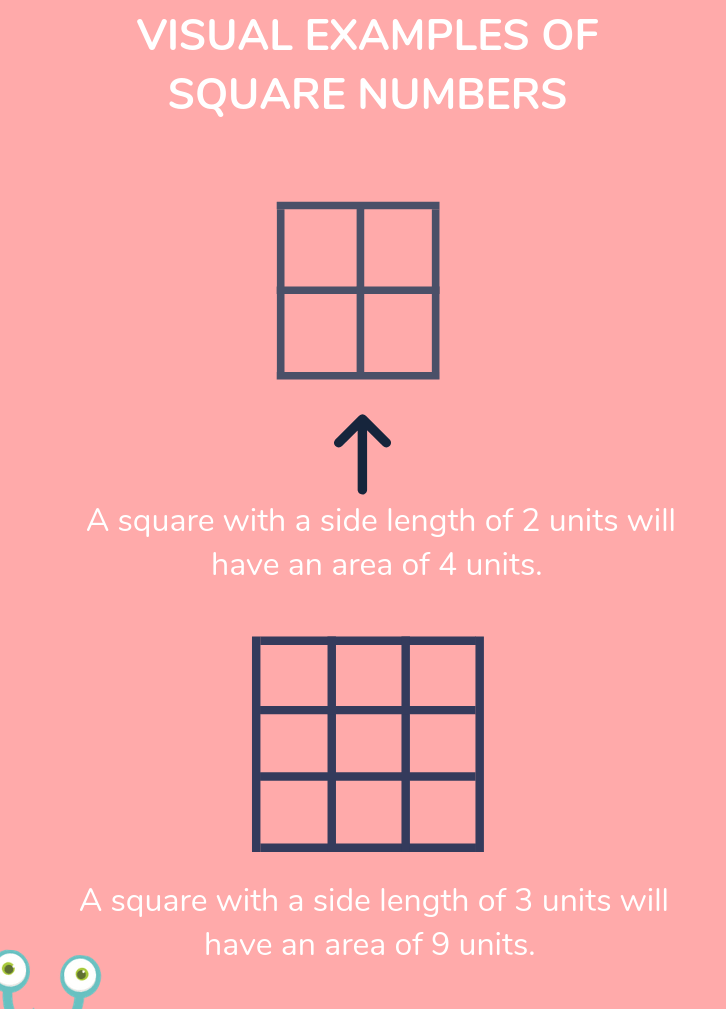Topic square root and exponents worksheet: Discover the importance and applications of square roots and exponents with our comprehensive worksheet. This resource is designed to help students of all grades master these fundamental concepts through clear explanations, varied practice problems, and engaging learning tools. Start your journey to mathematical proficiency today!
Table of Content
Square Root and Exponents Worksheet
Square root and exponents worksheets are essential tools for students to master the fundamental concepts of powers and roots. These worksheets provide practice problems that help reinforce learning and improve mathematical skills.
Understanding Exponents and Square Roots
Exponents represent repeated multiplication of a number by itself. For example, \(2^3\) means \(2 \times 2 \times 2 = 8\). Square roots, on the other hand, are values that, when multiplied by themselves, give the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4, because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
Importance in Education
Learning exponents and square roots is crucial in the 6th-grade math curriculum as they lay the foundation for advanced topics in algebra, geometry, and science. They help students understand patterns, relationships, and properties of numbers, which are essential for higher-level math and science courses.
Common Rules of Exponents
- Product Rule: When multiplying two powers with the same base, add the exponents: \(a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}\).
- Quotient Rule: When dividing two powers with the same base, subtract the exponents: \(a^m / a^n = a^{m-n}\).
- Power Rule: When raising a power to another power, multiply the exponents: \((a^m)^n = a^{m \cdot n}\).
