Topic what are the perfect square numbers: Perfect square numbers are the result of an integer multiplied by itself. These numbers form the foundation of various mathematical concepts and are essential for students and enthusiasts to understand. Explore the intriguing world of perfect squares and discover their unique properties, formulas, and applications in our detailed guide.
Table of Content
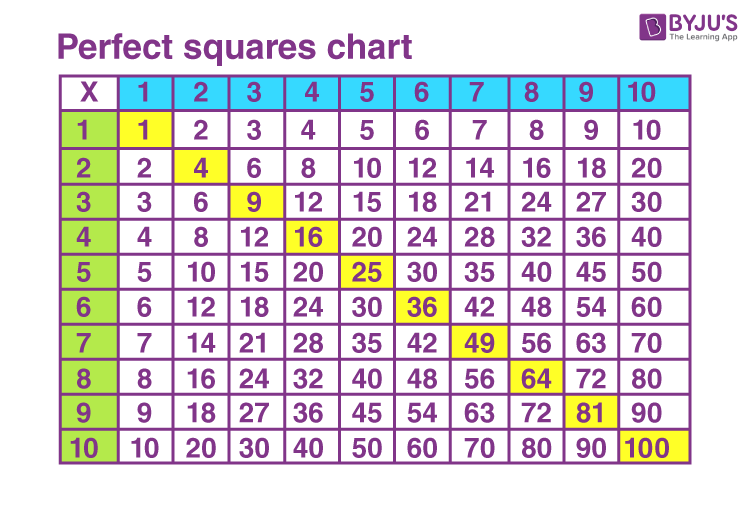
Perfect Square Numbers
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. In other words, if \( n \) is an integer, then \( n^2 \) is a perfect square.
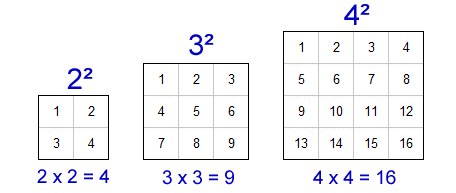
Examples of Perfect Squares
- 1 (\(1 \times 1\))
- 4 (\(2 \times 2\))
- 9 (\(3 \times 3\))
- 16 (\(4 \times 4\))
- 25 (\(5 \times 5\))
- 36 (\(6 \times 6\))
- 49 (\(7 \times 7\))
- 64 (\(8 \times 8\))
- 81 (\(9 \times 9\))
- 100 (\(10 \times 10\))
Properties of Perfect Squares
- The last digit of a perfect square can only be 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9.
- The square root of a perfect square is always an integer.
- Perfect squares have an even number of each prime factor.
Identifying Perfect Squares
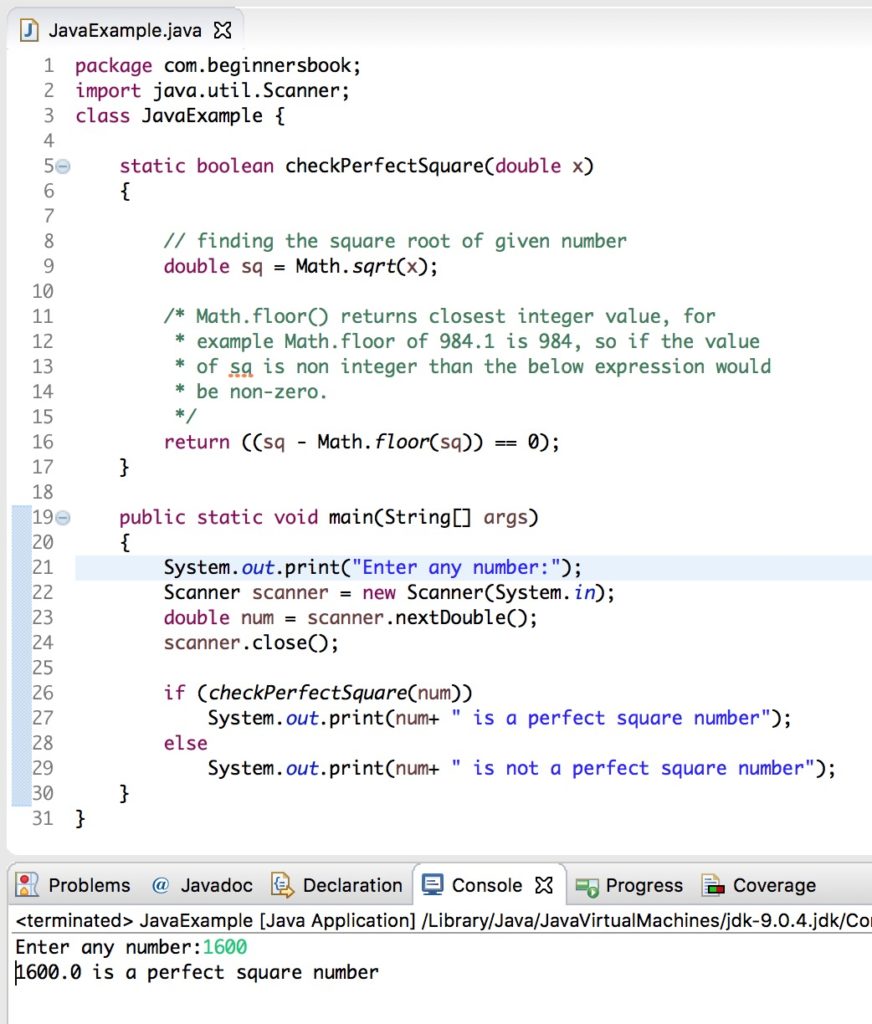
The simplest way to identify if a number is a perfect square is to take its square root. If the result is an integer, the number is a perfect square. For example:
- \(\sqrt{49} = 7\), so 49 is a perfect square.
- \(\sqrt{50} = 7.071\), so 50 is not a perfect square.
Perfect Square Formulas
To find the square of a number, use the formula:
\( n^2 = n \times n \)
