Topic is 0 a square number: Is 0 a square number? This article delves into the fascinating world of square numbers, starting with the unique case of zero. Join us as we explore definitions, properties, and examples to uncover why 0 holds a special place in the realm of perfect squares.
Table of Content
Is 0 a Square Number?
A square number, also known as a perfect square, is an integer that is the square of another integer. In mathematical terms, a number \( n \) is a square number if there exists an integer \( m \) such that \( n = m^2 \).
Square Number Definition
The concept of a square number can be understood through the operation of squaring, which involves multiplying a number by itself. For instance, the square of 3 is \( 3^2 = 3 \times 3 = 9 \). The number 9 is thus a square number.
Considering this definition, we can examine the case of 0:
- 0 squared is \( 0^2 = 0 \times 0 = 0 \)
Thus, 0 is indeed a square number because it can be expressed as the product of an integer (0) with itself.
Properties of Square Numbers
- A square number is always non-negative because the product of two integers with the same sign is non-negative.
- The sequence of square numbers begins with 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, and so on, which can be expressed as \( 0^2, 1^2, 2^2, 3^2, 4^2, \ldots \).
- Square numbers grow quadratically, meaning the difference between consecutive squares increases as the numbers get larger.
Calculating Square Numbers
To find the square of any number, you can use the formula:
\[
n^2 = n \times n
\]
For example, the square of 5 is:
\[
5^2 = 5 \times 5 = 25
\]
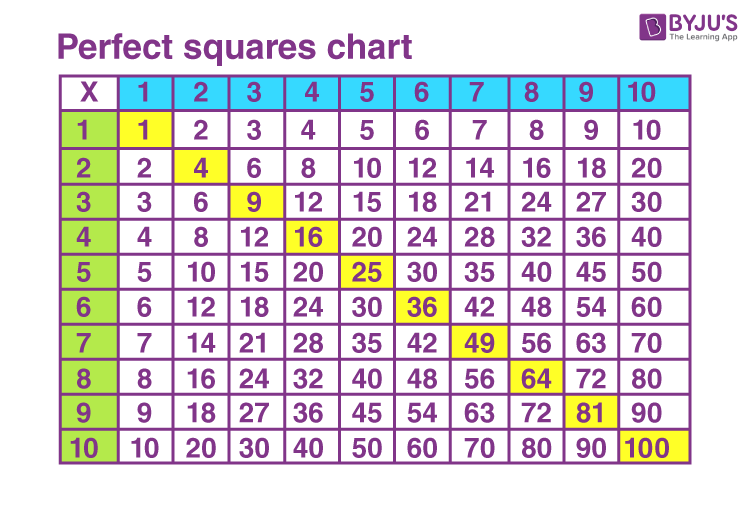
Square Numbers Table
| Number | Square |
|---|---|
| -5 | 25 |
| -4 | 16 |
| -3 | 9 |
| -2 | 4 |
| -1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 9 |
| 4 | 16 |
| 5 | 25 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, 0 is a square number as it fits the definition of being the square of an integer (0). Square numbers are fundamental in mathematics, with applications ranging from geometry to algebra and number theory.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Numbers
Square numbers, also known as perfect squares, are the result of an integer multiplied by itself. For example, \(1^2 = 1\), \(2^2 = 4\), and \(3^2 = 9\). These numbers form a fundamental part of mathematics and have unique properties and applications.
Mathematically, a square number can be represented as \(n^2\), where \(n\) is an integer. The sequence of square numbers begins with:
- \(0^2 = 0\)
- \(1^2 = 1\)
- \(2^2 = 4\)
- \(3^2 = 9\)
- \(4^2 = 16\)
- and so on.
The number 0 is indeed a square number because it can be expressed as \(0^2 = 0\). This makes zero unique among square numbers as it is the only non-positive perfect square.
Understanding square numbers helps in various mathematical contexts, such as geometry, algebra, and number theory. These numbers also appear in patterns and sequences, making them a fascinating topic for both beginners and advanced learners.
Definition of Square Numbers
A square number, also known as a perfect square, is an integer that is the square of another integer. In other words, a number \( n \) is a square number if there exists an integer \( m \) such that:
\[ n = m^2 \]
Here are some examples to illustrate this definition:
- \(1\) is a square number because \(1 = 1^2\)
- \(4\) is a square number because \(4 = 2^2\)
- \(9\) is a square number because \(9 = 3^2\)
- \(16\) is a square number because \(16 = 4^2\)
- And so on.
Zero (\(0\)) is also a square number because it can be expressed as the square of zero:
\[ 0 = 0^2 \]
This definition implies that square numbers are always non-negative, as the square of any real number (positive or negative) is non-negative.