Sample Worksheet Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find \(2^3\) | 8 |
| Find the square root of 25 | 5 |
| Simplify \(3^2 \times 3^3\) | 35 |
| Simplify \(4^4 / 4^2\) | 42 |
Resources

READ MORE:
Introduction
Square roots and exponents are fundamental concepts in mathematics, essential for understanding higher-level math topics. Exponents represent repeated multiplication, while square roots denote a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Mastering these concepts builds a strong mathematical foundation.
- Exponents: Represent repeated multiplication of a number. For example, \(3^4 = 3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3 = 81\).
- Square Roots: Find a number that, when squared, equals the original number. For example, \(\sqrt{49} = 7\) because \(7 \times 7 = 49\).
- Applications:
- Used in solving algebraic equations.
- Essential in geometry for calculating areas and volumes.
- Applied in scientific calculations and real-world problem solving.
| Concept | Explanation |
| Exponentiation | Expresses repeated multiplication of a base number. |
| Square Root | Finds the number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. |
Basic Concepts
Understanding the basic concepts of square roots and exponents is crucial for mastering more advanced mathematical topics. These foundational elements help in simplifying complex problems and are widely applicable in various fields of study.
- Definition of Exponents:
Exponents represent repeated multiplication of a number by itself. The expression \(a^n\) means \(a\) is multiplied by itself \(n\) times. For example, \(2^3 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 8\).
- Definition of Square Roots:
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is represented by the radical symbol \(\sqrt{}\). For instance, \(\sqrt{25} = 5\) because \(5 \times 5 = 25\).
- Relationship Between Exponents and Roots:
Square roots are the inverse operation of squaring a number. While exponents involve raising a number to a power, roots involve finding the base number. For example, if \(3^2 = 9\), then \(\sqrt{9} = 3\).
- Properties of Exponents:
- Product of Powers: \(a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}\)
- Quotient of Powers: \(\frac{a^m}{a^n} = a^{m-n}\)
- Power of a Power: \((a^m)^n = a^{mn}\)
- Power of a Product: \((ab)^n = a^n \times b^n\)
- Zero Exponent: \(a^0 = 1\) for any \(a \neq 0\)
- Properties of Square Roots:
- Product Property: \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\)
- Quotient Property: \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\)
- Simplifying Radicals: Reducing the expression under the radical to its simplest form. For example, \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
| Concept | Example |
| Exponentiation | \(4^3 = 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64\) |
| Square Root | \(\sqrt{81} = 9\) |
| Product of Powers | \(2^3 \times 2^2 = 2^{3+2} = 2^5 = 32\) |
| Simplifying Radicals | \(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{36 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2}\) |
Worksheets for Different Grades
Our comprehensive worksheets cater to different grade levels, providing age-appropriate practice problems and activities that help students grasp the concepts of square roots and exponents. These worksheets are designed to reinforce learning through a variety of engaging exercises.
- 6th Grade Worksheets:
- Introduction to Exponents: Basic problems involving small numbers and simple calculations.
