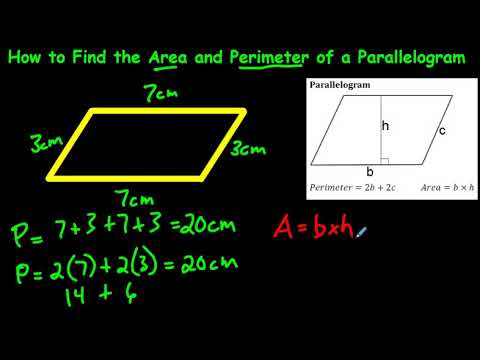
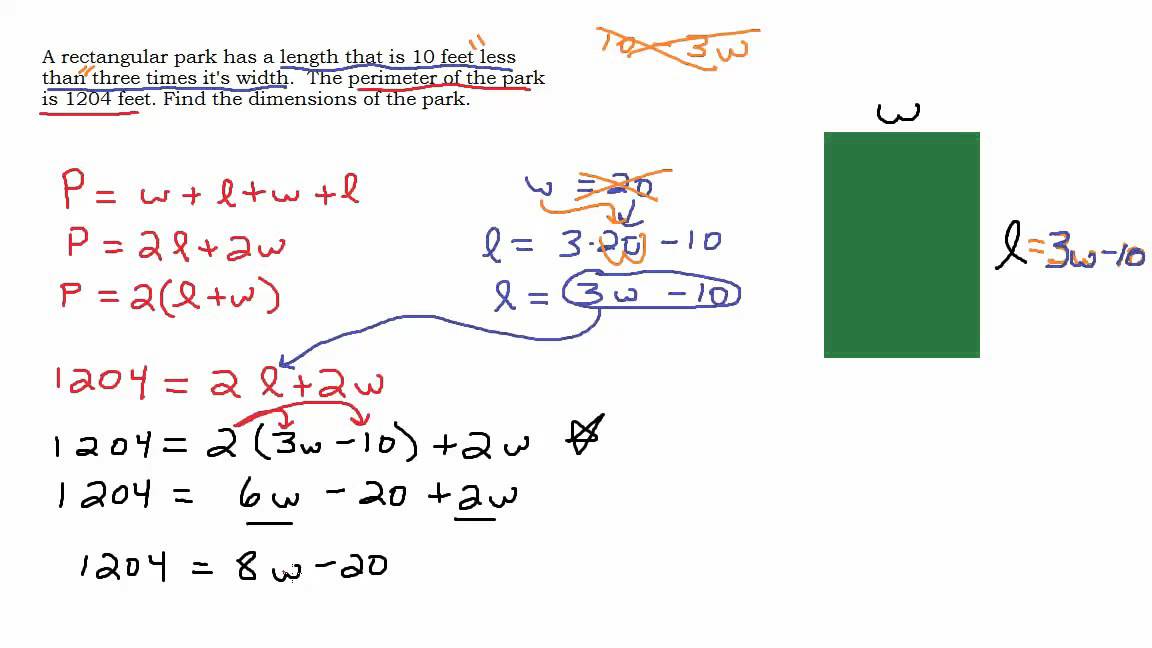
Topic area perimeter worksheets: Discover our comprehensive collection of area and perimeter worksheets designed to make learning fun and effective. Perfect for students, teachers, and parents, these worksheets cover various shapes and difficulty levels, helping everyone master essential math skills. Dive in and explore the engaging exercises that will boost your understanding and confidence in calculating area and perimeter.
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Understanding Area
- Understanding Perimeter
- Formulas and Definitions
- Word Problems Involving Area and Perimeter
- Advanced Problems and Applications
- Fun Activities and Games for Learning Area and Perimeter
- Area and Perimeter in Real-Life Situations
- Interactive Area and Perimeter Exercises
- Printable Worksheets and Resources
- Online Tools and Calculators
- Teacher Resources and Lesson Plans
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp, ví dụ hình chữ L, trong môn hình học. Toán với Mr. J sẽ giúp bạn nắm vững khái niệm này.
Area and Perimeter Worksheets
Welcome to our collection of Area and Perimeter Worksheets. These worksheets are designed to help students understand and calculate the area and perimeter of various geometric shapes. Whether you are a teacher, parent, or student, you will find these resources helpful for learning and practice.
Types of Worksheets
Rectangle Worksheets
These worksheets focus on calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles. Problems range from basic to advanced levels.
-
Basic Rectangle Problems:
Calculate the area and perimeter of rectangles with given lengths and widths.
-
Advanced Rectangle Problems:
Solve for missing sides when given the area or perimeter.
Square Worksheets
These worksheets help students practice finding the area and perimeter of squares, using both side lengths and area or perimeter to find missing values.
Triangle Worksheets
Our triangle worksheets include problems for various types of triangles: equilateral, isosceles, and scalene. Calculate both the area and perimeter of triangles with given dimensions.
Circle Worksheets
These worksheets involve finding the area and circumference of circles. Problems include using the radius or diameter.
- Find the area of a circle given the radius.
- Calculate the circumference of a circle given the diameter.