To summarize, a square number is a number that can be written as the product of an integer with itself. This property makes square numbers integral in various mathematical theories and applications, providing a foundational concept in number theory and algebra.
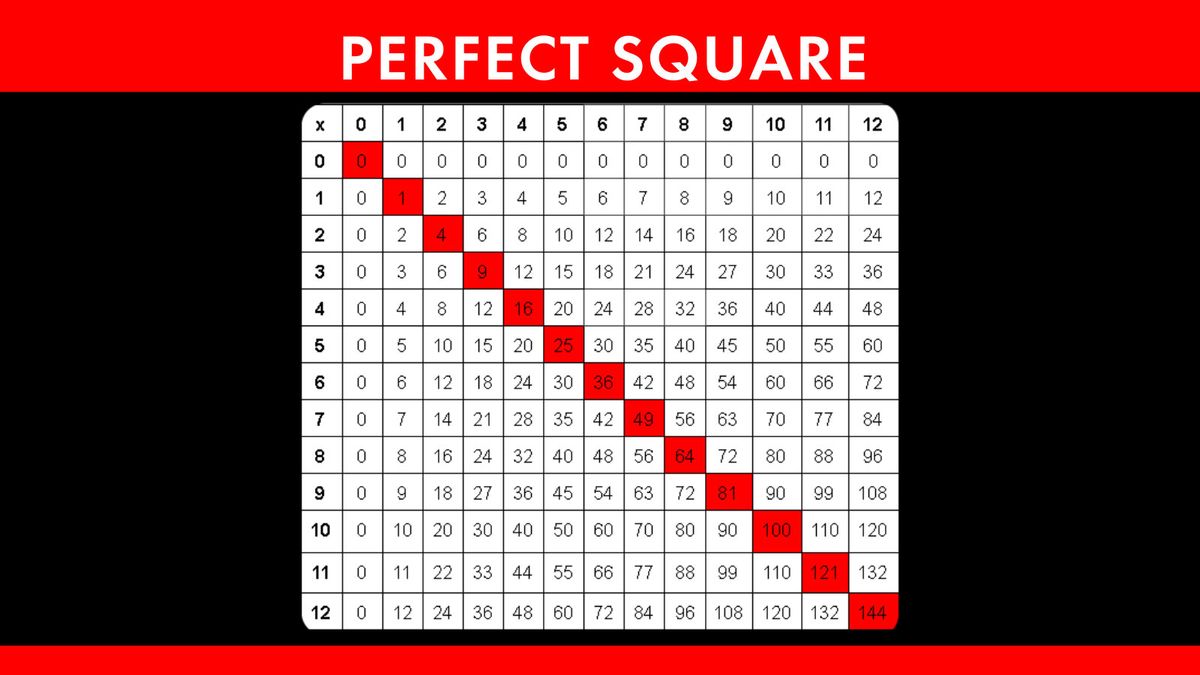
List of Square Numbers
Square numbers are integers that can be expressed as the square of another integer. Below is a detailed list of square numbers categorized into different ranges for easy reference.
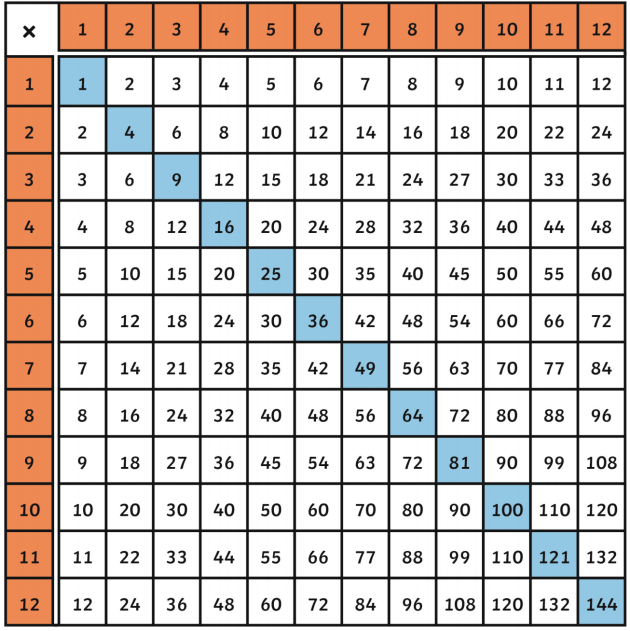
Square Numbers from 1 to 100
- \(0^2 = 0\)
- \(1^2 = 1\)
- \(2^2 = 4\)
- \(3^2 = 9\)
- \(4^2 = 16\)
- \(5^2 = 25\)
- \(6^2 = 36\)
