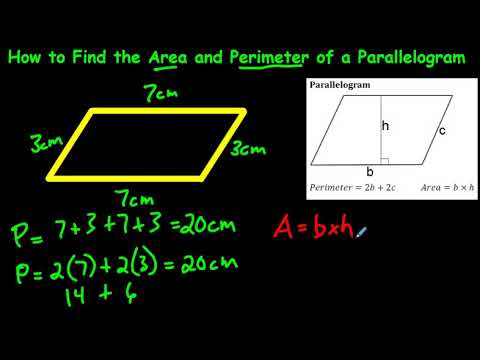
Topic how do you get the perimeter of a parallelogram: Discover how to get the perimeter of a parallelogram with this straightforward guide. Learn the essential formula, step-by-step calculations, and practical tips for measuring sides accurately. Perfect for students, teachers, and anyone looking to refresh their geometry skills. Let's make finding the perimeter of a parallelogram easy and intuitive!
Table of Content
- How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Parallelogram
- Introduction to Parallelograms
- Understanding the Perimeter
- Basic Properties of a Parallelogram
- Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
- Example Calculations
- Measuring the Sides of a Parallelogram
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applications in Real Life
- FAQs on Perimeter Calculation
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi hình bình hành một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu qua video hướng dẫn này.
How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon with opposite sides that are equal in length and parallel. To find the perimeter of a parallelogram, you need to know the lengths of its two adjacent sides.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Parallelogram
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a parallelogram is:
where a and b are the lengths of the two adjacent sides of the parallelogram.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the parallelogram (side a).
- Measure the length of the adjacent side (side b).
- Add the lengths of the two sides together: a + b.
- Multiply the sum by 2 to get the perimeter: 2 × (a + b).
Example Calculation
Suppose you have a parallelogram with side lengths of 5 cm and 8 cm. The perimeter calculation would be:
Properties of a Parallelogram
- Opposite sides are equal in length.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- The diagonals bisect each other.
- The sum of the interior angles is 360 degrees.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Parallelograms
A parallelogram is a four-sided polygon, also known as a quadrilateral, with opposite sides that are both equal in length and parallel. This geometric shape has several unique properties and characteristics that make it an important topic in geometry.
Key properties of parallelograms include:
- Opposite Sides: Opposite sides of a parallelogram are of equal length.
- Opposite Angles: Opposite angles in a parallelogram are equal.
- Adjacent Angles: The sum of adjacent angles in a parallelogram is 180 degrees.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Mathematically, if a parallelogram has sides a and b, and angles A and B, then the following relationships hold:
These properties are the foundation for understanding more complex geometric principles involving parallelograms, such as calculating the perimeter.
Understanding the Perimeter
The perimeter of a parallelogram is the total length of its boundaries. To find the perimeter, you need to know the lengths of its two adjacent sides. The formula for calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram is straightforward and involves simple arithmetic.
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) of a parallelogram is:
where a and b are the lengths of the two adjacent sides of the parallelogram.
Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter of a parallelogram:
- Identify the lengths of the two adjacent sides of the parallelogram. Let's call these sides a and b.
- Add the lengths of the two sides: .
- Multiply the sum by 2 to find the perimeter: .
For example, if a parallelogram has side lengths of 7 cm and 10 cm, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
- Add the lengths of the two sides: cm.
- Multiply the sum by 2: cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the parallelogram is 34 cm.
Basic Properties of a Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a type of quadrilateral with unique properties that differentiate it from other four-sided figures. Understanding these properties is essential for solving various geometric problems involving parallelograms.
Here are the basic properties of a parallelogram:
- Opposite Sides are Parallel and Equal: In a parallelogram, opposite sides are both parallel and equal in length. If a parallelogram has sides a and b, then the opposite sides will be:
- Opposite Angles are Equal: The angles opposite to each other in a parallelogram are equal. If A, B, C, and D are the angles, then:
- Adjacent Angles are Supplementary: The sum of the angles adjacent to each other is 180 degrees. This means:
- Diagonals Bisect Each Other: The diagonals of a parallelogram intersect at their midpoints, effectively bisecting each other. If AC and BD are the diagonals, then:
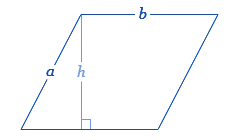
- Area: The area of a parallelogram can be calculated using the base and height with the formula:
These properties make parallelograms an interesting and versatile shape in geometry, often appearing in various mathematical problems and real-world applications.
Step-by-Step Calculation Guide
Calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram involves a few straightforward steps. Follow this guide to accurately determine the perimeter.
- Identify the Side Lengths
- Determine the length of one pair of opposite sides. Label this length as \(a\).
- Determine the length of the other pair of opposite sides. Label this length as \(b\).
