a calculator for more accuracy if necessary, especially for non-perfect cubes.
Let's look at some examples:
-
Example 1: Find the cube root of 27.
We know that \(3^3 = 27\). Therefore, \(\sqrt[3]{27} = 3\). -
Example 2: Find the cube root of 125.
We know that \(5^3 = 125\). Therefore, \(\sqrt[3]{125} = 5\). -
Example 3: Find the cube root of 8.
We know that \(2^3 = 8\). Therefore, \(\sqrt[3]{8} = 2\).
For non-perfect cubes, the cube root might not be an integer. For example, finding the cube root of 20 involves approximation:
\[
\sqrt[3]{20} \approx 2.7
\]
Understanding cube roots is essential for solving more complex mathematical problems, including those involving volume calculations and higher-level algebra.
Methods for Calculating Roots
Understanding how to calculate square roots and cube roots is essential for solving various mathematical problems. Here are the most common methods for finding these roots:
Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method:
- Factor the number into its prime factors.
- Group the factors into pairs of identical numbers.
- Take one number from each pair and multiply them together to get the square root.
- Estimation Method:
- Find the two perfect squares between which the number lies.
- Estimate the square root based on these perfect squares.
- Refine the estimate by averaging and adjusting as needed.
- Long Division Method:
- Group the digits in pairs starting from the decimal point.
- Find the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to the leftmost pair.
- Use long division steps to find the next digits of the square root.
Cube Roots
- Prime Factorization Method:
- Factor the number into its prime factors.
- Group the factors into triples of identical numbers.
- Take one number from each triple and multiply them together to get the cube root.
- Estimation Method:
- Find the two perfect cubes between which the number lies.
- Estimate the cube root based on these perfect cubes.
