Topic 5 square root 6: The concept of "5 square root 6" encompasses understanding square roots, their applications, and their significance in mathematics. This article will delve into how to simplify square roots, real-life applications, and the historical background of square roots to provide a comprehensive understanding for readers.
Table of Content
Simplifying and Understanding 5√6
The expression can be simplified and understood in different mathematical forms. Below is a detailed explanation:
Exact Form
In its exact form, the expression remains . This form is typically used when precision is required, and no decimal approximation is involved.
Decimal Form
To convert into a decimal, we approximate the square root of 6:
Properties and Calculation Methods
- Prime Factorization Method: Breaking down 6 into its prime factors, we get 6 = 2 × 3. Therefore,
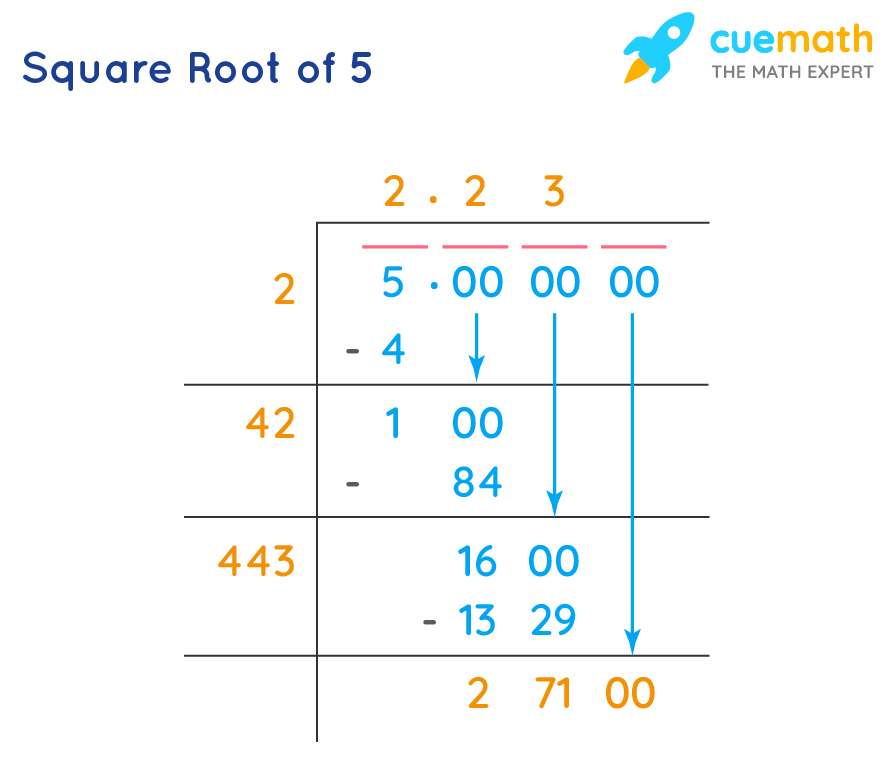
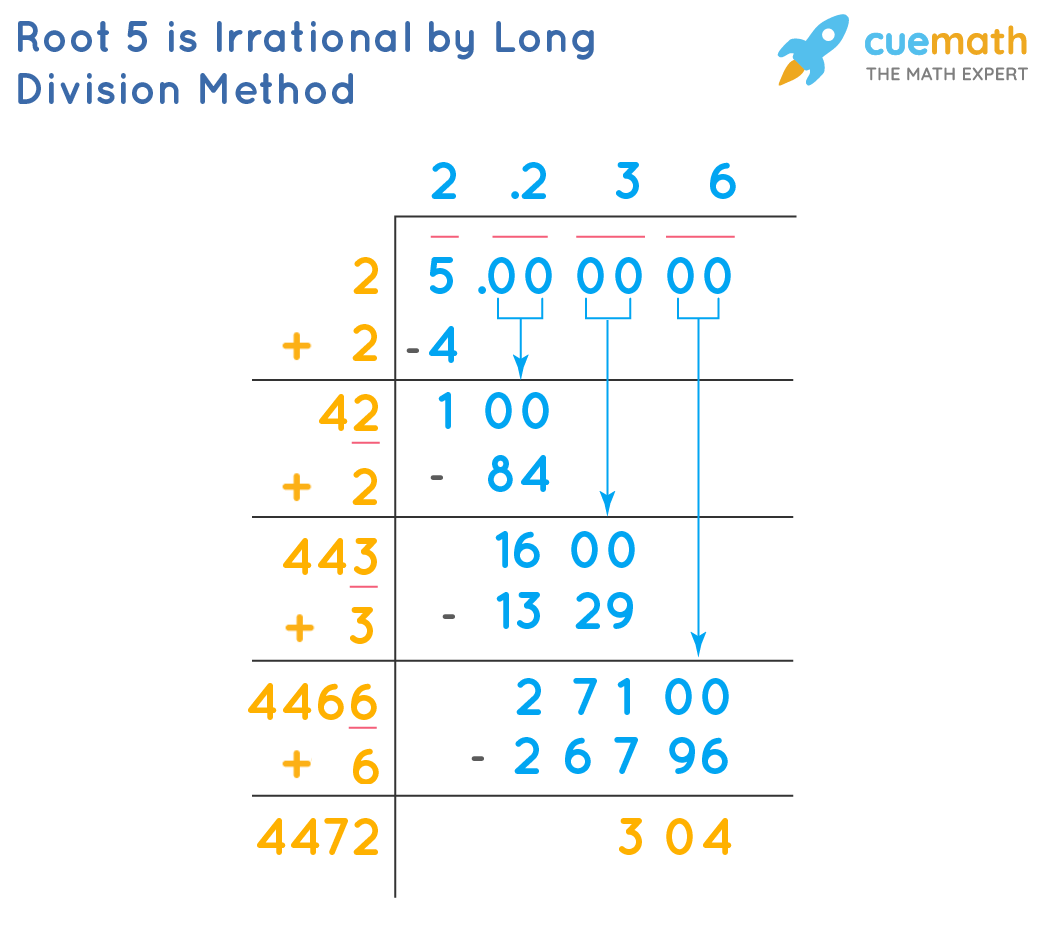
