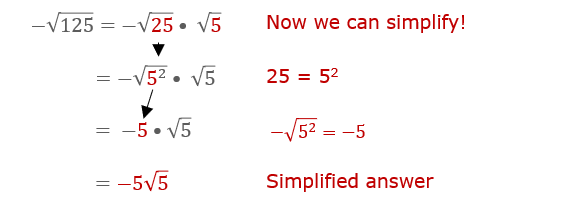Topic square root radical calculator: Discover how to effortlessly simplify complex square roots with the Square Root Radical Calculator. This powerful tool not only saves time but also enhances your mathematical understanding. Learn step-by-step methods, explore examples, and unlock the full potential of radical expressions in no time.
Table of Content
- Square Root Radical Calculator
- Introduction
- What is a Square Root Radical Calculator?
- Step-by-Step Guide to Simplifying Square Roots
- Understanding Radical Expressions
- Prime Factorization Method
- Perfect Square Method
- Applications of Square Root Radical Calculators
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Advanced Features and Tools
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz để đơn giản hóa các biểu thức căn bậc hai trong đại số. Học cách sử dụng máy tính để tính toán và đơn giản hóa các căn bậc hai nhanh chóng và chính xác.
Square Root Radical Calculator
A square root radical calculator is a useful tool for simplifying and calculating square roots of numbers. It helps in converting the square root of a number into its simplest radical form. Below are the key features and steps involved in using a square root radical calculator.
Features of a Square Root Radical Calculator
- Calculates square roots of both perfect and non-perfect squares.
- Converts square roots into simplest radical form.
- Provides step-by-step solutions for better understanding.
- Supports both integers and decimal numbers.
How to Use a Square Root Radical Calculator
- Enter the number for which you need to find the square root.
- Click on the "Calculate" button.
- The calculator will display the square root in its simplest radical form.
- It may also show the decimal approximation of the square root.
Example Calculations
Here are a few examples to illustrate how the calculator works:
- For \( \sqrt{28} \):
The prime factorization of 28 is \( 2^2 \times 7 \). Thus,
\[ \sqrt{28} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7} = 2\sqrt{7} \]
- For \( \sqrt{75} \):
The prime factorization of 75 is \( 3 \times 5^2 \). Thus,
\[ \sqrt{75} = \sqrt{3 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{3} \]
- For \( \sqrt{40} \):
The prime factorization of 40 is \( 2^3 \times 5 \). Thus,
\[ \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 5} = 2\sqrt{10} \]
Benefits of Using a Square Root Radical Calculator
- Saves time and reduces calculation errors.
- Helps in understanding the process of simplifying square roots.
- Provides accurate results quickly.

READ MORE:
Introduction
A Square Root Radical Calculator is a powerful tool designed to simplify and compute square roots efficiently. It provides instant results for mathematical expressions involving square roots, making it invaluable for students, educators, and professionals alike.
By utilizing advanced algorithms, these calculators can handle complex square root calculations accurately, saving time and effort in manual computations. Whether you're dealing with basic arithmetic or intricate mathematical problems, a Square Root Radical Calculator offers convenience and precision.
This tool is particularly beneficial in educational settings, allowing users to verify their work quickly and explore various approaches to solving square root equations. It promotes a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts by demonstrating the relationship between numbers and their roots.
Moreover, a Square Root Radical Calculator supports a wide range of applications, from everyday calculations to specialized fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. Its versatility and user-friendly interface make it a must-have for anyone dealing with numerical analysis or problem-solving involving square roots.
What is a Square Root Radical Calculator?
A Square Root Radical Calculator is a specialized tool used to compute square roots of numbers efficiently and accurately. It employs mathematical algorithms to simplify complex square root expressions, providing instant solutions for both basic and advanced calculations.
These calculators are equipped with user-friendly interfaces that allow users to input numbers or equations containing square roots directly. They facilitate quick verification of square root computations, making them indispensable for students, educators, and professionals in various fields.
By utilizing such a calculator, users can explore different methods of solving square root problems, enhancing their understanding of mathematical concepts. This tool is invaluable for anyone needing precise results in areas such as mathematics, science, engineering, and finance.
Additionally, Square Root Radical Calculators often include features like step-by-step solutions, graphical representations, and the ability to handle complex functions involving square roots, ensuring versatility in solving a wide range of mathematical challenges.
