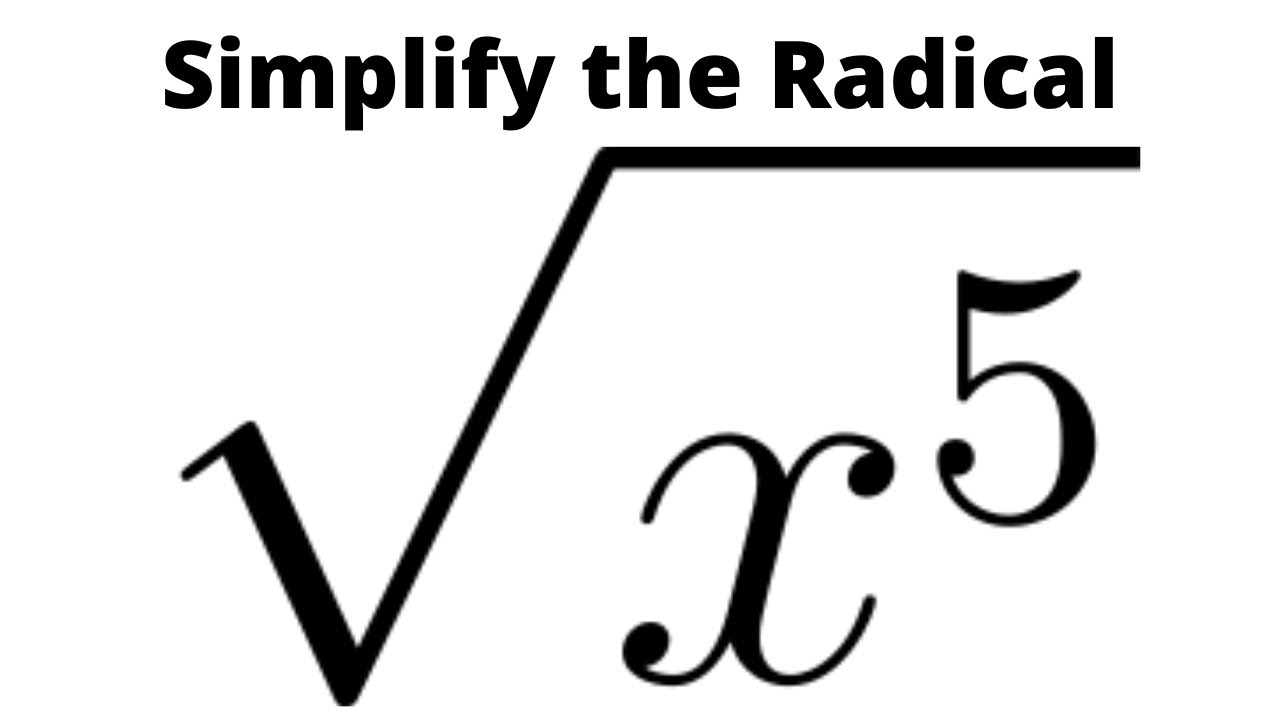Topic whats the square root of 50: The square root of 50 is an important mathematical concept often encountered in various fields of study. This article provides a thorough understanding of the square root of 50, its calculation methods, and practical applications. Whether you are a student, educator, or math enthusiast, this guide will enhance your knowledge and problem-solving skills.
Table of Content
Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 is represented as √50. It is an irrational number and can be expressed in different forms as follows:
- Radical form: √50 = 5√2
- Exponential form: √50 = 501/2
- Decimal form: √50 ≈ 7.0710678
Prime Factorization Method
To find the square root of 50 using prime factorization:
- Factorize 50 into its prime factors: 50 = 2 × 52
- Take the square root of the prime factors: √50 = √(2 × 52) = 5√2
- Using √2 ≈ 1.414, we get √50 ≈ 5 × 1.414 = 7.07
Long Division Method
The long division method can also be used to find the square root of 50:
- Pair the digits of 50 and place a bar over them. Since 50 is not a perfect square, use decimals.
- Determine the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 50. Here, 7 × 7 = 49. So, 7 is the quotient.
- Put a decimal after 7 and bring down pairs of zeros. Continue the process to get more decimal places.
- The result will be approximately 7.0710678.
Applications and Examples
Here are some examples of how the square root of 50 is used:
- Kevin wants to fence a square plot of land with an area of 50 square feet. The side length of the plot is √50 ≈ 7.071 feet, and the perimeter is 4 × 7.071 ≈ 28.284 feet.
- Randal travels at an average speed of 5√50 miles per hour for half an hour. The distance covered is 5 × 7.071 × 0.5 ≈ 17.677 miles.