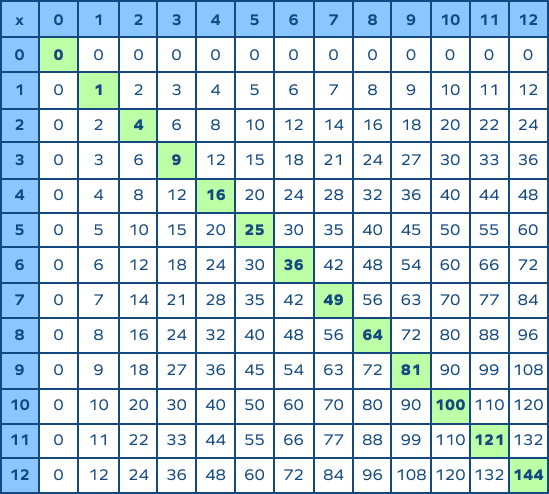
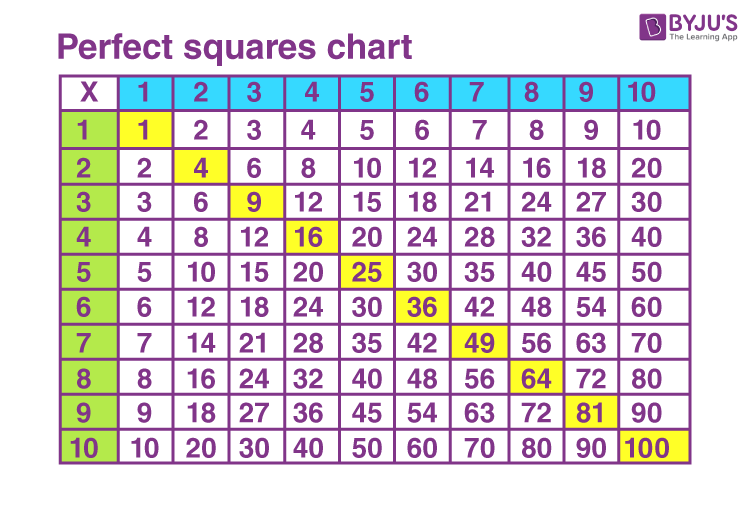
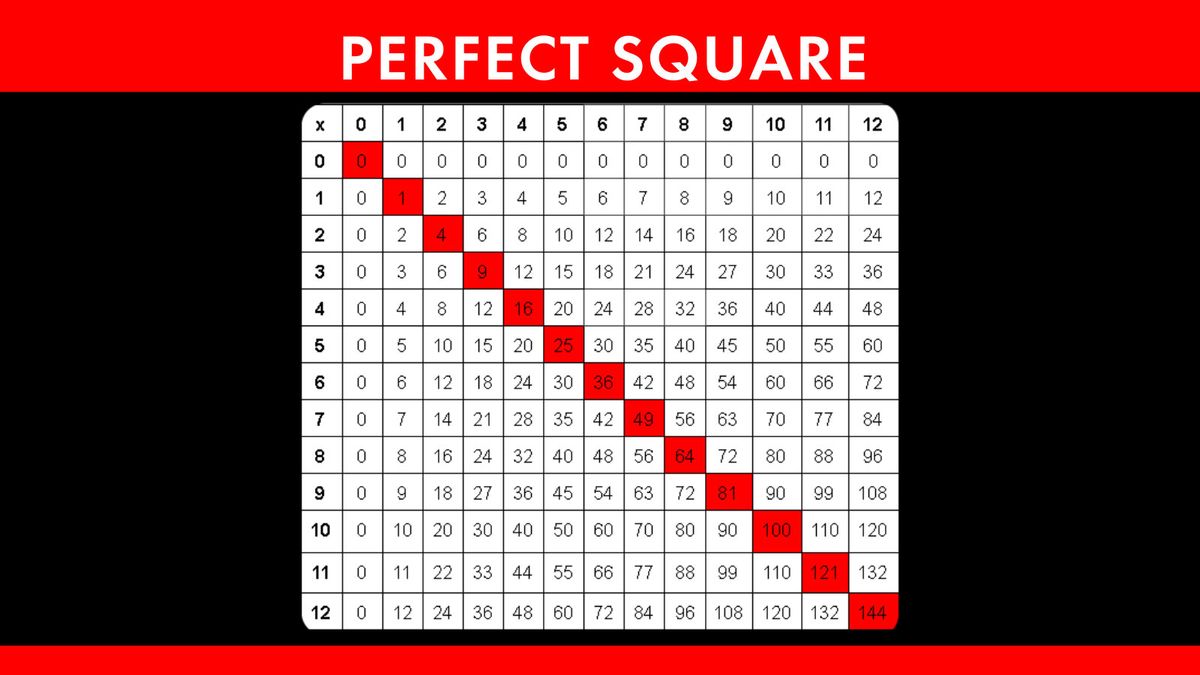
- Identifying Perfect Squares: Exercises to recognize and list perfect squares up to 100.
- Simple Square Roots: Basic problems finding square roots of perfect squares.