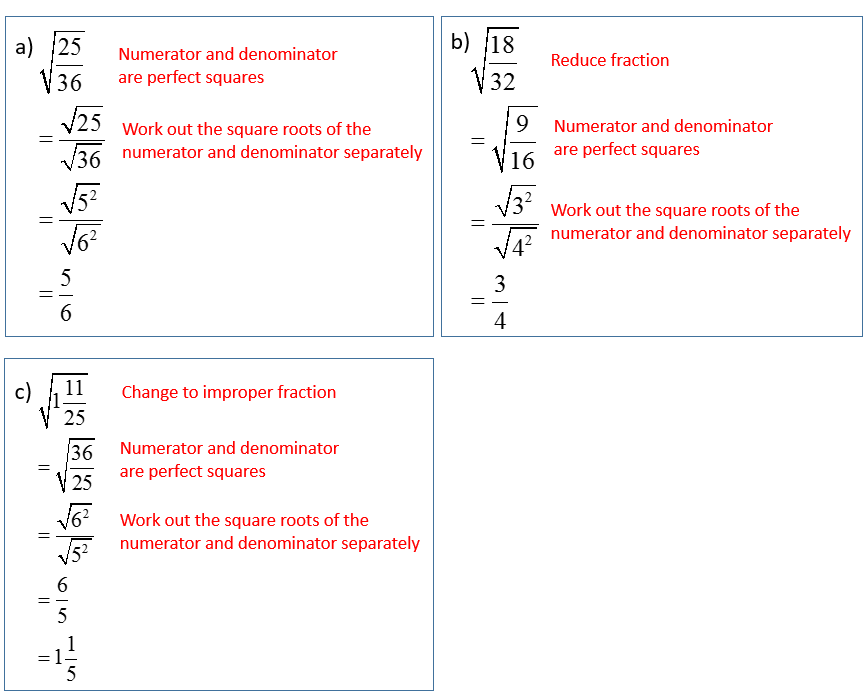
Step-by-Step Guide to Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down the number under the radical sign into its prime factors and then simplifying those factors to get the square root. Here is a step-by-step guide:
-
Prime Factorization
Start by finding the prime factorization of the number under the square root.
- Example: To simplify \( \sqrt{200} \), find the prime factors of 200.
- 200 can be factored into \( 2 \times 100 \), then \( 2 \times 2 \times 50 \), and finally \( 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 25 \).
- The prime factorization of 200 is \( 2^3 \times 5^2 \).
-
Group the Factors
Group the prime factors into pairs of equal factors.
- From the prime factorization \( 2^3 \times 5^2 \), we can group the factors as \( (2^2) \times (2 \times 5^2) \).
- Write the groups as products of squares: \( (2^2) \times (2 \times 5^2) = 2^2 \times 5^2 \times 2 \).
-
Apply the Square Root
Apply the square root to each group of prime factors.
- \( \sqrt{2^2 \times 5^2 \times 2} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{5^2} \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Simplify the square roots of the perfect squares: \( \sqrt{2^2} = 2 \) and \( \sqrt{5^2} = 5 \).
- This results in \( 2 \times 5 \times \sqrt{2} = 10 \sqrt{2} \).
Thus, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{200} \) is \( 10 \sqrt{2} \).
Additional Examples
| Expression | Prime Factorization | Simplified Form |
|---|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{75} \) | 75 = \( 3 \times 5^2 \) | \( 5 \sqrt{3} \) |
| \( \sqrt{50} \) | 50 = \( 2 \times 5^2 \) | \( 5 \sqrt{2} \) |
Following these steps, you can simplify any square root radical expression. Practice with different numbers to become more familiar with the process.
Understanding Radical Expressions
Radical expressions involve roots, such as square roots, cube roots, and so on. These expressions are fundamental in algebra and have several important properties and rules. Let's delve into the basics of radical expressions.
Properties of Radicals
- Product Property: For any nonnegative numbers \(a\) and \(b\): \[ \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a \cdot b} \]
- Quotient Property: For any nonnegative numbers \(a\) and \(b\) (with \(b \neq 0\)): \[ \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} = \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} \]
Simplifying Radical Expressions
To simplify a radical expression, we factor the number inside the radical and take out any factors that are perfect squares. For example:
\( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \cdot 2} = \sqrt{25} \cdot \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
Here are the steps to simplify a square root:
- Factor the number inside the radical into its prime factors.
- Group the factors into pairs of the same number.
- Move one number from each pair outside the radical.