- Write Down the Perimeter Formula
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a parallelogram is:
\( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Substitute the Side Lengths into the Formula
Plug the values of \(a\) and \(b\) into the formula:
\( P = 2a + 2b \)
For example, if \(a = 6 \, \text{cm}\) and \(b = 4 \, \text{cm}\):
\( P = 2(6 \, \text{cm}) + 2(4 \, \text{cm}) \)
- Perform the Addition Inside the Formula
Add the lengths of the sides together:
\( 2a + 2b = 2(6 \, \text{cm}) + 2(4 \, \text{cm}) \)
\( = 12 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} \)
- Calculate the Perimeter
Sum the results of the addition:
\( P = 12 \, \text{cm} + 8 \, \text{cm} \)
\( P = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
Therefore, the perimeter of the parallelogram is 20 cm.
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any parallelogram.

Example Calculations
Let's go through a few example calculations to better understand how to find the perimeter of a parallelogram.
Example 1
Given a parallelogram with side lengths \(a = 8 \, \text{cm}\) and \(b = 5 \, \text{cm}\):
- Identify the side lengths:
- \(a = 8 \, \text{cm}\)
- \(b = 5 \, \text{cm}\)
- Write down the formula for the perimeter:
\( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Substitute the values of \(a\) and \(b\) into the formula:
\( P = 2(8 \, \text{cm}) + 2(5 \, \text{cm}) \)
- Perform the addition inside the formula:
\( 2(8 \, \text{cm}) = 16 \, \text{cm} \)
\( 2(5 \, \text{cm}) = 10 \, \text{cm} \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
\( P = 16 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} \)
\( P = 26 \, \text{cm} \)
The perimeter of the parallelogram is 26 cm.
Example 2
Given a parallelogram with side lengths \(a = 12 \, \text{inches}\) and \(b = 7 \, \text{inches}\):
- Identify the side lengths:
- \(a = 12 \, \text{inches}\)
- \(b = 7 \, \text{inches}\)
- Write down the formula for the perimeter:
\( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Substitute the values of \(a\) and \(b\) into the formula:
\( P = 2(12 \, \text{inches}) + 2(7 \, \text{inches}) \)
- Perform the addition inside the formula:
\( 2(12 \, \text{inches}) = 24 \, \text{inches} \)
\( 2(7 \, \text{inches}) = 14 \, \text{inches} \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
\( P = 24 \, \text{inches} + 14 \, \text{inches} \)
\( P = 38 \, \text{inches} \)
The perimeter of the parallelogram is 38 inches.
Example 3
Given a parallelogram with side lengths \(a = 3 \, \text{m}\) and \(b = 4 \, \text{m}\):
- Identify the side lengths:
- \(a = 3 \, \text{m}\)
- \(b = 4 \, \text{m}\)
- Write down the formula for the perimeter:
\( P = 2a + 2b \)
- Substitute the values of \(a\) and \(b\) into the formula:
\( P = 2(3 \, \text{m}) + 2(4 \, \text{m}) \)
- Perform the addition inside the formula:
\( 2(3 \, \text{m}) = 6 \, \text{m} \)
\( 2(4 \, \text{m}) = 8 \, \text{m} \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
\( P = 6 \, \text{m} + 8 \, \text{m} \)
\( P = 14 \, \text{m} \)
The perimeter of the parallelogram is 14 meters.
These examples illustrate how to use the formula to find the perimeter of a parallelogram with different side lengths.
Measuring the Sides of a Parallelogram
Accurately measuring the sides of a parallelogram is crucial for calculating its perimeter. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you measure the sides of a parallelogram effectively.
- Identify the Sides of the Parallelogram
Locate the four sides of the parallelogram. Remember, opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length.
- Use a Ruler or Measuring Tape
To measure the sides, you will need a ruler or a measuring tape. Ensure the measuring tool is suitable for the size of the parallelogram.
- Measure One Pair of Opposite Sides
- Place the ruler or measuring tape along one side of the parallelogram.
- Note the length and label this side as \(a\).
- Repeat this process for the opposite side, which should be the same length as \(a\).
- Measure the Other Pair of Opposite Sides
- Place the ruler or measuring tape along one of the remaining sides.
- Note the length and label this side as \(b\).
- Repeat this process for the opposite side, which should be the same length as \(b\).
- Verify Your Measurements
Double-check all measurements to ensure accuracy. Correct measurements are essential for accurate perimeter calculation.
By following these steps, you can accurately measure the sides of a parallelogram, ensuring precise calculations for the perimeter.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram, several common mistakes can lead to incorrect results. Understanding these pitfalls can help you avoid them and ensure accurate calculations.
- Confusing Perimeter with Area: The perimeter measures the distance around the parallelogram, while the area measures the space enclosed within it. Ensure you use the correct formula for the perimeter: , where and are the lengths of the sides.