- Long Division Method: This method provides a step-by-step approach to finding the square root of 6, resulting in approximately 2.449.
Examples
Here are a few practical examples demonstrating the application of :
- If a cube has a total surface area of 36 cm2, the edge length is calculated as the square root of 6, which is approximately 2.45 cm.
- A person running at a speed of miles per hour would cover approximately 14.697 miles in one hour.
- The radius of a sphere with a surface area of 24π in2 is found by calculating inches.
In summary, the expression is versatile and can be represented in multiple forms, each useful for different mathematical contexts and applications.
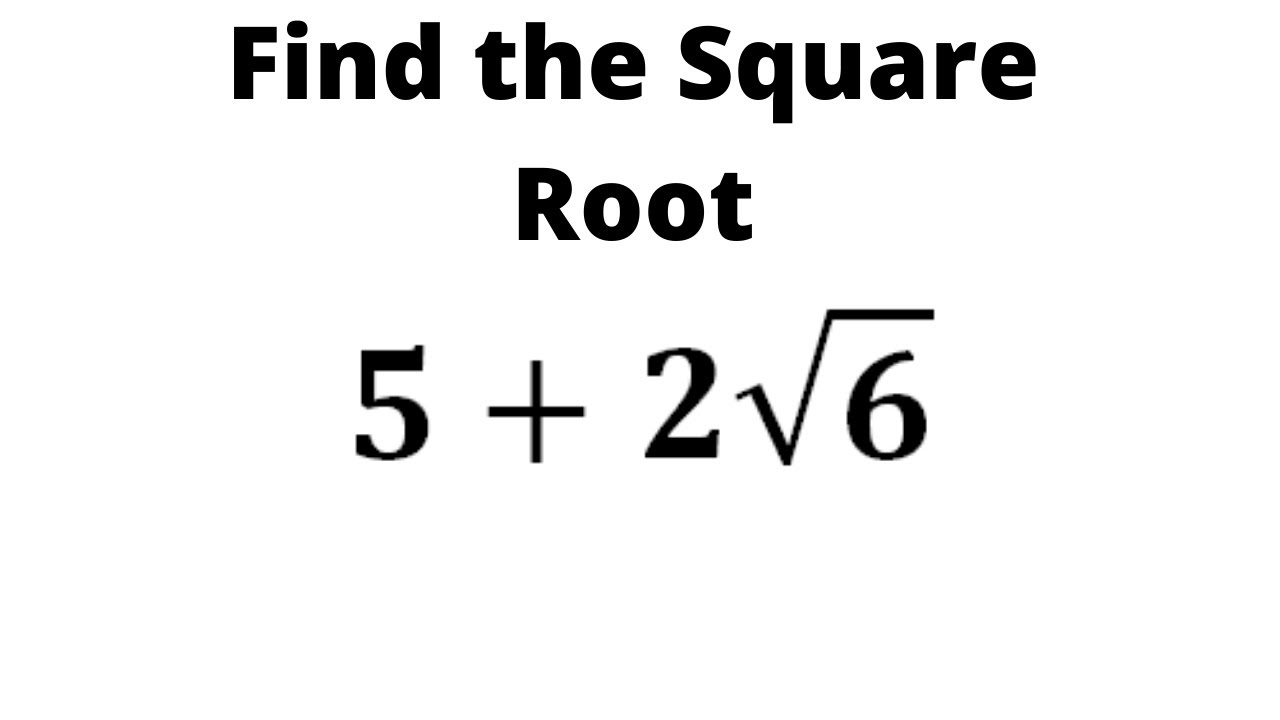
READ MORE:
Simplification and Calculation Methods
Understanding how to simplify and calculate the square root of a number is essential for various mathematical applications. Here, we outline the step-by-step methods to simplify and calculate the square root of 6.
