Topic how to find the perimeter of a half circle: Discover the simple steps to find the perimeter of a half circle with our comprehensive guide. Learn the essential formula, follow easy calculations, and explore practical examples to master this geometric concept. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, this article will make understanding the perimeter of a half circle effortless and enjoyable.
Table of Content
- Finding the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Introduction to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Understanding the Basic Concepts
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
- Components of the Formula
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Example Calculations
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practical Applications
- Advanced Considerations
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi nửa hình tròn. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ công thức và cách áp dụng vào các bài toán thực tế.
Finding the Perimeter of a Half Circle
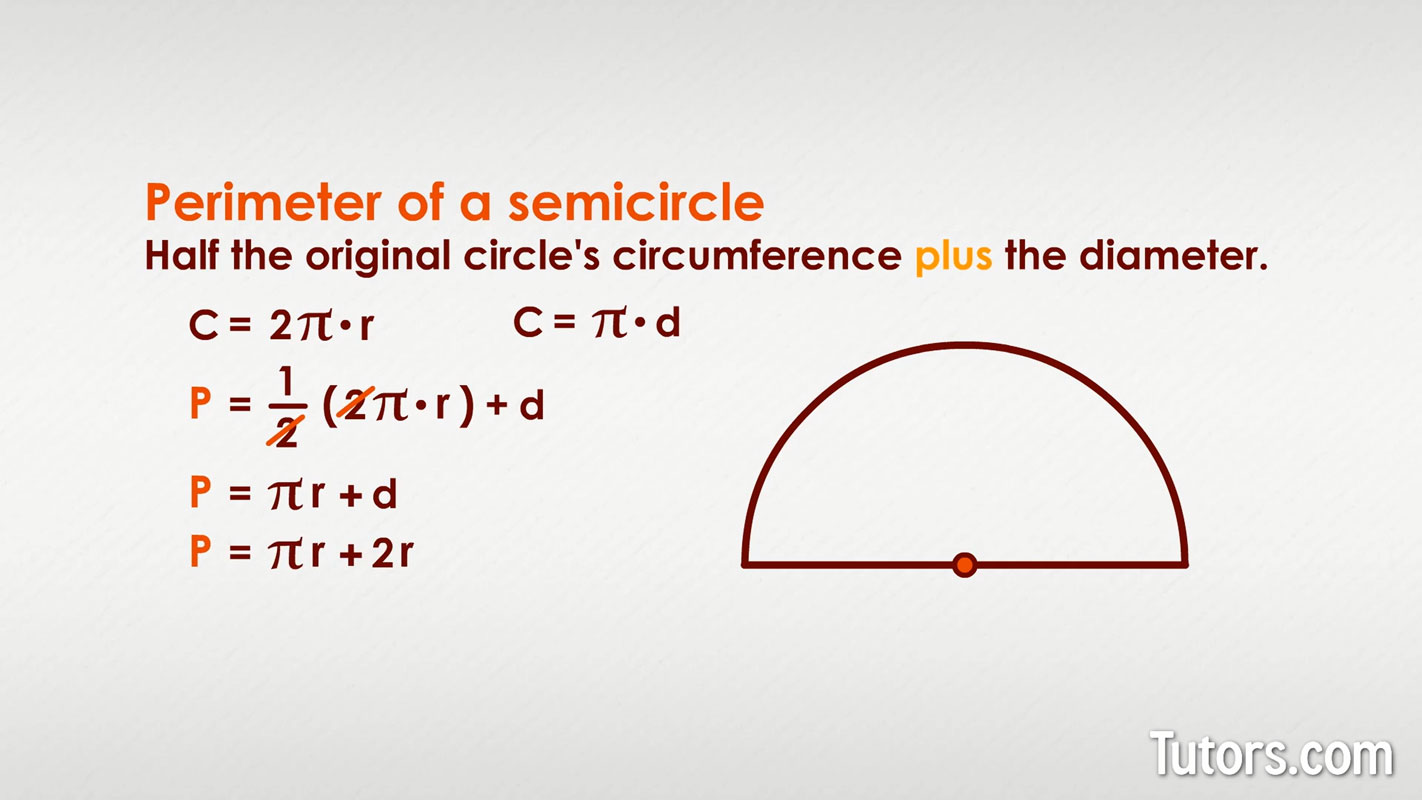
The perimeter of a half circle includes the curved part of the half circle and the diameter. The formula for finding the perimeter (or circumference) of a half circle is as follows:
Formula
The perimeter \( P \) of a half circle can be found using the formula:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
where:
- \( \pi \) is a constant (approximately 3.14159)
- \( r \) is the radius of the circle
This formula combines the half circumference of the full circle and the diameter (which is twice the radius).
