Topic formula for perimeter of pentagon: The formula for the perimeter of a pentagon is essential for students and professionals working with geometric shapes. This article provides a comprehensive guide on calculating the perimeter for both regular and irregular pentagons, offering clear examples and practical applications. Understanding this formula can simplify complex geometric problems and enhance your mathematical skills.
Table of Content
- Formula for Perimeter of a Pentagon
- Introduction to Pentagon Perimeter
- Understanding Polygons and Pentagons
- Basic Properties of Pentagons
- Types of Pentagons
- Regular Pentagon Perimeter Formula
- Irregular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
- Steps to Calculate Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon
- Applications of Pentagon Perimeter in Real Life
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- FAQs on Pentagon Perimeter
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi của ngũ giác, bao gồm ngũ giác đều và không đều, với công thức và ví dụ chi tiết để giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này.
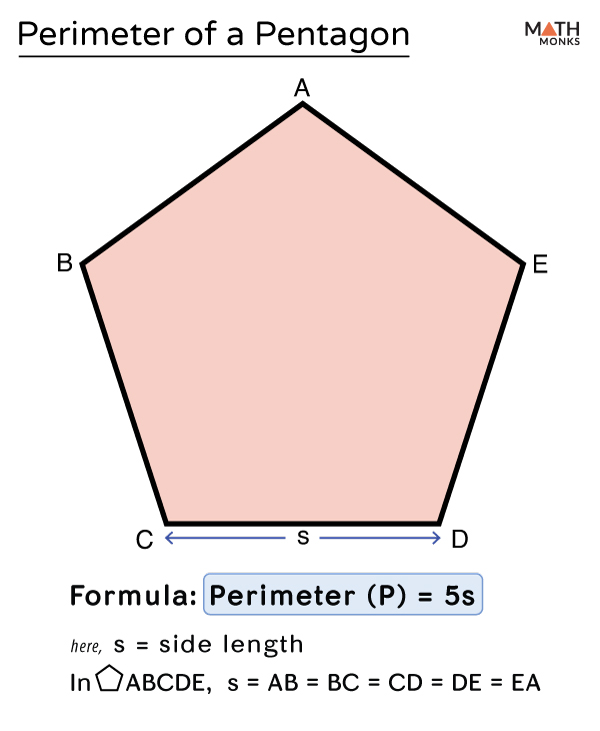
Formula for Perimeter of a Pentagon
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon. The perimeter of a pentagon is the total length around the shape, which is the sum of the lengths of its five sides. The formula to calculate the perimeter depends on whether the pentagon is regular (all sides are equal) or irregular (sides have different lengths).
Regular Pentagon
In a regular pentagon, all five sides are of equal length. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a regular pentagon is:
\[
P = 5s
\]
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Irregular Pentagon
In an irregular pentagon, the sides can have different lengths. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all five sides. The formula for the perimeter (P) of an irregular pentagon is:
\[
P = a + b + c + d + e
\]
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the five sides.
Example Calculations
- Regular Pentagon: If each side of a regular pentagon is 8 cm, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 5 \times 8 = 40 \, \text{cm}
\] - Irregular Pentagon: If the sides of an irregular pentagon are 7 cm, 9 cm, 5 cm, 8 cm, and 6 cm, the perimeter is:
\[
P = 7 + 9 + 5 + 8 + 6 = 35 \, \text{cm}
\]
Using the Perimeter Formula
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, is straightforward using the appropriate formula. For a regular pentagon, simply multiply the length of one side by five. For an irregular pentagon, sum the lengths of all five sides.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Pentagon Perimeter
The perimeter of a pentagon is the total distance around the five sides of the polygon. This measurement is crucial in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and mathematics. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of both regular and irregular pentagons is essential for solving many geometric problems.
For a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal, the perimeter \( P \) can be calculated using the formula:
\( P = 5a \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the pentagon.
For an irregular pentagon, where the sides may have different lengths, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all five sides. If the sides are denoted as \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \), the formula is:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e \)
Understanding these basic formulas allows for quick and accurate perimeter calculations. Below is a step-by-step guide for both regular and irregular pentagon perimeter calculations:
- Measure the length of one side (for regular pentagons) or all five sides (for irregular pentagons).
- For regular pentagons, multiply the length of one side by 5.
- For irregular pentagons, add the lengths of all five sides together.
This fundamental knowledge will help you in various practical applications, from designing shapes in construction to solving mathematical problems. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into the properties and types of pentagons, and explore more examples and applications of pentagon perimeter calculations.