- Advanced problems with missing radius or diameter.
Composite Shapes Worksheets
Students can practice finding the area and perimeter of composite shapes, which are made up of two or more basic shapes.
Sample Problems
Here are some sample problems you might find in these worksheets:
| Shape | Problem | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | If the length is 8 cm and the width is 5 cm, find the area and perimeter. | \[ \text{Area} = 8 \, \text{cm} \times 5 \, \text{cm} = 40 \, \text{cm}^2 \] \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (8 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm}) = 26 \, \text{cm} \] |
| Square | If the side length of a square is 6 cm, find the area and perimeter. | \[ \text{Area} = 6 \, \text{cm} \times 6 \, \text{cm} = 36 \, \text{cm}^2 \] \[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 6 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm} \] |
| Triangle | Find the area of a triangle with base 10 cm and height 7 cm. | \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \, \text{cm} \times 7 \, \text{cm} = 35 \, \text{cm}^2 \] |
| Circle | If the radius of a circle is 4 cm, find the area and circumference. | \[ \text{Area} = \pi \times 4^2 \approx 50.27 \, \text{cm}^2 \] \[ \text{Circumference} = 2 \pi \times 4 \approx 25.13 \, \text{cm} \] |
We hope you find these worksheets useful for your learning and teaching needs. Happy practicing!

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Understanding area and perimeter is fundamental in geometry and everyday life. These concepts are used in various applications, from calculating the space within a room to designing layouts for gardens. This introduction will help you grasp the basic definitions, formulas, and examples for different shapes.
What is Area?
Area is the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in square units, such as square centimeters (\(cm^2\)), square meters (\(m^2\)), or square inches (\(in^2\)).
- For a rectangle, the area is calculated by multiplying its length by its width: \[ \text{Area of Rectangle} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
- For a square, since all sides are equal, the area is the side length squared: \[ \text{Area of Square} = \text{side}^2 \]
- For a triangle, the area is half the product of its base and height: \[ \text{Area of Triangle} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \]
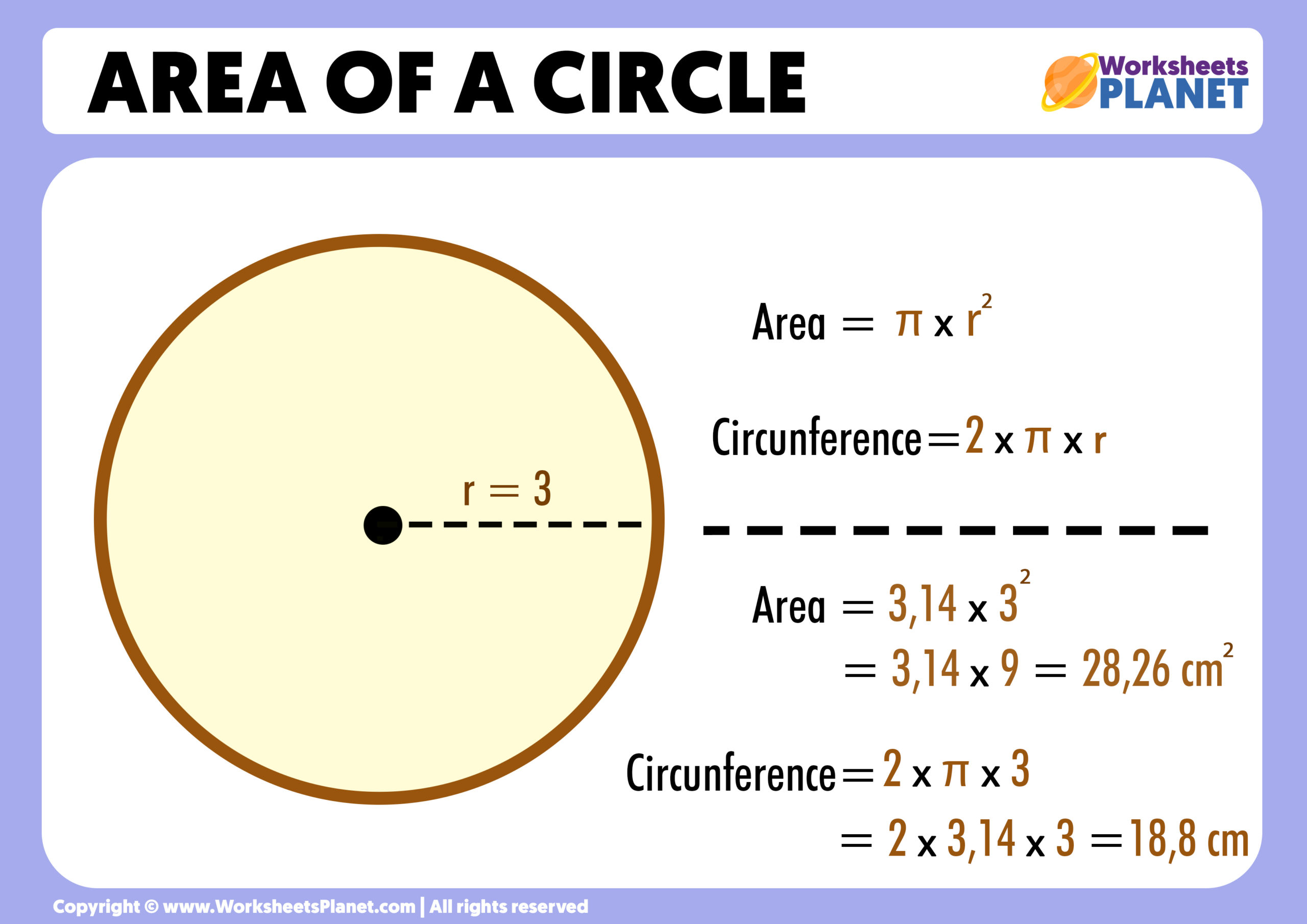
- For a circle, the area is calculated using the radius: \[ \text{Area of Circle} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \]
What is Perimeter?
Perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in linear units, such as centimeters (cm), meters (m), or inches (in).
- For a rectangle, the perimeter is the sum of all its sides: \[ \text{Perimeter of Rectangle} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
- For a square, the perimeter is four times the side length: \[ \text{Perimeter of Square} = 4 \times \text{side} \]
- For a triangle, the perimeter is the sum of its three sides: \[ \text{Perimeter of Triangle} = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3 \]
- For a circle, the perimeter is known as the circumference: \[ \text{Circumference of Circle} = 2 \pi \times \text{radius} \]
Understanding these basic concepts of area and perimeter will provide a strong foundation for tackling more complex geometric problems. In the following sections, you will find detailed worksheets and examples to practice these calculations for various shapes.
Understanding Area
The concept of area refers to the amount of space occupied by a two-dimensional shape or surface. It is measured in square units, such as square centimeters (cm2), square meters (m2), or square inches (in2).
To better understand area, consider the following key points:
- Definition: Area is the measure of the surface enclosed within a shape's boundaries.
- Units: The units of area are always squared, as they represent a two-dimensional measurement.
- Formulas: Different shapes have specific formulas to calculate their area.
Here are the formulas for calculating the area of common shapes:
| Shape | Formula | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Square | \(A = s^2\) | The area is the side length squared. |
| Rectangle | \(A = l \times w\) | The area is the length multiplied by the width. |
| Triangle | \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h\) | The area is half the base length multiplied by the height. |
| Circle | \(A = \pi r^2\) | The area is pi times the radius squared. |
| Parallelogram | \(A = b \times h\) | The area is the base length multiplied by the height. |
| Trapezoid | \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times (b_1 + b_2) \times h\) | The area is half the sum of the bases multiplied by the height. |
When working on area calculations, keep the following tips in mind:
- Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before calculating the area.
- For composite shapes, break them down into simpler shapes, calculate the area of each, and then sum them up.
- Use appropriate formulas for irregular shapes if they can be decomposed into regular shapes.
Understanding these basics will help you solve various problems involving the area of different shapes efficiently.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundaries. It is a linear measurement that represents the distance around a two-dimensional shape. Understanding the perimeter is crucial for solving various mathematical problems and real-life applications.
To calculate the perimeter, you add the lengths of all the sides of the shape. Here are some common shapes and their perimeter formulas:
- Rectangle: The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides are equal, the formula is:
\[ P = 2l + 2w \]
where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width. - Square: All four sides are equal in length. The formula is:
\[ P = 4s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side. - Triangle: The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of its three sides:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides. - Circle (Circumference): The perimeter of a circle is called the circumference, and it is calculated using the radius (\( r \)) or diameter (\( d \)):
\[ C = 2\pi r \]
or\[ C = \pi d \]
Steps to Calculate Perimeter
- Identify the shape and note down its dimensions (lengths of sides, radius, etc.).
- Use the appropriate formula for the shape.
- Plug the dimensions into the formula.
- Perform the arithmetic operations to get the perimeter.
Examples
Let's go through a couple of examples to illustrate the calculation of perimeter:
- Example 1: Rectangle
Given: length \( l = 5 \) cm, width \( w = 3 \) cm
Using the formula: \( P = 2l + 2w \)
Calculation: \( P = 2(5) + 2(3) = 10 + 6 = 16 \) cm
- Example 2: Triangle
Given: \( a = 4 \) cm, \( b = 6 \) cm, \( c = 5 \) cm
Using the formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
Calculation: \( P = 4 + 6 + 5 = 15 \) cm
- Example 3: Circle
Given: radius \( r = 7 \) cm
Using the formula: \( C = 2\pi r \)
Calculation: \( C = 2 \times \pi \times 7 \approx 44 \) cm (using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \))
Understanding and calculating the perimeter is essential for various practical applications, such as fencing a garden, framing a picture, or determining the length of material needed for a project. Practice with different shapes and dimensions to become proficient in finding perimeters.
Formulas and Definitions
Understanding the formulas and definitions for calculating the area and perimeter of various shapes is crucial for solving geometry problems. Below, we outline the key formulas and definitions used for different shapes:
Area
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is given by the formula \( A = l \times w \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: For a square, the area is \( A = s^2 \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: The area of a triangle is \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \), where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Circle: The area of a circle is \( A = \pi r^2 \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Parallelogram: The area is \( A = b \times h \), where \( b \) is the base and \( h \) is the height.