For example, to find the square of 15:
\( 15^2 = 15 \times 15 = 225 \)
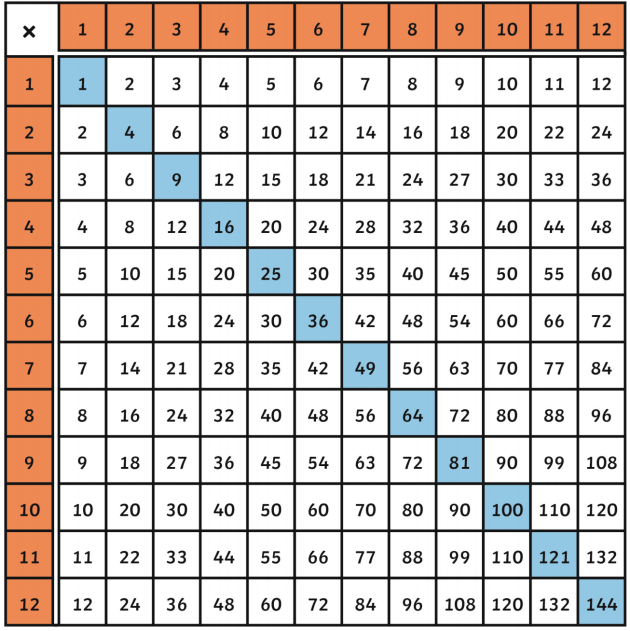
Perfect Squares from 1 to 30
| 1 | 1 \(\times\) 1 = 1 |
| 2 | 2 \(\times\) 2 = 4 |
| 3 | 3 \(\times\) 3 = 9 |
| 4 | 4 \(\times\) 4 = 16 |
| 5 | 5 \(\times\) 5 = 25 |
| 6 | 6 \(\times\) 6 = 36 |
| 7 | 7 \(\times\) 7 = 49 |
| 8 | 8 \(\times\) 8 = 64 |
| 9 | 9 \(\times\) 9 = 81 |
| 10 | 10 \(\times\) 10 = 100 |
| 11 | 11 \(\times\) 11 = 121 |
| 12 | 12 \(\times\) 12 = 144 |
| 13 | 13 \(\times\) 13 = 169 |
| 14 | 14 \(\times\) 14 = 196 |
| 15 | 15 \(\times\) 15 = 225 |
| 16 | 16 \(\times\) 16 = 256 |
| 17 | 17 \(\times\) 17 = 289 |
| 18 | 18 \(\times\) 18 = 324 |
| 19 | 19 \(\times\) 19 = 361 |
| 20 | 20 \(\times\) 20 = 400 |
| 21 | 21 \(\times\) 21 = 441 |
| 22 | 22 \(\times\) 22 = 484 |
| 23 | 23 \(\times\) 23 = 529 |
| 24 | 24 \(\times\) 24 = 576 |
| 25 | 25 \(\times\) 25 = 625 |
| 26 | 26 \(\times\) 26 = 676 |
| 27 | 27 \(\times\) 27 = 729 |
| 28 | 28 \(\times\) 28 = 784 |
| 29 | 29 \(\times\) 29 = 841 |
| 30 | 30 \(\times\) 30 = 900 |
Conclusion
Perfect squares are fundamental in mathematics and have various applications. By understanding their properties and how to identify them, one can solve many mathematical problems more efficiently.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Perfect Square Numbers
Perfect square numbers, a fundamental concept in mathematics, are integers that result from multiplying a number by itself. They possess unique properties that make them intriguing and useful in various mathematical contexts.
