Topic solve the square root equation calculator: Discover how to solve square root equations effortlessly with our advanced calculator. Whether you're a student or math enthusiast, this tool will help you tackle complex equations with ease, providing step-by-step solutions and eliminating errors. Unlock the power of efficient problem-solving today and enhance your mathematical skills.
Table of Content
- Solve the Square Root Equation Calculator
- Introduction to Square Root Equations
- How to Solve Square Root Equations
- Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Square Root Equation Calculator
- Examples of Solving Square Root Equations
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Verifying Solutions
- Benefits of Using a Calculator
- Best Practices for Accurate Results
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Solve the Square Root Equation Calculator
Solving square root equations involves isolating the square root expression and then squaring both sides of the equation to eliminate the square root. Below are steps and tips for using a square root equation calculator:
Steps to Solve Square Root Equations
- Isolate the square root term on one side of the equation.
- Square both sides of the equation to eliminate the square root.
- Solve the resulting polynomial equation.
- Check all potential solutions in the original equation to discard extraneous solutions.
Example of Solving a Square Root Equation
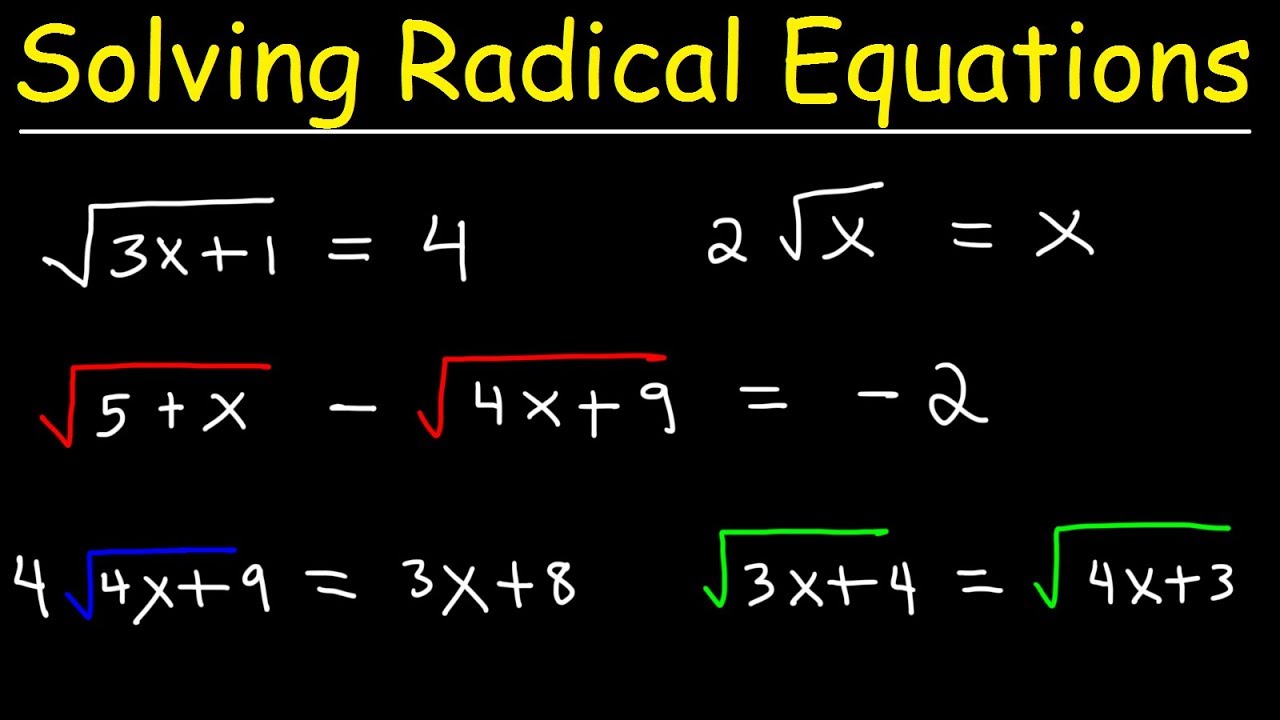
Consider the equation: \(\sqrt{x+3} = x - 1\)
- Isolate the square root term: \(\sqrt{x+3} = x - 1\)
- Square both sides: \((\sqrt{x+3})^2 = (x - 1)^2\) which simplifies to \(x + 3 = x^2 - 2x + 1\)
- Solve the resulting polynomial equation: \(0 = x^2 - 3x - 2\)
- Factor the polynomial: \((x - 1)(x + 2) = 0\)
- Find the solutions: \(x = 1\) and \(x = -2\)
- Check the solutions in the original equation:
- For \(x = 1\): \(\sqrt{1+3} = 1 - 1\) \(\rightarrow 2 \neq 0\) (extraneous)
- For \(x = -2\): \(\sqrt{-2+3} = -2 - 1\) \(\rightarrow 1 \neq -3\) (extraneous)
Using a Calculator to Solve Square Root Equations
- Input the equation into the calculator exactly as it appears.
