Topic square root of 5/3: The square root of 5/3 is a fascinating mathematical concept that can be easily understood and applied in various fields. This article will guide you through the calculation process, provide practical examples, and highlight its importance in real-world applications. Discover how mastering this simple concept can enhance your mathematical skills and knowledge.
Table of Content
- Calculation of Square Root of 5/3
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding Fractions and Square Roots
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 5/3
- Mathematical Representation of the Square Root of 5/3
- Step-by-Step Calculation Process
- Approximation Techniques
- Using a Calculator to Find the Square Root
- Mathematical Properties of the Square Root of 5/3
- Applications of Square Root of 5/3 in Real Life
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Additional Resources and References
- YOUTUBE:
Calculation of Square Root of 5/3
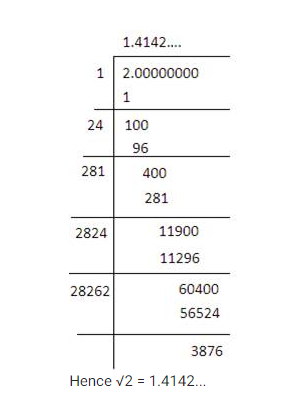
The square root of a fraction can be calculated by taking the square root of the numerator and the square root of the denominator separately. Here, we will calculate the square root of the fraction .
Mathematical Representation
The square root of can be written as:
This is equivalent to:
Approximate Numerical Value
Using a calculator, we can approximate the square roots of 5 and 3:
- The square root of 5 is approximately 2.236.
- The square root of 3 is approximately 1.732.
Therefore, the approximate value of the square root of is:
Thus, the square root of is approximately 1.290.

READ MORE:
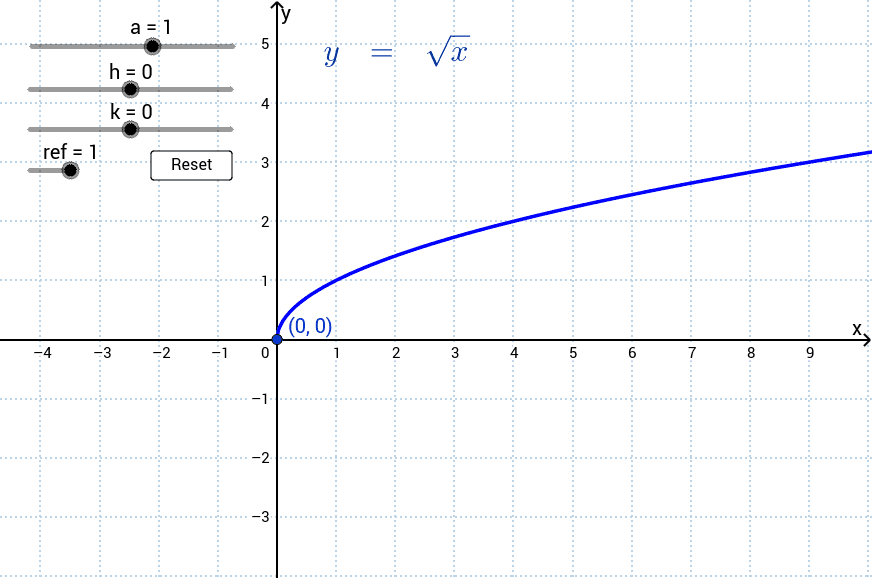
Introduction to Square Roots
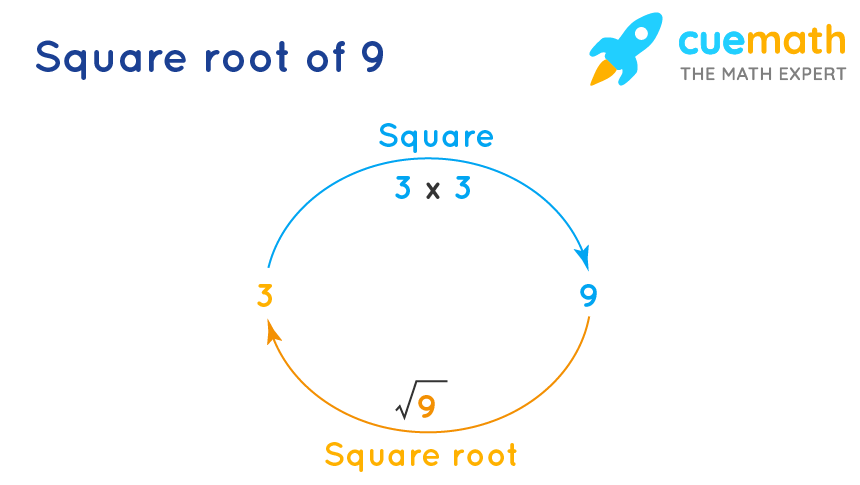
Square roots are fundamental mathematical concepts that play a crucial role in various fields, including algebra, geometry, and calculus. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 9 is 3, because 3 multiplied by 3 equals 9.