- Trapezoid: The area is \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (b_1 + b_2) \times h \), where \( b_1 \) and \( b_2 \) are the lengths of the parallel sides and \( h \) is the height.
Perimeter
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- Square: For a square, the perimeter is \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the side length.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Circle: The perimeter (circumference) of a circle is \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Parallelogram: The perimeter is \( P = 2(a + b) \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the adjacent sides.
- Trapezoid: The perimeter is \( P = a + b_1 + b_2 + c \), where \( a \) and \( c \) are the non-parallel sides, and \( b_1 \) and \( b_2 \) are the parallel sides.
Definitions
- Area: The amount of space inside the boundary of a flat (2-dimensional) object such as a triangle or circle. It is measured in square units (e.g., square centimeters, square meters).
- Perimeter: The total length of the sides or edges of a polygon. It is the distance around a two-dimensional shape.
- Base (of a triangle or parallelogram): The side of the shape that is perpendicular to the height.
- Height (of a triangle or parallelogram): The perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite side (or vertex).
- Radius: The distance from the center of a circle to any point on its circumference.
- Diameter: The distance across a circle through its center, equal to twice the radius (\( d = 2r \)).
Example Calculations
Let's look at an example for each shape:
- Rectangle: If \( l = 5 \) cm and \( w = 3 \) cm, then \( A = 5 \times 3 = 15 \) cm² and \( P = 2(5 + 3) = 16 \) cm.
- Square: If \( s = 4 \) cm, then \( A = 4^2 = 16 \) cm² and \( P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \) cm.
- Triangle: If \( b = 6 \) cm and \( h = 4 \) cm, then \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4 = 12 \) cm² and for sides \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b = 4 \) cm, \( c = 5 \) cm, \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) cm.
- Circle: If \( r = 3 \) cm, then \( A = \pi \times 3^2 = 28.27 \) cm² and \( C = 2 \pi \times 3 = 18.85 \) cm.
- Parallelogram: If \( b = 8 \) cm and \( h = 5 \) cm, then \( A = 8 \times 5 = 40 \) cm² and for sides \( a = 6 \) cm, \( b = 8 \) cm, \( P = 2(6 + 8) = 28 \) cm.
- Trapezoid: If \( b_1 = 6 \) cm, \( b_2 = 4 \) cm, and \( h = 5 \) cm, then \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (6 + 4) \times 5 = 25 \) cm² and for sides \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b_1 = 6 \) cm, \( b_2 = 4 \) cm, \( c = 5 \) cm, \( P = 3 + 6 + 4 + 5 = 18 \) cm.
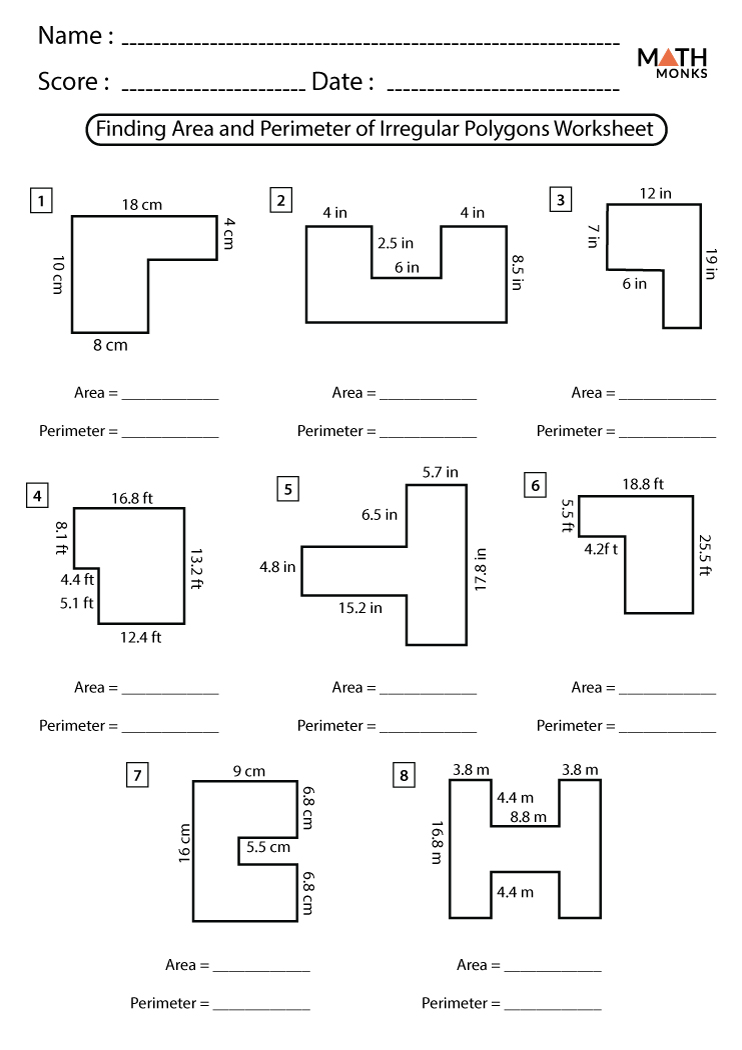
Word Problems Involving Area and Perimeter
Word problems involving area and perimeter help students apply their understanding of mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios. Here are some examples and practice problems to enhance your skills:
Example Problems
-
Problem: A rectangular garden has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. Calculate the area and perimeter of the garden.