- Follow the calculator's instructions for isolating and solving the square root term.
- Verify the solutions provided by the calculator by substituting back into the original equation.
Benefits of Using a Square Root Equation Calculator
- Quick and accurate solutions.
- Helps to visualize the steps involved in solving the equation.
- Useful for checking manual calculations.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root Equations
Square root equations are mathematical expressions where the variable is under a square root. These equations often appear in algebra and calculus, where finding the value of the variable involves isolating and removing the square root through various algebraic techniques.
To solve a square root equation, follow these general steps:
-
Identify the equation that contains the square root.
-
Isolate the square root expression on one side of the equation.
-
Square both sides of the equation to eliminate the square root. This step converts the square root equation into a quadratic equation.
-
Solve the resulting quadratic equation using methods such as factoring, the quadratic formula, or completing the square.
-
Check the solutions in the original equation to ensure they do not produce extraneous solutions.
Here is a detailed example to illustrate the process:
| Example: | Solve \( \sqrt{2x + 9} = 5 \) |
| Step 1: | Isolate the square root expression: \[ \sqrt{2x + 9} = 5 \] |
| Step 2: | Square both sides: \[ (\sqrt{2x + 9})^2 = 5^2 \] \[ 2x + 9 = 25 \] |
| Step 3: | Solve for x: \[ 2x + 9 = 25 \] \[ 2x = 16 \] \[ x = 8 \] |
By following these steps, you can solve square root equations effectively. It is important to always check your solutions in the original equation to verify their validity.
How to Solve Square Root Equations
Solving square root equations involves isolating the square root on one side of the equation and then squaring both sides to eliminate the square root. Here is a step-by-step guide to solve square root equations effectively:
- Isolate the Square Root: Ensure that the square root expression is by itself on one side of the equation.
- Square Both Sides: Apply the square function to both sides of the equation to remove the square root. For example, if you have √x = y, then squaring both sides gives x = y2.
- Simplify the Resulting Equation: After squaring, simplify the resulting equation. This may involve expanding binomials or combining like terms.
- Solve for the Variable: Solve the simplified equation for the variable. This could involve basic algebraic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
- Check for Extraneous Solutions: Substitute the solution back into the original equation to verify that it satisfies the equation. Square rooting can introduce extraneous solutions that do not satisfy the original equation.
Here is an example to illustrate the process:
| Example: |
| Solve the equation √(2x + 9) = 5. |
| Step 1: Isolate the square root. |
| Step 2: Square both sides: (√(2x + 9))2 = 52 |
| Step 3: Simplify the resulting equation: 2x + 9 = 25 |
| Step 4: Solve for x: 2x + 9 - 9 = 25 - 9 => 2x = 16 => x = 8 |
| Step 5: Check the solution: √(2(8) + 9) = √(16 + 9) = √25 = 5, which satisfies the original equation. |
This method can be used for more complex square root equations as well, following the same basic principles of isolating the square root, squaring both sides, simplifying, and verifying the solutions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Square Root Equation Calculator
Solving square root equations can be made easier with the use of an online calculator. This guide will walk you through the steps to efficiently use a square root equation calculator.
-
Navigate to an online square root equation calculator. These tools are readily available on various educational and mathematical websites.
-
Input the square root equation into the calculator. Ensure the equation is correctly formatted, such as \( \sqrt{2x + 9} = 5 \).
-
Click the "Solve" button to process the equation. The calculator will apply the necessary mathematical operations to find the solution.
-
Review the solution provided by the calculator. The answer will typically be displayed immediately, showing the value of the variable.
-
If needed, use the "Reset" button to clear the input fields and solve a new equation. This feature allows for multiple equations to be solved consecutively.
Example of solving a square root equation manually:
| Equation | \(\sqrt{2x + 9} = 5\) |
| Step 1 | Square both sides: \((\sqrt{2x + 9})^2 = 5^2\) |
| Step 2 | Simplify: \(2x + 9 = 25\) |
| Step 3 | Subtract 9 from both sides: \(2x + 9 - 9 = 25 - 9\) |
| Step 4 | Simplify: \(2x = 16\) |
| Step 5 | Divide by 2: \(x = \frac{16}{2} = 8\) |
Using an online calculator follows similar logic but simplifies the process by performing these operations automatically.
