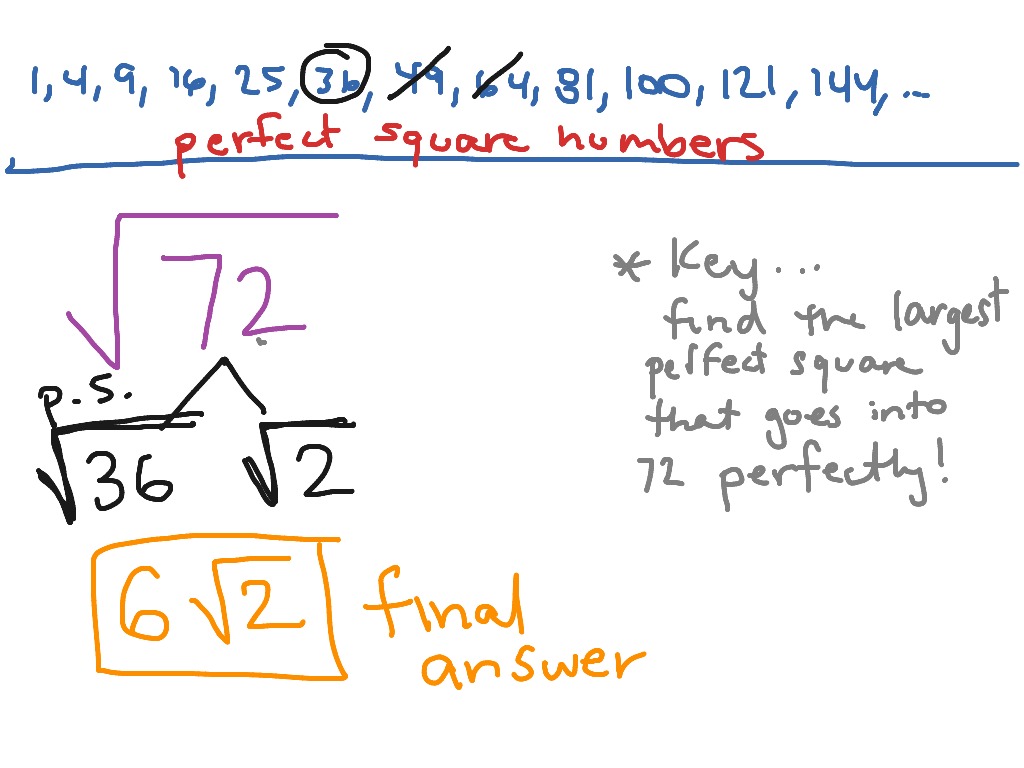Topic square root of 20 simplified: Discover how to simplify the square root of 20 with our step-by-step guide. Uncover the methods, understand the principles behind simplification, and enhance your math skills. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, this article will provide clear explanations and practical examples to make the concept easy to grasp.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 20 Simplified
- Introduction
- What is the Square Root of 20?
- Steps to Simplify the Square Root of 20
- Breaking Down 20
- Identifying Perfect Squares
- Expressing in Simplest Radical Form
- Mathematical Explanation
- Examples of Simplified Square Roots
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Practice Problems
- Applications of Simplified Square Roots
- Conclusion and Summary
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 20. Tìm hiểu cách giải √20 một cách dễ dàng và nhanh chóng.
Square Root of 20 Simplified
The process of simplifying the square root of 20 involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and finding perfect square factors. Here's a step-by-step guide to simplify √20:
Understanding Square Roots
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because 5 × 5 = 25.
Prime Factorization Method
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as the product of its prime factors. To simplify the square root of 20, we need to find the prime factors of 20:
- 20 = 2 × 10
- 10 = 2 × 5
- So, 20 = 2 × 2 × 5
Simplification Process
Next, we identify the perfect squares among the factors:
- √20 = √(2 × 2 × 5)
- Since 2 × 2 is a perfect square, we can simplify it:
- √(2 × 2 × 5) = √(4 × 5)
- √(4 × 5) = √4 × √5
- √4 = 2
- Therefore, √20 = 2√5
Conclusion
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 20 is 2√5. This process involves breaking down the number into its prime factors, identifying perfect square factors, and simplifying the expression accordingly.
