Topic what is the square of 72: Curious about the square of 72? In this article, we delve into the calculation, significance, and real-world applications of this intriguing number. Learn how to compute it, explore its properties, and understand its importance in various mathematical and practical contexts. Join us on this mathematical journey!
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square of 72
- Introduction
- Understanding Squaring
- Calculation Method
- Properties of 5184
- Perfect Squares
- Real-world Applications
- Geometric Applications
- Algebraic Applications
- Statistical Applications
- Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tính căn bậc hai của 72 một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết. Xem ngay để nắm vững kiến thức toán học cơ bản.
Understanding the Square of 72
The concept of squaring a number involves multiplying the number by itself. In this section, we will explore the square of 72 in detail.
What is the Square of 72?
The square of 72 is calculated as follows:
\[ 72^2 = 72 \times 72 = 5184 \]
Calculation of the Square of 72
- Write down the number to be squared: 72.
- Multiply the number by itself: \( 72 \times 72 \).
- The result is 5184.
Thus, the square of 72 is 5184.
Properties of the Square of 72
- Perfect Square: 5184 is a perfect square because it is the square of 72.
- Positive Number: Squaring any real number always results in a positive number.
- Even Number: Since 72 is an even number, its square (5184) is also an even number.
Applications of the Square of 72
Understanding the square of 72 can be useful in various mathematical and practical applications:
- Area Calculation: Squaring is often used to calculate the area of squares in geometry.
- Algebra: Squaring numbers is a common operation in algebraic equations and functions.
- Data Analysis: Squared values are used in statistics, such as in the calculation of variance.
Example Problems
Here are some example problems to practice calculating the square of numbers:
- What is the square of 10? \( 10^2 = 100 \)
- What is the square of 15? \( 15^2 = 225 \)
- What is the square of 20? \( 20^2 = 400 \)
Conclusion
The square of 72 is a fundamental mathematical concept that equals 5184. Understanding how to calculate and apply the square of a number is essential in various mathematical and practical fields.
READ MORE:
Introduction
The square of a number is a fundamental concept in mathematics, involving multiplying the number by itself. When we square the number 72, we get the product 5184. Squaring numbers is a common operation used in various mathematical computations and applications. In this section, we'll explore the concept of squaring, the process of calculating the square of 72, and its significance in mathematics.
- Understanding the concept of squaring
- Calculating the square of 72
- Applications of squaring in mathematics
Understanding Squaring
Squaring a number means multiplying the number by itself. This operation is fundamental in mathematics and appears frequently in various areas, such as algebra, geometry, and statistics.
Mathematically, squaring a number \(n\) can be represented as:
\(n \times n = n^2\)
For example, the square of 5 is calculated as:
\(5 \times 5 = 5^2 = 25\)
Let's take a look at squaring with a specific number:
What is the Square of 72?
The square of 72 is obtained by multiplying 72 by itself:
\(72 \times 72 = 5184\)
Therefore, \(72^2 = 5184\). This result can be confirmed using various methods, such as manual calculation, calculator, or computer software.
Properties of Squaring
- Even Number Property: The square of an even number is always even. Since 72 is even, \(72^2 = 5184\) is also even.
- Perfect Square: A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. 5184 is a perfect square because it is the result of squaring 72.
- Exponentiation: Squaring a number is an example of exponentiation where the exponent is 2. This can be written as \(n^2\).
- Sum of Odd Numbers: The square of a number is the sum of the first \(n\) odd numbers. For 72, this means:
\(72^2 = 1 + 3 + 5 + ... + 143 = 5184\)
Calculation Methods
There are different methods to calculate the square of a number:
- Manual Multiplication: Multiply the number by itself directly.
- Using a Calculator: Enter the number and use the square function.
- Using Computer Software: Use software like Excel or Google Sheets with the formula
=POWER(72,2)or=72^2. - Mathematical Identities: Use identities like \(n^2 = (n-1)^2 + (2n-1)\) to find the square based on known values.
Understanding squaring helps in various mathematical applications, making it a crucial concept to master.