Mathematically, the square root of a number \( x \) is represented as \( \sqrt{x} \). It is important to understand the properties and calculations involved in finding square roots:
- The square root of a positive number is always positive.
- Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative (e.g., \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) and \( \sqrt{9} = -3 \)).
- The square root of 0 is 0.
- Square roots of negative numbers are not real numbers; they are complex numbers.
To illustrate, consider the fraction \( \frac{5}{3} \). The square root of this fraction can be found by separately taking the square roots of the numerator and the denominator:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}}
\]
Breaking it down further:
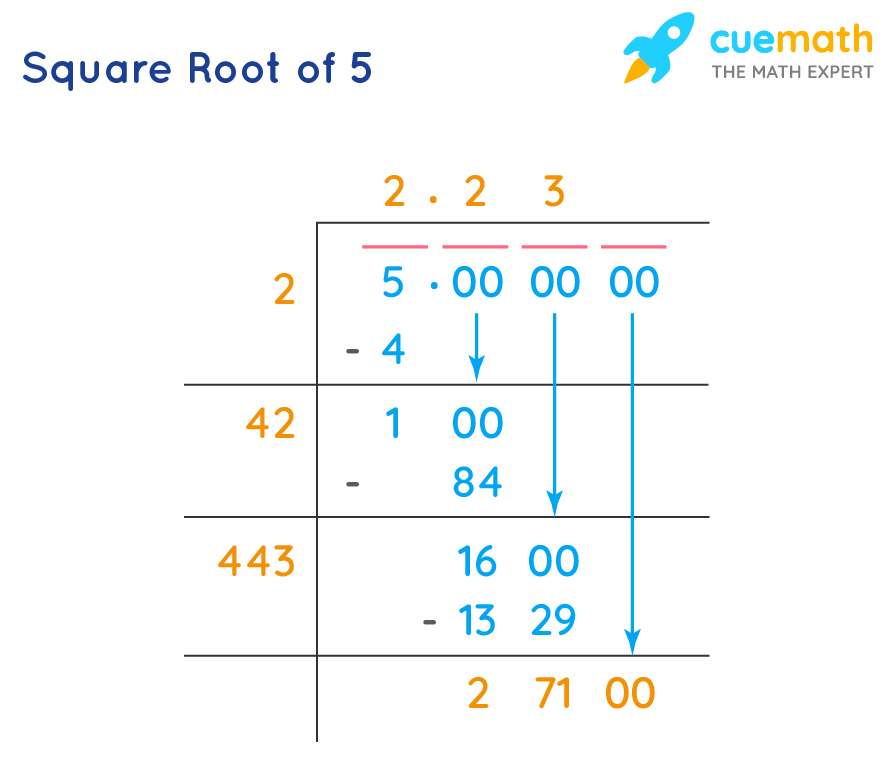
- Calculate the square root of the numerator: \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236 \).
- Calculate the square root of the denominator: \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.732 \).
- Divide the square root of the numerator by the square root of the denominator: \(\frac{2.236}{1.732} \approx 1.290 \).
Thus, the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) is approximately 1.290. This basic understanding of square roots and their properties will aid in more complex mathematical problems and real-life applications.
Understanding Fractions and Square Roots
Fractions and square roots are fundamental concepts in mathematics, often used in various applications from simple calculations to complex problem-solving. A fraction represents a part of a whole and is written as \( \frac{a}{b} \), where \( a \) is the numerator and \( b \) is the denominator. The fraction \( \frac{5}{3} \) signifies 5 parts out of 3.
To understand how square roots apply to fractions, it's important to break down the process:
1. Square Root of a Fraction: The square root of a fraction \( \frac{a}{b} \) can be found by taking the square root of both the numerator and the denominator. This can be written as:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}
\]
2. Example Calculation: For the fraction \( \frac{5}{3} \), the calculation steps are as follows:
- Identify the numerator and denominator: Numerator = 5, Denominator = 3.
