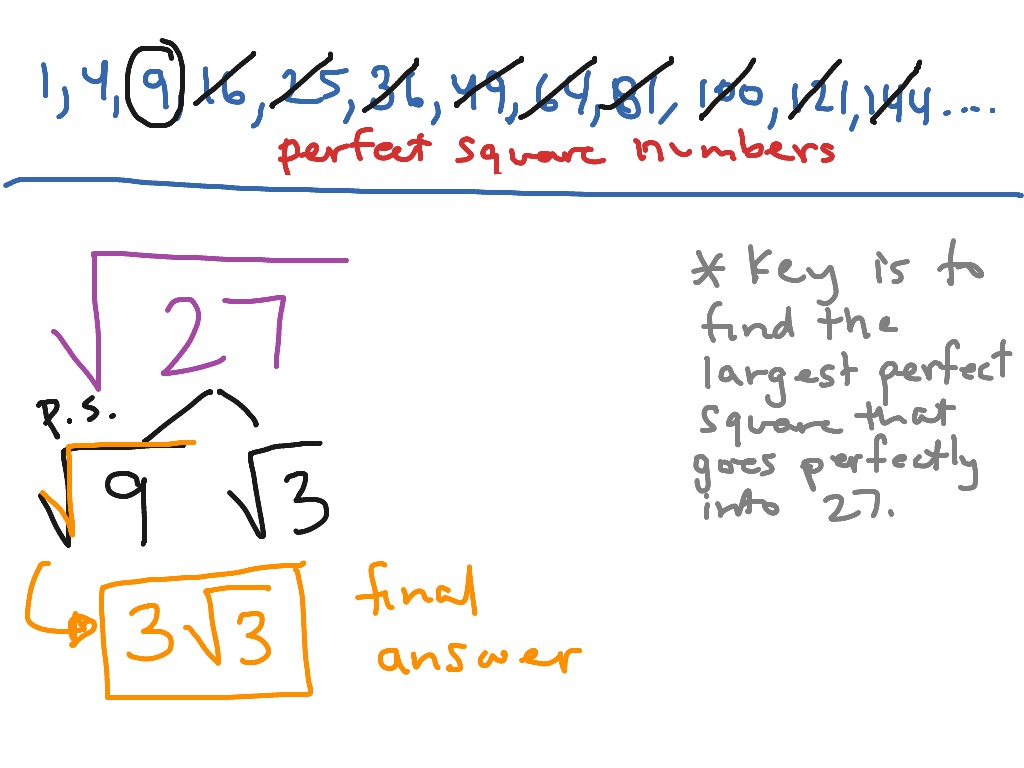Topic simplify square root calculator with steps: Discover how to simplify square roots effortlessly with our comprehensive calculator guide. Learn step-by-step methods and examples to simplify any square root expression. Whether you're dealing with perfect squares or irrational numbers, our tool provides clear explanations and detailed steps to enhance your mathematical understanding.
Table of Content
- Simplify Square Root Calculator with Steps
- Table of Contents
- Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
- Basic Steps for Simplifying Square Roots
- Examples of Simplifying Square Roots
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Benefits of Using a Square Root Simplifier
- Comparison of Different Square Root Calculators
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Square Root Calculator
- Advanced Techniques in Simplifying Square Roots
- Understanding Irrational Numbers in Square Roots
- Tips for Teaching Square Root Simplification
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai
Simplify Square Root Calculator with Steps
Here is a detailed step-by-step calculator to simplify square roots:
- Input the square root expression you want to simplify.
- Click "Calculate" to see the simplified result.
- The calculator will provide the simplified form of the square root along with detailed steps showing how it was simplified.
This tool is useful for understanding the process of simplifying square roots, whether dealing with perfect squares or irrational numbers. It ensures clarity by breaking down each step of the simplification process.
Example:
If you input √72, the calculator will show:
| Step 1: | Recognize factors of the number inside the square root. |
| Step 2: | Extract perfect squares when possible. |
| Step 3: | Combine the factors to get the simplified form. |
Use this tool to simplify square roots effortlessly and understand the underlying mathematical process.