Calculation Method
To find the square of 72, follow these steps:
-
Understand the Concept: Squaring a number means multiplying the number by itself. So, the square of 72 is calculated as:
\[72^2 = 72 \times 72\]
-
Perform the Multiplication: Multiply 72 by 72.
\[72 \times 72 = 5184\]
This can be broken down step-by-step:
- Multiply the units: \(2 \times 2 = 4\)
- Multiply the tens with units and vice versa: \(70 \times 2 = 140\) and \(2 \times 70 = 140\)
- Multiply the tens: \(70 \times 70 = 4900\)
- Add all the partial results: \(4 + 140 + 140 + 4900 = 5184\)
-
Verify the Result: To ensure the calculation is correct, you can use different methods like the distributive property:
\[(70 + 2)^2 = 70^2 + 2 \times 70 \times 2 + 2^2\]
\[= 4900 + 280 + 4 = 5184\]
By following these steps, you can confirm that the square of 72 is indeed 5184.
Properties of 5184
The number 5184 has several interesting mathematical properties. Below are some of the key properties:
-
Prime Factorization: 5184 can be expressed as a product of prime numbers:
\[5184 = 2^6 \times 3^4\]
-
Divisors: Due to its prime factorization, 5184 has many divisors. Some of the divisors include:
- 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 16, 18, 24, 27, 32, 36, 48, 54, 72, 81, 96, 108, 144, 162, 216, 324, 432, 648, 864, 1296, 1728, 2592, 5184
-
Perfect Square: 5184 is a perfect square since it is the square of 72:
\[5184 = 72^2\]
-
Even Number: 5184 is an even number because it is divisible by 2.
-
Sum of Digits: The sum of the digits of 5184 is:
\[5 + 1 + 8 + 4 = 18\]
-
Binary Representation: In binary, 5184 is represented as:
\[1010001000000_2\]
-
Hexadecimal Representation: In hexadecimal, 5184 is represented as:
\[1440_{16}\]
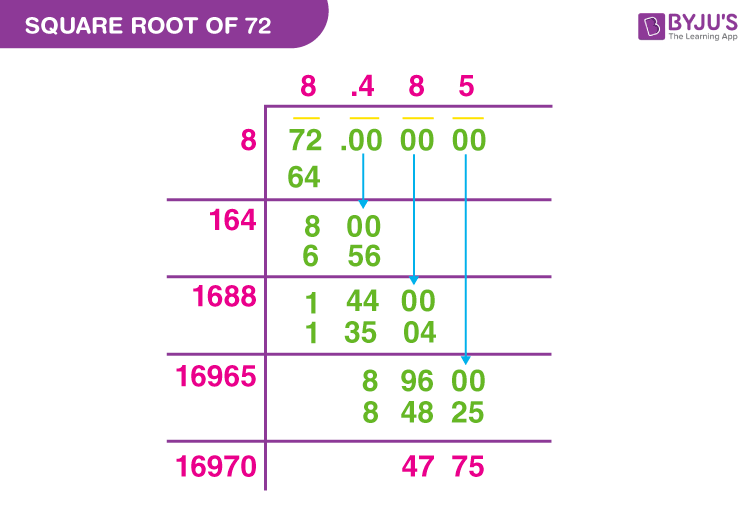
Perfect Squares
A perfect square is a number that is the square of an integer. In other words, if a number \( n \) can be expressed as \( k^2 \), where \( k \) is an integer, then \( n \) is a perfect square. Here are some key properties and examples of perfect squares:
- A perfect square always has an integer as its square root.
- Perfect squares end in 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9 in base 10.
- When squared, an integer will result in a perfect square.
Some examples of perfect squares include:
- \( 1 = 1^2 \)
- \( 4 = 2^2 \)
- \( 9 = 3^2 \)
- \( 16 = 4^2 \)
- \( 25 = 5^2 \)
- \( 36 = 6^2 \)
- \( 49 = 7^2 \)
- \( 64 = 8^2 \)
- \( 81 = 9^2 \)
- \( 100 = 10^2 \)
Perfect squares are fundamental in mathematics because they form the basis for various algebraic identities and geometric interpretations. For example, the area of a square with side length \( k \) is \( k^2 \), which is a perfect square. Additionally, perfect squares play a crucial role in solving quadratic equations and in the simplification of radical expressions.