- \(7^2 = 49\)
- \(8^2 = 64\)
- \(9^2 = 81\)
- \(10^2 = 100\)
Two-Digit Square Numbers
- \(4^2 = 16\)
- \(5^2 = 25\)
- \(6^2 = 36\)
- \(7^2 = 49\)
- \(8^2 = 64\)
- \(9^2 = 81\)
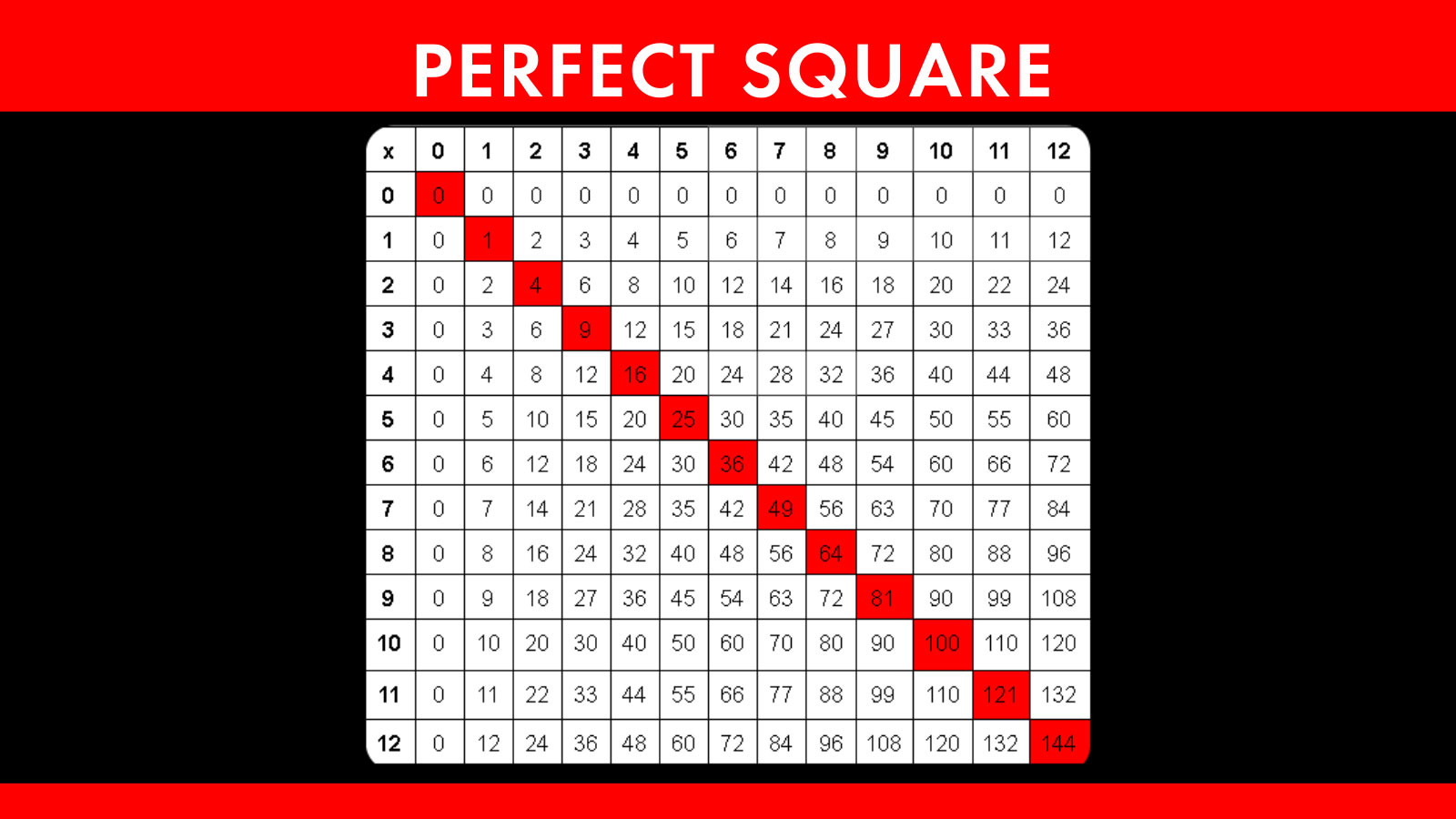
Three-Digit Square Numbers
- \(10^2 = 100\)
- \(11^2 = 121\)
- \(12^2 = 144\)
- \(13^2 = 169\)
- \(14^2 = 196\)
- \(15^2 = 225\)
- \(16^2 = 256\)
- \(17^2 = 289\)
- \(18^2 = 324\)
- \(19^2 = 361\)
- \(20^2 = 400\)
This list provides a comprehensive overview of square numbers, highlighting their progression and the patterns they form. Understanding these numbers is fundamental in various mathematical applications and problem-solving scenarios.