READ MORE:
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
- Understanding Basic Steps for Simplifying Square Roots
- Examples of Simplifying Square Roots
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Simplification
- Benefits of Using a Square Root Simplifier
- Comparison of Different Square Root Calculators
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Square Root Calculator
- Advanced Techniques in Simplifying Square Roots
- Understanding Irrational Numbers in Square Roots
- Tips for Teaching Square Root Simplification
- Conclusion and Summary
Introduction to Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves reducing a square root expression to its simplest form, which is essential in mathematics for solving equations and understanding concepts like irrational numbers. Here’s a step-by-step introduction:
- Definition of square roots and their significance in mathematics.
- Basic rules and properties of square roots, such as how to handle perfect squares.
- Importance of simplifying square roots for easier calculations and clearer understanding.
- Applications in real-life scenarios and various fields of mathematics.
- Overview of techniques and tools, including calculators, used for simplifying square roots.
Basic Steps for Simplifying Square Roots
Here are the fundamental steps to simplify square roots effectively:
- Step 1: Identify the square root expression you want to simplify.
- Step 2: Factorize the number under the square root into its prime factors.
- Step 3: Pull out any perfect square factors from under the square root.
- Step 4: Combine like terms inside the square root, if applicable.
- Step 5: Simplify the expression further if possible, ensuring no square root of a negative number remains.
- Step 6: Verify your simplified result by squaring it to ensure it equals the original expression.
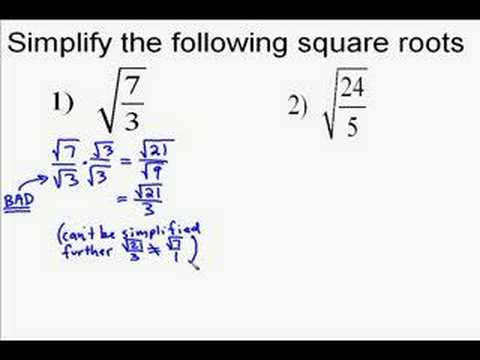
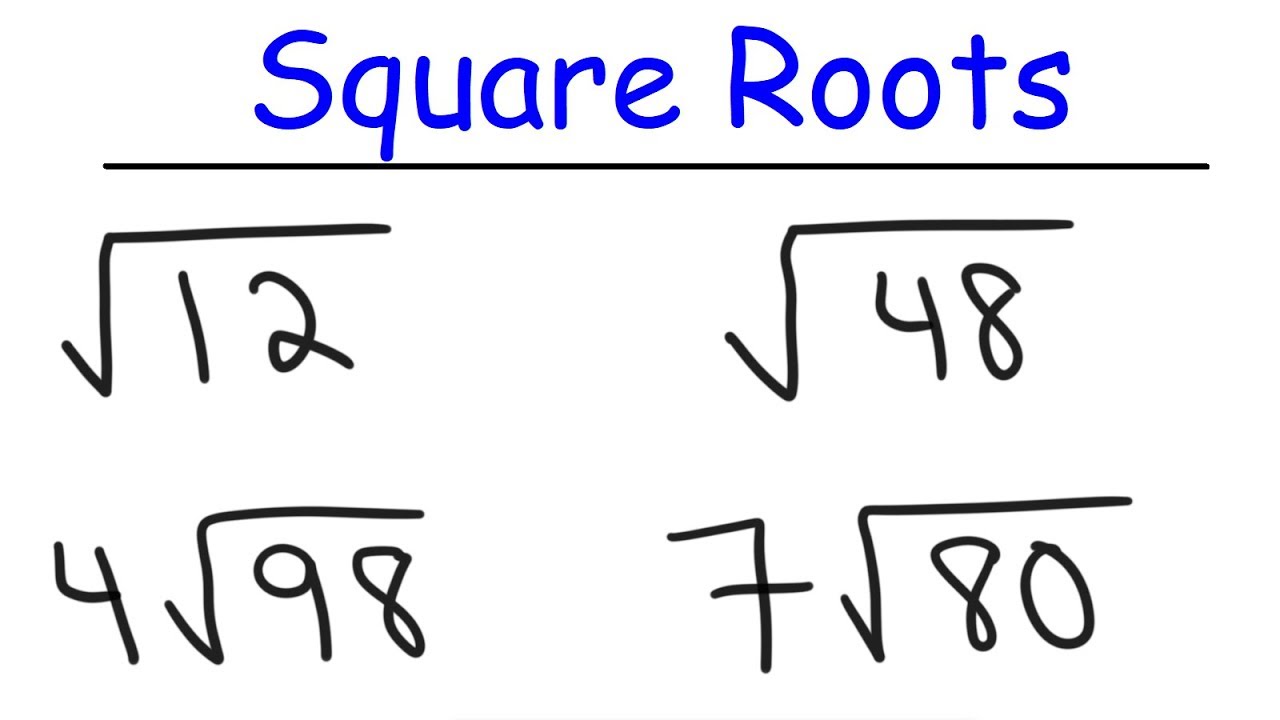
Examples of Simplifying Square Roots
Here are some detailed examples illustrating how to simplify square roots:
-
Example 1: Simplify \( \sqrt{48} \)
Step 1: Factorize 48 into prime factors: \( 48 = 2^4 \times 3 \). Step 2: Extract perfect squares: \( \sqrt{48} = \sqrt{16 \times 3} = 4\sqrt{3} \). -
Example 2: Simplify \( \sqrt{75} \)
Step 1: Factorize 75 into prime factors: \( 75 = 3 \times 5^2 \). Step 2: Extract perfect squares: \( \sqrt{75} = \sqrt{25 \times 3} = 5\sqrt{3} \). -
Example 3: Simplify \( \sqrt{162} \)
Step 1: Factorize 162 into prime factors: \( 162 = 2 \times 3^4 \). Step 2: Extract perfect squares: \( \sqrt{162} = \sqrt{81 \times 2} = 9\sqrt{2} \).

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying square roots, it's essential to be aware of common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Here are some of the most frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Not Identifying Perfect Squares: Always check if the number under the square root is a perfect square. For example, simplifies directly to 6.