Real-world Applications
The square of 72, which is 5184, has various real-world applications across multiple fields. Here are some notable examples:
-
Construction:
In building construction, squaring is used to ensure that structures have precise measurements. For instance, builders use squares to make sure that walls are perpendicular, while square roots help in calculating the length of diagonal braces and other components necessary for structural integrity.
-
Finance:
In finance, squares and square roots are used to assess stock market volatility. The square root of a stock's return variance provides insights into the investment's risk, aiding in better decision-making.
-
Architecture:
Architects use squaring to determine the natural frequency of structures such as bridges and buildings. This helps in predicting how these structures will respond to various loads, like wind or traffic, ensuring safety and stability.
-
Science:
In scientific calculations, squares and square roots are essential for determining velocities, radiation absorption, and sound wave intensities. These calculations help in advancing technology and medical research.
-
Statistics:
In statistics, the square root is used to compute the standard deviation from the variance, which indicates how much data points deviate from the mean. This is crucial for data analysis and making informed decisions.
-
Computer Science:
Squares and square roots play a role in various computer science applications, including encryption algorithms, image processing, and game physics. These operations are fundamental in developing secure and efficient digital systems.
-
Navigation:
In navigation, the square root helps calculate distances between points on a map or globe. For example, pilots use it to compute distances and directions during flight planning.
-
Electrical Engineering:
Electrical engineers use square roots to compute power, voltage, and current in circuits. These calculations are critical in designing and maintaining electrical systems, including power grids and communication networks.
Geometric Applications
In geometry, the square of 72 (5184) finds several practical applications:
- Area of a Square: If each side of a square measures 72 units, then its area is 5184 square units. This calculation is fundamental in determining the spatial coverage of a square-shaped region.
- Diagonal of a Square: The diagonal of a square with side length 72 units can be calculated using the formula \( \sqrt{2} \times \text{side length} = \sqrt{2} \times 72 \approx 102.07 \) units. This measurement is crucial in various geometric constructions and measurements.
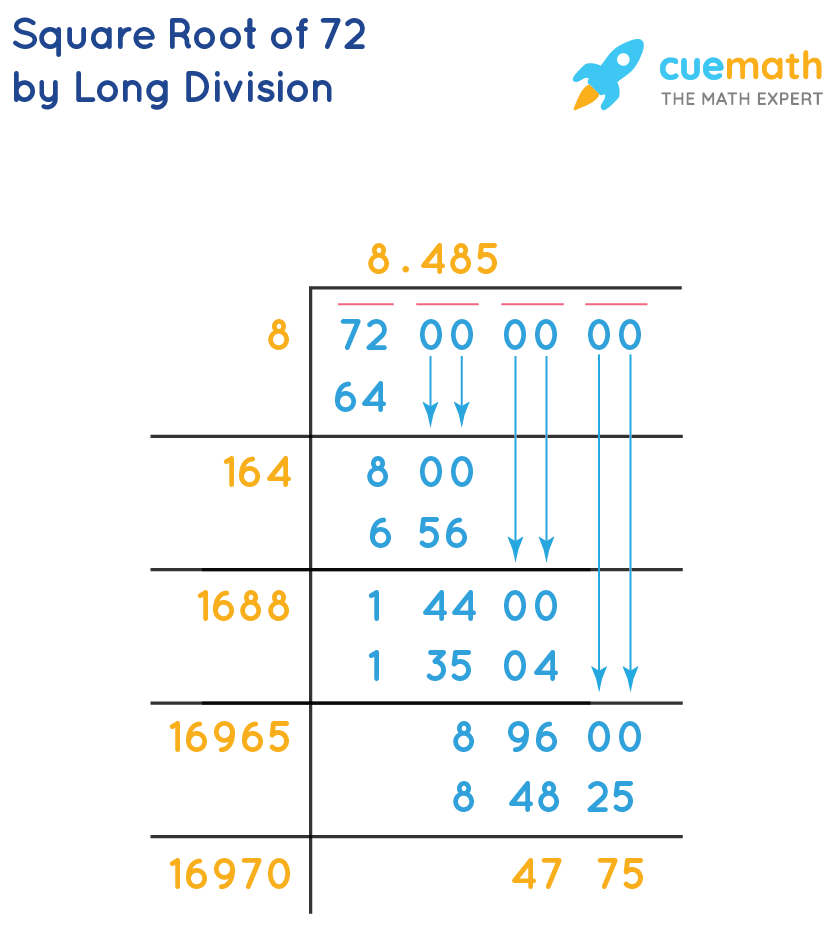
- Volume of a Cube: When considering a cube with each side measuring 72 units, the volume calculation is \( \text{side length}^3 = 72^3 = 373248 \) cubic units. This volume is significant in practical applications such as engineering and architecture.
