Topic square root of 5 squared: The square root of 5 squared is a mathematical concept that simplifies to 5. This result is derived from the fact that squaring a number and then taking the square root returns the original number. Understanding this concept helps in various areas of mathematics and science. Explore the significance and applications of this fundamental principle in our detailed guide.
Table of Content
Understanding the Square Root of 5 Squared
The mathematical expression for the square root of 5 squared is:
\[
\sqrt{5^2}
\]
Using properties of square roots and exponents, we can simplify this as follows:
\[
\sqrt{5^2} = \sqrt{25} = 5
\]
Mathematical Explanation
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Square of 5: When you square the number 5, you multiply it by itself: \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \).
- Square Root of a Number: The square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). For example, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \).
- Combining These Concepts: Thus, the square root of 5 squared is \( \sqrt{5^2} = 5 \).
Geometrical Context
In geometry, the square root of 5 has significance:
- It represents the length of the diagonal of a rectangle with sides 1 and 2, according to the Pythagorean theorem.
- It is also related to the golden ratio, appearing in various geometrical constructions.
Interesting Facts
Here are some additional interesting points:
- The square root of 5 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
- Its approximate value is \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236067977 \).
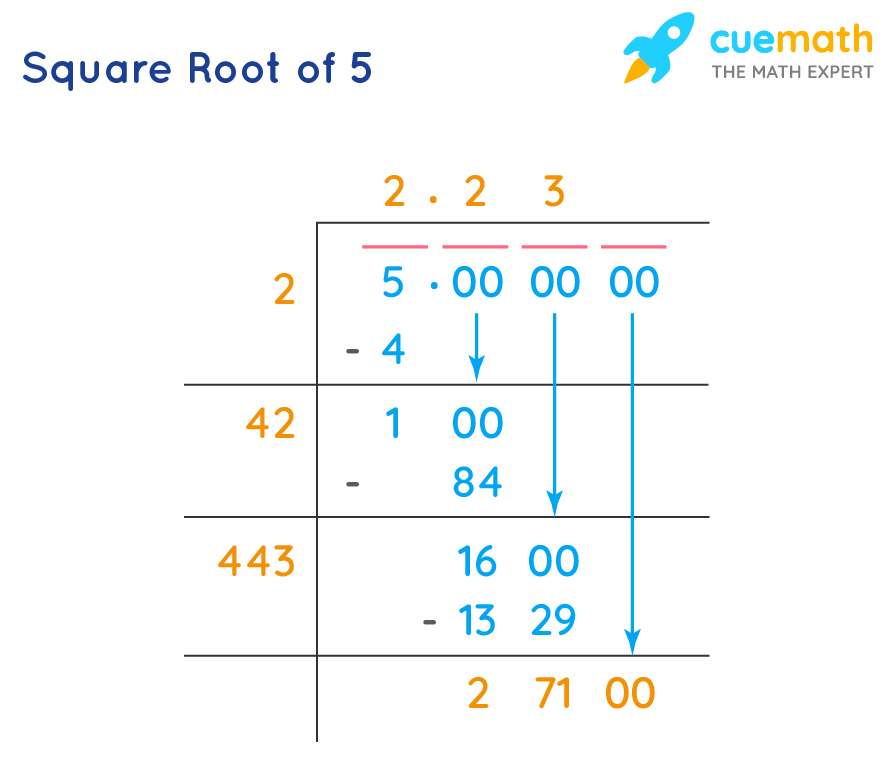
Calculation Methods
There are several methods to calculate the square root of a number:
- Long Division Method: A step-by-step approach to find the square root.
- Using a Calculator: Most scientific calculators have a square root function.
Application in Trigonometry and Algebra
The square root of 5 appears in formulas involving exact trigonometric constants and in various algebraic contexts.
