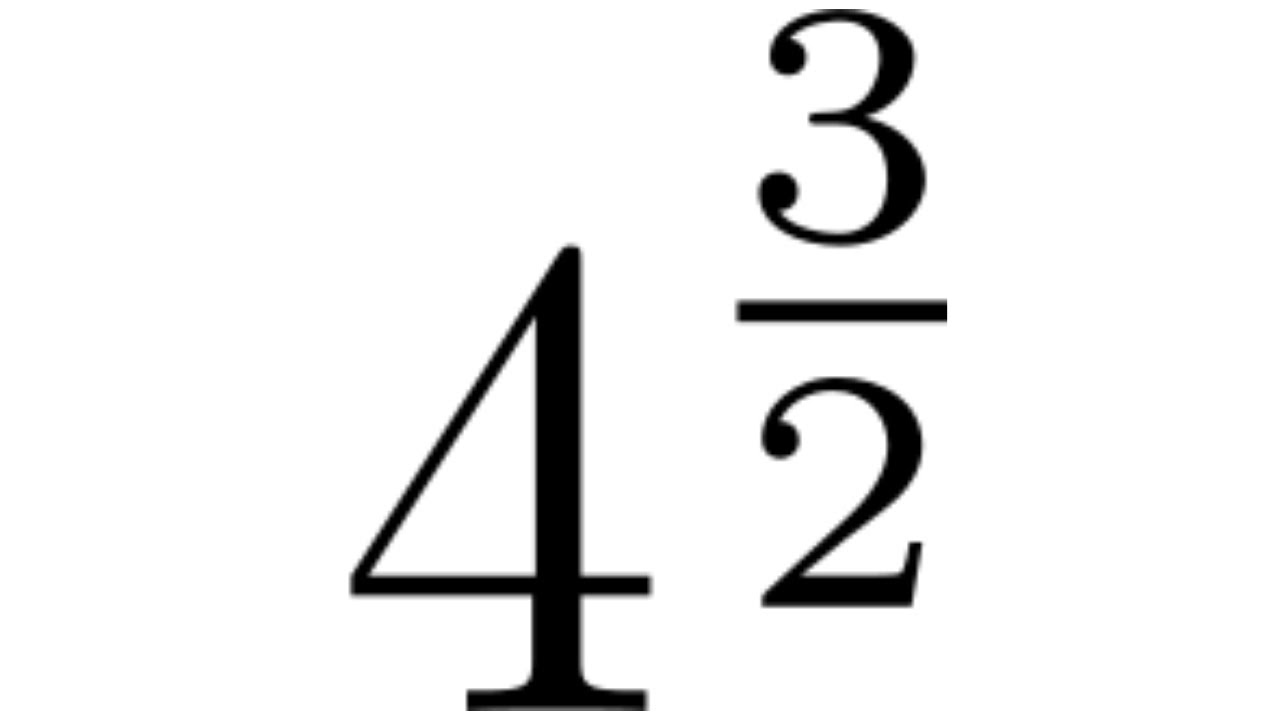Topic what are all the perfect square numbers: Discover the world of perfect square numbers with our comprehensive guide. Learn what perfect squares are, explore their properties, and find out how to identify them easily. Perfect for students and math enthusiasts alike, this article will help you understand and master perfect squares effortlessly.
Table of Content
- Perfect Square Numbers
- Definition of Perfect Squares
- Identifying Perfect Squares
- Examples of Perfect Squares
- Tips and Tricks for Finding Perfect Squares
- Applications of Perfect Squares
- Frequently Asked Questions on Perfect Squares
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để tìm hiểu về các số hoàn hảo và cách chúng được sử dụng trong toán học và cuộc sống hàng ngày.