Steps to Calculate
- Determine the radius \( r \) of the half circle.
- Calculate the half circumference using \( \frac{\pi r}{2} \).
- Calculate the diameter using \( 2r \).
- Add the half circumference and the diameter together.
Example Calculation
For a half circle with a radius of 5 units:
- Radius \( r = 5 \)
- Half circumference \( = \frac{\pi \times 5}{2} = 2.5\pi \)
- Diameter \( = 2 \times 5 = 10 \)
- Perimeter \( P = 2.5\pi + 10 \approx 3.14159 \times 2.5 + 10 \approx 7.854 + 10 = 17.854 \) units
Conclusion
To find the perimeter of a half circle, you need to add the length of the curved part (half the circumference of the full circle) to the length of the diameter. This can be quickly done using the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \).

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Perimeter of a Half Circle
Understanding the perimeter of a half circle is an essential part of geometry. A half circle, also known as a semicircle, is simply a circle divided into two equal parts. The perimeter of a half circle includes the length of the curved edge and the diameter, which is the straight edge.
To calculate the perimeter of a half circle, we need to consider two main components:
- The curved part, which is half of the circumference of the full circle.
- The straight part, which is the diameter of the circle.
The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a half circle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Where:
- \( \pi \) is approximately 3.14159
- \( r \) is the radius of the circle
This formula effectively combines half the circumference (\( \pi r \)) with the diameter (\( 2r \)), giving a complete measurement of the boundary of the half circle.
In the next sections, we will delve into detailed steps for calculating this perimeter, explore practical examples, and highlight common mistakes to avoid.
Understanding the Basic Concepts
A semicircle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that represents half of a circle. To understand the basic concepts related to the perimeter of a semicircle, it is important to familiarize yourself with some fundamental terms and properties.
- Circle: A set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point called the center.
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference.
- Diameter (d): The distance across the circle, passing through the center, equal to twice the radius (d = 2r).
- Perimeter of a Circle: The total distance around the circle, calculated as 2πr.
- Semicircle: Half of a circle, formed by cutting a whole circle along its diameter.
When discussing the perimeter of a semicircle, it is essential to understand that it includes both the curved part of the semicircle and the straight edge (the diameter).
Formula for the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The formula for the perimeter (P) of a semicircle combines the length of the curved edge with the diameter:
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle: 2πr
- Since the semicircle is half of the circle, the curved edge is: πr
- Add the diameter to account for the straight edge: P = πr + d
Given that the diameter (d) is twice the radius (r), the formula can also be expressed as:
P = πr + 2r or P = r(π + 2)
Example Calculation
Let's calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 cm:
- Curved edge: πr = π * 7
- Straight edge (diameter): 2r = 2 * 7 = 14
- Total perimeter: P = π * 7 + 14
- Using π ≈ 3.14, we get: P ≈ 3.14 * 7 + 14 ≈ 21.98 + 14 ≈ 35.98 cm
Thus, the perimeter of the semicircle is approximately 35.98 cm.
Understanding these basic concepts and the formula will help you accurately calculate the perimeter of a semicircle in various practical applications.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Half Circle
The perimeter of a half circle, also known as the semicircle, involves both the curved part of the semicircle and the diameter. The formula for finding the perimeter of a half circle is derived from the perimeter of a full circle and its diameter.
The formula is given by:
Perimeter of a semicircle, \( P \), can be calculated using the following formula:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
where:
- \( \pi \) (Pi) is approximately 3.14 or \(\frac{22}{7}\)
- \( r \) is the radius of the circle
This formula combines the length of the curved part of the semicircle, which is half the circumference of the full circle, and the diameter of the circle.
To break it down:
- The circumference of a full circle is \( 2\pi r \)
- Half of this circumference (the curved part of the semicircle) is \( \pi r \)
- The diameter of the circle, which is \( 2r \), needs to be added to the curved part to get the full perimeter
Thus, the total perimeter of the semicircle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
This formula ensures that both the curved and straight parts of the semicircle's boundary are accounted for.
Components of the Formula
The formula for finding the perimeter of a half circle, also known as a semicircle, includes two main components:
- The Curved Part: This is half the circumference of the full circle.
- The Diameter: This is the straight line that cuts the circle into two equal halves.
Given these components, the formula for the perimeter (P) of a semicircle is expressed as:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
Where:
- \( \pi \) (Pi) is approximately 3.14159.
- \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle.
This formula can also be written in terms of the diameter (d) since the diameter is twice the radius:
\( P = \left( \frac{1}{2} \pi d \right) + d \)
Here:
- \( d \) is the diameter of the semicircle.