Solution:
- Area = Length × Width = \(8 \, \text{m} \times 5 \, \text{m} = 40 \, \text{m}^2\)
- Perimeter = 2(Length + Width) = \(2 \times (8 \, \text{m} + 5 \, \text{m}) = 2 \times 13 \, \text{m} = 26 \, \text{m}\)
-
Problem: A circular park has a diameter of 14 meters. Calculate the area and the circumference of the park. (Use \(\pi \approx 3.14\))
Solution:
- Radius = Diameter / 2 = \(14 \, \text{m} / 2 = 7 \, \text{m}\)
- Area = \(\pi r^2 = 3.14 \times (7 \, \text{m})^2 = 3.14 \times 49 \, \text{m}^2 = 153.86 \, \text{m}^2\)
- Circumference = \(2 \pi r = 2 \times 3.14 \times 7 \, \text{m} = 43.96 \, \text{m}\)
-
Problem: A classroom is 10 meters long and 6 meters wide. How many square meters of carpet are needed to cover the entire floor?
Solution:
- Area = Length × Width = \(10 \, \text{m} \times 6 \, \text{m} = 60 \, \text{m}^2\)
Practice Problems
-
Problem: The length of a rectangular field is 15 meters, and its width is 10 meters. Calculate the area and perimeter of the field.
-
Problem: A square has a side length of 9 meters. What is the area and the perimeter of the square?
-
Problem: A triangle has a base of 8 meters and a height of 5 meters. Calculate the area of the triangle.
-
Problem: A swimming pool is 25 meters long and 10 meters wide. What is the perimeter of the pool?
-
Problem: The radius of a circular garden is 5 meters. Calculate the area and circumference of the garden. (Use \(\pi \approx 3.14\))
Advanced Problems
-
Problem: A rectangular piece of land is 50 meters long and 30 meters wide. A path of width 2 meters runs around the land. Calculate the area of the path.
-
Problem: A rectangular swimming pool is 20 meters long and 10 meters wide. A deck of width 3 meters surrounds the pool. What is the area of the deck?
-
Problem: A cylindrical water tank has a radius of 3 meters and a height of 10 meters. Calculate the surface area of the tank. (Use \(\pi \approx 3.14\))
By solving these word problems, students can improve their problem-solving skills and deepen their understanding of how to apply area and perimeter formulas in various contexts.
Advanced Problems and Applications
Advanced problems involving area and perimeter often require a deeper understanding of geometric principles and the ability to apply multiple steps and formulas. These problems can include working with complex shapes, missing dimensions, and real-world applications.
Problem 1: Complex Shapes
Calculate the area and perimeter of the following composite shape:
- A rectangle with dimensions 8 cm by 5 cm.
- A semicircle attached to one of the shorter sides of the rectangle with a diameter of 5 cm.
Steps to solve:
- Calculate the area of the rectangle: \( A_{\text{rectangle}} = 8 \times 5 = 40 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Calculate the area of the semicircle: \[ A_{\text{semicircle}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi \left(\frac{5}{2}\right)^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi \left(2.5\right)^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi \times 6.25 \approx 9.82 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
- Total area: \( A_{\text{total}} = 40 + 9.82 \approx 49.82 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
- Perimeter of the rectangle (excluding the side with the semicircle): \( P_{\text{rectangle}} = 8 + 8 + 5 = 21 \, \text{cm} \)
- Perimeter of the semicircle: \[ P_{\text{semicircle}} = \pi \times 2.5 \approx 7.85 \, \text{cm} \]
- Total perimeter: \( P_{\text{total}} = 21 + 7.85 \approx 28.85 \, \text{cm} \)
Problem 2: Missing Dimensions
Find the missing dimension of a triangle given the area and the length of one side.
- Area = 30 square units
- Base = 10 units
Steps to solve:
- Use the area formula for a triangle: \[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \]
- Substitute the known values: \[ 30 = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times h \]
- Solve for \( h \): \[ 30 = 5h \implies h = \frac{30}{5} = 6 \, \text{units} \]
Problem 3: Real-World Application
Calculate the cost to paint a rectangular wall with a window, given the cost per square meter.
- Dimensions of the wall: 12 m by 10 m
- Dimensions of the window: 2 m by 1.5 m
- Cost to paint per square meter: $15
Steps to solve:
- Calculate the area of the wall: \( A_{\text{wall}} = 12 \times 10 = 120 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Calculate the area of the window: \( A_{\text{window}} = 2 \times 1.5 = 3 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Subtract the area of the window from the area of the wall: \[ A_{\text{paintable}} = 120 - 3 = 117 \, \text{m}^2 \]
- Calculate the total cost: \[ \text{Total cost} = 117 \times 15 = 1755 \, \text{dollars} \]
These advanced problems and applications help students understand the practical uses of area and perimeter calculations in various contexts, enhancing their problem-solving skills and mathematical understanding.
