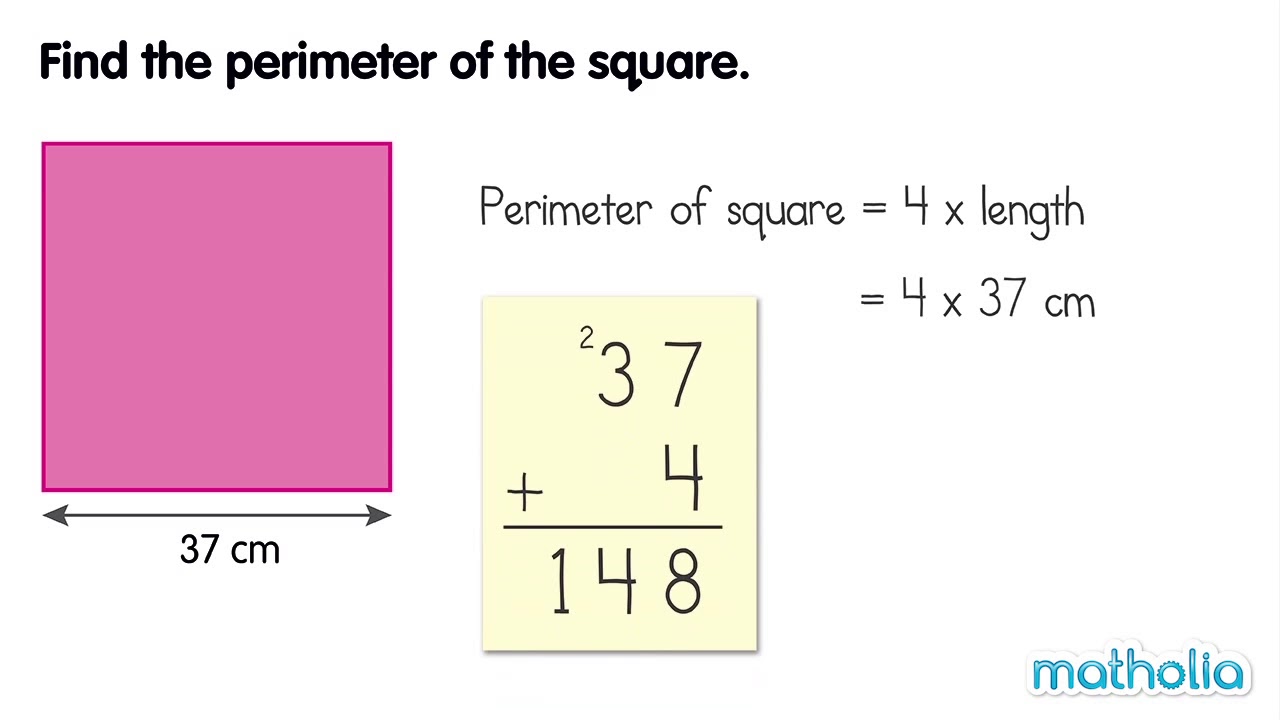
Topic how do i find perimeter of a square: Discover the easiest ways to calculate the perimeter of a square with our comprehensive guide. Whether you're a student, teacher, or simply curious, learn step-by-step methods and practical examples to accurately find the perimeter of any square. Start mastering this essential math skill today!
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Square
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
- Understanding the Perimeter
- Basic Properties of a Square
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Example Calculations
- Applications in Real Life
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Advanced Concepts
- Perimeter of Composite Shapes
- Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE:
How to Find the Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all its four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, finding the perimeter is straightforward. Here’s a comprehensive guide to calculating the perimeter of a square.
Perimeter Formula
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a square is:
where s is the length of one side of the square.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply the length of the side by 4.
- The result is the perimeter of the square.
Example Calculation
Let's say the side length of a square is 5 cm. Using the perimeter formula:
So, the perimeter of the square is 20 cm.