Common Misunderstandings
It's important not to confuse the square root of a squared number with the original number. For instance:
\[
\sqrt{5^2} = 5 \quad \text{but} \quad (\sqrt{5})^2 = 5
\]

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
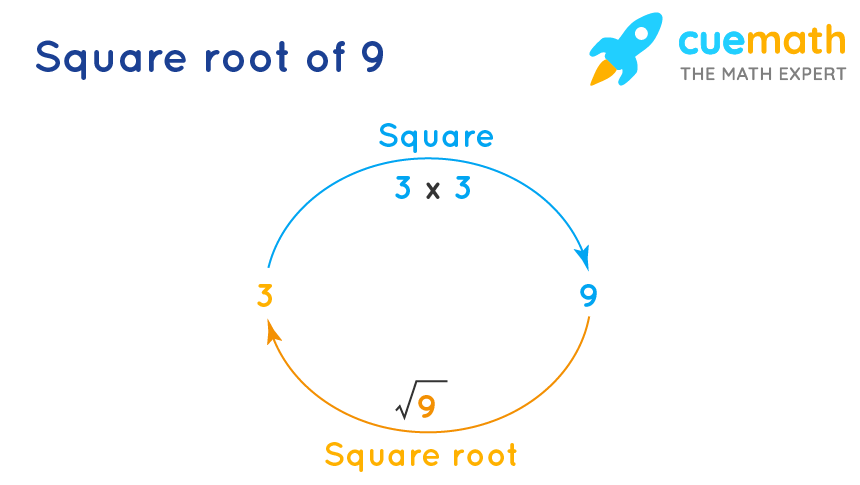
A square root is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The symbol for the square root is √. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because 3 × 3 = 9. Square roots are fundamental in various branches of mathematics and have numerous applications in science and engineering.
Square roots can be categorized into two types: perfect squares and non-perfect squares. Perfect squares are numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25, whose square roots are integers. Non-perfect squares, such as 2, 3, 5, and 7, have irrational square roots, which means their decimal expansions are non-repeating and non-terminating.
Understanding square roots involves a few key concepts:
- Radical Sign: The √ symbol is called a radical sign, used to denote the square root.
- Principal Square Root: The positive square root of a number is known as the principal square root. For example, √25 = 5.
- Negative Square Root: Every positive number also has a negative square root. For instance, the square roots of 25 are 5 and -5.
To find the square root of a number, one can use methods such as prime factorization, the long division method, or a calculator for quick results. For example, the square root of 5, which is an irrational number, can be approximated as 2.236.
In mathematical notation, the square root of 5 is expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{5} \approx 2.236
\]
Square roots play a crucial role in solving quadratic equations, understanding geometric shapes, and analyzing functions in calculus. They also have practical applications in physics, engineering, computer science, and various fields where measurements and calculations are required.
Definition and Properties
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 5 squared is an interesting topic in mathematics, particularly in understanding the properties and applications of square roots.
- Basic Definition: The square root of a number \( x \) is written as \( \sqrt{x} \). For example, the square root of 25 is 5 because \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \).
- Square Root Symbol: The symbol for the square root is \( \sqrt{} \), known as the radical symbol. It represents the principal square root, which is always non-negative.
- Properties of Square Roots:
- Non-Negative Numbers: The square root of any non-negative number is also non-negative.
- Negative Numbers: The square root of a negative number is not a real number but an imaginary number.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because their square roots are whole numbers.
- Product Property: \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \).
- Quotient Property: \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \), for \( b \neq 0 \).
In algebra, square roots play a crucial role in solving quadratic equations and in various applications in geometry, such as finding the lengths of sides in right triangles. Understanding the properties and behaviors of square roots helps in simplifying complex mathematical expressions and in performing accurate calculations in different fields of science and engineering.
Examples and Applications
Understanding the square root of a number, such as the square root of 5 squared, is fundamental in various mathematical applications and real-life scenarios. Here are some detailed examples and applications:
- Mathematics and Geometry:
In mathematics, the concept of square roots is essential for solving quadratic equations, finding side lengths of squares, and determining the length of the hypotenuse in right triangles using the Pythagorean theorem. For instance, the square root of 25 is 5 because 5 * 5 = 25.
- Statistics:
Square roots are used in statistics to calculate standard deviation, which is the square root of the variance. This measurement helps to understand how data points are spread out from the mean in a data set.
- Finance:
In finance, square roots are used to calculate stock market volatility, which involves taking the square root of the variance of stock returns. This helps investors assess the risk associated with different investments.
- Science:
Square roots are used in various scientific calculations, such as determining the velocity of moving objects, measuring radiation absorption, and calculating sound wave intensity. These calculations are crucial in fields like physics and engineering.
- Engineering:
In engineering, squaring is used to find the natural frequency of structures like bridges and buildings. This helps predict how structures will react to different loads and vibrations.