- Ignoring Prime Factorization: Failing to break down the number into its prime factors can complicate simplification. For instance, can be simplified by factoring it into .
- Overlooking Simplification Steps: Ensure all steps are followed to reach the simplest form. For example, should be simplified to , not just .
- Misplacing Decimal Points: Be cautious with decimal points, as a small error can lead to significant inaccuracies. Double-check your calculations to ensure precision.
- Forgetting the Radical Symbol: Ensure the radical symbol is correctly applied throughout the process. This symbol denotes the square root and is crucial for accurate representation.
- Neglecting Negative Solutions: Remember that square roots can have both positive and negative solutions. For example, .
- Rushing Through Calculations: Take your time to carefully perform each step. Rushing can lead to errors and overlooked factors.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and practicing regularly, you can improve your accuracy and efficiency in simplifying square roots. Regular practice and thorough checking of each step will ensure your calculations are precise and reliable.
Benefits of Using a Square Root Simplifier
Using a square root simplifier offers several significant advantages for students, teachers, and anyone working with mathematical expressions. Below are some key benefits:
- Time Efficiency: A square root simplifier can quickly reduce complex square root expressions to their simplest forms, saving time and effort compared to manual calculations.
- Accuracy: Automated simplification ensures accuracy in the results, eliminating the risk of human error that can occur during manual calculations.
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Many square root simplifiers provide detailed, step-by-step solutions, helping users understand the process and learn the underlying mathematical principles.
- Educational Value: By breaking down the simplification process into clear steps, these tools serve as valuable educational resources, making it easier for students to grasp the concepts involved in simplifying square roots.
- Handling Complex Expressions: Square root simplifiers are capable of handling complex expressions, including those involving variables and large numbers, which can be challenging to simplify manually.
- Convenience: Online square root simplifiers are easily accessible from any device with internet access, providing a convenient tool for homework, study, or professional use.
- Support for Irrational Numbers: These tools can effectively simplify expressions involving irrational numbers, helping users better understand and work with these challenging mathematical elements.