Examples and Practice Problems
- Simplify √50
- Simplify √72
- Simplify √98
By practicing these examples, you can improve your skills in simplifying square roots using the prime factorization method. Simplifying square roots helps in solving various mathematical problems more efficiently.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 20 can be simplified using prime factorization and other methods to express it in its simplest radical form. Simplifying square roots is a crucial skill in mathematics that helps in solving equations and understanding number properties. In this section, we will explore the concept of simplifying the square root of 20 step by step, ensuring a thorough understanding of the process.
Let's break down the steps to simplify the square root of 20:
- Prime Factorization: Start by finding the prime factors of 20. The prime factors are 2 and 5, as 20 can be expressed as 22 × 5.
- Group the Factors: Group the factors in pairs of identical numbers. Here, we have one pair of 2s and a single 5.
- Simplify the Radicals: Take the square root of each group. The square root of 22 is 2, and the square root of 5 remains √5.
- Combine the Results: Combine the simplified results to get the final simplified form. Thus, √20 = 2√5.
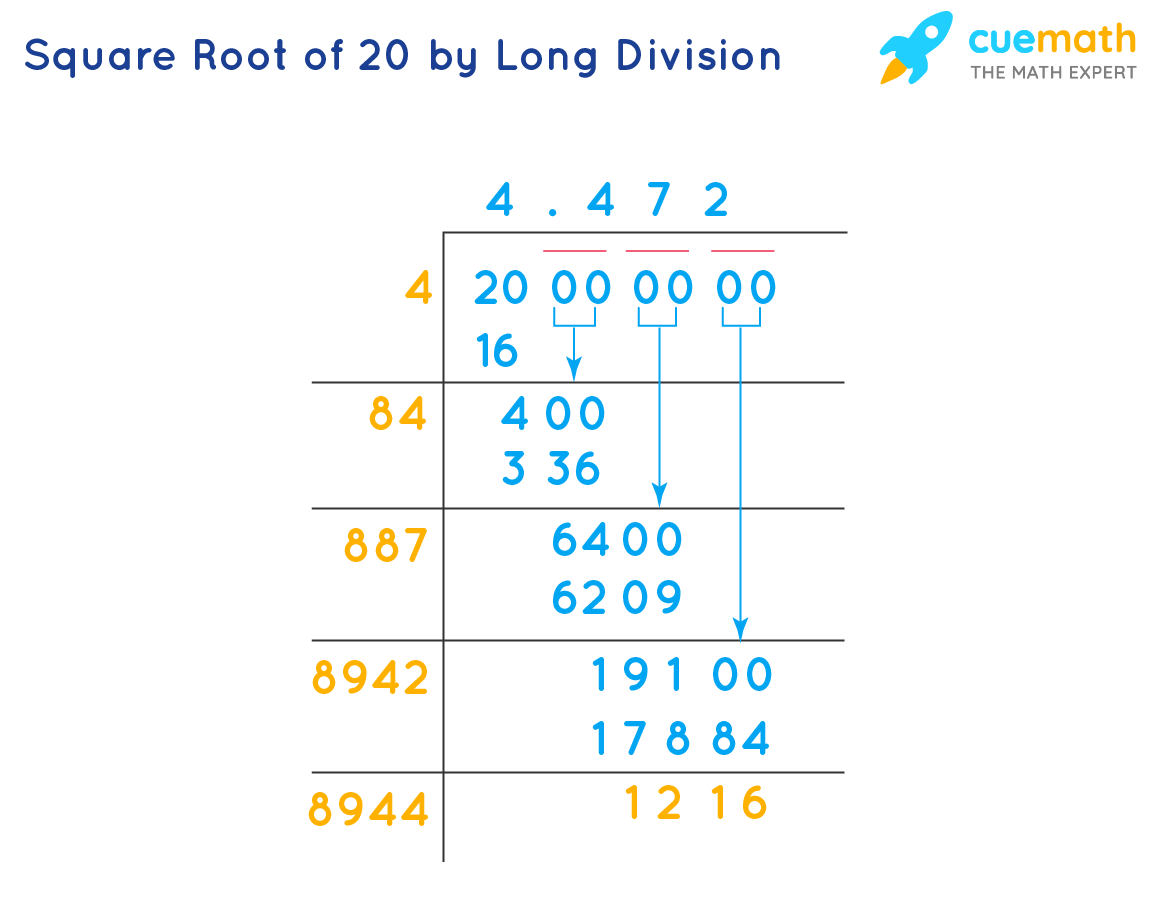
In decimal form, the square root of 20 is approximately 4.472. Simplifying it to 2√5 makes it easier to work with in mathematical equations and applications. Understanding how to simplify square roots like √20 is fundamental in algebra and higher-level math, providing a solid foundation for more complex calculations.