- 7th Grade Worksheets:
- Properties of Exponents: Problems involving the product, quotient, and power of powers properties.
- Calculating Square Roots: Exercises to find square roots of perfect squares and approximate non-perfect squares.
- Exponent Word Problems: Real-world scenarios where students apply exponent rules.
- 8th Grade Worksheets:
- Advanced Exponents: Problems involving negative exponents and exponents with fractions and decimals.
- Simplifying Radicals: Exercises to simplify expressions with square roots and higher-order roots.
- Scientific Notation: Practice converting numbers to and from scientific notation using exponents.
| Grade | Focus Areas |
| 6th Grade | Introduction to Exponents, Identifying Perfect Squares, Simple Square Roots |
| 7th Grade | Properties of Exponents, Calculating Square Roots, Exponent Word Problems |
| 8th Grade | Advanced Exponents, Simplifying Radicals, Scientific Notation |
Practice Problems
Engage with a variety of practice problems to reinforce your understanding of square roots and exponents. These exercises will help you develop proficiency and confidence in handling different types of mathematical challenges.
- Finding Squares and Cubes of Integers:
- Calculate \(5^2\)
- Calculate \(4^3\)
- Find the square of 12
- Find the cube of 7
- Finding Square Roots of Perfect Squares:
- \(\sqrt{64}\)
- \(\sqrt{144}\)
- Find the square root of 225
- Find the square root of 400
- Estimating Non-Perfect Squares:
- Estimate \(\sqrt{50}\)
- Estimate \(\sqrt{200}\)
- Approximate \(\sqrt{18}\)
- Approximate \(\sqrt{90}\)
- Operations with Exponents:
- Simplify \(3^2 \times 3^3\)
- Simplify \(\frac{4^5}{4^2}\)
- Calculate \((2^3)^2\)
- Calculate \((5^2 \times 2^3)\)
- Exponents with Decimals and Fractions:
- Simplify \( (0.5)^3 \)
- Simplify \( (1.2)^2 \)
- Calculate \( ( \frac{3}{4} )^2 \)
- Calculate \( ( \frac{5}{2} )^3 \)
| Problem Type | Example |
| Finding Squares | \(8^2 = 64\) |
| Finding Cubes | \(3^3 = 27\) |
| Square Root of Perfect Squares | \(\sqrt{81} = 9\) |
| Estimating Non-Perfect Squares | \(\sqrt{50} \approx 7.07\) |
| Operations with Exponents | \(2^3 \times 2^4 = 2^{3+4} = 2^7 = 128\) |
| Exponents with Decimals | \((0.4)^2 = 0.16\) |
| Exponents with Fractions | \(\left(\frac{2}{3}\right)^3 = \frac{8}{27}\) |

Advanced Topics
Delve deeper into the world of mathematics with advanced topics that build on the basics of square roots and exponents. These concepts are crucial for higher-level math and various scientific applications.