By breaking it down:
- Curved Part Calculation: The length of the curved part of the semicircle is half the circumference of the full circle, which is \( \pi r \).
- Diameter Calculation: The straight line across the semicircle is the diameter, which is \( 2r \).
Combining these two components, we get the total perimeter:
\( P = \pi r + 2r = r (\pi + 2) \)
This comprehensive understanding of the components helps in accurately calculating the perimeter of a semicircle.

Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the perimeter of a half circle, follow these steps:
-
Determine the radius of the semicircle:
The radius (r) is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. If you are given the diameter (d), you can find the radius by dividing the diameter by 2.
r = \frac{d}{2} -
Calculate the perimeter of the curved part:
The curved part of the semicircle is half of the circle's circumference. The circumference of a full circle is
2 \pi r, so the curved part of the semicircle is:\text{Curved Part} = \pi r -
Add the diameter to the curved part:
The total perimeter of the semicircle includes the curved part plus the diameter of the circle.
\text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r
Therefore, the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle is:
\text{Perimeter} = r(\pi + 2)
Let's go through an example calculation:
Example:
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 5 cm.
-
Given radius,
r = 5cm. -
Calculate the curved part:
\pi r = \pi \times 5 = 5\picm -
Add the diameter:
\text{Diameter} = 2 \times 5 = 10cm\text{Perimeter} = 5\pi + 10cm
So, the perimeter of the semicircle is 5\pi + 10 cm, which is approximately 25.7 cm when using \pi \approx 3.14.
Example Calculations
To understand how to find the perimeter of a half circle, let's go through some example calculations.
Example 1: Half Circle with Radius 5 units
Given: Radius \( r = 5 \) units
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \):
\( C = 2\pi \times 5 = 10\pi \) units
- Since we need the perimeter of a half circle, divide the circumference by 2:
\( \frac{C}{2} = \frac{10\pi}{2} = 5\pi \) units
- Add the diameter (which is twice the radius) to the half circumference:
Diameter \( D = 2r = 2 \times 5 = 10 \) units
Perimeter \( P = 5\pi + 10 \) units
Therefore, the perimeter of the half circle is \( 5\pi + 10 \) units.
Example 2: Half Circle with Radius 8 units
Given: Radius \( r = 8 \) units
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle:
\( C = 2\pi r = 2\pi \times 8 = 16\pi \) units
- Divide the circumference by 2:
\( \frac{C}{2} = \frac{16\pi}{2} = 8\pi \) units
- Add the diameter to the half circumference:
Diameter \( D = 2r = 2 \times 8 = 16 \) units
Perimeter \( P = 8\pi + 16 \) units
Therefore, the perimeter of the half circle is \( 8\pi + 16 \) units.
Example 3: Half Circle with Radius 3.5 units
Given: Radius \( r = 3.5 \) units
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Calculate the circumference of the full circle:
\( C = 2\pi r = 2\pi \times 3.5 = 7\pi \) units
- Divide the circumference by 2:
\( \frac{C}{2} = \frac{7\pi}{2} = 3.5\pi \) units
- Add the diameter to the half circumference:
Diameter \( D = 2r = 2 \times 3.5 = 7 \) units
Perimeter \( P = 3.5\pi + 7 \) units
Therefore, the perimeter of the half circle is \( 3.5\pi + 7 \) units.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a half circle, there are several common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Being aware of these can help ensure accurate calculations.
- Confusing the Perimeter with Half the Circumference:
A common error is to assume that the perimeter of a half circle is simply half the circumference of the full circle. While the curved part is indeed half the circumference, you must also add the diameter of the circle to account for the straight edge.
Formula: \( P = \pi r + 2r \)
- Incorrect Use of Diameter and Radius:
Sometimes, the diameter is used in place of the radius or vice versa. Remember that the diameter is twice the radius \( (d = 2r) \). Using the wrong value can significantly affect your result.
- Forgetting Units:
It's essential to keep track of units throughout the calculation. If the radius is given in centimeters, the perimeter will also be in centimeters. Ensure consistency in units to avoid errors.
- Misapplication of Pi:
Ensure you use the correct value for π (Pi). The most commonly used approximations are \( \pi \approx 3.14 \) or \( \pi \approx \frac{22}{7} \). Using an incorrect value can lead to significant discrepancies.
- Rounding Errors:
Rounding intermediate steps too early can introduce errors. For precise calculations, carry as many decimal places as possible through the calculation and only round the final result.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can more accurately determine the perimeter of a half circle and ensure your calculations are correct.