Understanding Polygons and Pentagons
Polygons are flat, two-dimensional shapes with straight sides. The term "polygon" comes from the Greek words "poly," meaning many, and "gonia," meaning angle. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they have:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
A pentagon is a five-sided polygon. There are two main types of pentagons:
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and angles are equal. The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is \( P = 5a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- Irregular Pentagon: Sides and angles can vary. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \), where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides.
In addition to sides and angles, pentagons can be convex or concave:
- Convex Pentagon: All interior angles are less than 180°, and no sides curve inward.
- Concave Pentagon: At least one interior angle is greater than 180°, and one or more sides curve inward.
Pentagons are commonly seen in nature, art, and architecture, making understanding their properties and calculations valuable for various practical applications. This knowledge forms a foundation for further exploration into more complex geometric concepts.
Basic Properties of Pentagons
Pentagons, characterized by their five sides, have several fundamental properties that distinguish them within the realm of polygons. These properties are crucial for understanding and working with pentagons in various mathematical and practical applications.
- Sides and Angles: A pentagon has five sides and five angles. In a regular pentagon, all sides and angles are equal. The internal angle of a regular pentagon is \(108^\circ\).
- Diagonals: A pentagon has five diagonals. The formula to calculate the number of diagonals in a polygon is \( \frac{n(n-3)}{2} \), where \( n \) is the number of sides. For a pentagon, \( \frac{5(5-3)}{2} = 5 \) diagonals.
- Sum of Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles of a pentagon is given by the formula \( (n-2) \times 180^\circ \). For a pentagon, this is \( (5-2) \times 180^\circ = 540^\circ \).
Pentagons can be classified into different types based on their properties:
- Regular Pentagon: All sides and angles are equal. Each internal angle is \(108^\circ\).
- Irregular Pentagon: Sides and angles are not equal. The sum of the internal angles is still \(540^\circ\), but individual angles may vary.
- Convex Pentagon: All internal angles are less than \(180^\circ\), and all vertices point outward.
- Concave Pentagon: At least one internal angle is greater than \(180^\circ\), causing one or more vertices to point inward.
Understanding these basic properties helps in identifying and working with pentagons in both theoretical and practical scenarios. Knowing how to calculate the perimeter, area, and other properties is essential for applications in geometry, engineering, and design.
Types of Pentagons
Pentagons are five-sided polygons that can be classified into different types based on their side lengths and angle measurements. Understanding these types is essential for various geometric applications and calculations. Below are the primary types of pentagons:
- Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has all five sides of equal length and all internal angles equal to \(108^\circ\). This symmetry makes calculations straightforward, with the perimeter given by \( P = 5a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- Irregular Pentagon: An irregular pentagon has sides and angles of different lengths and measurements. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides: \( P = a + b + c + d + e \), where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Convex Pentagon: In a convex pentagon, all internal angles are less than \(180^\circ\), and none of the sides bow inward. All vertices point outward, maintaining a simple shape.
- Concave Pentagon: A concave pentagon has at least one internal angle greater than \(180^\circ\), causing one or more sides to curve inward. This type of pentagon can have a more complex shape due to the inward-facing vertices.
- Cyclic Pentagon: A cyclic pentagon can be inscribed in a circle, meaning all its vertices lie on a single circle. This type can be either regular or irregular.
- Equilateral Pentagon: An equilateral pentagon has all sides of equal length, but the internal angles are not necessarily equal, distinguishing it from a regular pentagon.
Each type of pentagon has unique properties and applications. Regular pentagons are often used in design and architecture due to their symmetry, while understanding the properties of irregular and concave pentagons is crucial in more complex geometric problems. Knowing how to identify and calculate properties for each type enhances your ability to work with these versatile shapes effectively.

Regular Pentagon Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal in length, is straightforward to calculate. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a regular pentagon is given by:
\( P = 5a \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the pentagon. This formula is derived from the fact that a regular pentagon has five equal sides.
To calculate the perimeter of a regular pentagon, follow these steps:
- Measure the Length: Measure the length of one side of the pentagon. Ensure accuracy for precise perimeter calculation.
- Apply the Formula: Multiply the length of one side by 5 using the formula \( P = 5a \).
- Result: The resulting product is the perimeter of the regular pentagon.
For example, if each side of a regular pentagon measures 8 units, the perimeter calculation would be:
\( P = 5 \times 8 = 40 \) units
This simple formula allows for quick and efficient calculation of the perimeter, making it useful in various applications such as geometry, architecture, and design.
