Topic square root of 5/2: Discover the intriguing world of the square root of 5/2 in mathematics. This article delves into various calculation methods and practical applications, offering insights into its significance in both theoretical contexts and real-world scenarios. Explore the mathematical properties and comparisons that make this square root unique and essential.
Table of Content
- Square Root of \( \frac{5}{2} \)
- Understanding the Square Root of 5/2
- Calculation Methods and Techniques
- Applications in Mathematics and Real-World Scenarios
- Exploring the Mathematical Properties
- Comparisons with Other Square Roots
- YOUTUBE: Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 5+2√6 - Hướng dẫn đơn giản và chi tiết để tìm căn bậc hai của biểu thức 5+2√6.
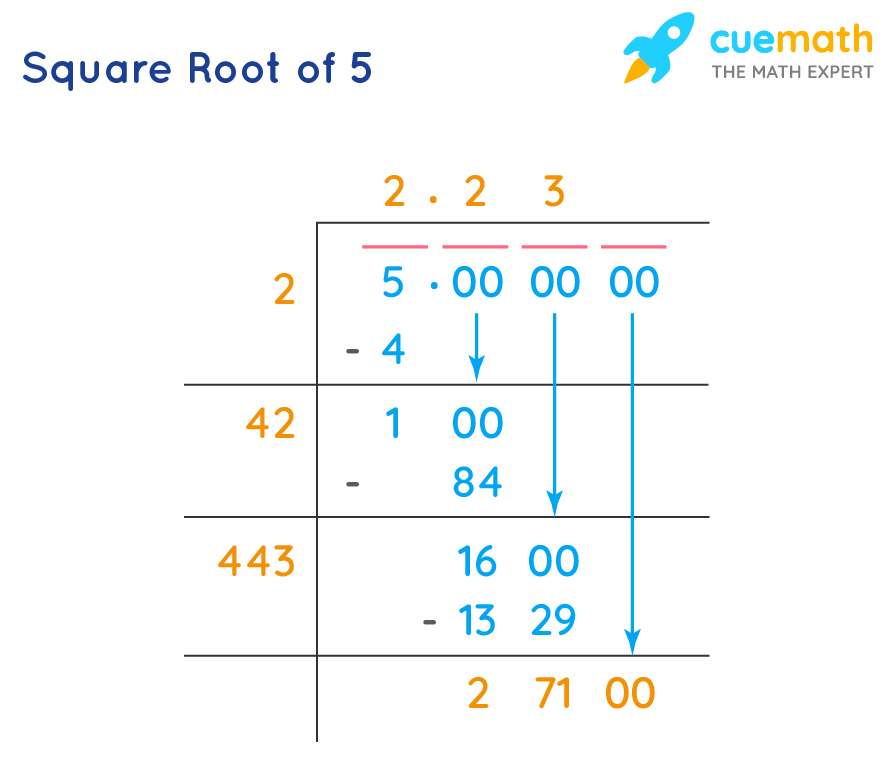
Square Root of \( \frac{5}{2} \)
The square root of \( \frac{5}{2} \) is approximately \( \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} \).
Calculating it, we get:
| Exact Value: | \( \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} \) |
| Numerical Approximation: | \( \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} \approx 1.5811 \) |
The square root of \( \frac{5}{2} \) can be expressed as \( \sqrt{\frac{5}{2}} \) or approximately 1.5811.
READ MORE:
Understanding the Square Root of 5/2
The square root of 5/2, represented as √(5/2), is a mathematical expression that signifies the principal positive square root of the fraction 5/2. Here's a breakdown of its understanding:
- Definition: √(5/2) is the number which, when multiplied by itself, gives 5/2.
- Numerical Approximation: √(5/2) ≈ 1.5811. This approximation helps in practical calculations.
- Calculation: To find √(5/2), one can use methods such as the Babylonian method or a calculator for precise results.