Examples of Square Numbers
Square numbers are integral to various mathematical concepts. Below are some detailed examples illustrating different aspects and uses of square numbers:
Basic Examples
- \(0^2 = 0\)
- \(1^2 = 1\)
- \(2^2 = 4\)
- \(3^2 = 9\)
- \(4^2 = 16\)
- \(5^2 = 25\)
Examples in Geometry
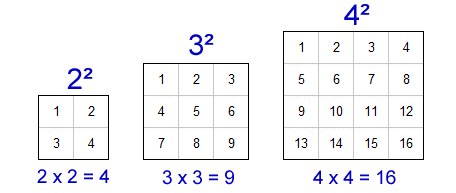
Square numbers often appear in geometric problems, particularly in calculating areas:
- The area of a square with side length 4 is \(4^2 = 16\) square units.
- The area of a square with side length 7 is \(7^2 = 49\) square units.
Examples in Algebra
In algebra, square numbers play a crucial role in quadratic equations and identities:
- Solving \(x^2 = 36\) gives \(x = \pm 6\).
- Using the identity \((a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2\):
For \(a = 3\) and \(b = 4\), \((3 + 4)^2 = 3^2 + 2(3)(4) + 4^2 = 9 + 24 + 16 = 49\).
Examples in Number Theory
Square numbers are also significant in number theory, particularly in the study of primes and divisors:
- The number 49 is a square number and can be expressed as \(7^2\).
- The number 64 is a square number and can be expressed as \(8^2\).
Special Examples
Some square numbers have unique properties:
- \(0\) is a square number because \(0^2 = 0\), making it the only non-positive square number.
- \(1\) is a square number because \(1^2 = 1\), making it the smallest positive square number.
These examples highlight the versatility and importance of square numbers in various mathematical contexts, from basic arithmetic to advanced theoretical concepts.
Sum of Square Numbers
The sum of square numbers is a concept that appears frequently in mathematics, particularly in series and sequence calculations. Below are detailed explanations and examples demonstrating how to find the sum of square numbers.
Sum of the First \( n \) Square Numbers
The sum of the first \( n \) square numbers can be calculated using the formula:
\[ S = \sum_{k=1}^{n} k^2 = \frac{n(n + 1)(2n + 1)}{6} \]
Let's see how this formula works with a few examples:
- For \( n = 1 \): \( S = \frac{1(1 + 1)(2 \cdot 1 + 1)}{6} = \frac{1 \cdot 2 \cdot 3}{6} = 1 \)
- For \( n = 2 \): \( S = \frac{2(2 + 1)(2 \cdot 2 + 1)}{6} = \frac{2 \cdot 3 \cdot 5}{6} = 5 \)
- For \( n = 3 \): \( S = \frac{3(3 + 1)(2 \cdot 3 + 1)}{6} = \frac{3 \cdot 4 \cdot 7}{6} = 14 \)
- For \( n = 4 \): \( S = \frac{4(4 + 1)(2 \cdot 4 + 1)}{6} = \frac{4 \cdot 5 \cdot 9}{6} = 30 \)
Sum of Square Numbers in Specific Ranges
To find the sum of square numbers within a specific range, we can add the squares of the integers within that range. For example:
- Sum of squares from 1 to 5: \( 1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2 = 1 + 4 + 9 + 16 + 25 = 55 \)
- Sum of squares from 6 to 10: \( 6^2 + 7^2 + 8^2 + 9^2 + 10^2 = 36 + 49 + 64 + 81 + 100 = 330 \)
Special Cases and Applications
Square numbers and their sums appear in various mathematical contexts and applications. For instance:
- In geometry, the sum of square areas can represent the total area of multiple squares.
- In algebra, the sum of squares is used in formulas for variance and standard deviation in statistics.
Understanding the sum of square numbers helps in various mathematical problems and provides insight into the properties of numbers and their relationships.
Video giải thích về số hình vuông bằng tiếng Việt, thu hút người xem và cung cấp kiến thức cơ bản về số hình vuông.
Số Hình Vuông Được Giải Thích
READ MORE:
Video giải thích cách bình phương một số và ý nghĩa của việc bình phương một số, bao gồm khái niệm về số mũ.
Cách Bình Phương Một Số | Bình Phương Một Số Nghĩa Là Gì? | Số Mũ | Toán Học với Thầy J