- Computer Science:
In computer science, squares and square roots are used in algorithms for encryption, image processing, and game physics. For example, calculating the distance between two points on a plane often involves the square root of the sum of the squares of the coordinates.
- Navigation:
Square roots are used in navigation to compute distances between points on a map or globe, helping pilots and navigators determine the shortest path and direction.
These examples illustrate the wide range of applications and the importance of understanding square roots in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Special Cases
Understanding the special cases of square roots and their properties is crucial in simplifying complex mathematical expressions. Here, we explore various scenarios where special properties of squares and square roots come into play, including perfect square trinomials and the difference of squares.
- Perfect Square Trinomials: A trinomial of the form \(a^2 + 2ab + b^2\) can be factored into \((a + b)^2\). Similarly, \(a^2 - 2ab + b^2\) can be factored into \((a - b)^2\). These are known as perfect square trinomials. For example, \(x^2 + 6x + 9\) factors to \((x + 3)^2\).
- Difference of Squares: Any expression of the form \(a^2 - b^2\) can be factored into \((a + b)(a - b)\). This is particularly useful in simplifying polynomial expressions. For instance, \(x^2 - 25\) can be rewritten as \((x + 5)(x - 5)\).
- Complex Numbers and Non-Real Roots: When dealing with negative numbers under the square root, we encounter complex numbers. For example, the square root of -1 is denoted as \(i\), the imaginary unit. Therefore, expressions involving square roots of negative numbers can be simplified using properties of \(i\).
- Applications in Geometry: The properties of squares and square roots are widely used in geometry, particularly in calculating distances and areas. The Pythagorean theorem, \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), is a prime example where square roots are essential in finding the lengths of sides of right triangles.
These special cases form the foundation of many algebraic manipulations and are essential tools for solving a wide range of mathematical problems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the square root of 5 squared?
The square root of 5 squared is 5. This is because squaring and then taking the square root of a number are inverse operations that cancel each other out: \( \sqrt{5^2} = 5 \).
-
Why is the square root of a squared number the original number?
When you square a number, you multiply it by itself. Taking the square root of a squared number reverses this multiplication. For any positive number \( x \), \( \sqrt{x^2} = x \). This property holds because squaring and square rooting are inverse functions.
-
Can the square root of 5 squared be negative?
No, the square root function typically returns the principal (non-negative) root. Therefore, \( \sqrt{5^2} = 5 \) and not -5. However, it's true that both 5 and -5 are solutions to the equation \( x^2 = 25 \), but the principal square root is positive.
-
How do you calculate the square root of 5 squared manually?
First, calculate 5 squared, which is \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \). Then, find the square root of 25. Since 25 is a perfect square, its square root is 5. Hence, \( \sqrt{5^2} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \).
-
Is there a difference between the square root of 5 squared and the absolute value of 5?
No, for positive numbers like 5, \( \sqrt{5^2} \) and \( |5| \) (the absolute value of 5) both equal 5. The absolute value function returns the non-negative value of a number, which is the same result given by the square root of a squared positive number.
-
What is the principal square root?
The principal square root is the non-negative root of a number. For any positive number \( x \), the principal square root of \( x \) is \( \sqrt{x} \). For example, the principal square root of 25 is 5.
Conclusion
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, with applications spanning various fields including algebra, geometry, and real-world problem-solving. Specifically, the square root of 5 is an intriguing example due to its properties and implications.
Here are the key takeaways:
- The square root of 5 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 2.236.
- It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has an infinite decimal expansion.
- Geometrically, √5 can be represented as the diagonal of a rectangle with side lengths of 1 and 2, according to the Pythagorean theorem.
- In algebra, the square root of 5 often appears in solving quadratic equations and other algebraic expressions.
- From a numerical perspective, √5 can be calculated using various methods, including approximation techniques and the use of calculators.
Understanding the square root of 5 and its properties provides a deeper insight into the nature of numbers and their relationships. This knowledge not only enhances mathematical comprehension but also equips one with the tools to tackle more complex mathematical problems and applications.
Video giải thích tại sao căn bậc hai của 5 bình phương bằng 5, hấp dẫn và dễ hiểu cho người xem.
Căn bậc hai của 5 bình phương bằng 5
READ MORE:
Video giải thích căn bậc hai là gì, được trình bày bởi thầy J, giúp người xem hiểu rõ khái niệm toán học quan trọng này.
Căn Bậc Hai Là Gì? | Toán Học với Thầy J