Topic simplify the square root of 45: Unlock the secrets to simplifying the square root of 45 with our comprehensive guide. Whether you're a student, teacher, or math enthusiast, this article breaks down the process into easy-to-follow steps, ensuring you grasp the concept effortlessly. Dive in and discover how simplifying √45 can be both engaging and educational!
Table of Content
- How to Simplify the Square Root of 45
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- Methods for Simplifying Square Roots
- Step-by-Step Simplification of √45
- Using the Long Division Method
- Visual and Interactive Examples
- Practical Applications
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 45. Tìm hiểu phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và cách sử dụng để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai.
How to Simplify the Square Root of 45
To simplify the square root of 45, we can break it down into simpler factors:
\[
\sqrt{45} = \sqrt{9 \times 5} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{5} = 3\sqrt{5}
\]
Therefore, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{45}\) is \(3\sqrt{5}\).
READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding how to simplify the square root of 45 can be a rewarding process in learning algebra. Simplifying square roots involves expressing the number in its simplest radical form. In this guide, we'll take you through a step-by-step process to simplify √45 using methods like factorization and properties of square roots. By the end, you'll be equipped with a clear understanding of the concept and how to apply it effectively.
Understanding Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental in mathematics, representing a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 25 is 5, because 5 multiplied by 5 equals 25. This concept is essential for various mathematical operations and problem-solving techniques.
To simplify a square root, you need to break down the number inside the radical into its prime factors and identify any perfect squares. Perfect squares are numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, etc., that are squares of whole numbers.
Here’s a step-by-step process to understand and simplify square roots:
- Identify the prime factors of the number inside the square root.
- Look for pairs of prime factors because each pair can be taken out of the square root as a single number.
- Rewrite the square root as a product of these factors.
For example, let's simplify √45:
- Find the prime factors of 45. It can be expressed as 45 = 9 × 5.
- Notice that 9 is a perfect square (3 × 3).
- So, √45 can be written as √(9 × 5).
- Using the property of square roots, we can split this into √9 × √5.
- Since √9 is 3, we get 3√5.
This method works for any number. By identifying and extracting perfect squares from the factors, you simplify the square root into its most basic form.
Understanding and simplifying square roots is not only a key mathematical skill but also a foundational tool for more complex math problems.
Methods for Simplifying Square Roots
When simplifying square roots, the goal is to express the number under the square root in its simplest form. This involves identifying and factoring out perfect squares from the radicand (the number under the square root symbol). Here are some common methods for simplifying square roots:
-
Prime Factorization Method
In this method, you break down the radicand into its prime factors and then pair the prime factors to simplify the square root.
For example, to simplify \( \sqrt{45} \):
- Prime factorize 45: \( 45 = 3 \times 3 \times 5 \)
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \( 45 = 3^2 \times 5 \)
- Take the square root of each pair of prime factors: \( \sqrt{3^2 \times 5} = 3\sqrt{5} \)
Thus, \( \sqrt{45} = 3\sqrt{5} \).
-
Identifying Perfect Squares
Look for perfect square factors within the radicand and simplify accordingly.
For example, to simplify \( \sqrt{45} \):
- Identify the perfect square factor: \( 45 = 9 \times 5 \)
- Rewrite the square root using this factor: \( \sqrt{45} = \sqrt{9 \times 5} \)
- Simplify by taking the square root of the perfect square: \( \sqrt{9 \times 5} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{5} = 3\sqrt{5} \)
Thus, \( \sqrt{45} = 3\sqrt{5} \).
-
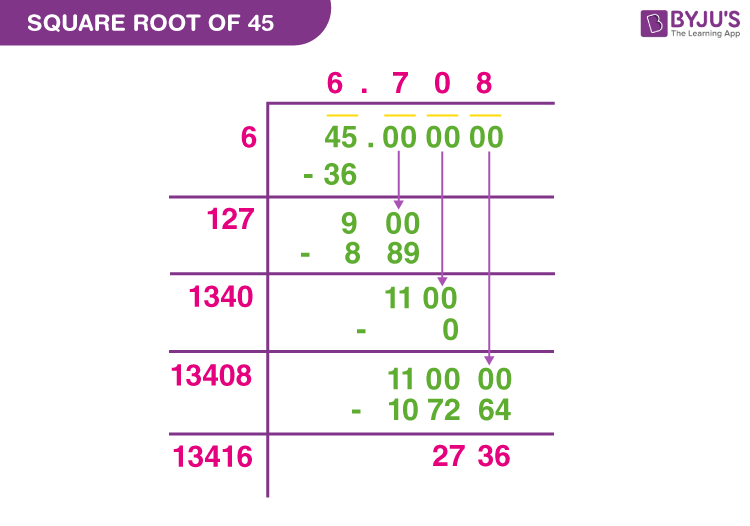
Long Division Method
The long division method is useful for finding the square root of numbers that are not perfect squares. It involves a step-by-step process of division to approximate the square root.