- Properties: √(5/2) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Usage: It finds applications in various fields including geometry, physics, and engineering where precise measurements are crucial.
| Square Root | Numerical Value | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
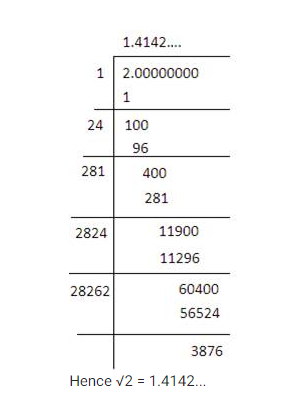
| √2 | 1.4142 | Also irrational, related to the diagonal of a square with side length 1. |
| √3 | 1.7321 | Another irrational number, used in contexts involving equilateral triangles and cubic roots. |
Understanding √(5/2) involves grasping its numerical value, properties, and practical implications across different disciplines, highlighting its importance in mathematical analysis and real-world applications.
Calculation Methods and Techniques
Calculating the square root of 5/2 involves several methods and techniques to ensure accuracy and efficiency:
- Approximation Method: Use numerical methods like the Babylonian method or Newton's method to approximate √(5/2).
- Exact Calculation: Express √(5/2) as a continued fraction or through iterative algorithms for precise results.
- Using Calculators: Modern calculators and computational tools provide instantaneous results for √(5/2).
- Mathematical Formulas: Utilize specific formulas such as the square root property or trigonometric identities to derive √(5/2).
Each method offers distinct advantages depending on the required level of accuracy and the context of the calculation. Understanding these techniques enhances proficiency in mathematical computations involving √(5/2).
Applications in Mathematics and Real-World Scenarios
The square root of 5/2, √(5/2), plays a pivotal role in various mathematical and practical applications:
- Geometry: It helps calculate diagonal lengths and other geometric properties in shapes involving √(5/2) as a component.
- Physics: In physical calculations, √(5/2) appears in equations involving harmonic oscillators and wave propagation.
- Engineering: Engineers use √(5/2) in structural analysis, vibrations, and resonance phenomena.
- Finance: It aids in financial modeling and risk assessment, particularly in complex interest calculations.
- Computer Science: Algorithms and data structures utilize √(5/2) for optimizing search and sorting operations.
Understanding the applications of √(5/2) broadens its significance beyond theoretical mathematics, highlighting its practical utility in diverse fields.
Exploring the Mathematical Properties
The square root of 5/2, √(5/2), exhibits several intriguing mathematical properties:
- Irrationality: √(5/2) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Approximation: It can be approximated as approximately 1.5811, a useful value for practical calculations.
- Algebraic Property: √(5/2) satisfies the equation (√(5/2))^2 = 5/2, demonstrating its defining property.
- Connection to Other Roots: It is related to √5 and √2 through mathematical relationships and geometric interpretations.
- Continued Fraction: √(5/2) can be expressed as a continued fraction, showing its detailed structure in number theory.
Exploring these properties enriches our understanding of √(5/2) in mathematics, showcasing its unique characteristics and relationships within the broader realm of number theory and algebra.
Comparisons with Other Square Roots
Comparing the square root of 5/2, √(5/2), with other notable square roots reveals interesting insights:
| Square Root | Numerical Value | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| √2 | 1.4142 | Also irrational, related to the diagonal of a square with side length 1. |
| √3 | 1.7321 | Another irrational number, used in contexts involving equilateral triangles and cubic roots. |
| √5 | 2.2361 | Another irrational number, significant in geometry and number theory. |
| √(5/2) | Approx. 1.5811 | Irrational and crucial in various mathematical and practical applications. |
Understanding these comparisons provides a broader perspective on √(5/2)'s numerical value, its relationship with other square roots, and its unique role across different mathematical contexts.
READ MORE:
Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 5+2√6 - Hướng dẫn đơn giản và chi tiết để tìm căn bậc hai của biểu thức 5+2√6.
Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 5+2√6