- Calculate the square root of the numerator: \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236 \).
- Calculate the square root of the denominator: \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.732 \).
- Divide the square root of the numerator by the square root of the denominator: \(\frac{2.236}{1.732} \approx 1.290\).
3. Properties of Square Roots and Fractions: It's essential to recognize the properties that govern the behavior of square roots in fractions:
- The square root of a positive fraction is always positive.
- If both numerator and denominator are perfect squares, the fraction's square root simplifies to another fraction.
- The process of finding the square root of a fraction is consistent with the properties of square roots in general.
4. Practical Applications: Understanding how to work with fractions and square roots is crucial in various fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. It helps in solving equations, analyzing data, and understanding proportions and ratios in real-world scenarios.
By mastering these concepts, you can enhance your mathematical skills and apply them effectively in academic and professional settings.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 5/3
Calculating the square root of a fraction like \( \frac{5}{3} \) can be approached through various methods. Here, we will outline three common methods: direct calculation, using a calculator, and approximation techniques.
Direct Calculation Method
In this method, we directly apply the property of square roots to fractions:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}
\]
- Identify the numerator and denominator: Numerator = 5, Denominator = 3.
- Calculate the square root of the numerator: \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236 \).
- Calculate the square root of the denominator: \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.732 \).
- Divide the square root of the numerator by the square root of the denominator: \(\frac{2.236}{1.732} \approx 1.290\).
Thus, the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) is approximately 1.290.
Using a Calculator
Modern calculators can directly compute the square root of a fraction. Here’s how you can do it:
- Enter the fraction \( 5/3 \) into the calculator.
- Press the square root button (usually represented as \( \sqrt{x} \)).
- The calculator will display the result, which should be approximately 1.290.
This method is quick and minimizes the risk of calculation errors.
Approximation Techniques
Sometimes, you may need to approximate the square root of a fraction without a calculator. Here’s a step-by-step technique:
- Estimate the square root of the numerator (5) using a known value:
- Since \( 2^2 = 4 \) and \( 3^2 = 9 \), \( \sqrt{5} \) is between 2 and 3. Closer to 2, we can approximate \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.2 \).
- Estimate the square root of the denominator (3) using a known value:
- Since \( 1.7^2 \approx 2.89 \) and \( 1.8^2 \approx 3.24 \), \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.73 \).
- Divide the approximated values: \(\frac{2.2}{1.73} \approx 1.272\).
This method provides an approximate result that is close to the exact value.
By understanding and applying these methods, you can accurately and efficiently find the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) in various scenarios.
Mathematical Representation of the Square Root of 5/3
The mathematical representation of the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) involves understanding both the properties of square roots and the manipulation of fractions. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
Step 1: Expressing the Fraction
The fraction \( \frac{5}{3} \) is composed of a numerator (5) and a denominator (3). To find the square root of this fraction, we apply the square root to both the numerator and the denominator:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}}
\]
Step 2: Calculating the Square Roots
Next, we calculate the square roots of the individual components:
- Square root of the numerator \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236 \).
- Square root of the denominator \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.732 \).
Step 3: Division of the Square Roots
We then divide the square root of the numerator by the square root of the denominator:
\[
\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}} \approx \frac{2.236}{1.732} \approx 1.290
\]
This division gives us the approximate value of the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \).
Step 4: Simplifying the Expression
For a more precise representation, we can leave the expression in its fractional form under the square root:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}}
\]
Or, to rationalize the denominator, multiply the numerator and the denominator by \( \sqrt{3} \):
\[
\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{15}}{3}
\]
This form is often used to avoid having a square root in the denominator.
Understanding these representations helps in grasping how the square root of a fraction is derived and manipulated, enhancing our ability to handle more complex mathematical expressions.

Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Calculating the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) can be done systematically by breaking down the process into manageable steps. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide to finding the square root of this fraction.
