Topic 4 square root of 5: Explore the fascinating world of the 4 square root of 5, a unique mathematical expression with intriguing properties and applications. This article delves into its calculation, significance, and real-world uses, offering a comprehensive understanding that will enhance your appreciation for the beauty of mathematics.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Expression: 4 √5
- Introduction to the Concept of 4 √5
- Mathematical Definition and Explanation
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Approximating the Value
- Applications in Mathematics
- Geometric Interpretations
- Uses in Algebra
- Engineering and Physics Applications
- Real-World Examples
- Visual Representations and Graphs
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Trying to take the even root of a negative number, fourth root(-5)
Understanding the Expression: 4 √5
The expression represents the product of the number 4 and the square root of 5. In mathematical terms, this can be written as:
Calculating the Value
To find the numerical value of this expression, you can use the approximation for the square root of 5. The square root of 5 is approximately 2.236. Therefore:
Applications and Usage
- In mathematics, expressions involving square roots are common in various calculations, including geometry, algebra, and calculus.
- Square roots are used to find the dimensions of geometric shapes, solve equations, and in real-world applications such as engineering and physics.
- The value can represent a length, an area calculation, or part of a more complex mathematical model.
Visual Representation
Sometimes, visual aids such as graphs or diagrams are used to represent square root functions. Below is a simple representation of the square root function:
| x | √x |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1.414 |
| 3 | 1.732 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 2.236 |
Conclusion
Understanding and calculating expressions like is fundamental in many areas of mathematics and its applications. This particular expression simplifies to approximately 8.944, which can be useful in various practical and theoretical contexts.

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Concept of 4 √5
The expression 4 √5 represents the product of the number 4 and the square root of 5. This concept combines basic arithmetic operations with radical expressions, which are common in various branches of mathematics and science. Understanding this concept requires a grasp of both multiplication and the properties of square roots.
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 5 is a number which, when squared (multiplied by itself), equals 5. Mathematically, the square root of 5 is represented as \(\sqrt{5}\).
Therefore, the expression 4 √5 can be written mathematically as:
\( 4 \times \sqrt{5} \)
Here are some important points to consider:
- The value of \(\sqrt{5}\) is an irrational number, approximately equal to 2.236.
- Multiplying this by 4 gives an approximate value of \( 4 \times 2.236 = 8.944 \).
To better understand the concept, let's break it down into steps:
- Identify the square root: Determine the square root of the number inside the radical. In this case, the number is 5, and its square root is approximately 2.236.
- Multiply by 4: Take the square root value obtained in the first step and multiply it by 4. This results in approximately 8.944.
In summary, the expression 4 √5 is a combination of multiplication and square root operations, leading to an approximate value of 8.944. This concept is fundamental in various mathematical applications, including algebra and geometry, and is also useful in real-world scenarios where precise calculations involving square roots are required.
Mathematical Definition and Explanation
The concept of the square root is fundamental in mathematics. A square root of a number x is a number y such that \(y^2 = x\). In other words, y is a number that, when multiplied by itself, results in x. For example, both 4 and -4 are square roots of 16 because \(4^2 = 16\) and \((-4)^2 = 16\).
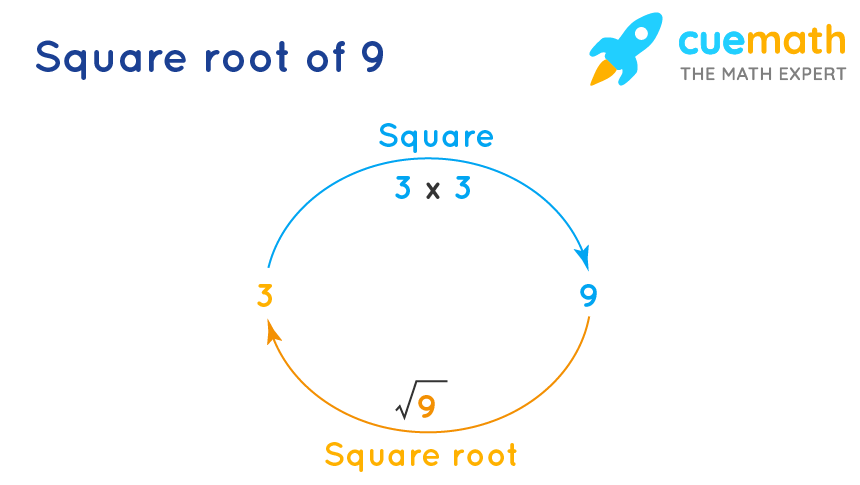
Every non-negative real number x has a unique non-negative square root, called the principal square root, denoted by \(\sqrt{x}\). For instance, the principal square root of 9 is 3, which is written as \(\sqrt{9} = 3\).