Fun Activities and Games for Learning Area and Perimeter
Engaging students in fun activities and games can make learning area and perimeter both enjoyable and effective. Here are some creative ideas to help students grasp these mathematical concepts through hands-on experiences and interactive games.
-
LEGO Bricks
Use LEGO bricks to create shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. This hands-on activity not only makes learning fun but also helps students understand the practical application of these concepts.
-
Math Mosaics
Have students use sticky notes to create mosaics of various shapes. They can then calculate the area and perimeter of their mosaics, combining art with math.
-
Area and Perimeter Songs
Teach students a catchy song about area and perimeter to help them remember the formulas and when to use them. This auditory method can reinforce their understanding in a fun way.
-
Floor Tiles Activity
Use square floor tiles and blue painter’s tape to create shapes on the classroom floor. Students can then measure and calculate the area and perimeter of these shapes.
-
Pentominoes
Using pentomino blocks, students can trace shapes on grid paper and calculate their area and perimeter. This activity combines spatial reasoning with mathematical calculations.
-
Kite Building
Have students design and build their own kites. They can calculate the area and perimeter of their kite designs, and then enjoy flying them while discussing how these measurements affect flight.
-
Interior Design Project
Engage students in a project where they design a room layout, placing furniture and calculating the area and perimeter of the spaces they create. This activity demonstrates real-life applications of math.
-
City Building
In a collaborative project, students can build a miniature city and calculate the area and perimeter of each building. This can also incorporate lessons on volume and other geometric concepts.
-
Island Conquer Game
In this game, students plot points on a grid to create rectangles (islands) and then calculate the area and perimeter of each island. The student with the most island area wins.
-
Pi Plate Activity
Introduce students to the concept of circles and pi by using pie plates. They can measure the circumference and area of the plates, linking everyday objects to mathematical concepts.
-
Pizza Party
After learning about the area and perimeter of circles, have students determine which is a better deal: two small pizzas or one large pizza. This tasty activity makes math deliciously fun.
-
Tiny House Project
Give students parameters for designing a tiny house using card stock. They can then calculate the area and perimeter of each part of the house, applying their math skills to a creative project.
These activities not only help students practice their math skills but also show them the relevance of area and perimeter in everyday life.
Area and Perimeter in Real-Life Situations
Understanding area and perimeter is crucial not only for solving mathematical problems but also for a variety of real-life applications. Here are some common scenarios where these concepts are applied:
-
Construction and Architecture:
When building homes, architects and engineers use the concepts of area and perimeter to determine the space available and the materials needed. For example, the area of rooms is calculated to decide the flooring required, while the perimeter is used to estimate the length of baseboards or walls to be painted.
- Calculating the area of each room to determine flooring materials.
- Using perimeter measurements to determine the length of baseboards or trim.
-
Gardening and Landscaping:
Gardeners often need to know the area of a garden bed to buy the right amount of soil or mulch. The perimeter is essential for fencing or bordering the garden.
- Determining the amount of soil needed by calculating the area of the garden bed.
- Planning the fencing by measuring the perimeter of the garden.
-
Home Improvement:
In home improvement projects, such as tiling a floor or painting walls, both area and perimeter calculations are necessary. The area helps in estimating the number of tiles or the amount of paint required, while the perimeter can help determine the length of trim or border materials.
- Estimating the number of tiles for a floor based on its area.
- Calculating the amount of paint needed for walls by determining their area.
- Using the perimeter to determine the length of decorative trim needed.
-
Land Purchase and Agriculture:
When buying or selling land, the area is often measured in acres or square feet to determine the value. Farmers use area measurements to plan the planting of crops and to allocate resources efficiently.
- Determining the value of land by calculating its area.
- Planning crop planting based on the available area.
-
Sports and Recreation:
In sports, the area and perimeter of fields and courts are crucial for setting up games. For example, the area of a soccer field determines the space available for play, while the perimeter is used to set up boundaries and fencing.
- Setting up a soccer field by measuring its area.
- Installing boundary fences using perimeter measurements.
These examples illustrate the importance of understanding and applying area and perimeter in everyday situations, enhancing our ability to plan, execute, and manage various tasks effectively.

Interactive Area and Perimeter Exercises
Engaging students in interactive exercises helps solidify their understanding of area and perimeter concepts. Here are some detailed activities and games designed to make learning these concepts fun and effective.
-
PhET Area Builder
This interactive simulation allows students to create shapes using colorful blocks and explore the relationship between area and perimeter. Students can compare the area and perimeter of two shapes side-by-side, build shapes with a given area or perimeter, and find the area of irregular shapes by decomposing them into smaller shapes like rectangles, triangles, and squares.