Overall, the use of a square root simplifier enhances the learning experience, improves accuracy, and saves valuable time, making it an indispensable tool for anyone dealing with square roots regularly.
Comparison of Different Square Root Calculators
There are several online tools available for simplifying square roots, each offering unique features and benefits. Below is a comparison of some popular square root calculators:
| Calculator | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omni Calculator |
|
|
|
| MathCracker |
|
|
|
| MadforMath |
|
|
|
| Mathway |
|
|
|
| Symbolab |
|
|
|
Each of these calculators offers unique features that can cater to different needs. Whether you are looking for detailed explanations, quick calculations, or practice problems, there is a square root calculator that fits your requirements.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Square Root Calculator
Using a square root calculator can simplify the process of finding the square root of a number. Here is a detailed step-by-step guide to using a square root calculator:
-
Enter the Radicand:
Begin by entering the number for which you want to find the square root into the calculator. This number is known as the radicand. For example, to find the square root of 25, you would enter 25.
-
Select the Operation:
Choose the square root operation. Many calculators have a specific button for the square root, often denoted as √ or √x. Press this button after entering your radicand.
-
View the Result:
The calculator will display the square root of the entered number. For instance, the square root of 25 will be shown as 5.
-
Review the Steps (Optional):
Some advanced calculators provide a step-by-step breakdown of how the square root was calculated. This is particularly useful for educational purposes and for understanding the underlying math. For example, it might show the factorization of the radicand and how the factors are grouped and simplified.
-
Check for Additional Information:
If the number is not a perfect square, the calculator might also show the result in decimal form. Additionally, some calculators will indicate if the number is a perfect square or provide the result in simplified radical form.
Using a square root calculator is straightforward and can save time, especially when dealing with larger numbers or more complex calculations. Here are a few tips to make the most out of your square root calculator:
- Use Exact Values: Whenever possible, use exact values rather than approximations to ensure accuracy.
- Understand the Output: If your calculator provides a step-by-step solution, take the time to understand each step, as this can help reinforce your understanding of square roots and their properties.
- Explore Additional Features: Some calculators offer additional functionalities such as solving for roots of negative numbers or finding complex solutions. Familiarize yourself with these features to fully leverage your calculator's capabilities.
By following these steps and tips, you can efficiently and accurately find square roots, making your mathematical tasks easier and more reliable.

Advanced Techniques in Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down the radicand (the number under the square root) into its prime factors and extracting the square factors. Here are some advanced techniques to simplify square roots:
-
Prime Factorization:
Prime factorization is the process of breaking down a number into its prime factors. For example, the prime factorization of 72 is:
\[ 72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 \]
To simplify \(\sqrt{72}\), we take the square roots of the square factors:
\[ \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^2} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 3^2} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2} \]
-
Multiplying and Dividing Square Roots:
Use the properties of square roots to simplify multiplication and division:
\[ \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a \times b} \]
For example, \(\sqrt{8} \times \sqrt{2} = \sqrt{16} = 4\).
\[ \sqrt{a} \div \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} \]
For example, \(\frac{\sqrt{18}}{\sqrt{2}} = \sqrt{\frac{18}{2}} = \sqrt{9} = 3\).
-
Rationalizing the Denominator:
To eliminate a square root in the denominator, multiply the numerator and the denominator by the same square root:
\[ \frac{a}{\sqrt{b}} \times \frac{\sqrt{b}}{\sqrt{b}} = \frac{a\sqrt{b}}{b} \]
For example, \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{5\sqrt{3}}{3}\).
-
Using Exponents:
Expressing square roots as exponents can simplify calculations:
\[ \sqrt{a} = a^{\frac{1}{2}} \]
This property can be extended to simplify higher-order roots:
\[ ^{n}\sqrt{a} = a^{\frac{1}{n}} \]
-
Simplifying Higher-Order Roots:
The process for simplifying higher-order roots is similar to square roots, but involves finding factors that are perfect cubes, fourth powers, etc. For example, to simplify \( \sqrt[3]{54} \), we break down 54 into prime factors:
\[ 54 = 2 \times 3^3 \]
\[ \sqrt[3]{54} = \sqrt[3]{2 \times 3^3} = 3\sqrt[3]{2} \]
By mastering these advanced techniques, you can efficiently simplify complex square roots and higher-order roots, making calculations more manageable.