- Pythagorean Theorem Application: In right-angled triangles where one of the angles is 45 degrees, and the legs measure 72 units, the hypotenuse is \( 72\sqrt{2} \approx 102.07 \) units. This theorem is pivotal in solving various problems in geometry and physics.
Algebraic Applications
Algebraic applications of the square of 72 are vast and varied, influencing multiple areas of mathematics and real-life situations. Here, we will explore a few key examples:
- Quadratic Equations: In algebra, the square of a number often appears in quadratic equations. For instance, consider the equation \( x^2 - 72 = 0 \). Solving for \( x \), we find \( x = \pm \sqrt{72} \). This concept extends to numerous algebraic problems, including optimization and projectile motion.
- Geometric Problems: The square of 72 is useful in geometric contexts, such as finding areas. For example, the area of a square with a side length of 72 units is \( 72^2 = 5184 \, \text{units}^2 \). This principle applies to more complex geometric shapes and designs where algebraic manipulation of areas is required.
- Distance Calculations: The Pythagorean theorem uses squares in calculating distances. If a right triangle has legs of 72 units and \( b \) units, the hypotenuse \( c \) can be found using \( c = \sqrt{72^2 + b^2} \). This method is crucial in fields like engineering and architecture.
- Algebraic Factorization: Factoring algebraic expressions can involve the square of 72. For instance, expressing \( 5184 \) as a product of primes is useful in simplifying algebraic expressions or solving higher-degree polynomials. In this case, \( 5184 = 2^6 \times 3^4 \).
Additionally, algebraic knowledge is fundamental in everyday tasks such as budgeting, where understanding percentages and proportions involves solving algebraic equations. The square of 72, and similar calculations, underpin many of these applications.
In summary, the square of 72 is not only a fundamental concept in algebra but also a practical tool in solving a variety of mathematical and real-world problems. Mastery of these applications enhances problem-solving skills and provides a solid foundation for advanced mathematical studies.