Examples
Let's look at some examples:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{72} \): \[ \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{36 \cdot 2} = \sqrt{36} \cdot \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2} \]
- Simplify \( \sqrt{98} \): \[ \sqrt{98} = \sqrt{49 \cdot 2} = \sqrt{49} \cdot \sqrt{2} = 7\sqrt{2} \]
Combining Radical Expressions
Radical expressions can be combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, similar to polynomial expressions. However, they need to be in their simplest form to combine them properly.
For example:
- Addition: \( 2\sqrt{3} + 4\sqrt{3} = 6\sqrt{3} \)
- Multiplication: \( \sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{16} = 4 \)
Rationalizing the Denominator
Sometimes, it's necessary to eliminate radicals from the denominator of a fraction. This process is called rationalizing the denominator. For example:
\( \frac{3}{\sqrt{2}} \) can be rationalized by multiplying the numerator and the denominator by \( \sqrt{2} \):
\[ \frac{3}{\sqrt{2}} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{3\sqrt{2}}{2} \]
Understanding and manipulating radical expressions are essential skills in algebra, providing a foundation for more advanced mathematics.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a straightforward way to simplify square roots by breaking down the number into its prime factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the prime factorization method:
-
Find the Prime Factors: Begin by finding the prime factors of the number whose square root you want to simplify. A prime factor is a factor that is a prime number.
-
Group the Prime Factors: Group the prime factors into pairs of the same numbers. Each pair represents a perfect square.
-
Take One Factor from Each Pair: From each pair, take one factor out. The product of these factors will be the simplified form of the square root.
-
Multiply the Factors: Multiply the factors obtained from each pair to get the simplified square root.
Here’s an example to illustrate the process:
Let’s simplify the square root of 144 using the prime factorization method:
First, find the prime factors of 144:
\(144 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\)
Next, group the prime factors into pairs:
\(144 = (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3)\)
Take one factor from each pair:
\(\sqrt{144} = 2 \times 2 \times 3\)
Finally, multiply the factors:
\(\sqrt{144} = 12\)
So, the simplified form of the square root of 144 is 12.
This method works well for perfect squares, where each prime factor can be paired. For non-perfect squares, the remaining prime factors that cannot be paired remain under the square root sign.
Perfect Square Method
The Perfect Square Method is a straightforward approach to simplifying square roots by identifying and utilizing perfect squares. Here is a step-by-step guide to this method:
-
Identify Perfect Squares:
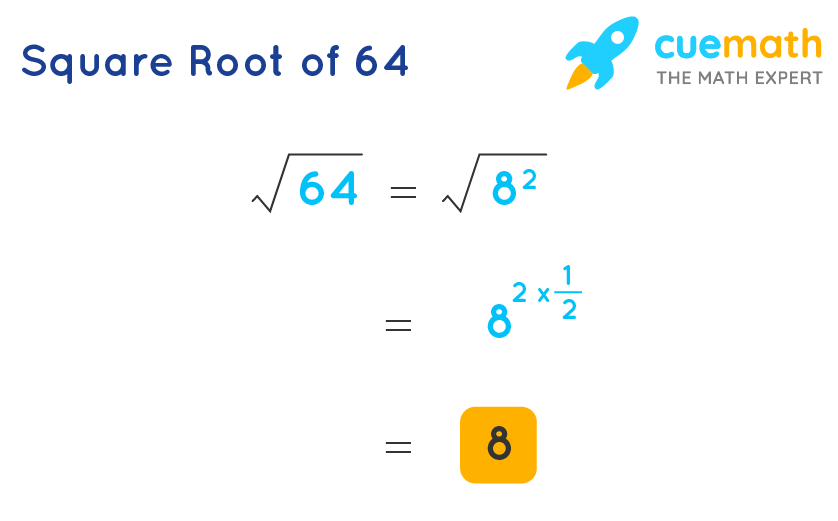
Perfect squares are numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, etc. These are numbers that can be expressed as the square of an integer (e.g., \(4 = 2^2\), \(9 = 3^2\), \(16 = 4^2\), etc.).
-
Factor the Radicand:
Break down the number under the square root (radicand) into its prime factors. For example, to simplify \(\sqrt{72}\), we factor 72 into prime factors: \(72 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3\).
-
Group the Factors:
Group the prime factors into pairs of identical factors. Each pair will represent a perfect square. In our example, \(72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 = (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 2\).
-
Move the Perfect Squares Outside the Radical:
For each pair of identical factors, move one factor outside the square root. Continuing with our example, \(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \times 2} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2}\).