-
Prime Factorization Method
Prime factorization involves expressing the number as a product of its prime factors and simplifying accordingly.
- Identify the prime factors of 6: 6 = 2 × 3.
- Express the square root using these factors: √6 = √(2 × 3).
- Since 2 and 3 are prime numbers, √6 cannot be simplified further using this method.
-
Multiplication and Grouping Method
This method involves breaking down the number under the square root and grouping for simplification.
- Write the number inside the square root as a product of its factors: √6 = √(2 × 3).
- Since neither factor is a perfect square, the expression remains √6.
-
Decimal Approximation Method
For practical purposes, the square root of 6 can be approximated using a calculator.
- Using a calculator, √6 ≈ 2.449.
- This approximation is useful for quick calculations and real-world applications.
Each of these methods provides a way to understand and work with the square root of 6, whether for exact simplification or practical approximation.
Mathematical Tools and Calculators
Various mathematical tools and calculators are available online to assist in solving expressions like \(5 \sqrt{6}\). These tools not only help in performing calculations but also aid in understanding the underlying mathematical concepts. Here are some key tools and methods:
- Square Root Calculators: Online square root calculators, such as those available on CalculatorSoup and CalculatorsHub, allow users to input any number to find its square root. These calculators provide both approximate and exact values, useful for educational and professional purposes.
- Simplification Tools: Tools designed to simplify radical expressions help break down complex expressions into more manageable forms. For instance, simplifying \(5 \sqrt{6}\) involves recognizing the multiplication of a coefficient (5) with the square root of 6.
- Step-by-Step Solvers: Many online platforms offer step-by-step solutions to mathematical problems. These solvers guide users through the process of solving equations, including those involving radicals, enhancing their problem-solving skills.
- Graphing Calculators: Advanced graphing calculators can plot functions and visualize the behavior of expressions involving square roots. This visual aid is particularly useful in understanding the properties and applications of such expressions in different mathematical contexts.
Using these tools, let's explore the step-by-step method to simplify the expression \(5 \sqrt{6}\):
- Identify the components: The expression consists of the coefficient 5 and the radical \(\sqrt{6}\).
- Approximate the square root: The square root of 6 is an irrational number, approximately 2.449.
- Multiply the coefficient by the approximate value: \(5 \times 2.449 \approx 12.245\).
The result is an approximate value, \(12.245\), which is useful for practical applications where exact precision is not necessary. For exact calculations, the expression \(5 \sqrt{6}\) can be used directly.
Utilizing these mathematical tools and calculators not only simplifies the process of solving such expressions but also deepens the understanding of the mathematical principles involved.
Mathematical Concepts and Explanations
The expression \(5 \sqrt{6}\) involves both multiplication and the square root function. To understand it fully, we need to break down the mathematical concepts involved, such as the properties of square roots and how they interact with multiplication.
Here's a detailed step-by-step explanation:
Understanding Square Roots
The square root of a number \(n\) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number \(n\). For example, the square root of 6 is denoted as \(\sqrt{6}\). Since 6 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number, approximately equal to 2.449.
Properties of Square Roots
- The square root function is only defined for non-negative numbers in the set of real numbers.
- \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\)
- \(\sqrt{n^2} = n\) if \(n \geq 0\)
Multiplying by a Constant
When a constant is multiplied by a square root, the constant is simply multiplied by the numerical value of the square root. In this case, 5 is the constant, and we multiply it by \(\sqrt{6}\). So, \(5 \sqrt{6}\) is approximately \(5 \times 2.449 = 12.245\).
Simplification and Calculation
- Recognize that \( \sqrt{6} \approx 2.449 \).
- Multiply the constant (5) by the approximate value of \(\sqrt{6}\).
- \(5 \times 2.449 = 12.245\).