What is the Square Root of 20?
The square root of 20 is an irrational number that can be expressed in its simplest radical form as \(2\sqrt{5}\). Understanding this value involves several steps to simplify and comprehend its properties:
-
Listing the Factors:
The factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, and 20. Identifying these factors helps in simplifying the square root.
-
Identifying Perfect Squares:
Among the factors, 1 and 4 are perfect squares. The largest perfect square factor is 4.
-
Simplifying the Square Root:
We use the property of square roots: \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \). Therefore, we can express \( \sqrt{20} \) as:
\[ \sqrt{20} = \sqrt{4 \times 5} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{5} = 2\sqrt{5} \]
-
Decimal Form:
When calculated, the decimal form of \( \sqrt{20} \) is approximately 4.47214, rounded to five decimal places.
-
Application Example:
Consider a square with an area of 20 square units. The length of each side of the square would be the square root of 20, which simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{5} \) or approximately 4.472 units.
In conclusion, the square root of 20, simplified to \(2\sqrt{5}\), provides a clear and simplified representation of this irrational number, useful in various mathematical and practical applications.
Steps to Simplify the Square Root of 20
The square root of 20 can be simplified by following these steps:
-
Prime Factorization: Begin by finding the prime factors of 20.
20 can be factored into prime numbers as follows:
\( 20 = 2 \times 2 \times 5 \)
-
Group the Prime Factors: Group the prime factors into pairs.
\( 20 = 2^2 \times 5 \)
-
Take One Factor from Each Pair: For each pair of identical factors, take one factor out of the square root.
\( \sqrt{20} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{5} \)
-
Simplify the Square Root: Simplify the expression by taking the square root of the perfect square.
\( \sqrt{2^2} = 2 \)
-
Combine the Results: Multiply the results to get the simplified form.
\( \sqrt{20} = 2 \sqrt{5} \)
Therefore, the square root of 20 simplified is \( 2 \sqrt{5} \).
This process uses the property that \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \), which helps in breaking down and simplifying square roots.
Breaking Down 20
To simplify the square root of 20, we start by breaking down the number into its prime factors. This process helps us identify any perfect square factors that can be simplified further.
Let's break down 20 step-by-step:
First, identify the prime factors of 20. The prime factorization of 20 is:
20 = 2 × 2 × 5
Or, expressed with exponents:
20 = 22 × 5
Next, rewrite the square root of 20 using these prime factors:
\(\sqrt{20} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5}\)
Separate the square root into the product of the square roots:
\(\sqrt{2^2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{5}\)
Simplify the square root of the perfect square factor:
\(\sqrt{2^2} = 2\)
Combine the simplified term with the remaining square root:
\(\sqrt{20} = 2\sqrt{5}\)
Thus, the square root of 20 simplifies to \(2\sqrt{5}\).
This method helps in breaking down the number into manageable parts, allowing us to simplify the square root effectively.
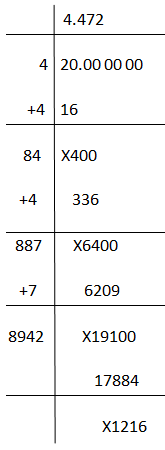
Identifying Perfect Squares
Identifying perfect squares is a crucial step in simplifying square roots. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because:
- 1 = 1 × 1
- 4 = 2 × 2
- 9 = 3 × 3
- 16 = 4 × 4
- 25 = 5 × 5
To simplify the square root of a number, we look for the largest perfect square factor of that number. For instance, consider the number 20:
- List the factors of 20: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, and 20.
- Identify the perfect square factors from the list: 1 and 4.
- The largest perfect square factor of 20 is 4.
Once we have identified the largest perfect square factor, we can use it to simplify the square root. For example, the square root of 20 can be simplified by factoring it into the product of 4 (a perfect square) and 5 (a non-perfect square):
Using the property of square roots, √(a * b) = √a * √b, we get:
\(\sqrt{20} = \sqrt{4 \times 5} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{5} = 2\sqrt{5}\)
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 20 is \(2\sqrt{5}\).