Practical Applications
The perimeter of a half circle is an important geometric measurement with numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some common applications:
-
Architecture and Engineering:
Architects and engineers frequently use the properties of semicircles in their designs. For example, semicircular arches are often used in bridges and buildings to provide structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Calculating the perimeter helps in determining the amount of materials needed for construction.
-
Urban Planning:
In urban planning, semicircular designs are used in the layout of parks, roundabouts, and amphitheaters. Understanding the perimeter is crucial for planning pathways, seating arrangements, and landscaping.
-
Recreational Equipment:
Designers of recreational equipment such as tracks for sports facilities, playgrounds, and skate parks often incorporate semicircular shapes. Knowing the perimeter aids in creating accurate and safe designs.
-
Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, especially in creating tools and machinery components, semicircular parts are common. Calculating the perimeter is essential for precision cutting, fitting, and assembly.
-
Art and Design:
Artists and designers use semicircles in various creative works, from sculptures to graphic designs. The perimeter measurement helps in achieving symmetry and balance in their creations.
Let's consider an example to understand the practical application better:
Example: Designing a Semicircular Garden
Imagine you are designing a semicircular garden with a diameter of 10 meters. You need to calculate the perimeter to determine the length of the fence required to enclose the garden.
- First, find the radius of the semicircle:
Radius = \(\frac{diameter}{2} = \frac{10 \, \text{meters}}{2} = 5 \, \text{meters}\)
- Next, calculate the length of the curved edge (half the circumference of a full circle):
Curved edge = \(\pi \times \text{radius} = \pi \times 5 \, \text{meters} \approx 15.71 \, \text{meters}\)
- Then, add the diameter to the curved edge to find the total perimeter:
Perimeter = Curved edge + Diameter = 15.71 \, \text{meters} + 10 \, \text{meters} = 25.71 \, \text{meters}
Therefore, you would need approximately 25.71 meters of fencing to enclose the semicircular garden. Understanding the perimeter calculation ensures you have the right amount of materials and can plan your garden layout effectively.
Advanced Considerations
When dealing with the perimeter of a half circle, there are several advanced considerations that can enhance understanding and application of the concept. These include detailed exploration of formulas, understanding nuances in calculations, and recognizing special cases.
Detailed Exploration of Formulas
The basic formula for the perimeter of a half circle is:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
Where:
- \( P \) is the perimeter
- \( r \) is the radius
- \( \pi \) (Pi) is approximately 3.14159
Nuances in Calculations
It is important to recognize that the perimeter of a semicircle includes both the curved part (half the circumference of a full circle) and the diameter. This means that:
- Half the circumference: \( \pi r \)
- Diameter: \( 2r \)
Thus, the total perimeter is the sum of these two components.
Additionally, when given different measurements (such as the diameter instead of the radius), the formula can be adjusted accordingly. For instance, if the diameter \( d \) is given, since \( d = 2r \), the formula can be rewritten as:
\[ P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \]
Special Cases and Applications
In some advanced problems, you might encounter semicircles in various orientations or combined with other geometric shapes. For example:
- Semicircles on a common diameter: If two semicircles share the same diameter, the total perimeter would be the sum of the perimeters of the individual semicircles minus the shared diameter.
- Semicircles inscribed in or circumscribed around other shapes: Calculating the perimeter in these cases might involve additional geometric properties and relationships.
Using Calculus for Perimeter
In higher mathematics, calculus can be used to derive the perimeter of a semicircle more rigorously. This involves integrating the arc length of the semicircle:
\[ \text{Arc Length} = \int_{-r}^{r} \sqrt{1 + \left( \frac{dy}{dx} \right)^2} \, dx \]
For a semicircle defined by the equation \( y = \sqrt{r^2 - x^2} \), the above integral evaluates to \( \pi r \), confirming the formula for the curved part of the perimeter.
Perimeter with Respect to Area
Sometimes, the problem may provide the area of the semicircle instead of the radius. The area \( A \) of a semicircle is given by:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 \]
Solving for \( r \) in terms of \( A \):
\[ r = \sqrt{\frac{2A}{\pi}} \]
Substituting this \( r \) back into the perimeter formula:
\[ P = \pi \left( \sqrt{\frac{2A}{\pi}} \right) + 2 \left( \sqrt{\frac{2A}{\pi}} \right) \]
This allows for perimeter calculations when only the area is known.
Conclusion
Understanding these advanced considerations helps in solving complex problems involving semicircles, ensuring accurate calculations and deeper comprehension of geometric properties.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính chu vi nửa hình tròn. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ công thức và cách áp dụng vào các bài toán thực tế.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tìm chu vi hình bán nguyệt từ đường kính và bán kính trong video này. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Tìm Chu Vi Hình Bán Nguyệt từ Đường Kính và Bán Kính | Hình Học