In the context of our specific number, 4 times the square root of 5, we denote this as \(4\sqrt{5}\). This expression represents 4 multiplied by the principal square root of 5. The principal square root of 5 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 2.236.
Thus, \(4\sqrt{5}\) can be approximated as follows:
- \(\sqrt{5} \approx 2.236\)
- \(4 \times 2.236 \approx 8.944\)
Therefore, \(4\sqrt{5} \approx 8.944\).
Properties of Square Roots
- Non-negativity: The principal square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative.
- Product Property: \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\)
- Quotient Property: \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\) (for \(b \neq 0\))
Applying these properties to our expression, we can break down \(4\sqrt{5}\) further if needed for specific applications in mathematics.
Examples
- If we want to find the square root of a number squared, such as \(\sqrt{(4\sqrt{5})^2}\), we first calculate \((4\sqrt{5})^2 = 16 \times 5 = 80\). Therefore, \(\sqrt{(4\sqrt{5})^2} = \sqrt{80}\), which simplifies back to \(4\sqrt{5}\).
- To solve \(\sqrt{50} + \sqrt{200}\), we use the product property:
- \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
- \(\sqrt{200} = \sqrt{100 \times 2} = 10\sqrt{2}\)
- So, \(\sqrt{50} + \sqrt{200} = 5\sqrt{2} + 10\sqrt{2} = 15\sqrt{2}\)
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate \( 4 \sqrt{5} \), follow these steps:
- Understand that \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) means four times the square root of 5.
- Identify that \( \sqrt{5} \) is approximately 2.236 (this is an approximate value for calculation purposes).
- Multiply 4 by \( \sqrt{5} \):
| 4 × \( \sqrt{5} \) | = | 4 × 2.236 | = | 8.944 |
Therefore, \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) is approximately 8.944.
Approximating the Value
To approximate \( 4 \sqrt{5} \), consider the following steps:
- Recognize that \( \sqrt{5} \) is approximately 2.236.
- Multiply 4 by \( \sqrt{5} \):
| 4 × \( \sqrt{5} \) | = | 4 × 2.236 | = | 8.944 |
Thus, \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) is approximately 8.944.

Applications in Mathematics
The value \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) finds applications in various mathematical contexts:
- Geometry: It can be used in geometric calculations involving shapes where the square root of 5 is a factor.
- Algebra: Appears in algebraic expressions and equations, particularly those involving radicals.
- Trigonometry: Utilized in trigonometric identities and calculations where radicals play a role.
- Complex Numbers: Relevant in discussions involving complex numbers and their real and imaginary components.
- Calculus: Occurs in calculus problems, especially when dealing with derivatives or integrals involving square roots.
Geometric Interpretations
The expression \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) can be interpreted geometrically in several ways:
- Area Calculations: In geometric figures such as rectangles or triangles, \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) could represent areas involving the square root of 5 as a dimension.
- Lengths and Dimensions: It may denote lengths or dimensions in three-dimensional objects where the square root of 5 is a factor.
- Pythagorean Theorem: Relevant in applications of the Pythagorean theorem where one of the sides or hypotenuse involves \( 4 \sqrt{5} \).
- Volume and Surface Area: Used in calculations of volumes or surface areas of shapes involving the square root of 5.
Uses in Algebra
In algebra, \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) has several applications and uses:
- Equations: It appears in equations where radicals are involved, often requiring simplification or solving.
- Expressions: Used in algebraic expressions to denote quantities involving the square root of 5 multiplied by 4.
- Quadratic Equations: Can be part of quadratic equations where solutions may include the square root of 5.
- Factorization: In factorizing expressions or equations where \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) is a factor.