This process can be applied to any number to simplify its square root by identifying and using the largest perfect square factor.
Expressing in Simplest Radical Form
To express the square root of 20 in its simplest radical form, follow these steps:
- Prime Factorization
First, find the prime factorization of 20:
20 can be factored into 2 × 2 × 5, which can be written as \(2^2 \times 5\).
- Identify Pairs
Next, identify and extract the pairs of factors under the square root sign:
\(\sqrt{20} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5}\)
- Simplify
Take the square root of the pairs out of the radical. In this case, the pair is \(2^2\):
\(\sqrt{2^2 \times 5} = 2 \sqrt{5}\)
- Final Result
Thus, the simplest radical form of the square root of 20 is:
\(\sqrt{20} = 2 \sqrt{5}\)
This method ensures that the square root is expressed in its simplest form, making it easier to work with in further calculations.
Mathematical Explanation
The square root of 20 can be simplified by expressing it in its simplest radical form. Here's a step-by-step explanation:
-
First, perform the prime factorization of 20:
\[ 20 = 2 \times 2 \times 5 = 2^2 \times 5 \]
-
Next, use the property of square roots that allows you to separate the factors under the radical:
\[ \sqrt{20} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5} \]
-
Then, apply the square root to each factor separately:
\[ \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{5} = 2 \times \sqrt{5} \]
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 20 is:
\[ \sqrt{20} = 2\sqrt{5} \]
In decimal form, this can be approximated as:
\[ 2\sqrt{5} \approx 2 \times 2.236 \approx 4.472 \]
To verify this, you can check the prime factorization and the multiplication:
| Prime Factorization of 20: | \[ 20 = 2 \times 2 \times 5 = 2^2 \times 5 \] |
| Applying the square root: | \[ \sqrt{20} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5} = 2\sqrt{5} \] |
| Approximate Decimal Value: | \[ 2\sqrt{5} \approx 4.472 \] |
Therefore, the square root of 20 is simplified to \( 2\sqrt{5} \), which is approximately 4.472 when expressed in decimal form.
Examples of Simplified Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down the number under the square root into its prime factors and then simplifying by removing pairs of prime factors from under the radical sign. Here are several examples:
Example 1: Simplifying √20
The square root of 20 can be simplified as follows:
- Prime factorize 20: \(20 = 2 \times 2 \times 5\)
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(2^2 \times 5\)
- Take the square root of each pair and multiply: \(\sqrt{20} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5} = 2\sqrt{5}\)
Thus, \(\sqrt{20} = 2\sqrt{5}\).
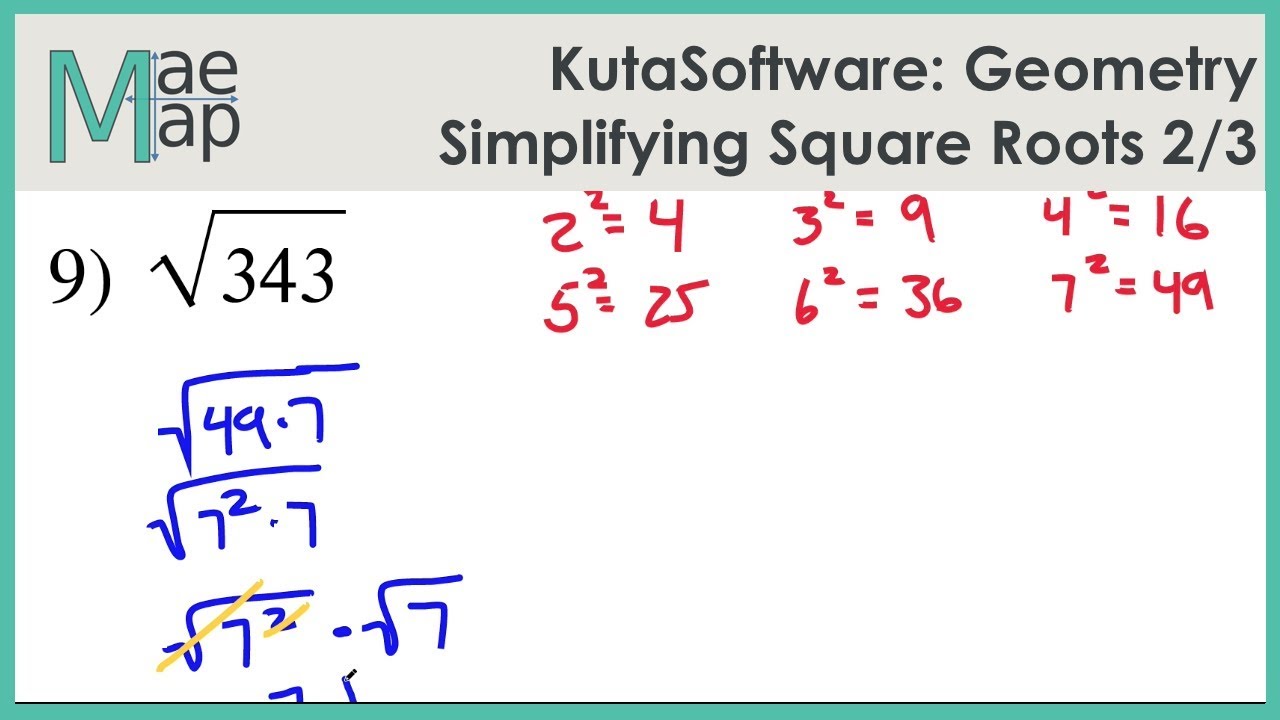
Example 2: Simplifying √72
To simplify the square root of 72:
- Prime factorize 72: \(72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\)
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(2^3 \times 3^2 = (2^2 \times 2) \times 3^2\)
- Take the square root of each pair and multiply: \(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 3^2) \times 2} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2}\)