Examples of Solving Square Root Equations
Solving square root equations involves isolating the square root on one side of the equation and then squaring both sides to eliminate the square root. Below are detailed examples of solving such equations:
-
Example 1: Solve the equation \( \sqrt{x - 2} = 5 \).
- Start with the equation: \( \sqrt{x - 2} = 5 \).
- Square both sides to remove the square root: \( (\sqrt{x - 2})^2 = 5^2 \).
- This simplifies to: \( x - 2 = 25 \).
- Solving for \( x \): \( x = 25 + 2 \).
- Solution: \( x = 27 \).
-
Example 2: Solve the equation \( \sqrt{x + 7} = 10 \).
- Start with the equation: \( \sqrt{x + 7} = 10 \).
- Square both sides: \( (\sqrt{x + 7})^2 = 10^2 \).
- This simplifies to: \( x + 7 = 100 \).
- Solving for \( x \): \( x = 100 - 7 \).
- Solution: \( x = 93 \).
-
Example 3: Solve the equation \( \sqrt{x^2 - 4} = 9 \).
- Start with the equation: \( \sqrt{x^2 - 4} = 9 \).
- Square both sides: \( (\sqrt{x^2 - 4})^2 = 9^2 \).
- This simplifies to: \( x^2 - 4 = 81 \).
- Solving for \( x \): \( x^2 = 81 + 4 \).
- This simplifies to: \( x^2 = 85 \).
- Solution: \( x = \pm \sqrt{85} \).
These examples illustrate the step-by-step process of solving square root equations by squaring both sides to eliminate the square root and then solving the resulting equation. Using an online square root equation calculator can help verify these solutions quickly and accurately.
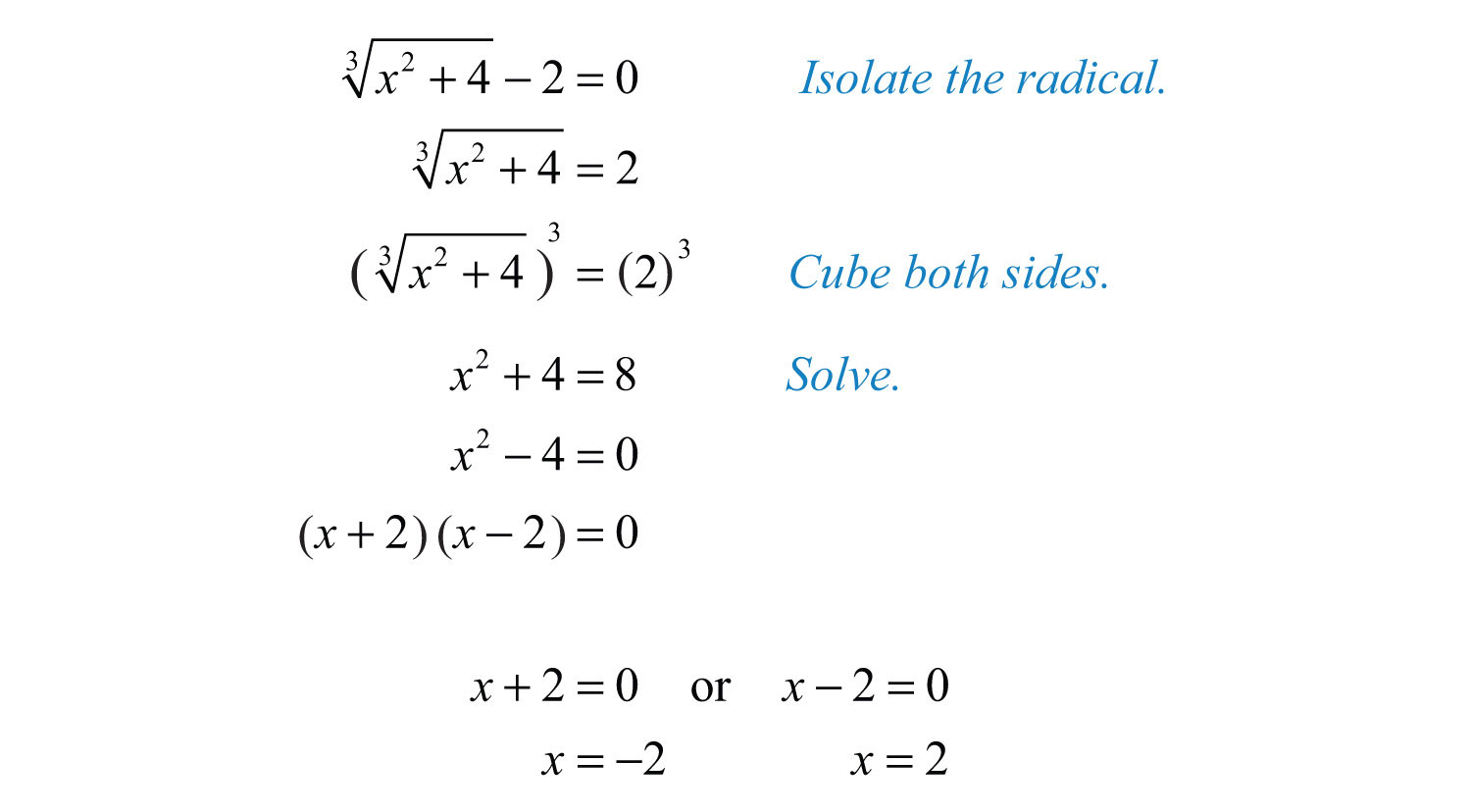
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Solving square root equations can be challenging, and there are common mistakes that learners often make. Being aware of these mistakes and understanding how to avoid them is crucial for accurate solutions. Here are some of the most frequent errors and tips to prevent them:
- Incorrectly Squaring Both Sides: When solving a square root equation, ensure you correctly square both sides of the equation. Failing to do so accurately can lead to incorrect results.
- Forgetting to Check for Extraneous Solutions: After solving the equation, always substitute your solutions back into the original equation to verify their validity. Squaring both sides can sometimes introduce extraneous solutions.
- Misunderstanding the Addition under the Square Root: Remember that . This is a common misconception and can lead to errors in simplification.
- Canceling Terms Incorrectly: Avoid canceling terms unless they are factors of both the numerator and the denominator. Improper cancellation can lead to incorrect simplifications and solutions.
- Neglecting Negative Roots: When solving square root equations, don't forget that . Both positive and negative roots should be considered where applicable.