- Negative Exponents:
Negative exponents represent the reciprocal of the base raised to the positive exponent. For example, \(a^{-n} = \frac{1}{a^n}\). Practice problems include:
- Simplify \(2^{-3}\)
- Simplify \(10^{-2}\)
- Calculate \( (3^{-1})^2 \)
- Calculate \( 5^{-1} \times 4^{-1} \)
- Higher Order Roots:
Beyond square roots, higher order roots like cube roots and fourth roots are essential. For example, \(\sqrt[3]{27} = 3\) because \(3^3 = 27\). Practice problems include:
- Calculate \(\sqrt[3]{64}\)
- Calculate \(\sqrt[4]{81}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt[5]{32}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt[6]{64}\)
- Simplifying Radical Expressions:
Simplifying radicals involves expressing roots in their simplest form. For example, \(\sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2}\). Practice problems include:
- Simplify \(\sqrt{72}\)
- Simplify \( \sqrt{45} \)
- Simplify \( \sqrt{98} \)
- Simplify \( \sqrt{200} \)
- Scientific Notation:
Scientific notation expresses large or small numbers using powers of ten. For example, \(5,000 = 5 \times 10^3\). Practice problems include:
- Convert \(4,500\) to scientific notation
- Convert \(0.003\) to scientific notation
- Simplify \((3 \times 10^4) \times (2 \times 10^3)\)
- Simplify \(\frac{6 \times 10^5}{3 \times 10^2}\)
- Logarithms:
Logarithms are the inverses of exponents, answering the question of what power a base must be raised to yield a given number. For example, \(\log_{10}{100} = 2\) because \(10^2 = 100\). Practice problems include:
- Evaluate \(\log_{2}{8}\)
- Evaluate \(\log_{10}{1,000}\)
- Calculate \(\log_{5}{125}\)
- Calculate \(\log_{3}{27}\)
| Advanced Topic | Example |
| Negative Exponents | \(2^{-3} = \frac{1}{2^3} = \frac{1}{8}\) |
| Higher Order Roots | \(\sqrt[3]{27} = 3\) |
| Simplifying Radical Expressions | \(\sqrt{72} = 6\sqrt{2}\) |
| Scientific Notation | \(7,000 = 7 \times 10^3\) |
| Logarithms | \(\log_{10}{1000} = 3\) |
Learning Resources
To enhance your understanding and practice of square roots and exponents, we offer a variety of learning resources. These tools and materials are designed to cater to different learning styles and help you master these concepts effectively.
- Interactive Videos:
Engage with dynamic visual content that explains the principles of square roots and exponents in an easy-to-understand manner. These videos often include step-by-step tutorials and practical examples.
- Quizzes and Tests:
Test your knowledge and track your progress with quizzes and tests. These assessments are designed to reinforce learning and identify areas that need improvement.
- Printable Worksheets:
Access a variety of printable worksheets that provide ample practice problems. These worksheets are great for offline study and review sessions.
- Online Practice Tools:
Utilize interactive online tools that offer instant feedback and detailed solutions. These tools can help you practice and refine your skills efficiently.
| Resource Type | Description |
| Interactive Videos | Step-by-step tutorials and practical examples explaining square roots and exponents. |
| Quizzes and Tests | Assessments to test knowledge and track progress. |
| Printable Worksheets | Variety of practice problems for offline study. |
| Online Practice Tools | Interactive tools with instant feedback and detailed solutions. |
Conclusion
Understanding square roots and exponents is fundamental to mastering higher-level math and various real-world applications. Through consistent practice and utilization of diverse learning resources, students can develop a strong foundation in these concepts. Remember, the key to success is regular practice, persistence, and a positive attitude towards learning. Keep exploring, practicing, and challenging yourself to achieve mastery in square roots and exponents.
- Review Key Concepts:
Regularly revisit the basic and advanced topics to reinforce your understanding and retention of the material.
- Practice Consistently:
Engage with a variety of practice problems and worksheets to build and maintain your skills.
- Use Available Resources:
Take advantage of interactive videos, quizzes, printable worksheets, and online tools to support your learning journey.
- Stay Positive and Persistent:
Keep a positive mindset and persist through challenges. Every problem solved brings you one step closer to mastery.
| Tip | Description |
| Review Key Concepts | Revisit both basic and advanced topics regularly. |
| Practice Consistently | Engage with practice problems and worksheets. |
| Use Available Resources | Leverage videos, quizzes, worksheets, and tools. |
| Stay Positive and Persistent | Maintain a positive attitude and persist through challenges. |
Video Toán Học Cơ Bản giải thích về số mũ và căn bậc hai, giúp học sinh hiểu rõ hơn về các khái niệm quan trọng này.
Toán Học Cơ Bản - Số Mũ và Căn Bậc Hai
READ MORE:
Video giải thích về căn bậc hai với Thầy J, giúp học sinh hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm quan trọng này trong toán học.
Căn Bậc Hai Là Gì? | Toán Học với Thầy J