So, \(\sqrt{72} = 6\sqrt{2}\).
Example 3: Simplifying √50
The square root of 50 can be simplified by:
- Prime factorizing 50: \(50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5\)
- Grouping the prime factors: \(50 = 2 \times 5^2\)
- Taking the square root of each pair: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
Hence, \(\sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
Example 4: Simplifying √180
To simplify the square root of 180:
- Prime factorize 180: \(180 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5\)
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(180 = 2^2 \times 3^2 \times 5\)
- Take the square root of each pair: \(\sqrt{180} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 3^2) \times 5} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{5} = 6\sqrt{5}\)
Therefore, \(\sqrt{180} = 6\sqrt{5}\).
These examples illustrate the process of simplifying square roots by breaking down the radicand into its prime factors, grouping the pairs, and then simplifying the radical expression.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When simplifying square roots, students often encounter several common mistakes. Understanding these errors and how to avoid them can significantly enhance your mathematical proficiency.
- Incorrect Addition of Square Roots:
A frequent mistake is assuming that the square root of a sum is the sum of the square roots. This is incorrect. For example:
\(\sqrt{x + y} \ne \sqrt{x} + \sqrt{y}\)
To avoid this mistake, remember that square roots can only be combined if they have the same radicand (the number under the square root). For instance, \(\sqrt{4} + \sqrt{9} = 2 + 3 = 5\), not \(\sqrt{4 + 9}\).
- Failure to Factor Completely:
Another common error is not factoring the number inside the square root completely. When simplifying \(\sqrt{20}\), you must recognize that 20 can be factored into 4 and 5:
\(\sqrt{20} = \sqrt{4 \times 5} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{5} = 2\sqrt{5}\)
Ensure you identify all possible factors to simplify correctly.
- Incorrect Canceling:
Students often mistakenly cancel terms incorrectly. For example, when simplifying \(\frac{\sqrt{x^2}}{x}\), the correct simplification is:
\(\frac{\sqrt{x^2}}{x} = \frac{x}{x} = 1\)
Instead of canceling incorrectly, ensure that you only cancel terms when the entire numerator and denominator share the common factor.
- Misapplying Rules of Exponents:
Misapplying exponent rules can lead to errors. For instance, assuming that \((a + b)^2 = a^2 + b^2\) is incorrect:
\((a + b)^2 \ne a^2 + b^2\)
To avoid this, apply the correct formula: \((a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2\).
By understanding these common mistakes and how to avoid them, you can simplify square roots more accurately and confidently.
Practice Problems
Practicing simplifying square roots can help reinforce your understanding and improve your skills. Below are several practice problems along with solutions to help you master the process.
-
Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \).