Irregular Pentagon Perimeter Calculation
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, where the sides may have different lengths, requires summing the lengths of all five sides. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of an irregular pentagon is:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e \)
where \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \) are the lengths of the sides of the pentagon. Follow these steps to calculate the perimeter:
- Measure Each Side: Measure the length of each of the five sides of the pentagon accurately.
- List the Measurements: Write down the lengths of the sides. For example, let the side lengths be \( a = 5 \) units, \( b = 7 \) units, \( c = 6 \) units, \( d = 8 \) units, and \( e = 7 \) units.
- Apply the Formula: Substitute the side lengths into the formula \( P = a + b + c + d + e \).
- Calculate the Sum: Add the lengths of all the sides to find the perimeter.
For example, given the side lengths \( a = 5 \) units, \( b = 7 \) units, \( c = 6 \) units, \( d = 8 \) units, and \( e = 7 \) units, the calculation would be:
\( P = 5 + 7 + 6 + 8 + 7 = 33 \) units
This method ensures an accurate calculation of the perimeter for any irregular pentagon, providing a straightforward approach for various geometric and practical applications.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter of a Regular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of a regular pentagon, where all sides are of equal length, is a simple process. Follow these steps to determine the perimeter:
- Measure the Length of One Side: Measure the length of one side of the pentagon accurately. Let this length be denoted as \( a \).
- Use the Perimeter Formula: The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a regular pentagon is:
- Multiply by 5: Multiply the length of the measured side by 5 to find the perimeter.
- Result: The resulting product is the perimeter of the regular pentagon.
\( P = 5a \)
For example, if the length of one side of the pentagon is 6 units, the calculation would be:
\( P = 5 \times 6 = 30 \) units
This straightforward method allows for quick and efficient calculation of the perimeter, which is useful in various geometric, architectural, and design applications. By following these steps, you can easily determine the perimeter of any regular pentagon.
Steps to Calculate Perimeter of an Irregular Pentagon
Calculating the perimeter of an irregular pentagon, where the sides may have different lengths, involves summing the lengths of all five sides. Follow these detailed steps to determine the perimeter:
- Measure the Length of Each Side: Measure the length of each of the five sides of the pentagon accurately. Denote these lengths as \( a, b, c, d, \) and \( e \).
- Record the Measurements: Write down the measured lengths of each side. For example, let the side lengths be:
- \( a = 4 \) units
- \( b = 5 \) units
- \( c = 6 \) units
- \( d = 7 \) units
- \( e = 8 \) units
- Sum the Lengths: Add the lengths of all the sides using the formula:
- Calculate the Perimeter: Substitute the measured values into the formula and perform the addition. For the example values, the calculation would be:
\( P = a + b + c + d + e \)
\( P = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 = 30 \) units
This step-by-step method ensures an accurate calculation of the perimeter for any irregular pentagon. By following these steps, you can determine the perimeter easily, which is essential for various practical applications in geometry, construction, and design.
Applications of Pentagon Perimeter in Real Life
The perimeter of a pentagon is an essential measurement in various real-life applications, ranging from architectural design to land surveying. Understanding how to calculate and apply this measurement can be crucial in many fields. Here are some detailed applications:
-
Architecture and Construction:
In architecture, the perimeter of a pentagon is often used in the design of buildings and structures with pentagonal shapes. Architects and engineers calculate the perimeter to determine the amount of materials needed for construction, such as fencing, flooring, and roofing.
-
Land Surveying:
Surveyors use the perimeter of a pentagon to measure plots of land that are pentagonal in shape. Accurate perimeter measurements help in creating maps and planning the use of land for agricultural, commercial, or residential purposes.
-
Interior Design:
Interior designers might use pentagonal shapes in various elements such as tables, floor patterns, and decorative objects. Knowing the perimeter allows for precise placement and fitting of these items within a given space.
-
Urban Planning:
In urban planning, pentagonal layouts can be used for parks, plazas, and other public spaces. Planners use the perimeter to allocate space efficiently and to design accessible and aesthetically pleasing areas for public use.
-
Crafts and Hobbies:
Hobbyists and crafters often use pentagonal shapes in their projects, such as creating quilts, tiles, and decorative pieces. Calculating the perimeter helps in cutting materials accurately and ensuring the pieces fit together properly.