- Refine the estimate by averaging and adjusting as needed.
- Newton's Method:
- Choose an initial guess for the cube root.
- Use the formula \( x_{n+1} = \frac{2x_n + \frac{N}{x_n^2}}{3} \) to improve the guess.
- Repeat the process until the desired accuracy is achieved.
By mastering these methods, you can efficiently calculate square and cube roots for a wide range of numbers, enhancing your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities.

Perfect Squares and Cubes
Understanding perfect squares and cubes is essential for mastering the concepts of square and cube roots. A perfect square is an integer that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. For example, \(4 = 2 \times 2\) and \(16 = 4 \times 4\). Similarly, a perfect cube is an integer that can be expressed as the product of an integer multiplied by itself twice more. For example, \(27 = 3 \times 3 \times 3\) and \(64 = 4 \times 4 \times 4\).
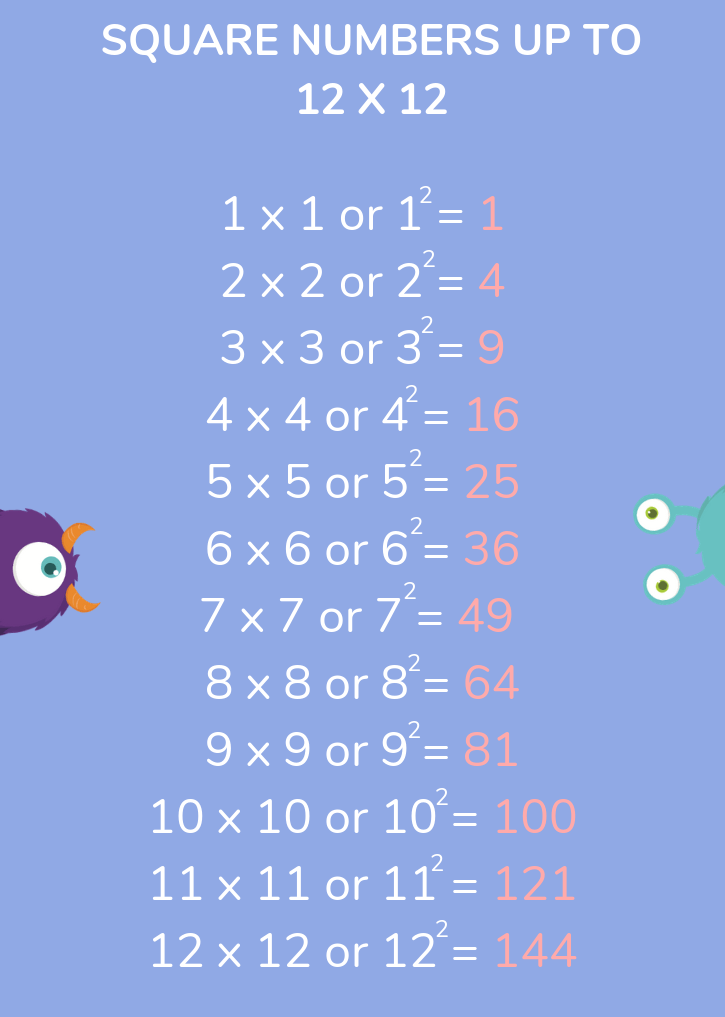
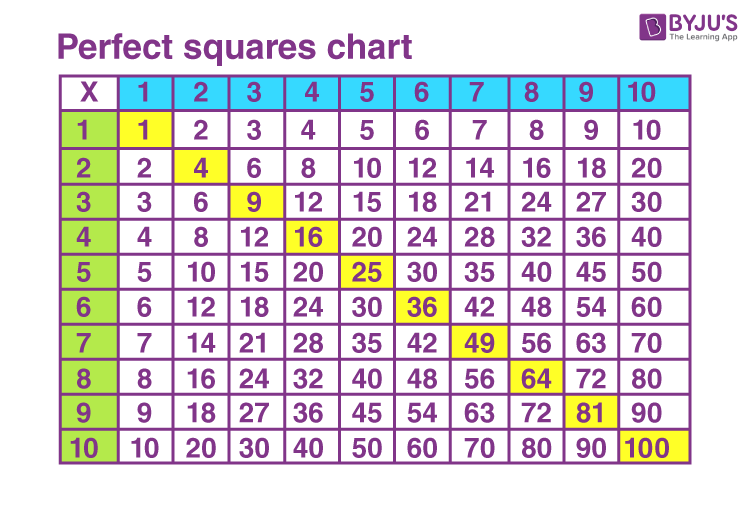
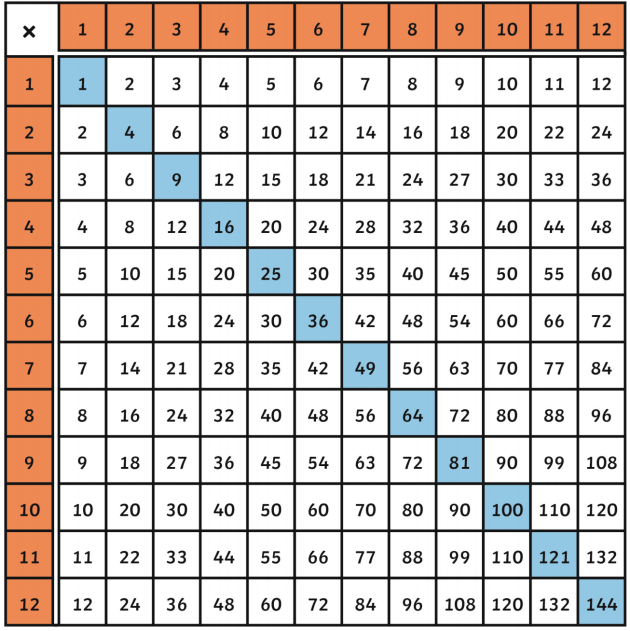
Identifying Perfect Squares
Perfect squares are often encountered in various mathematical problems. Here are some key perfect squares to remember:
- \(1^2 = 1\)
- \(2^2 = 4\)
- \(3^2 = 9\)
- \(4^2 = 16\)
- \(5^2 = 25\)
- \(6^2 = 36\)
- \(7^2 = 49\)
- \(8^2 = 64\)
- \(9^2 = 81\)
- \(10^2 = 100\)
Identifying Perfect Cubes
Perfect cubes are equally important. Here are some key perfect cubes:
- \(1^3 = 1\)
- \(2^3 = 8\)
- \(3^3 = 27\)
- \(4^3 = 64\)
- \(5^3 = 125\)
- \(6^3 = 216\)
- \(7^3 = 343\)
- \(8^3 = 512\)
- \(9^3 = 729\)
- \(10^3 = 1000\)
Applications
Perfect squares and cubes have various applications in solving equations and simplifying expressions. Recognizing these values quickly can help in simplifying roots and powers in algebraic expressions and equations. For example, solving \(x^2 = 49\) is straightforward when recognizing that \(49\) is a perfect square (\(7^2\)).