By recognizing these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can improve your accuracy and efficiency in solving square root equations.
Verifying Solutions
After solving a square root equation, it is crucial to verify the solutions to ensure they are correct. Verification helps to confirm that the solutions satisfy the original equation and are not extraneous.
- Step 1: Substitute the Solutions
- Step 2: Simplify Both Sides
- Step 3: Check for Equality
- Example Verification
- For \( x = 1 \):
- Substitute \( x = 1 \) into the original equation: \( \sqrt{5(1) + 11} - 1 = 1 \).
- Simplify: \( \sqrt{16} - 1 = 1 \).
- Since \( 4 - 1 = 3 \), which is not equal to 1, \( x = 1 \) is an extraneous solution.
- For \( x = 3 \):
- Substitute \( x = 3 \) into the original equation: \( \sqrt{5(3) + 11} - 1 = 3 \).
- Simplify: \( \sqrt{26} - 1 = 3 \).
- Since \( \sqrt{26} - 1 \) does not equal 3, \( x = 3 \) is also an extraneous solution.
Take each solution and substitute it back into the original equation. This step checks whether the left-hand side equals the right-hand side.
Simplify both sides of the equation after substitution. Ensure all operations are correctly performed, including dealing with radicals.
Compare the simplified left-hand side with the right-hand side. If they are equal, the solution is valid; otherwise, it is an extraneous solution.
Consider the equation \( \sqrt{5x+11} - 1 = x \). Suppose we find the solutions \( x = 1 \) and \( x = 3 \).
As shown, it is important to verify solutions as both potential solutions in this example are extraneous.
Benefits of Using a Calculator
Using a square root equation calculator offers numerous advantages, especially when dealing with complex mathematical problems. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Accuracy: Calculators provide precise results, minimizing the risk of human error in manual calculations.
- Efficiency: Solving square root equations manually can be time-consuming. A calculator speeds up the process, allowing you to focus on understanding the results.
- Complex Equations: Calculators can handle complex and large numbers effortlessly, which might be cumbersome to solve manually.
- Learning Aid: They serve as a valuable educational tool, helping students verify their answers and understand the steps involved in solving equations.
- Convenience: Calculators are readily available online and can be used anywhere, making them convenient for students, professionals, and anyone needing quick calculations.
- Consistency: Ensures consistent results, which is crucial for repetitive calculations in fields like engineering and finance.