To comprehend perfect square numbers fully, it's essential to grasp their definition and characteristics. They are numbers that can be expressed as the square of an integer. For instance, 9 is a perfect square because it equals 3 × 3.
These numbers exhibit intriguing patterns. For instance, the units digit of a perfect square is limited to specific values, namely 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9. Additionally, the nature of the original number, whether it's even or odd, influences the nature of its square.
Furthermore, the process of identifying perfect squares involves various techniques. One common method is to calculate the square root of the number. If the square root is an integer, the number is a perfect square.
Understanding perfect square numbers is crucial in multiple mathematical domains, such as algebra, number theory, and geometry. They serve as building blocks in solving equations, analyzing number properties, and exploring geometric concepts.
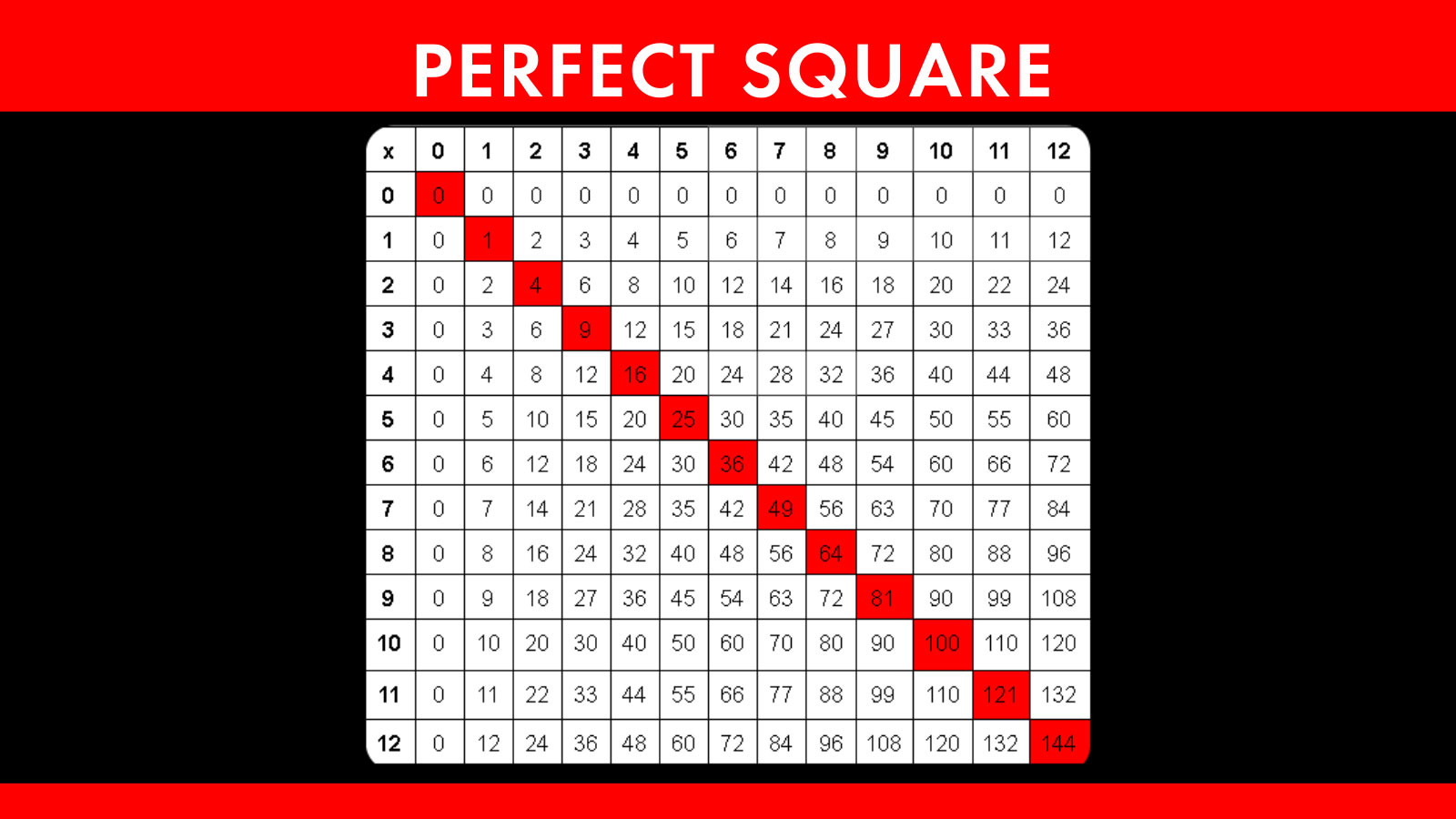
Definition and Properties
Perfect square numbers, a cornerstone of number theory, possess distinct characteristics that distinguish them from other integers. Let's delve into their definition and explore their notable properties:
- Definition: A perfect square is a non-negative integer that can be expressed as the square of an integer. In simpler terms, it is the product of an integer multiplied by itself.
- Characteristics:
- Digit Patterns: The units digit of a perfect square is always one of the following: 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9.
- Parity: The square of an even integer is always even, while the square of an odd integer is always odd.
- Total Factors: Perfect squares have an odd number of total factors. This property distinguishes them from other integers.
- Divisibility: When divided by certain numbers, perfect squares exhibit specific remainders. For example, when divided by 3 or 4, a perfect square leaves a remainder of either 0 or 1.
These properties make perfect square numbers fascinating subjects of study in mathematics. Understanding them enhances problem-solving skills and fosters a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of number theory.
List of Perfect Squares
| Number | Perfect Square |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 9 |
| 4 | 16 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 6 | 36 |
| 7 | 49 |
| 8 | 64 |
| 9 | 81 |
| 10 | 100 |
This table provides a concise list of the first ten perfect square numbers along with their respective values. These numbers are foundational in mathematics and serve as the building blocks for understanding various mathematical concepts and principles.