- Pair the digits of the number from right to left: 45 (becomes 45.000000 for detailed division)
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the leftmost pair: \( 6^2 = 36 \leq 45 \)
- Subtract and bring down the next pair of digits, doubling the quotient for the next divisor: continue until the desired precision is reached
For example, the square root of 45 using long division is approximately 6.708.
Step-by-Step Simplification of √45
To simplify the square root of 45, we will follow a systematic process involving factorization and identification of perfect squares. Here are the detailed steps:
-
Step 1: Prime Factorization
First, we factorize 45 into its prime factors:
\(45 = 3 \times 3 \times 5\)
Or, more formally:
\(45 = 3^2 \times 5\)
-
Step 2: Identifying Perfect Squares
Next, we identify the perfect squares in the factorization. Here, \(3^2\) is a perfect square:
\(45 = 3^2 \times 5\)
-
Step 3: Simplification Process
We then take the square root of each factor:
\(\sqrt{45} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 5}\)
Since the square root of a product is the product of the square roots:
\(\sqrt{3^2 \times 5} = \sqrt{3^2} \times \sqrt{5}\)
Simplify further by taking the square root of \(3^2\), which is 3:
\(\sqrt{3^2} \times \sqrt{5} = 3\sqrt{5}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{45}\) is:
\(\sqrt{45} = 3\sqrt{5}\)
Let's summarize the steps in a table for better understanding:
| Step | Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prime Factorize 45 | \(45 = 3^2 \times 5\) |
| 2 | Identify Perfect Squares | \(3^2\) is a perfect square |
| 3 | Simplify | \(\sqrt{45} = 3\sqrt{5}\) |
By following these steps, you can simplify any square root by breaking it down into its prime factors, identifying perfect squares, and then simplifying the expression.

Using the Long Division Method
The long division method is a systematic way to find the square root of a number, especially useful for larger or non-perfect squares. Here is a detailed, step-by-step explanation of how to simplify the square root of 45 using the long division method:
-
Pair the Digits: Start by pairing the digits of 45 from right to left. Since 45 has only two digits, we consider it as a single pair: 45.
-
Estimate the Largest Digit: Find the largest digit whose square is less than or equal to the first pair. For 45, the closest perfect square is 36 (6²), so our first digit is 6.
Place 6 above the bar and subtract its square from the first pair of digits:
\[
\begin{array}{r|l}
6 & 45 \\
& -36 \\
& \hline
& 9 \\
\end{array}
\] -
Bring Down the Next Pair: In this case, since there are no more digits, we add a decimal point and bring down a pair of zeros. The new number to be divided is 900.
-
Double the Result: Double the result obtained so far (6) and place it next to the new divisor space: 12_.
Now we need to find a digit to place in the blank such that 12_ multiplied by this digit gives a number less than or equal to 900. The suitable digit here is 7:
127 × 7 = 889
Place 7 next to 6 in the quotient and subtract 889 from 900:
\[
\begin{array}{r|l}
6.7 & 45.00 \\
& -36 \\
& \hline
& 9.00 \\
& -8.89 \\
& \hline
& 0.11 \\
\end{array}
\] -
Repeat the Process: Continue the process by bringing down pairs of zeros, doubling the current result, and finding new digits to approximate the square root to more decimal places.
By following these steps, you can find that the square root of 45 is approximately 6.7, but the process can be continued for more precise results.
Visual and Interactive Examples
Visual and interactive examples are a great way to understand the process of simplifying square roots. Here are some methods you can use to visualize the simplification of √45:
Visual Models
Visual models can help illustrate the process of breaking down the square root of a number into its simplest form. For example, you can use a grid to show how the area of a square relates to its side length. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Draw a large square and label its area as 45 units2.
- Divide this square into smaller squares, each representing a perfect square factor of 45. In this case, use 9 (32) and 5.
- Visualize that the large square (45) can be broken down into a square of 9 units and a rectangle representing 5 units.
- This helps illustrate that √45 = √(9 × 5) = 3√5.
Interactive Tools
Interactive tools, such as online calculators and math software, can also help in understanding the simplification process. These tools often provide step-by-step solutions and visual aids. For example:
- Use an online square root calculator to input 45 and see the step-by-step simplification process.
- Interactive websites like GeoGebra allow you to manipulate visual elements to better understand how square roots are simplified.