Overall, a square root equation calculator enhances productivity and understanding by providing quick, accurate, and reliable solutions to mathematical problems.
Best Practices for Accurate Results
To ensure accurate results when solving square root equations using a calculator, follow these best practices:
-
Understand the Equation:
Before inputting the equation into the calculator, ensure you understand its structure. Identify the square root term and any constants or variables involved.
-
Use Proper Formatting:
Ensure the equation is formatted correctly. For instance, an equation like \( \sqrt{x+4} = 5 \) should be input with the square root symbol and any operations outside the root properly placed.
-
Double-Check Inputs:
Verify that all numbers and symbols are correctly entered into the calculator. Even a small mistake can lead to incorrect results.
-
Follow Calculator Instructions:
Different calculators may have specific ways they require inputs. Follow the instructions provided by the calculator to ensure it interprets your equation correctly.
-
Consider Both Positive and Negative Roots:
Remember that square root equations can have both positive and negative solutions. Check both possibilities to ensure you have found all solutions.
-
Use the Right Mode:
Ensure the calculator is in the correct mode for the type of equation you are solving. Some calculators have specific modes for solving algebraic equations that should be used.
-
Verify Results:
Once you have a solution, substitute it back into the original equation to verify its correctness. This helps to confirm that the solution is accurate.
-
Understand the Limitations:
Be aware of the limitations of your calculator. Some calculators may not handle very complex equations or large numbers accurately.
-
Seek Help When Needed:
If you encounter difficulties, consult online resources or seek help from a teacher or tutor. Understanding how to use the calculator effectively is crucial for accurate results.
-
Practice Regularly:
Regular practice helps you become familiar with the calculator's functions and improves your problem-solving skills.

Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is a square root equation?
A square root equation is an equation in which the variable is inside a square root. For example, an equation like \( \sqrt{x+3} = 5 \) is a square root equation.
-
How do you solve a square root equation?
To solve a square root equation, follow these steps:
- Isolate the square root expression on one side of the equation.
- Square both sides of the equation to eliminate the square root.
- Solve the resulting equation.
- Check all solutions in the original equation to ensure they do not produce extraneous results.
-
What are extraneous solutions?
Extraneous solutions are solutions that arise from the process of solving the equation but do not satisfy the original equation. It's essential to check all potential solutions by substituting them back into the original equation.
-
Why is it important to verify the solutions?
Verification ensures that the solutions are correct and not extraneous. This step is crucial because operations like squaring both sides can introduce solutions that do not satisfy the original equation.
-
Can a square root equation have more than one solution?
Yes, a square root equation can have multiple solutions. For example, \( \sqrt{x^2} = 4 \) leads to \( x = 4 \) or \( x = -4 \).
-
Are there any specific tools or calculators for solving square root equations?
Yes, there are online calculators specifically designed to solve square root equations. These tools can quickly compute the solutions and help verify the accuracy of manual calculations.
-
What are some common mistakes to avoid?
Common mistakes include not isolating the square root before squaring both sides, failing to check for extraneous solutions, and incorrectly simplifying the resulting equations.
-
What should I do if I get a complex or non-real solution?
If a square root equation leads to a complex or non-real solution, it usually means the equation has no real solutions. This can happen when you end up with a negative number under the square root after isolating the square root expression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, solving square root equations can be made significantly easier with the use of a dedicated calculator. These tools not only save time but also ensure accuracy, which is crucial for both simple and complex equations. Here are the key takeaways for effectively using a square root equation calculator:
- Efficiency: Calculators provide quick solutions, allowing you to focus on understanding the process rather than getting bogged down by manual calculations.
- Accuracy: By minimizing human error, calculators help in achieving precise results, which is essential for complex mathematical problems.
- Learning Aid: They serve as an excellent learning tool, enabling students and professionals to verify their solutions and understand the steps involved in solving square root equations.
- Versatility: Modern calculators are equipped to handle a wide range of equations, from simple to highly complex, making them invaluable for various mathematical tasks.
Ultimately, incorporating a square root equation calculator into your toolkit will enhance your problem-solving capabilities and ensure that you can tackle mathematical challenges with confidence and accuracy.
Hướng dẫn Sử dụng Máy tính: Căn Bậc Hai trên Máy Tính Khoa Học
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách sử dụng máy tính Texas Instruments TI-30IIS để tính căn bậc hai. Phù hợp cho học sinh, sinh viên và những ai cần giải phương trình căn bậc hai.
Cách tính căn bậc hai bằng máy tính Texas Instruments TI-30IIS