Perfect Square Numbers
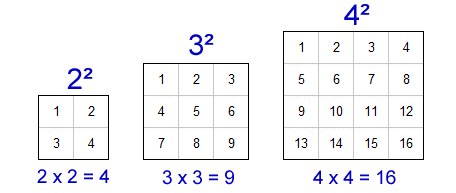
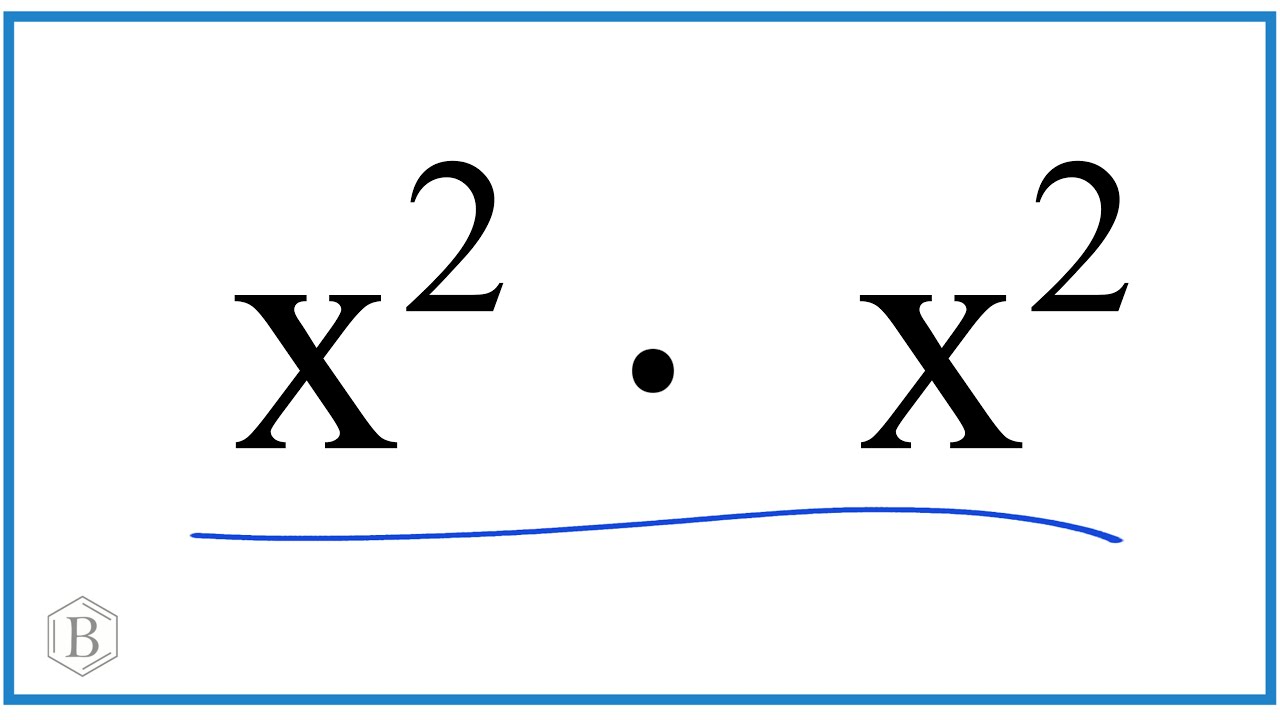
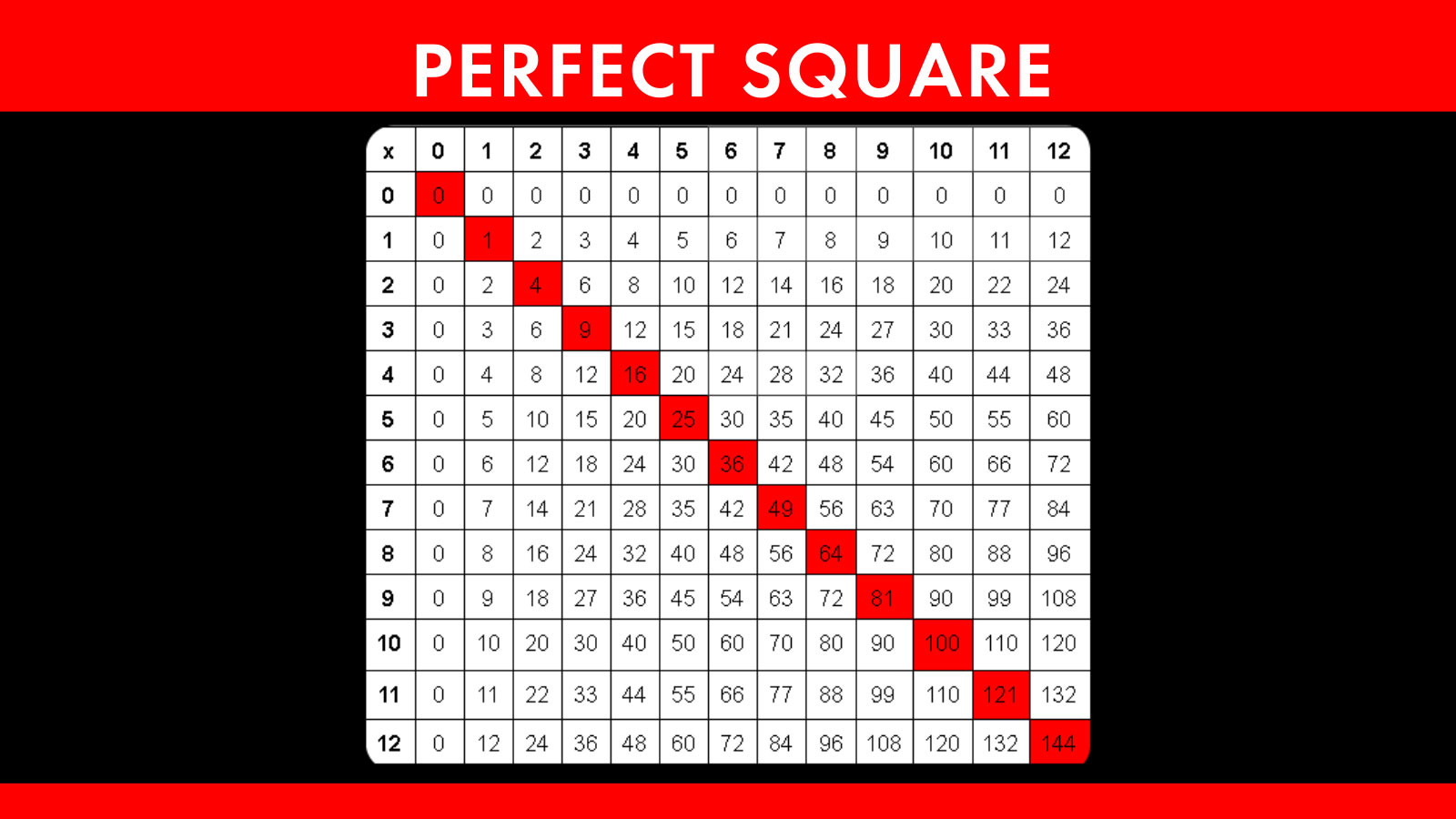
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer multiplied by itself. For example, the number 9 is a perfect square because it can be written as \(3 \times 3\) or \(3^2\).
List of Perfect Squares
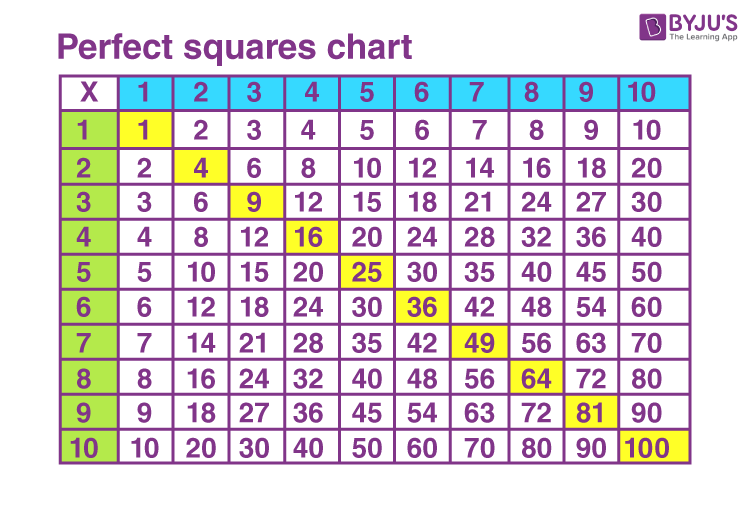
Here is a list of perfect square numbers between 1 and 100:
- 1 (\(1^2\))
- 4 (\(2^2\))
- 9 (\(3^2\))
- 16 (\(4^2\))
- 25 (\(5^2\))
- 36 (\(6^2\))
- 49 (\(7^2\))
- 64 (\(8^2\))
- 81 (\(9^2\))
- 100 (\(10^2\))
Properties of Perfect Squares
- All perfect squares end in 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9.
- The square root of a perfect square is always an integer.
- If a number ends in 2, 3, 7, or 8, it is not a perfect square.
