Topic how do you find the perimeter of a trapezoid: Discover how to find the perimeter of a trapezoid with our simple and straightforward guide. Whether you're a student, teacher, or geometry enthusiast, our step-by-step instructions and helpful tips will make the process easy to understand and apply. Enhance your math skills and confidence by learning the basics of trapezoid perimeter calculations today.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Trapezoid
- Introduction to Trapezoids
- Understanding the Perimeter
- Basic Formula for Perimeter
- Special Cases of Trapezoids
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Additional Tips for Accuracy
- Applications in Real Life
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích và chu vi hình thang bằng phương pháp dễ hiểu và chi tiết, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức hình học.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Trapezoid
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the total distance around the shape. To find the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of all four sides of the trapezoid.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Identify the lengths of the four sides of the trapezoid. Let these lengths be \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\).
- Add the lengths of the four sides together using the formula:
Example Calculation
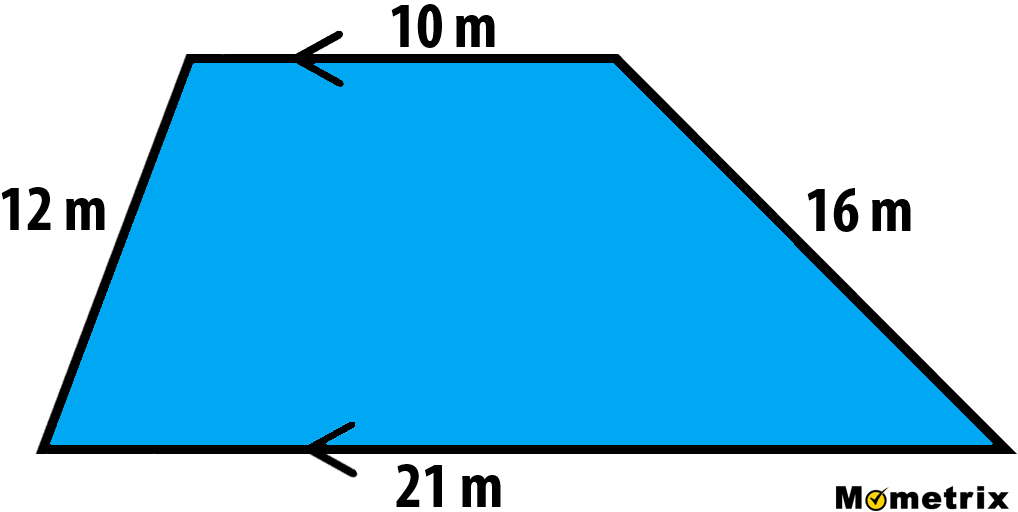
Suppose you have a trapezoid with side lengths 5 cm, 7 cm, 10 cm, and 12 cm. To find the perimeter, you would follow these steps:
- Identify the side lengths: \(a = 5 \, \text{cm}\), \(b = 7 \, \text{cm}\), \(c = 10 \, \text{cm}\), and \(d = 12 \, \text{cm}\).
- Add the side lengths together:
Therefore, the perimeter of the trapezoid is 34 cm.
Additional Tips
- Ensure you use the same units for all side lengths.
- Double-check your measurements to ensure accuracy.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Trapezoids
A trapezoid, also known as a trapezium in some regions, is a four-sided polygon with at least one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are referred to as the bases, while the non-parallel sides are called the legs.
Key characteristics of trapezoids include:
- Two parallel sides (bases)
- Two non-parallel sides (legs)
- The height (altitude), which is the perpendicular distance between the bases
Trapezoids can be classified into different types based on their properties:
- Isosceles Trapezoid: Both non-parallel sides (legs) are of equal length, and the base angles are equal.
- Right Trapezoid: Has two right angles.
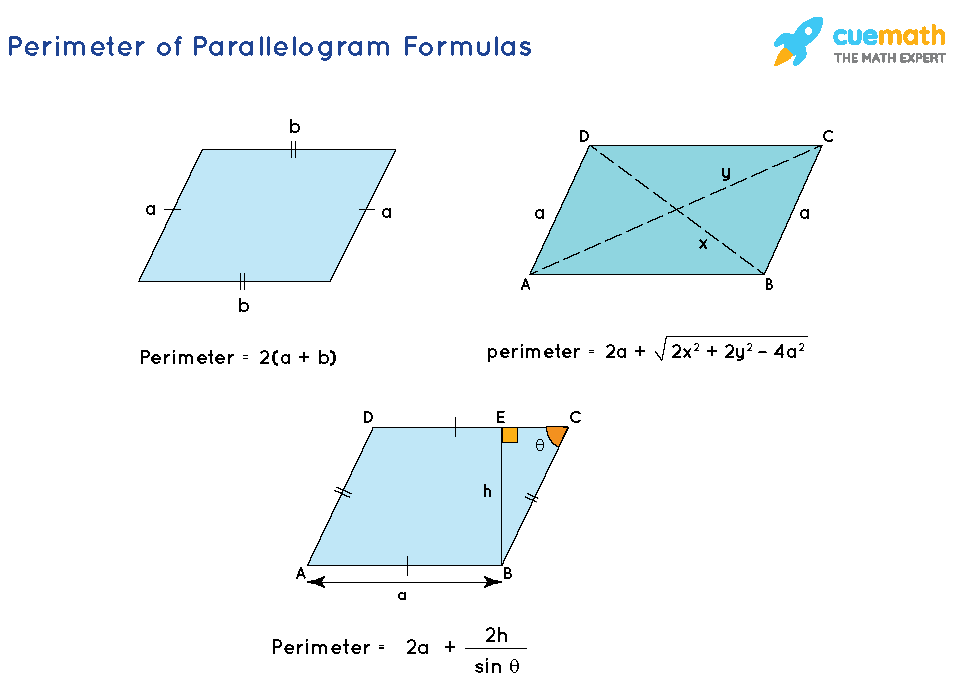
The basic formula for finding the perimeter of a trapezoid involves adding the lengths of all four sides. If the sides are labeled as \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\), the perimeter \(P\) is calculated as follows:
Understanding these fundamental aspects of trapezoids will help you easily calculate their perimeters and apply this knowledge to various mathematical problems.