-
Simplify the Expression:
Combine the factors outside the radical and leave the remaining factors inside. The final simplified form of \(\sqrt{72}\) is \(6\sqrt{2}\).
Using this method makes it easy to simplify square roots by systematically breaking down the radicand into its prime factors and identifying perfect squares. Below are some additional examples:
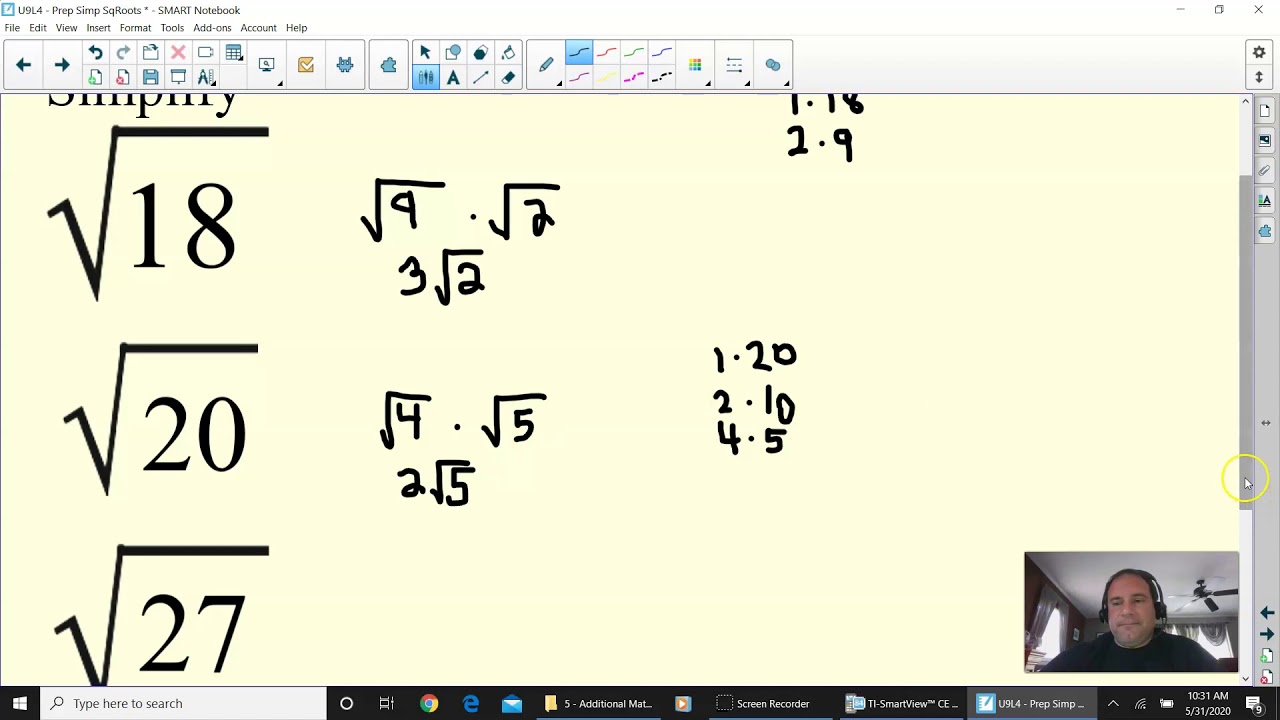
- \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{(5 \times 5) \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
- \(\sqrt{18} = \sqrt{(3 \times 3) \times 2} = 3\sqrt{2}\)
- \(\sqrt{45} = \sqrt{(3 \times 3) \times 5} = 3\sqrt{5}\)
Mastering the Perfect Square Method will enhance your ability to simplify square roots efficiently and accurately, which is particularly useful in various mathematical applications.
Applications of Square Root Radical Calculators
Square root radical calculators are valuable tools across various fields due to their ability to simplify and calculate roots accurately. Here are some key applications:
- Mathematics Education: These calculators help students understand and simplify radical expressions, perform operations with radicals, and solve equations involving square roots. They are particularly useful in algebra and geometry classes.
- Engineering: Engineers use square root calculators to determine stress and strain in materials, solve for dimensions in design problems, and perform electrical circuit analysis, including calculating root mean square (RMS) values.
- Physics: In physics, square root calculators assist in solving problems related to wave mechanics, quantum physics, and other areas where square root functions appear frequently. For example, calculating the speed of sound in various media often involves square roots.