- Perfect squares can be identified using their digital root, which is always 1, 4, 7, or 9.
- Perfect squares are always positive as \((-ve) \times (-ve) = (+ve)\).
How to Identify a Perfect Square
One way to identify a perfect square is to calculate its square root. If the square root is an integer, then the number is a perfect square. For example, \(\sqrt{49} = 7\), hence 49 is a perfect square.
Examples
- Example 1: Is 24 a perfect square?
Solution: \(\sqrt{24} = 4.89\), which is not an integer. Hence, 24 is not a perfect square. - Example 2: Is 81 a perfect square?
Solution: \(\sqrt{81} = 9\), which is an integer. Hence, 81 is a perfect square.
Tips and Tricks
- For numbers ending in 5, separate the digits and multiply the tens digit by its successor, then append 25. For example, \(75^2 = 5625\).
- Use the formula \((a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2\) for larger numbers. For example, \(67^2 = (60 + 7)^2 = 4489\).
Conclusion
Perfect squares are fundamental in mathematics and have various properties that make them easy to identify. Understanding perfect squares helps in learning multiplication, square roots, and recognizing patterns in numbers.
READ MORE:
Definition of Perfect Squares
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer multiplied by itself. Mathematically, a number n is a perfect square if there exists an integer m such that \( n = m^2 \). This means that the square root of a perfect square is always an integer.
For example:
- 1 is a perfect square because \(1 = 1^2\).
- 4 is a perfect square because \(4 = 2^2\).
- 9 is a perfect square because \(9 = 3^2\).
Some important properties of perfect squares include:
- The square of an even number is always even, and the square of an odd number is always odd.
- All odd squares can be written in the form \(4n + 1\).
- All even squares are divisible by 4.
- A perfect square always ends in 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9.
Perfect squares are fundamental in mathematics because they appear frequently in various mathematical concepts and operations. Identifying perfect squares can be done easily by taking the square root of the number. If the square root is an integer, then the number is a perfect square.
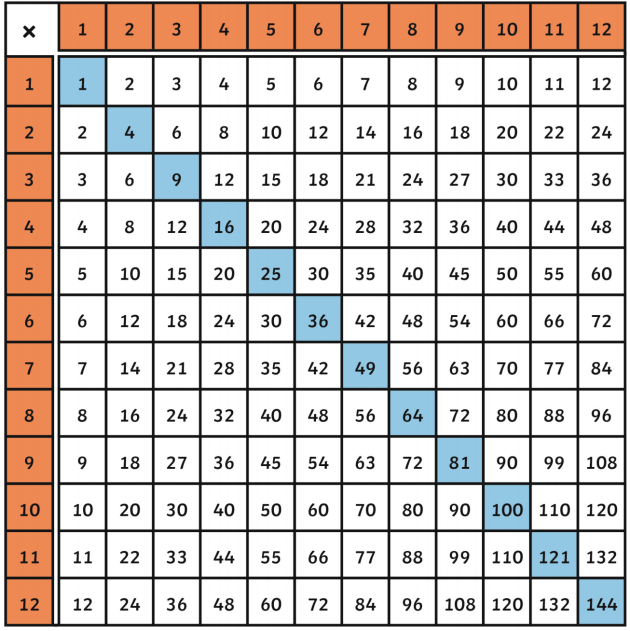
Here's a table showing some perfect squares:
| Integer | Perfect Square |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 9 |
| 4 | 16 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 6 | 36 |
| 7 | 49 |
| 8 | 64 |
| 9 | 81 |
| 10 | 100 |
Identifying Perfect Squares
Identifying perfect squares is a fundamental concept in mathematics. A perfect square is an integer that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. For example, 36 is a perfect square because it can be written as 6 × 6 or \(6^2\).
Here are some steps to identify if a number is a perfect square:
- Find the square root of the number. For instance, the square root of 25 is 5.
- Check if the square root is an integer. If the square root is a whole number, then the original number is a perfect square.
- If the square root is not a whole number, then the number is not a perfect square. For example, the square root of 20 is approximately 4.47, which is not an integer, so 20 is not a perfect square.
Here are some characteristics of perfect squares:
- They always end with 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9 in base 10.
- The number of zeros at the end of a perfect square is always even.
- The difference between the squares of two consecutive integers is always an odd number.
Example: Is 144 a perfect square?