- Incorrectly Identifying Sides: Ensure you correctly identify the pairs of opposite sides. A parallelogram has two pairs of equal-length sides.
- Forgetting to Double the Sum of the Sides: The formula requires doubling the sum of the lengths of one pair of adjacent sides. Don't forget this step as it is crucial for accurate perimeter calculation.
- Using Diagonal Lengths Instead of Side Lengths: The formula for the perimeter does not involve the lengths of the diagonals. Ensure you use the side lengths in your calculations.
- Incorrect Units: Always use consistent units for all measurements and express the final answer in the same unit. Converting units mid-calculation can lead to errors.
- Rounding Errors: Be careful with rounding intermediate steps in your calculation. It's best to round only the final result to avoid cumulative rounding errors.
- Ignoring Decimal Precision: When dealing with measurements that include decimals, ensure precision is maintained throughout the calculation to avoid inaccurate results.
- Misinterpreting the Shape: Ensure you are indeed working with a parallelogram and not another quadrilateral like a rectangle or rhombus, which have different properties and formulas for perimeter calculation.
Applications in Real Life
The concept of the perimeter of a parallelogram has various practical applications in real life. Here are some examples:
-
Architecture and Construction:
In architecture, the design and layout of buildings often involve parallelograms. Calculating the perimeter helps in determining the amount of materials needed, such as the total length of trim or framing required for windows and doors, which are typically parallelogram-shaped.
-
Landscaping and Agriculture:
In landscaping, the perimeter of garden beds, pathways, and plots are often calculated to determine the length of fencing or edging materials needed. Similarly, in agriculture, parallelogram-shaped fields require perimeter measurements for fencing and irrigation planning.
-
Interior Design:
Interior designers use the concept of the perimeter when creating layouts for flooring, rugs, and tiles. For example, knowing the perimeter of a room helps in accurately estimating the amount of baseboard or crown molding required.
-
Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, particularly in the creation of various products such as tables, picture frames, and other items, the perimeter of parallelogram components is crucial for cutting materials to the correct dimensions.
-
Education:
Understanding the perimeter of parallelograms is an essential part of the geometry curriculum in schools, helping students grasp fundamental concepts of shapes and measurements which are applicable in various fields of science and engineering.
Overall, the perimeter of a parallelogram is a fundamental geometric concept with wide-ranging applications in multiple disciplines, highlighting its importance in both theoretical and practical aspects of everyday life.
FAQs on Perimeter Calculation
Below are some frequently asked questions regarding the calculation of the perimeter of a parallelogram:
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a parallelogram?
The perimeter \(P\) of a parallelogram is calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 2(a + b) \]
where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the adjacent sides. - How do you find the perimeter if only the diagonals and one side are given?
If the diagonals \(x\) and \(y\) and one side \(a\) are given, the perimeter can be calculated using:
\[ P = 2a + \sqrt{2x^2 + 2y^2 - 4a^2} \] - What units are used to measure the perimeter?
The perimeter is measured in linear units such as meters (m), centimeters (cm), inches (in), feet (ft), or yards (yd).
- Does the height of the parallelogram affect the perimeter calculation?
No, the height of the parallelogram does not affect the perimeter calculation. The perimeter is solely dependent on the lengths of the sides.
- Are the formulas for the perimeter of a parallelogram and a rectangle the same?
Yes, since a rectangle is a special type of parallelogram where all angles are right angles, the formula for the perimeter is the same:
\[ P = 2(l + w) \]
where \(l\) is the length and \(w\) is the width of the rectangle. - How can you verify if your calculation of the perimeter is correct?
To verify the calculation, ensure you have correctly identified the side lengths and applied the formula properly. Double-check your arithmetic operations and ensure the units are consistent throughout the calculation.
- What is a common mistake to avoid when calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram?
A common mistake is confusing the side lengths with the diagonals. Remember, the formula \( P = 2(a + b) \) uses the lengths of the adjacent sides, not the diagonals.
Additional Resources
Here are some useful resources for further understanding and calculating the perimeter of a parallelogram:
-
This resource provides a detailed explanation of the perimeter formula for parallelograms, interactive diagrams, and examples to help visualize the concepts.
-
Cuemath offers comprehensive examples and multiple formulas for calculating the perimeter of parallelograms with various given parameters, such as side lengths and diagonals.
-
BYJU'S provides step-by-step instructions, solved examples, and practical applications of the perimeter formula for parallelograms in real-life scenarios.
For more advanced topics and related concepts in geometry, you can explore:
These resources provide video tutorials, interactive exercises, and additional practice problems to enhance your understanding of parallelograms and their properties.
Tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi hình bình hành một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu qua video hướng dẫn này.
Cách Tính Chu Vi Hình Bình Hành
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu cách tính diện tích và chu vi hình bình hành một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu qua video hướng dẫn này.
Cách Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi Hình Bình Hành