Interactive Exercises
Engage your students with interactive exercises designed to reinforce their understanding of square and cube roots. These activities are perfect for in-class participation or as homework assignments. Here are some interactive exercises:
- Count the Dots and Get the Squares
Students will count the dots in given patterns to identify perfect squares. This exercise helps visualize the concept of squaring numbers.
- Provide a grid of dots.
- Ask students to count and form squares with the dots.
- Identify the number of dots in each square and its square root.
- Match the Squares and Cubes
Students match given numbers with their corresponding squares and cubes. This exercise strengthens their ability to recognize and compute squares and cubes.
Number Square Cube 2 4 8 3 9 27 4 16 64 - Interactive Quiz: Square and Cube Roots
This online quiz provides instant feedback and covers a range of problems from basic identification to more complex calculations involving square and cube roots.
- Solve for the square root of 49.
- Find the cube root of 27.
- What is the square of 7?
- Calculate the cube of 5.
- Puzzle: Simplify the Expressions
Students simplify given expressions involving square and cube roots. This activity can be made competitive by setting a time limit.
- Simplify √(16) + ∛(8).
- Simplify √(81) - ∛(27).
- Find the value of √(64) * ∛(125).
These exercises are designed to be fun and engaging, while also providing valuable practice in calculating and understanding square and cube roots.
Simplifying Expressions Involving Exponents
This section provides detailed methods and examples for simplifying expressions involving exponents. Understanding how to manipulate exponents is essential for solving more complex mathematical problems. Here are some key methods:
- Multiplication of Powers:
When multiplying two expressions with the same base, you add the exponents. For example, \( a^m \cdot a^n = a^{m+n} \).
- Division of Powers:
When dividing two expressions with the same base, you subtract the exponents. For example, \( \frac{a^m}{a^n} = a^{m-n} \).
- Raising a Power to a Power:
When raising an expression to another power, you multiply the exponents. For example, \( (a^m)^n = a^{m \cdot n} \).
- Negative Exponents:
A negative exponent indicates the reciprocal of the base raised to the opposite positive exponent. For example, \( a^{-n} = \frac{1}{a^n} \).
- Zero Exponents:
Any non-zero base raised to the power of zero is equal to one. For example, \( a^0 = 1 \).
Examples
- Simplify \( 3^2 \cdot 3^3 \):
Solution: \( 3^{2+3} = 3^5 = 243 \)
- Simplify \( \frac{5^7}{5^2} \):
Solution: \( 5^{7-2} = 5^5 = 3125 \)
- Simplify \( (2^3)^4 \):
Solution: \( 2^{3 \cdot 4} = 2^{12} = 4096 \)
- Simplify \( 4^{-2} \):
Solution: \( \frac{1}{4^2} = \frac{1}{16} \)
- Simplify \( 7^0 \):
Solution: \( 1 \)
Practice Problems
- Simplify \( 6^3 \cdot 6^2 \)
- Simplify \( \frac{8^5}{8^3} \)
- Simplify \( (5^2)^3 \)
- Simplify \( 9^{-1} \)
- Simplify \( 10^0 \)
Understanding and practicing these rules will help you simplify expressions and solve equations involving exponents with confidence. Happy learning!