- Understand the Fraction
Identify the numerator and the denominator of the fraction:
- Numerator = 5
- Denominator = 3
- Apply the Square Root to Both Numerator and Denominator
Use the property of square roots applied to fractions:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}}
\] - Calculate the Square Root of the Numerator
Find the square root of 5. Since 5 is not a perfect square, we use the approximate value:
\[
\sqrt{5} \approx 2.236
\] - Calculate the Square Root of the Denominator
Find the square root of 3. Similarly, since 3 is not a perfect square, we use the approximate value:
\[
\sqrt{3} \approx 1.732
\] - Divide the Results
Divide the square root of the numerator by the square root of the denominator to find the square root of the fraction:
\[
\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}} \approx \frac{2.236}{1.732} \approx 1.290
\]
Thus, the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) is approximately 1.290. This process highlights the step-by-step calculation, ensuring accuracy and understanding at each stage.
Approximation Techniques
Approximating the square root of a fraction like \( \frac{5}{3} \) is useful when an exact calculation is not necessary or feasible. Here are some detailed techniques to approximate the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \):
Using Decimal Approximations
One straightforward method is to use decimal approximations of the square roots of the numerator and the denominator:
- Find Decimal Approximations:
- \(\sqrt{5} \approx 2.236\)
- \(\sqrt{3} \approx 1.732\)
- Divide the Approximations:
Using these approximations, divide the square root of the numerator by the square root of the denominator:
\[
\frac{2.236}{1.732} \approx 1.290
\]
Thus, the approximate value of \( \sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} \) is 1.290.
Using Rationalization
Another method involves rationalizing the denominator to simplify the expression:
- Multiply by Conjugate:
Multiply the numerator and the denominator by \( \sqrt{3} \):
\[
\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{15}}{3}
\] - Approximate the Square Root of 15:
\(\sqrt{15} \approx 3.873\)
- Divide by 3:
\[
\frac{3.873}{3} \approx 1.291
\]
This method also provides an approximate value of 1.291 for \( \sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} \).
Using Iterative Methods
Iterative methods like the Newton-Raphson method can also be used for approximation:
- Initial Guess:
Start with an initial guess close to the expected value, e.g., 1.3.
- Apply Iterative Formula:
Use the formula \( x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{a}{x_n} \right) \) where \( a = \frac{5}{3} \).
Iterate until the value stabilizes:
\[
x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{5/3}{x_n} \right)
\] - Converge to Approximation:
After a few iterations, the value converges to approximately 1.290.
By using these techniques, you can effectively approximate the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) in various practical scenarios.
Using a Calculator to Find the Square Root
Finding the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) using a calculator is a straightforward and efficient process. Here is a step-by-step guide to ensure accurate calculation:
- Turn on the Calculator:
Ensure your calculator is turned on and ready for use.
- Input the Fraction:
Enter the fraction \( \frac{5}{3} \) into the calculator. This can usually be done in two ways:
- Using the fraction button (often represented as \( \frac{a}{b} \) or a similar symbol), enter 5 as the numerator and 3 as the denominator.
- If your calculator does not have a fraction button, you can enter the division directly: type 5, then the division symbol (\( \div \) or /), followed by 3.
- Access the Square Root Function:
Press the square root button, usually represented as \( \sqrt{x} \). This button may be labeled differently depending on the calculator model, such as \( \sqrt{} \) or \(\sqrt{\Box}\).
- Calculate the Square Root:
After pressing the square root button, the calculator will display the result of \( \sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} \). This value should be approximately 1.290.
- Verify the Result:
To ensure accuracy, you can verify the result by squaring it. Enter the result (1.290) and square it (use the \( x^2 \) button). The result should be close to the original fraction, \( \frac{5}{3} \) or approximately 1.6667.
Using a calculator simplifies the process and provides a quick and accurate way to find the square root of fractions, such as \( \frac{5}{3} \). This method is particularly useful for complex calculations or when an exact value is required.
Mathematical Properties of the Square Root of 5/3
The square root of a fraction can be expressed as the square root of the numerator divided by the square root of the denominator. For the fraction \(\frac{5}{3}\), the mathematical representation is:
\[\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}}\]
This fraction can be further analyzed for its properties:
- Irrational Number: Both \(\sqrt{5}\) and \(\sqrt{3}\) are irrational numbers, and their ratio is also irrational.