Applications
Knowing how to calculate the perimeter of a square is useful in various real-life situations, such as:
- Determining the length of the fencing needed for a square garden.
- Calculating the border length for a square-shaped artwork.
- Planning the layout for square tiles on a floor.
Conclusion
Calculating the perimeter of a square is a simple but essential mathematical skill. By understanding and applying the formula P = 4s, you can quickly find the perimeter for any square, whether in practical applications or academic exercises.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of its boundary, calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides. Since all sides of a square are equal, finding the perimeter is straightforward and essential for various practical applications. Understanding how to determine the perimeter helps in fields like geometry, construction, and art.
Here are the fundamental concepts:
- Definition: The perimeter of a square is the sum of the lengths of its four sides.
- Properties: A square has four equal sides and four right angles.
- Formula: The formula to find the perimeter (P) of a square is:
where s represents the length of one side of the square.
- Measure the Side Length: Determine the length of one side of the square using a ruler or any measuring tool.
- Apply the Formula: Multiply the measured side length by 4 to get the perimeter.
- Example Calculation: If one side of the square is 5 cm, then:
This means the perimeter of the square is 20 cm.
Calculating the perimeter of a square is a fundamental skill that can be applied in various scenarios, from academic exercises to real-world applications such as determining the length of a fence needed for a square garden or the amount of trim required to frame a square picture.
Understanding the Perimeter
Perimeter is a fundamental concept in geometry that refers to the total length of the boundaries of a two-dimensional shape. For a square, the perimeter is particularly easy to calculate due to its equal sides.
Here are key points to understand the perimeter of a square:
- Definition: The perimeter of a square is the total distance around the outside of the square. It is the sum of the lengths of all four sides.
- Properties of a Square:
- All four sides are of equal length.
- Each of the four angles is a right angle (90 degrees).
- Perimeter Formula:
where s is the length of one side of the square.
Understanding how to use this formula is essential. Here's a step-by-step process:
- Measure One Side: Use a ruler or another measuring tool to determine the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply by Four: Since all sides of a square are equal, multiply the length of one side by four to get the perimeter.
- Example Calculation: If the side length of the square is 7 cm, the perimeter calculation is:
This means the perimeter of the square is 28 cm.
The concept of perimeter is not only confined to squares but also extends to other polygons and shapes. For each shape, the perimeter is calculated based on the sum of its side lengths. However, for squares, the calculation is straightforward due to their equal sides.
Understanding the perimeter is crucial for various practical applications, such as:
- Calculating the amount of material needed to frame a square picture or tile a square area.
- Determining the length of fencing required to enclose a square garden.
- Planning layouts in construction and design projects where square dimensions are involved.
Mastering the concept of perimeter provides a strong foundation for further geometric studies and practical problem-solving in everyday life.
Basic Properties of a Square
A square is a special type of quadrilateral with unique properties that distinguish it from other shapes. Understanding these properties is essential for calculating the perimeter and solving various geometric problems.
Here are the basic properties of a square:
- Equal Sides: All four sides of a square are of equal length. This is one of the defining characteristics of a square.
- Right Angles: Each of the four angles in a square is a right angle, measuring 90 degrees.
- Parallel Sides: Opposite sides of a square are parallel to each other.
- Diagonals:
- Diagonals of a square are equal in length.
- They bisect each other at right angles (90 degrees).
- Each diagonal divides the square into two congruent isosceles right triangles.
- Symmetry:
- A square has four lines of symmetry.
- It is rotationally symmetric about its center, with a rotation of 90 degrees preserving the shape.
The combination of these properties makes the square a highly regular and symmetrical shape. These characteristics simplify many calculations and provide a strong foundation for understanding more complex geometric concepts.
To visualize these properties, consider a square with side length s. The perimeter (P) of the square can be calculated using the formula:
For example, if s is 6 cm, then:
This means the perimeter of the square is 24 cm.
Understanding the basic properties of a square is crucial for various real-life applications, such as:
- Designing square-shaped objects or spaces.