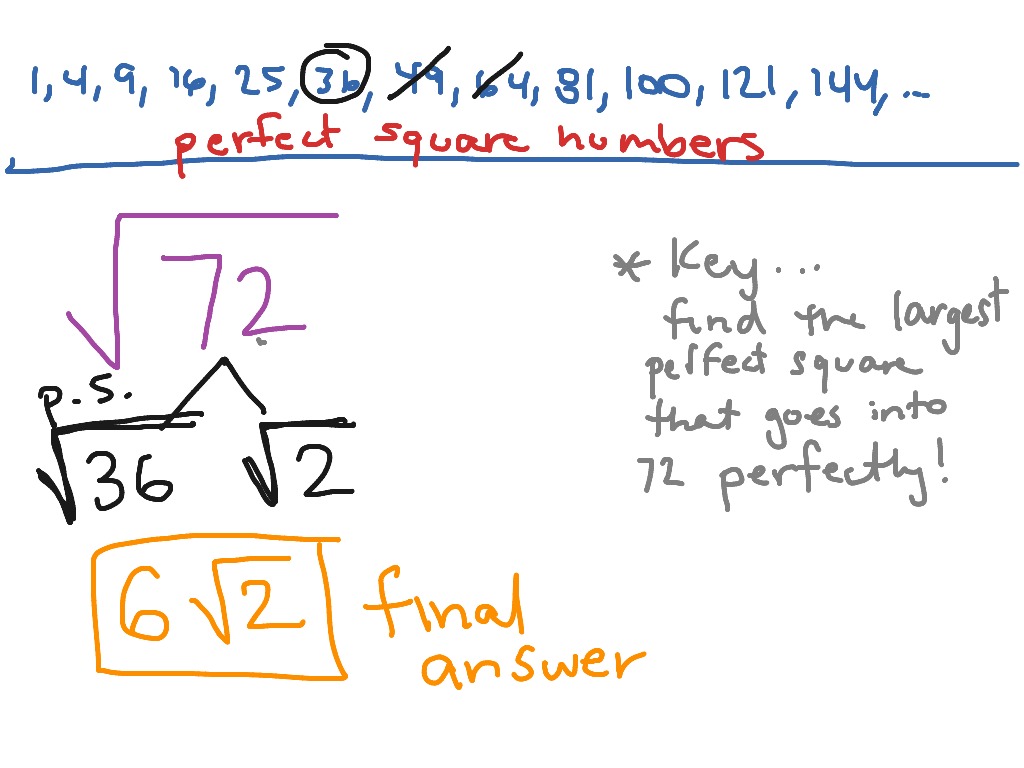
Statistical Applications
Understanding the square of 72, which is 5184, can be beneficial in various statistical applications. Here, we explore a few key concepts:
1. Mean and Standard Deviation
The mean and standard deviation are fundamental concepts in statistics, used to summarize data sets. For example, consider a data set representing the test scores of students. If the average (mean) score is 72, and we calculate the square of 72 (5184), we can use this value in further statistical calculations.
- Mean: The average value of a data set.
- Standard Deviation: A measure of the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values.
2. Variance
Variance is the square of the standard deviation and represents the average of the squared differences from the mean. For example, if the standard deviation of a data set is 72, then the variance is:
\[
\text{Variance} = 72^2 = 5184
\]
3. Chi-Square (χ²) Test
The chi-square test is a statistical method used to compare observed data with data we would expect to obtain according to a specific hypothesis. It helps in testing relationships between categorical variables. The formula for chi-square is:
\[
\chi^2 = \sum \frac{(O_i - E_i)^2}{E_i}
\]
Where \( O_i \) is the observed frequency, and \( E_i \) is the expected frequency.
4. Goodness of Fit
The goodness of fit test determines how well the sample data matches the expected distribution. For instance, if we expect a theoretical distribution with a mean of 72, we can use the chi-square test to see how well the observed data fits this distribution.
5. Test of Independence
This test evaluates whether two categorical variables are independent. For example, if we want to test whether students' performance (scores) is independent of their study methods, we can use the chi-square test. Here, 5184 (the square of 72) might represent expected frequencies in a larger data set used for testing independence.
6. Real-world Application Example
Consider a scenario where a company wants to understand if there is a relationship between employee training hours and productivity scores. By squaring the average training hours (if it's 72), we get 5184. This value can be used in calculating variances, standard deviations, and in setting up chi-square tests to analyze the data.
Understanding these applications of the square of 72 in statistics can enhance the interpretation and analysis of data, aiding in making more informed decisions based on statistical evidence.
Practice Problems
To master the concept of squaring numbers, it is important to practice with various types of problems. Below are a series of practice problems involving the square of 72, perfect squares, and related algebraic concepts. Try to solve each problem and check your answers.
Problem 1: Basic Squaring
- Calculate the square of 72. Show your work step-by-step.