Applications and Importance
Perfect square numbers hold significant relevance across various mathematical disciplines and real-world applications. Here are some key areas where they are utilized:
- Algebra: Perfect squares play a crucial role in algebraic expressions and equations. They often appear in quadratic equations, where identifying perfect square trinomials simplifies factoring processes.
- Number Theory: In the realm of number theory, perfect square numbers are studied extensively due to their unique properties. They contribute to understanding number patterns, divisibility rules, and prime factorization.
- Geometry: Perfect squares are integral to geometry, particularly in the context of geometric shapes and measurements. They help in calculating areas and perimeters of squares and rectangles, as well as understanding Pythagorean triples.
- Computer Science: In computer science, perfect squares find applications in various algorithms and data structures. They are used in optimization problems, cryptographic protocols, and error-correcting codes.
Understanding the significance of perfect square numbers enhances problem-solving abilities and fosters a deeper appreciation for the elegance of mathematics. Their applications extend beyond theoretical concepts, influencing practical aspects of everyday life and technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is a perfect square?
A perfect square is a non-negative integer that can be expressed as the square of an integer. In simpler terms, it is the result of multiplying a whole number by itself.
-
How can I identify a perfect square?
The easiest method is to calculate the square root of the given number. If the square root is an integer, then the number is a perfect square.
-
How many perfect squares are there between 1 and 100?
There are exactly 10 perfect squares between 1 and 100: 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, and 100.
-
Is every integer a perfect square?
No, not every integer is a perfect square. Perfect squares are specific integers that result from multiplying a number by itself, whereas other integers may not have this property.
These frequently asked questions provide insights into the nature and characteristics of perfect square numbers, aiding in a deeper understanding of their significance in mathematics.
Xem video 'Căn bậc hai của các số hoàn hảo' để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm của các số hoàn hảo và cách tính căn bậc hai của chúng.
Căn bậc hai của các số hoàn hảo | Toán với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Xem video 'Các Số Hoàn Hảo' để tìm hiểu về các số hoàn hảo và các tính chất của chúng trong toán học.
Các Số Hoàn Hảo