- Calculating materials needed for construction and crafts involving square shapes.
- Solving mathematical problems related to area, perimeter, and symmetry.
By mastering these properties, you can confidently tackle both academic and practical challenges involving squares.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Finding the perimeter of a square involves a straightforward process that can be followed step by step. Below is a detailed guide to calculating the perimeter of a square.
- Measure the Side Length:
- Apply the Perimeter Formula:
- Perform the Multiplication:
- Verify Your Result:
First, measure the length of one side of the square. This length will be referred to as s. Ensure that the measurement is accurate, using a ruler or any other measuring tool. For example, let's say the side length is 6 cm.
The formula for the perimeter (P) of a square is:
Where s is the side length of the square. Substitute the measured side length into the formula. For our example, it becomes:
Multiply the side length by 4 to get the perimeter. Using our example, the calculation is:
This means the perimeter of the square is 24 cm.
Double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy. It is important to verify the length of the side and the multiplication to confirm the perimeter.
Here’s a summary of the step-by-step calculation:
- Measure the length of one side (s).
- Use the formula:
- Multiply the side length by 4.
- Verify your result.
By following these steps, you can accurately determine the perimeter of any square. This method is essential for solving mathematical problems and practical applications, such as determining the amount of material needed for construction projects or understanding spatial layouts.

Example Calculations
Here are some example calculations to help you understand how to find the perimeter of a square:
-
Example 1: Simple Calculation
If the side length of a square is 8 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 4 \times \text{side}
\]Substituting the given side length:
\[
P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \text{ cm}
\] -
Example 2: Given Perimeter, Find Side Length
If the perimeter of a square is 60 meters, the side length \( s \) can be found by rearranging the perimeter formula:
\[
s = \frac{P}{4}
\]Substituting the given perimeter:
\[
s = \frac{60}{4} = 15 \text{ m}
\] -
Example 3: Using Area to Find Perimeter
If the area of a square is 49 square inches, the side length \( s \) is:
\[
s = \sqrt{\text{Area}}
\]Substituting the given area:
\[
s = \sqrt{49} = 7 \text{ inches}
\]Now, use the side length to find the perimeter:
\[
P = 4 \times s = 4 \times 7 = 28 \text{ inches}
\] -
Example 4: Using Diagonal to Find Perimeter
If the diagonal of a square is 10 cm, the side length \( s \) can be found using:
\[
s = \frac{\text{Diagonal}}{\sqrt{2}}
\]Substituting the given diagonal:
\[
s = \frac{10}{\sqrt{2}} \approx 7.07 \text{ cm}
\]Now, use the side length to find the perimeter:
\[
P = 4 \times s \approx 4 \times 7.07 \approx 28.28 \text{ cm}
\]
By following these steps, you can find the perimeter of a square in various scenarios.
Applications in Real Life
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry with numerous practical applications in various fields. Understanding how to calculate and utilize the perimeter can be beneficial in everyday situations and professional contexts.
-
Architecture and Construction
Architects and construction workers frequently use the perimeter of squares to determine the lengths of materials needed for projects. For example:
- Calculating the length of the boundary fence around a square garden or plot of land.
- Determining the amount of trim or molding required for a square room.
-
Interior Design
Interior designers often use perimeter calculations to plan room layouts and furnishings. For example:
- Measuring the perimeter of a square room to install baseboards or carpet edging.
- Ensuring that furniture arrangements do not exceed the available wall space.
-
Landscaping
Landscapers use perimeter measurements to design and layout garden beds, patios, and other outdoor features. For example:
- Designing a square patio and determining the amount of pavers required.
- Planning the edging materials needed for a square flower bed.
-
Education
Teachers and students use perimeter calculations in mathematics education to build a foundation for understanding more complex geometric concepts. For example:
- Solving problems involving the perimeter of squares to strengthen mathematical skills.
- Using perimeter calculations in practical classroom activities and projects.