- Chemistry: Chemists use square root calculators to solve equations involving reaction rates and concentrations. These calculations are essential for understanding reaction kinetics and equilibrium.
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and builders use these calculators to determine the lengths of diagonals, areas, and other dimensions necessary for creating accurate building plans. They are also used in calculating slopes and angles for cutting materials.
- Finance: In finance, square root calculators are used to compute standard deviations and variances in statistical analyses, which are essential for risk assessment and portfolio management.
Step-by-Step Guide to Simplifying Square Roots Using a Calculator
- Enter the radical expression into the calculator.
- Identify if the number under the radical has any perfect square factors.
- If perfect square factors exist, rewrite the expression as the product of the perfect square and another number.
- Take the square root of the perfect square factor outside the radical.
- Multiply the result by the remaining radical to simplify the expression.
Example Calculations
Let's look at some examples:
- Simplifying √45:
- Identify perfect square factors: 45 = 9 × 5
- Rewrite as √(9 × 5) = √9 × √5 = 3√5
- Simplifying √72:
- Identify perfect square factors: 72 = 36 × 2
- Rewrite as √(36 × 2) = √36 × √2 = 6√2
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When using a square root radical calculator, there are several common mistakes that users should be aware of and avoid to ensure accurate calculations. Here are some of the most frequent errors and how to prevent them:
- Misinterpreting the Radical Symbol: Always ensure that you correctly identify and enter the radical symbol (√) when inputting your numbers. Incorrect use can lead to inaccurate results.
- Ignoring Negative Solutions: When solving equations involving square roots, remember that there are both positive and negative solutions. For instance, both \( x = 3 \) and \( x = -3 \) are solutions to \( x^2 = 9 \).
- Forgetting to Simplify Radicals: Always simplify the radical expressions to their simplest form. For example, \( \sqrt{72} \) should be simplified to \( 6\sqrt{2} \).
- Incorrectly Entering Numbers: Double-check your entries for any typos or misplaced decimal points. Incorrect input can drastically alter your results.
- Misunderstanding Calculator Functions: Ensure you understand how to use the square root function on your calculator. Different calculators might have different methods or buttons for calculating square roots.
- Ignoring Calculator Limitations: Be aware that some calculators might not handle very large numbers or complex radicals accurately. Verify with manual calculations if necessary.
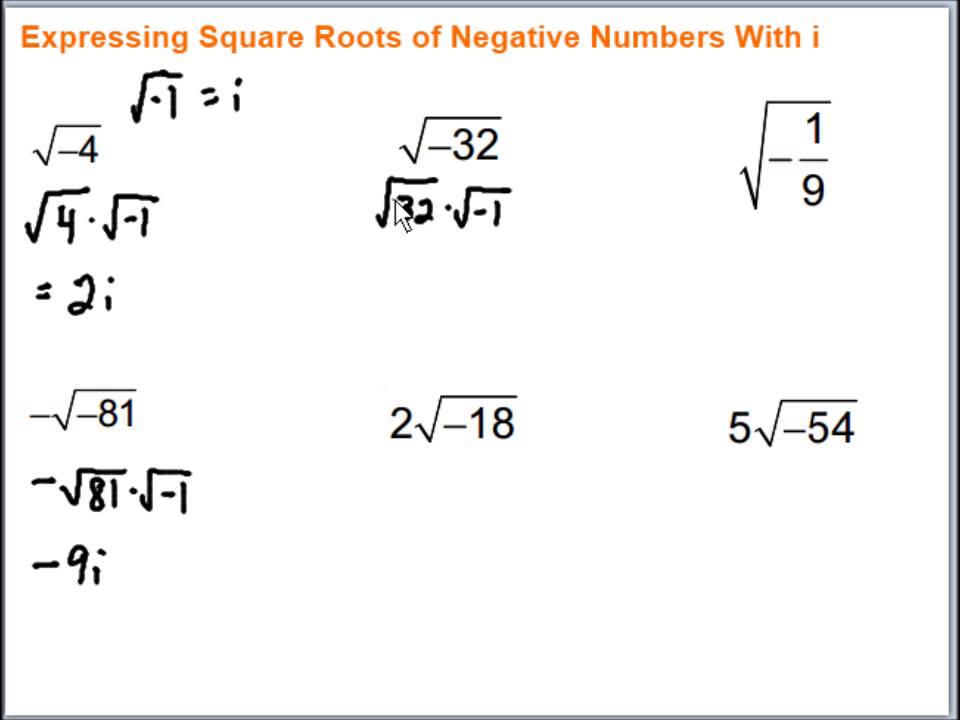
- Incorrectly Handling Complex Numbers: When dealing with negative numbers under the square root (e.g., \( \sqrt{-1} \)), remember that these involve imaginary numbers (i.e., \( \sqrt{-1} = i \)).