FAQs
- What is the square root of 50? The square root of 50 is approximately 7.071.
- Is the square root of 50 a rational number? No, the square root of 50 is an irrational number.
- How can the square root of 50 be simplified? The simplified form of the square root of 50 is 5√2.
Additional Information
| Index | Radicand | Root Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 50 | Square Root of 50 | ±7.0710678119 |
| 3 | 50 | Cube Root of 50 | 3.6840314986 |
| 4 | 50 | Fourth Root of 50 | ±2.6591479485 |
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root symbol is √, and it denotes the principal square root, which is the non-negative root of a number. For example, the square root of 50 can be written as √50. The square root of any positive real number has two roots: a positive root and a negative root.
To understand square roots better, let us explore their properties and methods for calculating them.
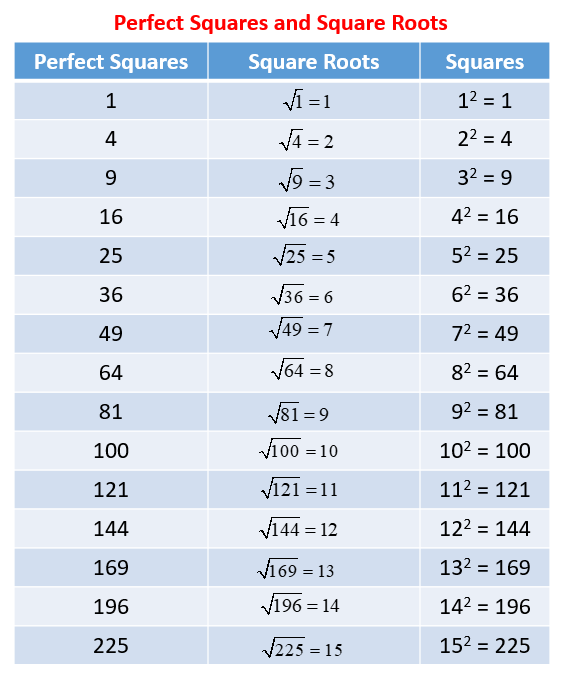
- Definition: The square root of a number x is a number y such that y² = x. For instance, the square roots of 9 are 3 and -3 because 3² = 9 and (-3)² = 9.
- Principal Square Root: The non-negative root of a number is called the principal square root. For example, the principal square root of 25 is 5.
-
Methods to Find Square Roots:
- Prime Factorization: This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors. For example, the prime factors of 50 are 2 and 5². Thus, the square root of 50 is 5√2.
- Long Division Method: This method is used for more accurate calculations, especially for non-perfect squares. It involves a step-by-step process of dividing and averaging.
-
Representation: Square roots can be expressed in different forms:
- Radical Form: √50 = 5√2
- Decimal Form: √50 ≈ 7.071
- Exponential Form: 501/2
Understanding square roots is essential for various applications in algebra, geometry, and real-world problem-solving. Mastering both the conceptual and computational aspects of square roots lays a solid foundation for advanced mathematical learning.
Understanding the Square Root of 50
The square root of 50 is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number 50. This concept is fundamental in mathematics and can be found using different methods, such as prime factorization and long division.
To start, let's express 50 as a product of its prime factors:
- 50 = 2 × 5 × 5
Using the prime factorization method:
- √50 = √(25 × 2)
- √50 = √25 × √2
- √50 = 5√2
Thus, the square root of 50 simplifies to 5√2, which is approximately 7.071.
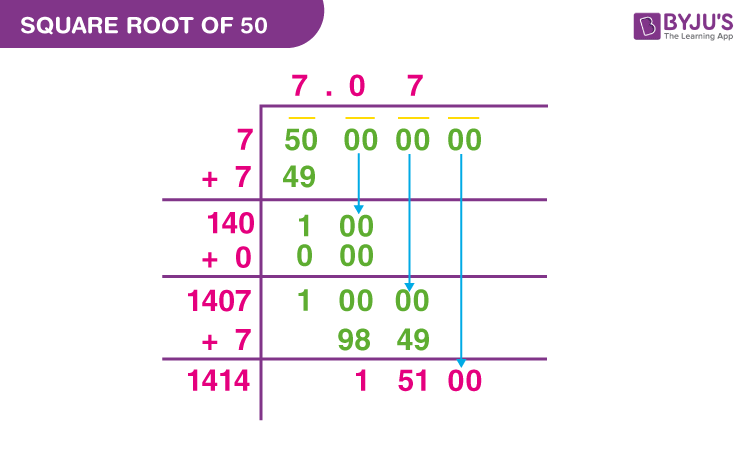
For a more precise calculation, the long division method is employed:
- Group the digits in pairs, starting from the decimal point. For 50, we write it as 50.000000.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 50. This is 7, because 7 × 7 = 49.