-
Sports and Recreation
In sports and recreational activities, understanding the perimeter of square areas is essential for planning and executing various activities. For example:
- Marking the boundary lines of a square playing field or court.
- Calculating the length of a track around a square sports field.
-
Home Improvement
Homeowners frequently use perimeter calculations for DIY projects and home improvement tasks. For example:
- Installing a square deck or patio and determining the amount of railing needed.
- Calculating the materials required for building a square shed or gazebo.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a square, several common mistakes can occur. Being aware of these can help ensure accuracy and a better understanding of the concept.
- Confusing Perimeter with Area
One of the most common mistakes is confusing the perimeter with the area of a square. Remember, the perimeter is the total distance around the square, calculated as \(4 \times \text{side}\), while the area is the space within the square, calculated as \(\text{side}^2\).
- Incorrect Addition of Sides
Sometimes, students mistakenly add the sides incorrectly. Since a square has four equal sides, the correct way to find the perimeter is to multiply one side length by 4, rather than adding unequal or incorrect side lengths.
- Mixing Units of Measurement
Always ensure that all side lengths are in the same units before calculating the perimeter. Mixing units (e.g., inches with centimeters) without proper conversion can lead to incorrect results. Convert all measurements to the same unit first.
- Neglecting the Commutative Property
While the order of addition doesn’t matter due to the commutative property of addition, neglecting to account for all four sides can lead to errors. Ensure all four sides are included in the calculation.
- Misinterpreting Problem Statements
Word problems can sometimes be tricky. Carefully read the problem to ensure you’re interpreting the side lengths and required calculations correctly. If a problem provides the area and asks for the perimeter, remember to first find the side length by taking the square root of the area.
- Incorrect Application of Formulas
Ensure the correct formula is applied for the given problem. For example, when given the diagonal, use the specific formula for perimeter involving the diagonal, which is \( P = 2\sqrt{2} \times \text{diagonal} \).
- Neglecting Units in the Final Answer
Always include the correct units in your final answer. Whether the measurement is in meters, centimeters, inches, or another unit, specifying this is crucial for clarity and correctness.
Avoiding these common mistakes will help ensure accurate and efficient calculation of the perimeter of a square.
Advanced Concepts
Understanding the perimeter of a square can extend beyond basic calculations. Here, we explore some advanced concepts that involve the perimeter of a square.
1. Perimeter in Terms of the Diagonal
If the diagonal of a square is known, the perimeter can be calculated using the relationship between the side length and the diagonal. For a square with a diagonal \(d\), the side length \(a\) is given by:
\[ a = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} \]
Using the perimeter formula \(P = 4a\), we can express the perimeter in terms of the diagonal:
\[ P = 4 \times \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} = 2\sqrt{2} \times d \]
2. Perimeter and Area Relationship
When the area of a square is known, the side length can be derived from the area. If the area \(A\) is known, the side length \(a\) is:
\[ a = \sqrt{A} \]
The perimeter can then be calculated using the side length:
\[ P = 4 \times \sqrt{A} \]
3. Perimeter of Inscribed and Circumscribed Figures
In some geometric problems, squares are inscribed in or circumscribe other figures, such as circles. For an inscribed square in a circle with radius \(r\), the diagonal of the square is equal to the diameter of the circle:
\[ d = 2r \]
The side length of the inscribed square is:
\[ a = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{2r}{\sqrt{2}} = r\sqrt{2} \]
Thus, the perimeter of the inscribed square is:
\[ P = 4a = 4r\sqrt{2} \]
4. Applications in Coordinate Geometry
In coordinate geometry, the perimeter of a square can be found if the coordinates of its vertices are known. By calculating the distance between adjacent vertices, we determine the side length \(a\). Using the distance formula for two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\):
\[ a = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
The perimeter is then calculated as:
\[ P = 4a \]
5. Perimeter in Algebraic Problems
Advanced algebraic problems might involve expressing the perimeter in terms of variables and solving equations. For instance, if the perimeter of a square is given by an algebraic expression, solving for the side length involves manipulating the expression:
\[ P = 4a \]
\[ a = \frac{P}{4} \]
These advanced concepts demonstrate the versatility of the perimeter formula and its application in various mathematical contexts.