-
Khan Academy Practice
Khan Academy offers various interactive exercises, including quizzes and practice problems that cover areas such as finding the area of triangles, rectangles, and composite shapes. These exercises help students identify their areas for growth and solidify their understanding through repetitive practice.
-
Math Mammoth Area and Perimeter Builder
This activity involves creating shapes with given areas and perimeters using unit squares. It helps students understand how to calculate the area by counting unit squares and explore the relationship between different shapes' areas and perimeters through interactive games.
-
LEGO Bricks Activity
Using LEGO bricks, students can build shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. This hands-on activity is engaging and helps visualize mathematical concepts in a fun and tangible way.
-
Desmos Classroom Activity
Desmos offers interactive activity builders where students can plot points to create rectangles or other shapes and calculate their area and perimeter. These activities are highly engaging and provide immediate feedback, making them ideal for classroom use.
These interactive exercises not only make learning area and perimeter enjoyable but also enhance students' problem-solving skills and understanding of mathematical concepts through practical application and visual aids.
Printable Worksheets and Resources
Printable area and perimeter worksheets are valuable resources for students to practice and reinforce their understanding of these important geometric concepts. These worksheets are designed to cover various shapes and complexities, catering to different grade levels and learning needs. Here are some detailed sections and examples:
-
Basic Shapes Worksheets
Worksheets that focus on calculating the area and perimeter of basic shapes like rectangles, squares, and triangles. These are ideal for younger students who are just beginning to learn these concepts.
- Area and perimeter of rectangles
- Area and perimeter of squares
- Area and perimeter of triangles
-
Advanced Shapes Worksheets
Worksheets that include more complex shapes such as circles, trapezoids, and polygons. These worksheets often come with step-by-step solutions to help students understand the process.
- Area and circumference of circles
- Area and perimeter of trapezoids
- Area and perimeter of polygons
-
Composite Shapes Worksheets
These worksheets require students to find the area and perimeter of composite shapes, which are made up of multiple basic shapes combined. This helps students apply their knowledge in more complex scenarios.
-
Real-World Applications
Worksheets that apply area and perimeter calculations to real-life situations, such as finding the amount of material needed for a project or the fencing required for a garden.
-
Interactive and Visual Worksheets
Interactive worksheets that use visual simulations and step-by-step guides to help students understand and solve area and perimeter problems. These worksheets often include answer keys for self-paced learning.
-
Grade-Specific Worksheets
Worksheets tailored to different grade levels, ensuring that the content is appropriate for the student's learning stage.
- 3rd Grade Area and Perimeter Worksheets
- 4th Grade Area and Perimeter Worksheets
- 5th Grade Area and Perimeter Worksheets
- 6th Grade Area and Perimeter Worksheets
- 7th Grade Area and Perimeter Worksheets
Examples of Printable Worksheets
Here are some examples of specific worksheets available for download:
- - Includes problems on calculating the area for various shapes like rectangles, triangles, and circles.
- - Interactive worksheets with detailed solutions and visual aids.
- - Comprehensive worksheets covering a range of shapes and difficulty levels.
By using these printable worksheets, students can enhance their understanding and skills in calculating area and perimeter, preparing them well for their academic assessments and real-world applications.
Online Tools and Calculators
There are numerous online tools and calculators available that can help students and teachers with area and perimeter calculations. These tools offer interactive experiences, step-by-step solutions, and are often accompanied by worksheets for additional practice. Below are some of the most useful tools and calculators for learning and practicing area and perimeter concepts:
- Interactive Area and Perimeter Calculator: This tool allows students to input the dimensions of various shapes such as rectangles, triangles, and circles, and calculates the area and perimeter automatically. It's a great way to check homework answers and understand the calculation process.
- Mathway Calculator: Mathway provides a comprehensive calculator that covers a wide range of math topics, including area and perimeter. Students can type in their own problems or use the provided examples to see step-by-step solutions.
- Live Worksheets: Live Worksheets offers interactive worksheets that can be completed online. These worksheets often include problems related to finding the area and perimeter of different shapes, and they provide instant feedback to help students learn more effectively.
- Common Core Sheets: This site offers a variety of customizable worksheets for different grade levels. Teachers and students can select specific worksheets focusing on area and perimeter, and the site provides options for both printable and online interactive versions.
Examples of Online Tools
-
Interactive Rectangle Area and Perimeter Calculator
This calculator allows you to input the length and width of a rectangle. It then calculates and displays the area and perimeter. This is particularly useful for visual learners who benefit from seeing the calculation process.
-
Live Worksheets Example
Live Worksheets provides an engaging platform where students can solve area and perimeter problems interactively. The worksheets include a variety of problems that adapt to the student's level and provide immediate feedback.
-
Common Core Area and Perimeter Sheets
Common Core Sheets offers worksheets that help students practice finding missing side lengths when given the area or perimeter. These sheets are great for reinforcing classroom learning and providing additional practice at home.
Using these online tools and calculators can enhance the learning experience by making math more interactive and accessible. They provide immediate feedback, which is crucial for effective learning and helps students understand and correct their mistakes promptly.