Advanced Problems
Advanced problems involving square roots and cube roots often require a deep understanding of mathematical concepts, including simplifying expressions, handling negative numbers, and working with imaginary numbers. Below are some detailed exercises to challenge your skills:
Simplifying Square Roots with Negative Numbers
Understand that the square root of a negative number involves imaginary numbers. For example, \( \sqrt{-16} \) can be written as \( \sqrt{16} \times \sqrt{-1} = 4i \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit.
Practice problems:
- Find \( \sqrt{-25} \)
- Find \( \sqrt{-81} \)
- Simplify \( \sqrt{-144} \)
Simplifying in Terms of Imaginary Numbers
When working with imaginary numbers, it's crucial to understand how to manipulate them. Here are some examples and steps to follow:
Simplify \( \sqrt{-9} \). Since \( \sqrt{-9} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{-1} = 3i \).
Simplify \( \sqrt{-50} \):
- First, break it down: \( \sqrt{-50} = \sqrt{50} \times \sqrt{-1} \)
- Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \) to \( \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
- Combine: \( 5\sqrt{2} \times i = 5i\sqrt{2} \)
Complex Number Exercises
- Simplify \( \sqrt{-36} \) and express the answer in terms of \( i \).
- Simplify \( \sqrt{-49} \) and express the answer in terms of \( i \).
- Simplify \( \sqrt{-100} \) and express the answer in terms of \( i \).
Advanced Cube Root Problems
Cube roots can be tricky, especially when dealing with larger numbers or negative values. Here are some problems to enhance your skills:
- Find the cube root of -27: \( \sqrt[3]{-27} = -3 \)
- Find the cube root of -64: \( \sqrt[3]{-64} = -4 \)
- Find the cube root of -125: \( \sqrt[3]{-125} = -5 \)
Practice with Radical Expressions
Simplifying radical expressions involves combining like terms and rationalizing denominators. Try these exercises:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{50} + 3\sqrt{2} \)
- Simplify \( 2\sqrt{18} - \sqrt{8} \)
- Simplify \( \frac{\sqrt{72}}{\sqrt{2}} \)

Additional Resources
Explore a variety of resources to further enhance your understanding of square roots and cube roots. These materials are designed to provide comprehensive support for students and educators alike.
-
Related Worksheets
- : A vast collection of printable worksheets focusing on square roots and cube roots, tailored for different grade levels.
- : Worksheets that cover the basics of square roots and cube roots, including practice problems and detailed solutions.
-
Interactive Resources
- : Engage with interactive worksheets that provide instant feedback, helping students to learn and correct mistakes in real-time.
- : These interactive sheets allow for individual question selection and are ideal for classroom and revision use.
-
GCSE Maths Revision Resources
- : Practice questions and video tutorials specifically aimed at preparing for GCSE exams, focusing on squares, cubes, and their roots.
- : A comprehensive guide to GCSE Maths, including sections on square and cube roots, with step-by-step explanations and practice questions.
Video 'Căn bậc hai và căn bậc ba' giới thiệu các khái niệm cơ bản và phương pháp tính toán với các ví dụ minh họa rõ ràng, giúp người học nắm vững kiến thức.
Căn bậc hai và căn bậc ba | Toán với thầy J
READ MORE:
Video 'Toán Vui - Số Mũ và Căn Bậc Hai' giải thích chi tiết về số mũ và căn bậc hai, giúp người học hiểu rõ các khái niệm và ứng dụng trong toán học.
Toán Vui - Số Mũ và Căn Bậc Hai