Perimeter of Composite Shapes
Composite shapes, or compound shapes, are formed by combining two or more simple geometric shapes. Finding the perimeter of such shapes involves calculating the perimeter of each individual shape and then summing them appropriately. Here, we will look at some methods and examples to understand how to calculate the perimeter of composite shapes that include squares.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To find the perimeter of composite shapes, follow these steps:
- Identify Individual Shapes: Break down the composite shape into recognizable simple shapes (e.g., squares, rectangles).
- Calculate Individual Perimeters: Determine the perimeter of each individual shape using the relevant formulas.
- Combine Perimeters: Sum the perimeters of individual shapes, ensuring to subtract any shared sides that are counted twice.
Example Calculations
Consider a composite shape made up of two squares and one rectangle.
- Square A: Side length = 4 cm
- Square B: Side length = 3 cm
- Rectangle C: Length = 6 cm, Width = 2 cm
First, calculate the perimeter of each shape:
- Perimeter of Square A: \( P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \) cm
- Perimeter of Square B: \( P = 4 \times 3 = 12 \) cm
- Perimeter of Rectangle C: \( P = 2 \times (6 + 2) = 16 \) cm
If the shapes are arranged such that some sides are shared, subtract the lengths of these shared sides from the total perimeter.
Advanced Example
Consider a composite shape where a small square is cut out from a larger square.
- Large Square: Side length = 10 cm
- Small Square (cut out): Side length = 4 cm
To find the perimeter of the remaining shape:
- Perimeter of Large Square: \( P = 4 \times 10 = 40 \) cm
- Perimeter of Small Square: \( P = 4 \times 4 = 16 \) cm
Since the small square is completely cut out from the large square, it does not contribute to the external perimeter. Thus, the perimeter of the remaining shape is the perimeter of the large square alone.
Applications in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of composite shapes is useful in various real-life applications, such as:
- Landscaping: Calculating the perimeter of gardens that include multiple geometric shapes for fencing purposes.
- Architecture: Designing floor plans that include various rooms with different shapes and ensuring accurate boundary measurements.
- Art and Craft: Creating complex designs from simple geometric shapes and determining the amount of material needed to outline the design.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems to test your understanding:
- Find the perimeter of a shape formed by combining a square of side 5 cm and a rectangle of length 8 cm and width 3 cm, where one side of the square is adjacent to the length of the rectangle.
- A garden is in the shape of a large square with a small square pond cut out from one corner. If the side length of the large square is 15 m and the side length of the small square is 5 m, what is the perimeter of the garden area excluding the pond?
Practice Problems
Practice problems are essential to mastering the concept of finding the perimeter of a square. Here are some problems to help you understand and apply the formula effectively:
-
Problem 1: Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 8 cm.
Solution:
- Perimeter formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Substitute \( s = 8 \) cm
- Calculate: \( P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \) cm
- Answer: The perimeter is 32 cm.
-
Problem 2: A square has a perimeter of 48 inches. What is the length of one side?
Solution:
- Perimeter formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Given \( P = 48 \) inches
- Solve for \( s \): \( s = \frac{P}{4} = \frac{48}{4} = 12 \) inches
- Answer: Each side is 12 inches long.
-
Problem 3: Calculate the perimeter of a square where the area is 64 square meters.
Solution:
- Area formula: \( A = s^2 \)
- Given \( A = 64 \) square meters
- Solve for \( s \): \( s = \sqrt{A} = \sqrt{64} = 8 \) meters
- Perimeter formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Calculate: \( P = 4 \times 8 = 32 \) meters
- Answer: The perimeter is 32 meters.