Let's check:
- Find the square root of 144: \(\sqrt{144} = 12\).
- Since 12 is an integer, 144 is a perfect square.
Example: Is 50 a perfect square?
Let's check:
- Find the square root of 50: \(\sqrt{50} \approx 7.07\).
- Since 7.07 is not an integer, 50 is not a perfect square.
Perfect squares play a significant role in various mathematical problems and are essential for understanding higher-level concepts in algebra and geometry.
Examples of Perfect Squares
Perfect squares are numbers that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. Here are some examples of perfect squares:
- 1 is a perfect square because \(1 \times 1 = 1\)
- 4 is a perfect square because \(2 \times 2 = 4\)
- 9 is a perfect square because \(3 \times 3 = 9\)
- 16 is a perfect square because \(4 \times 4 = 16\)
- 25 is a perfect square because \(5 \times 5 = 25\)
- 36 is a perfect square because \(6 \times 6 = 36\)
- 49 is a perfect square because \(7 \times 7 = 49\)
- 64 is a perfect square because \(8 \times 8 = 64\)
- 81 is a perfect square because \(9 \times 9 = 81\)
- 100 is a perfect square because \(10 \times 10 = 100\)
These examples show the pattern of perfect squares as the product of an integer multiplied by itself.
| Number | Perfect Square |
|---|---|
| 11 | \(11 \times 11 = 121\) |
| 12 | \(12 \times 12 = 144\) |
| 13 | \(13 \times 13 = 169\) |
| 14 | \(14 \times 14 = 196\) |
| 15 | \(15 \times 15 = 225\) |
| 16 | \(16 \times 16 = 256\) |
| 17 | \(17 \times 17 = 289\) |
| 18 | \(18 \times 18 = 324\) |
| 19 | \(19 \times 19 = 361\) |
| 20 | \(20 \times 20 = 400\) |
Understanding these examples helps in identifying patterns and properties of perfect squares, making it easier to recognize them in different mathematical contexts.
Tips and Tricks for Finding Perfect Squares
Identifying perfect squares can be made easier with some helpful tips and tricks. These methods can simplify the process and save time, especially when dealing with larger numbers. Here are some strategies:
- Observing the Last Digit: A number ending in 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9 can be a perfect square. Numbers ending in 2, 3, 7, or 8 are not perfect squares.
- Sum of Digits: If the sum of the digits of a number results in 1, 4, 7, or 9 after repeated addition (digital root), it could be a perfect square.
- Square Root Method: Finding the square root of a number can quickly determine if it is a perfect square. If the square root is an integer, the number is a perfect square.
- Prime Factorization: In the prime factorization of a perfect square, each prime factor will appear an even number of times.
- Special Patterns: Recognize patterns such as squares of numbers ending in 5 (e.g., \(75^2 = 5625\)).
Applying these tricks can help you quickly identify and confirm perfect squares, making mathematical problems easier to solve.
Applications of Perfect Squares
Perfect square numbers find applications in various fields, including:
- Mathematics: In algebra, perfect squares are fundamental in understanding equations, factoring, and solving problems related to geometry and arithmetic.
- Geometry: Perfect squares are used in geometry to calculate areas of squares and to find distances in coordinate geometry.
- Physics: In physics, perfect squares appear in equations related to motion, energy, and wave phenomena.
- Engineering: Engineers often encounter perfect squares when dealing with measurements, dimensions, and calculations in various fields such as structural engineering and signal processing.
- Computer Science: Perfect squares are utilized in computer algorithms, particularly in areas like image processing, cryptography, and data compression.
Frequently Asked Questions on Perfect Squares
Here are some common questions about perfect square numbers:
- What is a perfect square number?
- How do you identify perfect square numbers?
- What are some properties of perfect square numbers?
- How are perfect square numbers used in mathematics?
- What are some real-life applications of perfect square numbers?
- Can perfect square numbers be negative?
- How do you find the square root of a perfect square number?
- Are there any patterns or rules for determining if a number is a perfect square?
Xem video này để tìm hiểu về các số hoàn hảo và cách chúng được sử dụng trong toán học và cuộc sống hàng ngày.
Các Số Hoàn Hảo
READ MORE:
Xem video này để hiểu về khái niệm về căn bậc hai và các số hoàn hảo trong toán học.
Khái Niệm Về Căn Bậc Hai và Số Hoàn Hảo