Understanding Irrational Numbers in Square Roots
Square roots often result in irrational numbers. An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction; its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating.
Here are some important points about irrational numbers in the context of square roots:
- Definition: An irrational number cannot be written as a ratio of two integers. Its decimal form goes on forever without repeating.
- Examples of Irrational Square Roots: The square roots of non-perfect squares, such as √2, √3, and √5, are all irrational numbers.
To understand why certain square roots are irrational, consider the following:
- Prime Factorization:
Prime factorization can help identify whether a number's square root is irrational. If a number has any prime factor with an odd exponent in its prime factorization, its square root will be irrational.
Example:
- √50 = √(2 * 5^2) = 5√2 (since √2 is irrational, so is √50).
- Proof by Contradiction:
One way to prove the irrationality of numbers like √2 is through proof by contradiction. Assume √2 is rational, meaning it can be expressed as a fraction a/b in lowest terms. Then:
\[
\sqrt{2} = \frac{a}{b} \implies 2 = \frac{a^2}{b^2} \implies 2b^2 = a^2
\]This implies a^2 is even, so a must be even. Let a = 2k:
\[
2b^2 = (2k)^2 \implies 2b^2 = 4k^2 \implies b^2 = 2k^2
\]This implies b^2 is even, so b must be even. However, this contradicts the assumption that a/b is in lowest terms, proving that √2 is irrational.
Understanding irrational numbers helps in various mathematical concepts, especially when dealing with square roots. Recognizing the nature of these numbers ensures accurate simplification and proper usage in equations and real-world applications.
When using a square root calculator, it's important to note that the calculator might provide a decimal approximation for irrational numbers. The true value, however, remains non-terminating and non-repeating.
Tips for Teaching Square Root Simplification
Teaching square root simplification can be a rewarding experience as it helps students develop a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. Here are some tips to make the process engaging and effective:
-
Start with the Basics:
Begin by explaining what a square root is and how it relates to squares of numbers. Use visual aids such as squares of different sizes to illustrate this concept.
-
Prime Factorization:
Teach students how to break down a number into its prime factors. This foundational skill is crucial for simplifying square roots.
Example: Simplify √72
- Prime factorize 72: \(72 = 2^3 \times 3^2\)
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(72 = (2^2 \times 3^2) \times 2\)
- Take the square root of each pair: \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{3^2} \times \sqrt{2} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2}\)
-
Use a Square Root Calculator:
Introduce students to online tools like square root calculators that show step-by-step simplification. This can help them verify their answers and understand the process better.
-
Incorporate Real-World Examples:
Show how square roots are used in real life, such as in architecture, engineering, and nature. This contextual learning can make the topic more interesting and relevant.
-
Practice, Practice, Practice:
Provide plenty of practice problems of varying difficulty. Include problems that require simplification of both perfect and imperfect squares.
-
Common Mistakes:
Highlight common mistakes students make when simplifying square roots, such as incorrectly factoring numbers or not fully simplifying the radicals.
-
Interactive Learning:
Use interactive methods such as group activities, math games, and online quizzes to reinforce the concepts. Encouraging collaboration can also help students learn from each other.
-
Review and Reinforce:
Regularly review the concepts and reinforce them through periodic quizzes and discussions. Encourage students to ask questions and explore different methods of simplification.
By following these tips, you can help students gain a solid understanding of square root simplification, making them more confident in their math skills.
Conclusion and Summary
The process of simplifying square roots is a fundamental skill in mathematics that helps in reducing complex radical expressions into their simplest form. This practice is not only essential for solving equations but also for a deeper understanding of algebraic concepts.
Using a square root calculator can greatly simplify this process by providing step-by-step solutions, allowing users to follow along and learn the methodology. Here's a summary of the key points covered:
- Understanding Square Roots: Square roots represent the number which, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Simplifying these involves breaking down the radicand into its prime factors.