Engineering and Physics Applications
The value \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) finds practical applications in engineering and physics:
- Structural Analysis: Used in calculating dimensions or forces in structures involving the square root of 5.
- Mechanical Engineering: Relevant in mechanical systems where precise calculations involving \( \sqrt{5} \) are necessary.
- Electrical Engineering: Appears in calculations related to impedance, resonance, or other electrical parameters.
- Wave Propagation: Applied in analyzing wave behavior or propagation where \( \sqrt{5} \) influences calculations.
- Optics: Utilized in optics for calculations involving refractive indices or optical paths affected by the square root of 5.
Real-World Examples
The value \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) manifests in various real-world scenarios:
- Construction: Used in construction projects where dimensions involving \( \sqrt{5} \) are multiplied by 4 for scaling.
- Finance: Appears in financial calculations where mathematical models utilize values incorporating \( \sqrt{5} \).
- Technology: Applied in technological innovations requiring precise calculations involving the square root of 5.
- Research: Found in scientific research involving data analysis or theoretical models incorporating \( \sqrt{5} \).
- Economics: Relevant in economic models or analyses that incorporate mathematical constants like \( \sqrt{5} \).
Visual Representations and Graphs
Visualizing \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) can be depicted in various graphical forms:
- Coordinate Plane: Plotting points or lines where \( x = 4 \sqrt{5} \) on a Cartesian coordinate system.
- Graphical Models: Representing functions or equations involving \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) on graphs to illustrate its mathematical relationships.
- Geometric Figures: Using geometric shapes or diagrams to illustrate dimensions or relationships involving \( 4 \sqrt{5} \).
- Data Visualization: Presenting statistical data or trends where \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) plays a role in influencing outcomes.
- Mathematical Models: Using visual representations to explain theoretical models or calculations involving \( 4 \sqrt{5} \).
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Common mistakes and misconceptions regarding \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) include:
- Confusion with Absolute Value: Incorrectly interpreting \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) as the absolute value of \( 4 \) times \( \sqrt{5} \).
- Incorrect Calculation: Miscalculating the value of \( \sqrt{5} \) or misapplying it in calculations involving multiplication or division.
- Not Simplifying Properly: Failing to simplify expressions involving \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) to their simplest radical form.
- Geometric Misinterpretation: Misunderstanding how \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) relates to geometric figures or dimensions.
- Overestimation of Value: Overestimating or underestimating the actual numeric value of \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) in practical contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some frequently asked questions about the mathematical concept of \( 4 \sqrt{5} \):
- What is \( 4 \sqrt{5} \)?
\( 4 \sqrt{5} \) is the mathematical expression that represents 4 times the square root of 5. It's an irrational number, approximately equal to 8.944. - How do you calculate \( 4 \sqrt{5} \)?
To calculate \( 4 \sqrt{5} \), multiply 4 by the square root of 5. Using an approximate value, \( 4 \times 2.236 \approx 8.944 \). - What are the applications of \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) in mathematics?
\( 4 \sqrt{5} \) appears in various mathematical equations and geometric calculations where the square root of 5 is involved, such as in algebraic expressions and geometric theorems. - Can \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) be simplified?
No, \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) cannot be simplified further because 5 is a prime number and its square root is irrational. - What are some real-world examples of \( 4 \sqrt{5} \)?
Examples include calculations involving distances, areas, or volumes where the square root of 5 is a factor, such as in architectural designs or engineering blueprints. - Are there misconceptions about \( 4 \sqrt{5} \)?
One common misconception is trying to find a simpler form or a rational approximation for \( 4 \sqrt{5} \), which is not possible due to its irrational nature.

Conclusion and Summary
In conclusion, \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) is a significant mathematical expression representing 4 times the square root of 5. It is an irrational number with various applications in mathematics, engineering, and physics. Throughout this guide, we've explored its definition, calculation methods, real-world applications, and common misconceptions.
By understanding \( 4 \sqrt{5} \), mathematicians and scientists can apply it to solve complex problems involving distances, areas, volumes, and geometric interpretations. Its exact value, approximately 8.944, makes it indispensable in theoretical and practical contexts.
Further research and exploration of \( 4 \sqrt{5} \) continue to unveil its deeper implications across different disciplines, reinforcing its role as a fundamental mathematical constant.