Problem 2: Perfect Squares
Identify if the following numbers are perfect squares:
- 5184
- 4096
- 7225
Problem 3: Simplifying Square Roots
Simplify the square roots of the following numbers:
- √144
- √256
- √576
Problem 4: Completing the Square
Solve the following quadratic equations by completing the square:
- x² + 8x + 16 = 0
- 2x² + 10x + 12 = 0
- 3x² - 18x + 27 = 0
Problem 5: Real-World Applications
Use the concept of squaring in the following real-world scenarios:
- A square garden has an area of 5184 square feet. Find the length of one side of the garden.
- The population of a city is approximately the square of 72,000. Estimate the population of the city.
Problem 6: Algebraic Expressions
Simplify the following algebraic expressions involving squares:
- (5x)²
- (7 + 2)²
- (x + 6)² - (x - 4)²
Answers
| Problem | Answer |
|---|---|
| Problem 1 | 5184 |
| Problem 2 | 5184 (yes), 4096 (yes), 7225 (yes) |
| Problem 3 | 12, 16, 24 |
| Problem 4 |
|
| Problem 5 |
|
| Problem 6 |
|
Common Mistakes
Understanding and avoiding common mistakes is essential for mastering the calculation of square numbers. Here are some frequent errors to watch out for when working with the square of 72, or any other number:
- Incorrect Multiplication: A common mistake is multiplying the base number incorrectly. For example, miscalculating \(72 \times 72\) can lead to an incorrect result. Always double-check your multiplication steps.
- Misidentifying Perfect Squares: Sometimes, students incorrectly identify a number as a perfect square or fail to recognize it. Remember that 72 is not a perfect square, but its square (5184) is the product of perfect squares.
- Errors in Prime Factorization: Incorrectly breaking down numbers into prime factors can lead to wrong results. For 5184, correct prime factorization is crucial for simplification. Ensure each factor is accurately identified and used.
- Forgetting to Simplify: Often, intermediate steps are not simplified completely. For instance, forgetting to simplify \( \sqrt{5184} \) correctly can cause errors. Always break down to the simplest form.
- Sign Mistakes: When dealing with algebraic expressions involving squares, sign errors can occur. For example, mishandling positive and negative signs in expressions like \( (72 + x)^2 \) can alter the outcome.
- Misapplication of Formulas: Misapplying formulas like the difference of squares or the distributive property is common. For example, incorrectly applying \( (a+b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2 \) can lead to wrong answers.
- Misunderstanding the Properties of Exponents: Errors can arise from not applying exponent rules correctly, such as misunderstanding \( (72^2)^2 \) as \( 72^4 \) instead of calculating \( 5184^2 \).
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can improve accuracy and efficiency in your calculations. Always verify each step and practice regularly to develop a solid understanding of the concepts involved.
Additional Resources
For further reading and tools related to understanding and calculating the square of 72, consider exploring the following resources:
-
Calculator Soup - Square Calculator: An online tool to calculate the square of any number, along with detailed explanations of squaring numbers. It provides insights into squaring negative numbers and the properties of perfect squares.
-
Square Root Calculator: This site offers a calculator for finding the square roots of numbers and provides an explanation of the process, useful for understanding the inverse operation of squaring a number.
-
Mathway - Algebra Examples: A platform for solving various algebra problems, including simplifying square roots and understanding related algebraic concepts. It shows step-by-step solutions which are helpful for learning.
-
Math On Demand: Offers detailed solutions and explanations for mathematical problems, including the square and square roots of numbers, along with a glossary of related terms.
-
Square-Root.net: Provides comprehensive articles explaining the squaring and square root processes for various numbers, including 72. It also includes calculators and links to related calculations.
These resources will enhance your understanding of squaring numbers and their applications. Utilize the calculators and explanations provided to deepen your mathematical knowledge and skills.

Hướng dẫn cách tính căn bậc hai của 72 một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết. Xem ngay để nắm vững kiến thức toán học cơ bản.
Cách Tính Căn Bậc Hai của 72: Sqrt(72)
READ MORE:
Video giải thích chi tiết về bình phương của số 72 và các ứng dụng của nó trong toán học. Xem ngay để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này.
Bình Phương của 72