Applications of Square Roots
- Square roots are used in solving quadratic equations.
- They are essential in geometry, for example, in calculating the sides of right triangles using the Pythagorean theorem.
- Square roots are also used in various fields of science and engineering to describe physical phenomena.
Step-by-Step Problem Solving
Solving equations involving square roots can be a straightforward process if approached methodically. Here, we will break down the steps for solving an equation involving the expression \(5\sqrt{6}\).
Example Problem
Let's consider the equation \(5\sqrt{6x} = 30\). Our goal is to solve for \(x\).
-
Isolate the square root term: Divide both sides of the equation by 5.
\[\frac{5\sqrt{6x}}{5} = \frac{30}{5}\]
Simplifying, we get:
\[\sqrt{6x} = 6\]
-
Square both sides of the equation: This step eliminates the square root.
\[\left(\sqrt{6x}\right)^2 = 6^2\]
Which simplifies to:
\[6x = 36\]
-
Solve for \(x\): Divide both sides by 6.
\[\frac{6x}{6} = \frac{36}{6}\]
Simplifying, we get:
\[x = 6\]
-
Verify the solution: Substitute \(x = 6\) back into the original equation to ensure it holds true.
\[5\sqrt{6 \times 6} = 5\sqrt{36} = 5 \times 6 = 30\]
Since the original equation is satisfied, \(x = 6\) is the correct solution.
Additional Example
Consider another equation with multiple square roots: \(\sqrt{2x - 5} - \sqrt{x - 1} = 1\).
-
Isolate one of the square roots: Add \(\sqrt{x - 1}\) to both sides.
\[\sqrt{2x - 5} = 1 + \sqrt{x - 1}\]
-
Square both sides: This step eliminates the first square root.
\[\left(\sqrt{2x - 5}\right)^2 = \left(1 + \sqrt{x - 1}\right)^2\]
Which simplifies to:
\[2x - 5 = 1 + 2\sqrt{x - 1} + x - 1\]
Combining like terms:
\[2x - 5 = x + 2\sqrt{x - 1}\]
-
Isolate the remaining square root: Subtract \(x\) from both sides.
\[x - 5 = 2\sqrt{x - 1}\]
-
Square both sides again: This step eliminates the second square root.
\[\left(x - 5\right)^2 = \left(2\sqrt{x - 1}\right)^2\]
Which simplifies to:
\[x^2 - 10x + 25 = 4(x - 1)\]
Expanding and combining like terms:
\[x^2 - 10x + 25 = 4x - 4\]
Move all terms to one side:
\[x^2 - 14x + 29 = 0\]
-
Solve the quadratic equation: Using the quadratic formula \(x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\) where \(a = 1\), \(b = -14\), and \(c = 29\).
\[x = \frac{14 \pm \sqrt{196 - 116}}{2}\]
\[x = \frac{14 \pm \sqrt{80}}{2}\]
\[x = \frac{14 \pm 8.94}{2}\]
Which gives us the solutions:
\[x = 11.47\] and \[x = 2.53\]
-
Verify the solutions: Substitute both \(x = 11.47\) and \(x = 2.53\) back into the original equation to check for extraneous roots.
After verification, \(x = 11.47\) is the valid solution.

Additional Learning Resources
Expanding your knowledge and understanding of square roots, particularly involving expressions like \(5\sqrt{6}\), can be achieved through a variety of resources. Here are some recommended tools and materials:
-
Further Reading on Square Roots
Enhance your theoretical understanding by exploring these comprehensive articles and textbooks:
- - A beginner-friendly guide covering the basics of square roots.
- - Detailed lessons and practice problems on radicals and their properties.
- - A comprehensive resource for learning about radical expressions and operations.
-
Interactive Math Tools and Games
Engage with interactive tools and games to practice and solidify your understanding of square roots:
- - A powerful tool for visualizing and calculating square roots and other mathematical functions.
- - Offers a variety of math games that include square root calculations.
- - Fun and educational games that challenge your understanding of square roots and other concepts.
-
Educational Videos and Tutorials
Watch these educational videos to see visual explanations and step-by-step problem solving:
- - A video tutorial on how to simplify radical expressions.
- - A comprehensive guide to understanding square roots.
- - Step-by-step video lessons on simplifying square roots.
Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 5+2√6
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách đơn giản hóa phân số dưới dấu căn với thủ thuật toán học hợp pháp. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu giúp bạn nắm bắt nhanh chóng.
Đơn Giản Hóa Phân Số Dưới Dấu Căn - Thủ Thuật Toán Học Hợp Pháp