- Basic Steps for Simplification: Identify and extract perfect square factors from the radicand, and apply the product and quotient rules to simplify the expression.
- Common Techniques: Techniques like factoring, combining like terms, and rationalizing denominators are crucial for efficient simplification.
- Tools and Calculators: Utilizing tools like square root calculators can provide immediate and accurate simplifications, enhancing both learning and problem-solving efficiency.
By consistently practicing these techniques and leveraging available tools, students and educators can develop a robust understanding of square root simplification. This not only aids in solving mathematical problems but also in appreciating the underlying principles of algebra.
In conclusion, the journey of mastering square root simplification is a blend of understanding fundamental concepts, applying systematic techniques, and using modern calculators for verification. Embrace the learning process, and utilize these strategies to simplify your mathematical journey.
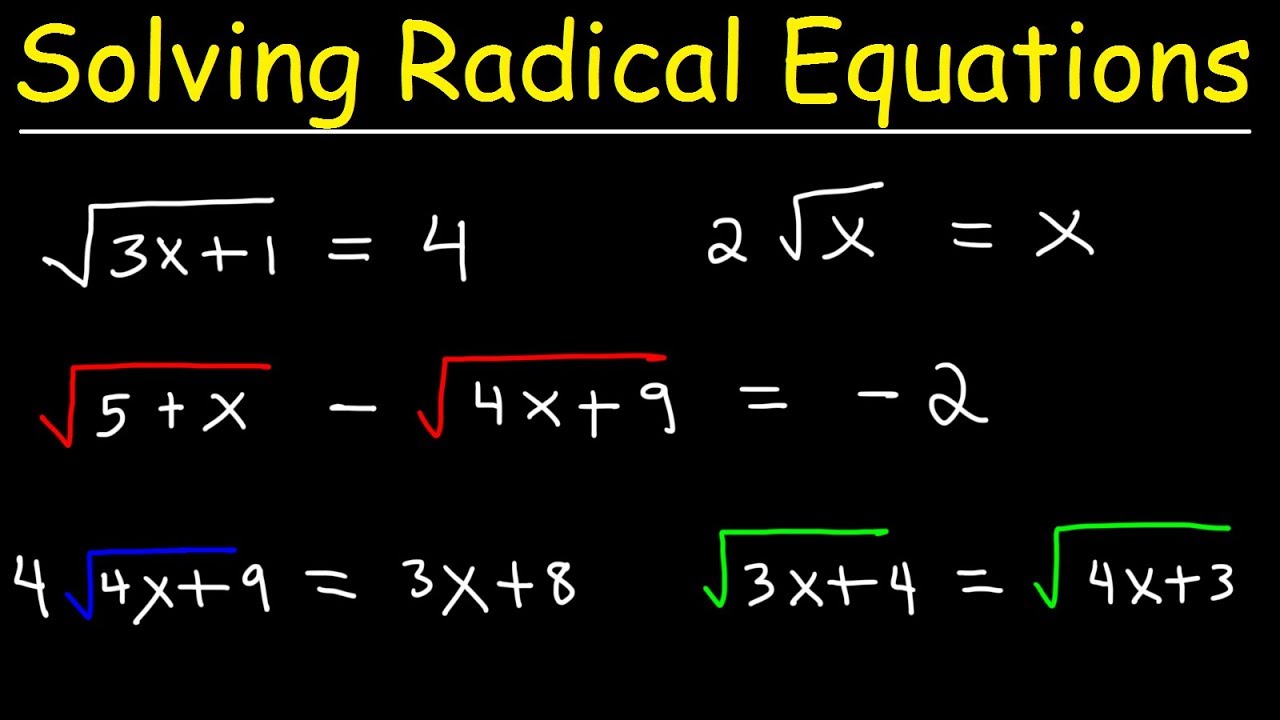
Cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai
Cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai một cách nhanh chóng và dễ dàng trong video này. Phù hợp cho những ai đang tìm kiếm cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai - Nhanh Chóng và Dễ Dàng