- Subtract 49 from 50 to get 1. Bring down a pair of zeros to get 100.
- Double the quotient (7) to get 14. Find a digit X such that 14X × X is less than or equal to 100. This digit is 0, because 140 × 0 = 0.
- Repeat the process to get more decimal places, resulting in a more accurate value of approximately 7.071.
This shows that the square root of 50 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
| Method | Result |
| Prime Factorization | 5√2 ≈ 7.071 |
| Long Division | ≈ 7.071 |
In conclusion, understanding the square root of 50 involves recognizing its properties as an irrational number and utilizing methods like prime factorization and long division to compute its value.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 50
Calculating the square root of 50 involves several methods, each with varying levels of complexity. Below are some common approaches:
1. Prime Factorization Method
This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors:
- Step 1: Write 50 as a product of its prime factors: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \).
- Step 2: Rewrite the expression to group the pairs: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} \).
- Step 3: Simplify by taking the square root of the perfect square: \( \sqrt{50} = 5 \times \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2} \).
2. Long Division Method
This traditional method involves a step-by-step division process:
- Step 1: Group the digits in pairs, starting from the decimal point.
- Step 2: Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first group.
- Step 3: Subtract the square of this number from the first group and bring down the next pair of digits.
- Step 4: Double the divisor and determine the next digit of the quotient.
- Step 5: Repeat the steps until you achieve the desired precision.
The result of the long division method will be approximately \( \sqrt{50} = 7.071 \).
3. Using a Calculator
The simplest method is to use a scientific calculator:
- Step 1: Enter the number 50.
- Step 2: Press the square root (√) button.
- Step 3: The display will show \( \sqrt{50} \approx 7.071 \).
4. Estimation and Averaging
This method uses approximation and refinement:
- Step 1: Estimate two close numbers whose squares surround 50 (e.g., 7 and 8).
- Step 2: Average these numbers: \( (7 + 8) / 2 = 7.5 \).
- Step 3: Square the average: \( 7.5^2 = 56.25 \).
- Step 4: Refine the average by using better estimates until the desired accuracy is achieved.
5. Using Excel or Google Sheets
For quick calculations, you can use software functions:
- Step 1: Open Excel or Google Sheets.
- Step 2: Use the SQRT function:
=SQRT(50). - Step 3: The cell will display \( \sqrt{50} \approx 7.071 \).
Each of these methods provides a way to calculate the square root of 50, offering different levels of precision and complexity.
Decimal and Radical Forms
The square root of 50 can be expressed in both decimal and radical forms. Understanding these forms is essential for various mathematical calculations.
Radical Form: The square root of 50 in its simplest radical form is expressed as:
- \(\sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
This radical form is derived by factoring 50 into its prime factors and simplifying under the square root.
Decimal Form: When calculated, the square root of 50 is approximately:
- \(\sqrt{50} \approx 7.0710678\)
The decimal form is a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal, indicating that it is an irrational number.
Understanding the Conversion:
- Identify the prime factors of 50: \(50 = 2 \times 5 \times 5\).
- Express under the square root: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
- Approximate the value of \(\sqrt{2}\) as 1.414 to find the decimal form: \(5 \times 1.414 = 7.07\).
The exact form and decimal form of the square root of 50 provide different perspectives useful in algebraic and numerical contexts respectively.

FAQ on Square Root of 50
Understanding the square root of 50 involves recognizing its properties and common questions. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify this mathematical concept:
- What is the square root of 50?
The square root of 50 is approximately 7.071. In radical form, it is represented as √50 or 5√2.
- Is the square root of 50 a rational number?
No, the square root of 50 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
- How can the square root of 50 be simplified?
The simplified radical form of the square root of 50 is 5√2. This is derived from factorizing 50 into its prime factors: 50 = 2 × 5², and then taking the square root of each factor.
- How is the square root of 50 calculated manually?
One common method to manually calculate the square root of 50 is through the long division method, which provides a step-by-step approximation of the square root.
- What are the applications of the square root of 50?
The square root of 50 can be applied in various fields such as engineering, physics, and geometry, particularly in solving problems involving right triangles and calculating distances.
Video hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 50. Theo dõi để hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính căn bậc hai của số 50.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 50: Sqrt(50)
READ MORE:
Video giải thích căn bậc hai của 50. Theo dõi để hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính căn bậc hai của số 50.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 50 (Giải Thích)