Solution:
- Prime factorize 50: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \)
- Simplify the square root: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
-
Simplify \( \sqrt{72} \).
Solution:
- Prime factorize 72: \( 72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 \)
- Simplify the square root: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^2} = 3\sqrt{8} = 3 \times 2\sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
-
Simplify \( \sqrt{128} \).
Solution:
- Prime factorize 128: \( 128 = 2^7 \)
- Simplify the square root: \( \sqrt{128} = \sqrt{2^7} = 2^3\sqrt{2} = 8\sqrt{2} \)
-
Simplify \( \sqrt{200} \).
Solution:
- Prime factorize 200: \( 200 = 2^3 \times 5^2 \)
- Simplify the square root: \( \sqrt{200} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{8} = 5 \times 2\sqrt{2} = 10\sqrt{2} \)
-
Simplify \( \sqrt{450} \).
Solution:
- Prime factorize 450: \( 450 = 2 \times 3^2 \times 5^2 \)
- Simplify the square root: \( \sqrt{450} = \sqrt{2 \times 3^2 \times 5^2} = 3 \times 5\sqrt{2} = 15\sqrt{2} \)
By practicing these problems, you'll become more proficient in simplifying square roots. Remember to always look for pairs of prime factors and simplify step by step.
Applications of Simplified Square Roots
Simplified square roots play a crucial role in various real-life applications across different fields. Understanding these applications can help illustrate the importance of mastering this concept. Here are some common uses:
- Architecture and Engineering: Square roots are used in calculating areas and dimensions, which are essential for designing buildings, bridges, and other structures. For example, determining the length of the diagonal of a square area involves using the square root of the sum of the squares of the sides.
- Physics: Square roots appear in formulas related to motion, energy, and waves. For instance, the period of a pendulum is proportional to the square root of its length, helping in solving problems involving time and frequency.
- Finance: In finance, square roots help determine the volatility of stock prices and are used in various financial models to predict investment risks and returns. The standard deviation, which measures volatility, involves the square root of the variance.
- Computer Graphics: Rendering realistic lighting and shadows, calculating distances between points, and algorithms for image processing all involve square roots. For example, the distance between two points in a 3D space can be found using the square root of the sum of the squares of their differences in coordinates.
- Navigation: GPS technology uses square roots to calculate the shortest distance between two points on the earth's surface, enhancing accuracy in mapping and location services.
- Accident Investigations: Police use square roots to determine the speed of a car based on the length of skid marks. The speed is proportional to the square root of the skid distance, helping in reconstructing accident scenarios.
These applications highlight the versatility and necessity of square roots in solving complex problems and performing precise calculations in many fields.
Conclusion and Summary
In this guide, we have explored the process of simplifying the square root of 20. We began by understanding the concept of square roots and why certain numbers, like 20, do not have exact integer square roots. Through the prime factorization method, we broke down 20 into its prime factors to express it in its simplest radical form as \(2\sqrt{5}\).
The mathematical explanation involved detailed steps, including identifying perfect squares and simplifying the radical. We also provided several examples of simplified square roots to illustrate the process further. Common mistakes, such as incorrect factorization or misidentifying perfect squares, were highlighted along with tips to avoid them.
We concluded with practice problems to reinforce the concepts learned and discussed the practical applications of simplified square roots in real-world scenarios, such as geometry and algebra.
In summary, mastering the simplification of square roots not only enhances mathematical skills but also provides a foundation for more advanced topics. By following the steps and avoiding common pitfalls, one can confidently simplify square roots and apply this knowledge effectively.
Additional Resources
For further reading and practice on simplifying square roots, here are some valuable resources:
-
This website provides a clear explanation of the process of simplifying square roots with examples and interactive tools to practice.
-
Khan Academy offers instructional videos and practice problems to help you master the concept of simplifying square roots.
-
This resource breaks down the rules and steps for simplifying radicals and provides practice problems with detailed solutions.
-
A comprehensive guide on simplifying square roots, including a calculator tool to check your work.
-
LibreTexts provides an in-depth explanation of simplifying square root expressions with examples and exercises.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 20. Tìm hiểu cách giải √20 một cách dễ dàng và nhanh chóng.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 20: √20
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai để chuẩn bị cho việc học số ảo, bao gồm √9 và √20.
Đại Số 2 - Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai để Chuẩn Bị cho Số Ảo, √9, √20