The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is given by:
\[ P = 5s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side. For irregular pentagons, the perimeter is the sum of all side lengths:
\[ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 \]
These calculations are fundamental in applying the concept of pentagon perimeter in the various fields mentioned above, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in practical scenarios.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of a pentagon can sometimes lead to common mistakes. Understanding these errors and how to avoid them ensures accurate and reliable results. Here are some common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
-
Incorrect Formula Usage:
One of the most frequent mistakes is using the wrong formula. For a regular pentagon, the correct formula is:
\[ P = 5s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side. For an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is the sum of all side lengths:
\[ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 \]
How to Avoid: Ensure you are using the correct formula based on whether the pentagon is regular or irregular.
-
Measurement Errors:
Errors in measuring the sides can lead to inaccurate perimeter calculations.
How to Avoid: Use precise measuring tools and double-check measurements for accuracy.
-
Unit Conversion Mistakes:
Failing to convert units consistently can result in incorrect perimeter values.
How to Avoid: Always convert all measurements to the same unit before performing calculations. For example, convert all lengths to meters or centimeters.
-
Adding Incorrect Side Lengths:
In irregular pentagons, it is crucial to add the correct side lengths. Mixing up sides or missing one can lead to errors.
How to Avoid: Label each side clearly and keep track of which sides have been added.
-
Rounding Errors:
Rounding side lengths too early in the calculation process can lead to significant discrepancies.
How to Avoid: Perform calculations with the full precision of your measurements and round only the final result.
By being aware of these common mistakes and following the suggested steps to avoid them, you can ensure accurate and reliable perimeter calculations for any pentagon.
FAQs on Pentagon Perimeter
Here are some frequently asked questions about the perimeter of a pentagon, along with detailed answers to help you understand the concepts better.
-
Q: What is the formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon?
A: The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is:
\[ P = 5s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side. This formula works because all sides of a regular pentagon are equal.
-
Q: How do I calculate the perimeter of an irregular pentagon?
A: For an irregular pentagon, the perimeter is the sum of all its side lengths. The formula is:
\[ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 \]
Each \( s_i \) represents the length of a different side.
-
Q: Can the perimeter of a pentagon be calculated if only the area is known?
A: No, the perimeter and area are different properties. Knowing the area alone is insufficient to determine the perimeter. You need the side lengths to calculate the perimeter.
-
Q: What units should be used for measuring the perimeter of a pentagon?
A: The units for the perimeter should be the same as the units used for the side lengths. Common units include meters, centimeters, feet, and inches. Ensure consistency in unit usage throughout the calculation.
-
Q: Is the perimeter of a pentagon always greater than its area?
A: Not necessarily. The perimeter and area measure different aspects of a shape. The perimeter measures the distance around the shape, while the area measures the surface covered by the shape. Comparing these two directly depends on the specific dimensions of the pentagon.
-
Q: How can I verify my perimeter calculation?
A: To verify your calculation, remeasure all sides and recompute the perimeter using the appropriate formula. Cross-check your results with a calculator or software designed for geometric calculations to ensure accuracy.
Conclusion
Understanding the formula for the perimeter of a pentagon, whether regular or irregular, is crucial for various practical applications in fields like architecture, construction, land surveying, and more. By accurately calculating the perimeter, you can ensure efficient material use, precise measurements, and effective planning.
To summarize:
-
Regular Pentagon:
For a regular pentagon, where all sides are equal, the perimeter is calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 5s \]
This straightforward formula highlights the simplicity of dealing with regular polygons.
-
Irregular Pentagon:
For an irregular pentagon, where side lengths vary, the perimeter is the sum of all its sides:
\[ P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 \]
This formula ensures that all sides are accounted for, providing an accurate total perimeter.
Key points to remember include:
- Use the correct formula based on the type of pentagon.
- Ensure accurate measurements of all side lengths.
- Maintain consistent units throughout your calculations.
- Double-check your work to avoid common mistakes such as measurement errors or incorrect formula application.
By mastering these calculations, you can confidently apply the concepts of pentagon perimeter in real-life scenarios, ensuring precision and effectiveness in your projects. Whether you are an architect, surveyor, designer, or hobbyist, understanding the perimeter of pentagons enhances your ability to create accurate and functional designs.

Tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi của ngũ giác, bao gồm ngũ giác đều và không đều, với công thức và ví dụ chi tiết để giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này.
Chu vi của Ngũ giác, Chu vi cho Ngũ giác Đều và Không Đều cùng Công thức & Ví dụ
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của ngũ giác, bao gồm các bước tính toán và công thức cụ thể, giúp bạn dễ dàng nắm bắt và áp dụng.
Cách Tìm Chu vi của Ngũ giác