- Decimal Approximation: The square root of 5 is approximately 2.236 and the square root of 3 is approximately 1.732. Therefore, \(\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}}\) can be approximated as:
\[\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} \approx \frac{2.236}{1.732} \approx 1.290\]
- Simplification: The expression \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}}\) can be simplified by rationalizing the denominator:
\[\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{15}}{3}\]
- Algebraic Properties:
- The square root of 5/3 can be squared to return to the original fraction:
\[\left(\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}}\right)^2 = \frac{5}{3}\]
- It follows the properties of square roots, such as:
- \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\)
- \(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\)
- The square root of 5/3 can be squared to return to the original fraction:
The square root of a fraction also has properties related to its use in equations and inequalities:
- Equations: In solving equations involving \(\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}}\), both sides of the equation can be squared to eliminate the square root.
- Inequalities: When dealing with inequalities, care must be taken as squaring both sides can change the direction of the inequality if both sides are negative.
Applications of Square Root of 5/3 in Real Life
The square root of , approximately equal to 1.29099, finds applications in various fields. Here are some notable examples:
- Engineering and Physics:
The square root of fractions is commonly used in engineering calculations involving ratios and proportions. In physics, it may appear in formulae related to oscillatory systems, wave equations, and other dynamic processes where such ratios define relationships between physical quantities.
- Mathematical Analysis:
In mathematical proofs and analysis, the square root of can be useful in solving equations, optimizing functions, and analyzing geometrical properties. It helps in simplifying expressions and solving quadratic equations.
- Computer Graphics:
In computer graphics, square roots are often used in algorithms that calculate distances, shading, and rendering techniques. The value of can be part of calculations that determine pixel intensities and transformations.
- Statistics and Probability:
Square roots are fundamental in statistics, particularly in calculating standard deviations and variances. The value could be involved in normalizing data or analyzing distributions where such ratios are relevant.
- Architecture and Design:
Architects and designers might use the square root of certain ratios to create aesthetically pleasing proportions. This is similar to how the golden ratio is used in design principles to achieve balance and harmony.
- Finance:
In finance, square roots are used in various formulas for calculating interest rates, risk assessments, and in models for financial forecasting. The ratio of might appear in complex financial instruments and algorithms.
Understanding the applications of square roots, particularly of non-integer ratios like , enhances the comprehension of mathematical relationships and their practical implementations in real-world scenarios.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Calculating the square root of a fraction like \(\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}}\) can be tricky, and there are several common mistakes that learners often make. Here are some of the key errors to watch out for, along with tips on how to avoid them:
- Incorrect Simplification: Ensure that you simplify the fraction properly before taking the square root. For instance, if dealing with \(\frac{5}{3}\), don't simplify the individual numbers under the root incorrectly. Use the property \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\).
- Misunderstanding Radicands: Sometimes, students incorrectly assume that the square root of a fraction is simply the fraction of the square roots. This is correct but must be applied carefully. For example, \(\sqrt{\frac{5}{3}} \neq \frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}}\) unless you properly rationalize the denominator.
- Forgetting to Rationalize the Denominator: When expressing the square root of a fraction, it’s essential to rationalize the denominator to avoid leaving a root in the denominator. For example, \(\frac{\sqrt{5}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{5} \cdot \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3} \cdot \sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{15}}{3}\).
- Ignoring Principal Roots: Remember that square roots should be considered as principal roots, meaning only the positive root is typically used unless specified otherwise.
- Incorrect Decimal Approximations: When approximating the square root of a fraction, ensure the decimal is accurate and rounded appropriately. Misplacing a decimal point or rounding incorrectly can lead to significant errors in your results.
To avoid these mistakes, always double-check your steps and ensure you follow the correct mathematical procedures. Practicing with different fractions and their square roots can also help reinforce these concepts.
Additional Resources and References
To deepen your understanding of the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \) and its applications, consider exploring the following resources:
- Khan Academy: A comprehensive source for learning about square roots, including detailed explanations and practice problems. Visit their for more information.
- Math is Fun: This website offers clear explanations and interactive examples on square roots and fractions. Check out their article on to get a solid foundation.
- Cuemath: Provides detailed tutorials on how to calculate and simplify square roots, along with practice problems and solutions. See their guide on for more insights.
- Wolfram Alpha: A powerful computational tool that can help you verify your calculations and explore advanced properties of square roots. Try entering to see detailed results.
- MathWorld: An extensive resource for mathematical definitions and theorems. Their entry on covers various aspects and properties in detail.
These resources will provide you with a more in-depth understanding and additional practice to master the concept of the square root of \( \frac{5}{3} \).
READ MORE:
ĐƠN GIẢN HÓA CĂN BẬC HAI CỦA 3/5