Teacher Resources and Lesson Plans
Providing comprehensive and engaging lesson plans for teaching area and perimeter can greatly enhance students' understanding and retention of these fundamental mathematical concepts. Here are some valuable resources and strategies for teachers:
Comprehensive Lesson Plans
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter: Start with basic definitions and visual examples. Use manipulatives like tiles or graph paper to help students grasp the concepts of area (the space inside a shape) and perimeter (the distance around a shape).
- Real-World Applications: Incorporate real-world problems such as designing a garden or planning a room layout. This helps students understand the practical applications of area and perimeter.
- Interactive Activities: Utilize interactive whiteboards and online tools to create dynamic lessons. Tools like Google SketchUp can help students create models of rooms to calculate area and perimeter.
Engaging Worksheets
Worksheets are essential for practice and assessment. Here are some types of worksheets you can use:
- Basic Calculation Worksheets: Worksheets that involve calculating the area and perimeter of basic shapes such as rectangles, squares, triangles, and circles.
- Word Problems: Worksheets with word problems that require students to apply their knowledge to solve practical problems.
- Creative Projects: Assignments like the "Haunted House Project" where students design a house and calculate the area and perimeter of different rooms.
Interactive Learning Tools
Interactive tools can make learning about area and perimeter more engaging. Consider incorporating the following:
- Online Calculators: Use online calculators to help students check their work and explore different scenarios quickly.
- Digital Games and Simulations: Games that involve building and designing with specific area and perimeter constraints can make learning fun.
- Virtual Manipulatives: Tools like virtual geoboards can help students visualize and understand the concepts of area and perimeter.
Assessment and Review
Regular assessment is crucial to ensure students are understanding the material. Use a variety of assessment methods:
- Quizzes and Tests: Standard quizzes and tests to evaluate students' grasp of area and perimeter calculations.
- Peer Teaching: Encourage students to explain concepts to each other, reinforcing their own understanding.
- Project-Based Assessments: Assess students through projects that require them to apply their knowledge in practical scenarios.
Additional Resources
Here are some recommended resources for finding lesson plans and worksheets:
- : A vast marketplace for teacher-created resources, including lesson plans and worksheets on area and perimeter.
- : Offers curated lesson plans and teaching resources reviewed by educators.
- : Provides a variety of teaching resources, including interactive activities and printable worksheets.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the difference between area and perimeter?
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of its boundary, calculated by adding the lengths of all sides. The area is the measure of the space enclosed within the shape's boundary, calculated using specific formulas depending on the shape (e.g., length × width for rectangles).
- How do you find the perimeter of a rectangle?
The perimeter of a rectangle is found by adding the lengths of all four sides. This can be simplified to the formula: \( P = 2(l + w) \), where \( l \) is the length and \( w \) is the width.
- How do you calculate the area of a triangle?
The area of a triangle is calculated using the formula: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \).
- What tools can help students learn area and perimeter?
Interactive tools and calculators, printable worksheets, and online games are excellent resources to help students learn and practice area and perimeter calculations. Websites like Math Goodies and Cuemath offer extensive resources and practice worksheets.
- Can area and perimeter be applied to real-life situations?
Yes, understanding area and perimeter is essential in many real-life scenarios, such as determining the amount of paint needed for a wall (area) or the length of fencing required for a garden (perimeter).
- What are common mistakes when calculating area and perimeter?
Common mistakes include confusing the formulas for area and perimeter, not using the same units for all measurements, and miscalculating the dimensions of the shape. Double-checking calculations and practicing with various problems can help prevent these errors.
- Where can I find printable area and perimeter worksheets?
Printable worksheets can be found on educational websites like Math Goodies and Cuemath, which offer a variety of exercises for different grade levels and complexity.
Conclusion
Learning about area and perimeter is crucial for students as these concepts have practical applications in real life, such as in construction, gardening, and interior design. Understanding how to calculate the area and perimeter helps students develop problem-solving skills and logical thinking.
The use of various resources, including printable worksheets, interactive exercises, and online tools, can significantly enhance the learning experience. These resources provide a structured approach to mastering the concepts, catering to different learning styles and promoting consistent practice.
Teachers and parents can utilize these materials to support and guide students in their learning journey. Interactive activities, real-life word problems, and engaging games make learning fun and effective. The immediate feedback from online tools and calculators helps build confidence and reinforce understanding.
In conclusion, a comprehensive approach that combines theory with practical exercises, real-life applications, and diverse resources will ensure students not only grasp the concepts of area and perimeter but also enjoy the learning process. By integrating these methods into their curriculum, educators can foster a deeper appreciation and understanding of mathematics in their students.
Hướng dẫn cách tìm chu vi và diện tích của hình hợp, ví dụ hình chữ L, trong môn hình học. Toán với Mr. J sẽ giúp bạn nắm vững khái niệm này.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích của Hình Hợp | Ví Dụ Hình Chữ L | Hình Học | Toán với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm diện tích và chu vi của hình chữ nhật. Video này sẽ giúp bạn nắm vững các bước cần thiết trong việc tính toán diện tích và chu vi hình chữ nhật.
Cách tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi của Hình Chữ Nhật