-
Problem 4: The diagonal of a square is 10√2 cm. Find its perimeter.
Solution:
- Diagonal formula: \( d = s\sqrt{2} \)
- Given \( d = 10\sqrt{2} \) cm
- Solve for \( s \): \( s = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{10\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}} = 10 \) cm
- Perimeter formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Calculate: \( P = 4 \times 10 = 40 \) cm
- Answer: The perimeter is 40 cm.
-
Problem 5: If the side length of a square is reduced by 3 cm and the new perimeter is 28 cm, find the original side length.
Solution:
- Let original side length be \( s \)
- New side length: \( s - 3 \)
- New perimeter formula: \( P = 4(s - 3) \)
- Given \( P = 28 \) cm
- Solve: \( 4(s - 3) = 28 \)
- Simplify: \( s - 3 = 7 \)
- Calculate: \( s = 10 \) cm
- Answer: The original side length was 10 cm.
These problems will help reinforce your understanding of the perimeter of a square and how to apply the formula in various scenarios. Practice regularly to build confidence and proficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the Perimeter of a Square?
The perimeter of a square is the total length around its boundary. It is calculated by summing the lengths of all four equal sides, or by multiplying one side length by 4. The formula is: \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
-
How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Square?
To calculate the perimeter of a square, multiply the length of one side by 4. For example, if one side of the square is 5 units, the perimeter is \( 5 \times 4 = 20 \) units.
-
What is the Formula for the Perimeter of a Square?
The formula for the perimeter of a square is \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \), where "side" represents the length of one of the square's sides.
-
How to Find the Side Length of a Square When the Perimeter is Given?
If you know the perimeter of a square, you can find the length of one side by dividing the perimeter by 4. For example, if the perimeter is 20 units, then the side length is \( 20 / 4 = 5 \) units.
-
How to Find the Perimeter of a Square When the Area is Given?
First, find the side length by taking the square root of the area. Then, use the perimeter formula. For instance, if the area is 36 square units, the side length is \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \) units. Therefore, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 6 = 24 \) units.
-
What Units are Used to Measure the Perimeter of a Square?
The perimeter of a square is measured in linear units such as meters (m), centimeters (cm), inches (in), feet (ft), etc.
-
How to Find the Perimeter of a Square When the Diagonal is Given?
The diagonal \( d \) of a square is related to the side length \( s \) by the formula \( d = s\sqrt{2} \). To find the side length, divide the diagonal by \( \sqrt{2} \). Then, use the perimeter formula \( P = 4s \). For example, if the diagonal is 10 units, the side length is \( 10 / \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2} \) units, and the perimeter is \( 4 \times 5\sqrt{2} = 20\sqrt{2} \) units.
Conclusion and Summary
Finding the perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry that is simple and straightforward. The perimeter is the total distance around the edge of the square. To conclude, let's summarize the key points covered in this guide:
- Definition: The perimeter of a square is the total length of all four sides.
- Formula: The perimeter (P) of a square can be calculated using the formula: , where s is the length of one side of the square.
- Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4.
- The result is the perimeter of the square.
- Example: If one side of the square is 5 units, then the perimeter is .
- Applications: Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a square is useful in various real-life contexts such as construction, design, and any field requiring spatial measurements.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid: Ensure that all sides are equal and that the correct formula is applied.
By mastering the concept of the perimeter of a square, you build a foundation for more complex geometric calculations and enhance your problem-solving skills. Continue practicing with different examples and applying this knowledge to practical scenarios.

Làm thế nào để tìm chu vi của một hình vuông | Toán với thầy J
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi hình vuông sử dụng biến số. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính chu vi của hình vuông một cách dễ dàng.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Vuông Sử Dụng Biến Số
READ MORE:
Video ngắn hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi hình vuông. Xem video này để hiểu rõ cách tính chu vi của hình vuông một cách nhanh chóng và dễ dàng.
Chu Vi Hình Vuông #shorts