Understanding the Perimeter
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the total length around the figure. Calculating the perimeter involves summing the lengths of all four sides. This measurement is essential in various practical applications, such as determining the boundary length of land plots or the frame length required for construction projects.
To understand the perimeter calculation better, let's consider the following key points:
- The two parallel sides are known as the bases. We'll label them as \(a\) and \(b\).
- The non-parallel sides are known as the legs. We'll label them as \(c\) and \(d\).
- The perimeter \(P\) is the sum of the lengths of all four sides.
The formula to calculate the perimeter \(P\) of a trapezoid is:
Let's break this down step by step:
- Measure the Lengths: Accurately measure the lengths of all four sides of the trapezoid. Use a ruler or measuring tape for precision.
- Label the Sides: Assign labels to the sides as \(a\), \(b\), \(c\), and \(d\). Typically, \(a\) and \(b\) are the parallel sides (bases), and \(c\) and \(d\) are the non-parallel sides (legs).
- Sum the Lengths: Add the lengths of all four sides using the formula:
For example, if the lengths of the sides are 6 cm, 8 cm, 5 cm, and 7 cm, then the perimeter is calculated as follows:
Thus, the perimeter of the trapezoid is 26 cm. Understanding and applying this basic concept is crucial for accurately determining the perimeter of any trapezoid.
Basic Formula for Perimeter
The perimeter of a trapezoid is the total length around the figure. To find the perimeter, you need to add the lengths of all four sides. Here's a step-by-step guide to using the basic formula:
- Identify the Sides: Label the four sides of the trapezoid. Typically, the two parallel sides are called the bases and are labeled as \(a\) and \(b\). The other two sides are called the legs and are labeled as \(c\) and \(d\).
- Measure the Sides: Use a ruler or measuring tape to find the lengths of all four sides. Make sure to measure accurately and use the same units for all sides.
- Apply the Formula: The formula for the perimeter \(P\) of a trapezoid is given by:
Let's break this down with an example:
- Example Values: Suppose we have a trapezoid with the following side lengths:
- Base 1 (\(a\)): 8 cm
- Base 2 (\(b\)): 6 cm
- Leg 1 (\(c\)): 5 cm
- Leg 2 (\(d\)): 7 cm
- Plug in the Values: Using the formula, we get:
- Calculate the Perimeter: Adding these values together:
Thus, the perimeter of the trapezoid is 26 cm. This straightforward formula can be applied to any trapezoid as long as the side lengths are known. Always ensure your measurements are accurate and in the same units to get the correct perimeter.
Special Cases of Trapezoids
While the basic formula for calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid is straightforward, certain special cases require additional considerations. Here are some special cases and how to handle them:
1. Isosceles Trapezoid
An isosceles trapezoid has non-parallel sides (legs) that are equal in length. This property can simplify the perimeter calculation:
- Identify the Sides: Let the parallel sides (bases) be \(a\) and \(b\), and the equal legs be \(c\) (where \(c = d\)).
- Perimeter Formula:
2. Right Trapezoid
A right trapezoid has two right angles. This type of trapezoid can be easier to work with due to its predictable angles:
- Identify the Sides: Let the bases be \(a\) and \(b\), and the legs be \(c\) and \(d\) (one of which will form a right angle with one of the bases).
- Perimeter Formula: The perimeter is still the sum of all sides:
3. Trapezoid with Equal Bases
In some cases, the trapezoid might have equal length bases, making it look more like a parallelogram:
- Identify the Sides: Let the bases both be \(a\) (so \(a = b\)), and the legs be \(c\) and \(d\).
- Perimeter Formula: Simplify the formula by combining the equal bases:
Understanding these special cases can help simplify the process of calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid. By recognizing these patterns, you can apply the most efficient method to determine the perimeter accurately.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid, there are several common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Here are the most frequent errors and how to avoid them:
- Incorrectly Identifying the Sides:
Ensure you correctly identify all four sides of the trapezoid. Remember that the bases are the parallel sides, labeled as \(a\) and \(b\), and the non-parallel sides are the legs, labeled as \(c\) and \(d\).