Manipulatives
Physical manipulatives, such as algebra tiles, can be used in classrooms or at home to provide a hands-on approach to simplifying square roots:
- Use tiles to represent the number 45.
- Group the tiles into a square representing the largest perfect square factor (9) and another group representing the remaining factor (5).
- This tangible method helps reinforce the concept that √45 simplifies to 3√5.
Digital Math Escape Rooms
For a more engaging approach, digital math escape rooms challenge students to simplify square roots and solve puzzles to unlock the next level. These activities provide instant feedback and keep learners motivated.
Using these visual and interactive methods, students can gain a deeper understanding of the process and reasoning behind simplifying square roots, making it easier to apply the concepts to other problems.
Practical Applications
The process of simplifying square roots, such as the square root of 45, is not just a mathematical exercise but has several practical applications across various fields. Here are some examples of how simplified square roots are used in real-world scenarios:
-
Architecture and Construction
In architecture and construction, accurate measurements are crucial. The square root of areas and lengths is often needed to determine the dimensions of a square or rectangular space. For instance, if you need to determine the length of a side of a square area with 45 square feet, you can simplify the square root of 45 to approximate this dimension.
-
Physics and Engineering
Square roots are frequently used in physics and engineering to solve problems involving areas, distances, and quadratic equations. For example, when calculating the time it takes for an object to fall to the ground, the square root of the height divided by a constant is used:
\[ t = \frac{\sqrt{h}}{4} \]
If an object is dropped from a height of 45 feet, simplifying \(\sqrt{45}\) helps in quickly estimating the fall time.
-
Finance
In finance, the concept of volatility often involves calculating the standard deviation, which requires the square root function. For instance, to assess the risk of an investment, one might need to simplify the square root of the variance of returns to determine the standard deviation.
-
Accident Investigations
Police officers use square roots to calculate the speed of a vehicle based on the length of skid marks left during an accident. The formula typically involves the square root of the product of a constant and the length of the skid marks:
\[ v = \sqrt{24d} \]
Here, \( d \) is the length of the skid marks, and simplifying square roots enables investigators to quickly determine the vehicle's speed before braking.
These practical applications illustrate the importance of understanding and being able to simplify square roots efficiently, as they form a foundational skill necessary for various professional fields and everyday problem-solving.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some common questions and answers related to simplifying the square root of 45:
-
What is the simplified form of \(\sqrt{45}\)?
The simplified form of \(\sqrt{45}\) is \(3\sqrt{5}\). This is obtained by finding the prime factors of 45, which are \(3 \times 3 \times 5\), and then simplifying to \(3\sqrt{5}\).
-
How do you simplify square roots in general?
To simplify a square root, you should:
- Find the prime factorization of the number inside the square root.
- Group the prime factors into pairs.
- Move one factor from each pair outside the square root.
- Multiply the factors outside the square root together.
For example, for \(\sqrt{180}\):
\[
180 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5 \quad \Rightarrow \quad \sqrt{180} = 2 \times 3 \sqrt{5} = 6\sqrt{5}
\]
-
Can square roots of non-perfect squares be simplified?Yes, square roots of non-perfect squares can be simplified by finding and extracting the square factors. For instance, \(\sqrt{72}\) can be simplified to \(6\sqrt{2}\) because \(72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\) which simplifies to \(2 \times 3 \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2}\).
-
Why is simplifying square roots useful?
Simplifying square roots is useful in mathematics because it makes calculations easier and results more manageable. It is particularly helpful in algebra, geometry, and higher-level math where simpler forms are required for further operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the process of simplifying the square root of 45 demonstrates fundamental concepts in mathematics such as prime factorization and the nature of irrational numbers. By breaking down 45 into its prime factors, we simplified √45 to its simplest radical form, \(3\sqrt{5}\), highlighting the importance of identifying perfect squares in the factorization process.
Furthermore, understanding the properties of irrational numbers enriches our comprehension of number theory. Since \( \sqrt{45} \) cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, it is classified as an irrational number, possessing a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion, approximately 6.708.
The methods discussed, including prime factorization and the long division method, provide valuable tools for simplifying and approximating square roots. Whether through manual calculation or using technological aids like calculators, mastering these techniques enhances mathematical proficiency and problem-solving skills.
Ultimately, simplifying square roots is not just an exercise in arithmetic but a deeper exploration of mathematical principles that underlie much of algebra and number theory. By continually practicing these methods, students and enthusiasts can develop a stronger foundation in mathematics and apply these skills to more complex problems and real-world scenarios.
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 45. Tìm hiểu phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và cách sử dụng để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 45: sqrt(45)
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 45. Tìm hiểu phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và cách áp dụng để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 45