- Misinterpreting Error Messages: Pay attention to any error messages your calculator might display. These messages often indicate input errors or unsupported operations.
- Assuming Perfect Square Results: Not all numbers are perfect squares. If your calculator gives a decimal result, it may be due to the number not being a perfect square. Always check if the result can be simplified.
- Forgetting Units in Applied Problems: In real-world applications, always include the appropriate units with your answers to avoid confusion, especially in fields like physics or engineering.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure more accurate and reliable results when using a square root radical calculator.

Advanced Features and Tools
Advanced square root radical calculators offer a range of powerful features designed to enhance user experience and functionality:
- Decimal Approximations: Provides decimal approximations for square roots of non-perfect squares.
- Fractional Exponents: Supports calculations involving fractional exponents, allowing for precise results.
- Variable Calculations: Enables computation of square roots involving variables and algebraic expressions.
- Complex Numbers: Capable of handling square roots of negative numbers, outputting results in complex number format.
- History and Memory: Keeps a history of calculations and allows users to store results for future reference.
- Graphical Representations: Visualizes square roots and related calculations on graphs or charts.
- Multi-Functionality: Integrates with other mathematical functions such as logarithms and trigonometric calculations.
- Customization: Offers customization options for interface layout, themes, and preferred output formats.
- Educational Tools: Includes educational resources such as step-by-step guides and example problems for learning purposes.
These advanced features make square root radical calculators invaluable tools for students, professionals, and anyone needing accurate and efficient square root calculations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is a square root radical calculator?
A square root radical calculator is a tool used to compute the square root of a given number or expression. It simplifies the process of finding square roots, especially for complex or large numbers.
-
How accurate are square root radical calculators?
Square root radical calculators are highly accurate, providing precise results for both perfect squares and non-perfect squares. They utilize algorithms that ensure accurate computation within specified decimal places or exact values.
-
Can square root radical calculators handle complex numbers?
Yes, advanced square root radical calculators can handle complex numbers, including square roots of negative numbers. They output results in standard complex number notation, aiding in both theoretical and applied mathematical calculations.
-
Are square root radical calculators useful for educational purposes?
Absolutely. Square root radical calculators are valuable educational tools, assisting students in learning and understanding square roots, radical expressions, and mathematical operations involving square roots. They often include educational resources such as examples and step-by-step guides.
-
What are some common features of square root radical calculators?
Common features include decimal approximations, fractional exponent calculations, support for variables and algebraic expressions, memory functions, graphical representations, and integration with other mathematical functions like logarithms and trigonometry.
-
Can square root radical calculators be used for professional applications?
Yes, square root radical calculators are widely used in various professional fields such as engineering, physics, finance, and computer science. They facilitate quick and accurate calculations essential for these disciplines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, square root radical calculators are indispensable tools for anyone needing to compute square roots quickly and accurately. Whether you are a student learning about radical expressions or a professional requiring precise mathematical calculations, these calculators offer a range of features that simplify complex operations.
From handling perfect squares to managing non-perfect squares and even complex numbers, square root radical calculators provide results with high precision. They enhance learning experiences with educational resources and step-by-step guides, making mathematical concepts more accessible.
Moreover, the versatility of these calculators extends to various fields including engineering, physics, finance, and computer science, where precise calculations are crucial. Their user-friendly interfaces and advanced functionalities make them ideal tools for both educational and professional applications.
Overall, square root radical calculators not only streamline mathematical computations but also contribute to a deeper understanding of square roots and related mathematical concepts.
Xem video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz để đơn giản hóa các biểu thức căn bậc hai trong đại số. Học cách sử dụng máy tính để tính toán và đơn giản hóa các căn bậc hai nhanh chóng và chính xác.
Hướng dẫn sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz - Đại số 4-1 Đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai
READ MORE:
Xem video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính TI 84 Plus CE để đơn giản hóa các biểu thức căn bậc hai và các căn bậc khác. Học cách sử dụng máy tính để tính toán và đơn giản hóa các căn bậc hai nhanh chóng và chính xác.
Hướng dẫn sử dụng TI 84 Plus CE - Đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai và các căn bậc khác