- Mixing Up Units:
Always use the same units of measurement for all sides. Mixing units (e.g., centimeters and inches) will result in incorrect calculations. Convert all measurements to the same unit before performing the addition.
- Incorrect Measurements:
Double-check your measurements to ensure accuracy. Use precise tools like a ruler or measuring tape and measure each side carefully.
- Forgetting to Add All Sides:
It's easy to overlook one of the sides when calculating the perimeter. Make sure to include all four sides in your calculation:
- Misinterpreting Special Cases:
Be aware of special cases such as isosceles or right trapezoids, as they may have properties that can simplify the calculation. Ensure you understand these properties and apply them correctly.
- Rounding Errors:
If measurements involve decimals, avoid premature rounding. Perform the addition with full precision and round only the final result if necessary.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can ensure accurate and reliable calculations of the trapezoid's perimeter. Taking the time to double-check each step will help avoid errors and achieve correct results.
Additional Tips for Accuracy
Ensuring accuracy when calculating the perimeter of a trapezoid involves careful measurement and precise arithmetic. Here are some additional tips to help you achieve the most accurate results:
- Double-Check Measurements: Measure each side of the trapezoid twice to confirm the lengths. Small errors in measurement can lead to incorrect perimeter calculations.
- Use a Reliable Measuring Tool: Utilize a high-quality ruler or measuring tape to ensure precision. Digital measuring tools can provide more accurate readings.
- Verify Right Angles: For trapezoids with right angles, ensure the angles are exactly 90 degrees. Even slight deviations can affect the accuracy of your measurements.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: If the trapezoid has irregular sides or angles, consider breaking it down into simpler shapes. Calculate the perimeter of these simpler shapes and then combine the results.
- Check for Parallel Sides: Confirm that the two bases of the trapezoid are truly parallel. Non-parallel sides can indicate an error in shape identification, leading to inaccurate calculations.
- Use Mathematical Tools: Employ geometric formulas and tools like the Pythagorean theorem to verify side lengths, especially if you only have partial measurements.
- Account for Units: Ensure all measurements are in the same unit. Convert measurements if necessary to avoid discrepancies in the final calculation.
- Utilize Software: Use geometry software or online calculators designed for trapezoid perimeter calculations to double-check your manual calculations.
- Review and Revise: After calculating the perimeter, review each step and measurement. Revising your work can help catch and correct any mistakes.
- Consider the Context: In practical applications, consider any external factors that might affect measurements, such as temperature changes causing expansion or contraction of materials.
Applications in Real Life
The perimeter of a trapezoid is a concept that finds numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some real-life examples and uses:
- Architecture and Construction:
Trapezoidal shapes are often used in architectural designs, such as roofs, bridges, and windows. Knowing the perimeter is essential for estimating materials needed for construction and ensuring structural integrity.
- Landscaping:
In landscaping, trapezoidal plots are common. Calculating the perimeter helps in planning fencing, pathways, and planting areas. It ensures accurate measurement for resource allocation.
- Manufacturing:
Manufacturing processes often involve creating parts with trapezoidal shapes. Knowing the perimeter helps in material cutting and minimizing waste, leading to cost-efficient production.
- Fashion and Textile Industry:
Designers use trapezoidal patterns in clothing and accessories. Calculating the perimeter is crucial for cutting fabric correctly and creating well-fitting garments.
- Urban Planning:
Urban planners use trapezoidal shapes in designing parks, parking lots, and recreational areas. Accurate perimeter calculations ensure proper layout and space utilization.
- Art and Design:
Artists and designers use trapezoids in their work to create unique geometric patterns and structures. Calculating the perimeter helps in framing and presenting artworks appropriately.
These applications highlight the importance of understanding and accurately calculating the perimeter of trapezoids in various professional and everyday contexts. Whether it's for practical construction or creative design, mastering this concept is valuable across different disciplines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, finding the perimeter of a trapezoid is a straightforward process once you know the lengths of all its sides. The formula for the perimeter is the sum of all four sides:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d
\]
where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the parallel sides (bases), and \(c\) and \(d\) are the lengths of the non-parallel sides (legs).
Understanding how to accurately measure and sum the sides is crucial for various practical applications, from construction to design. The perimeter calculation helps in determining the boundary length, which is essential in planning and resource allocation.
By mastering the steps to calculate the perimeter, you can avoid common mistakes and ensure precise measurements, enhancing both your mathematical skills and practical problem-solving abilities. Whether for academic purposes or real-life projects, knowing how to find the perimeter of a trapezoid is an invaluable tool in your geometry toolkit.

Video hướng dẫn cách tìm diện tích và chu vi hình thang bằng phương pháp dễ hiểu và chi tiết, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức hình học.
Cách Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi Hình Thang
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi hình thang một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu, giúp bạn nắm vững kiến thức hình học.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Thang