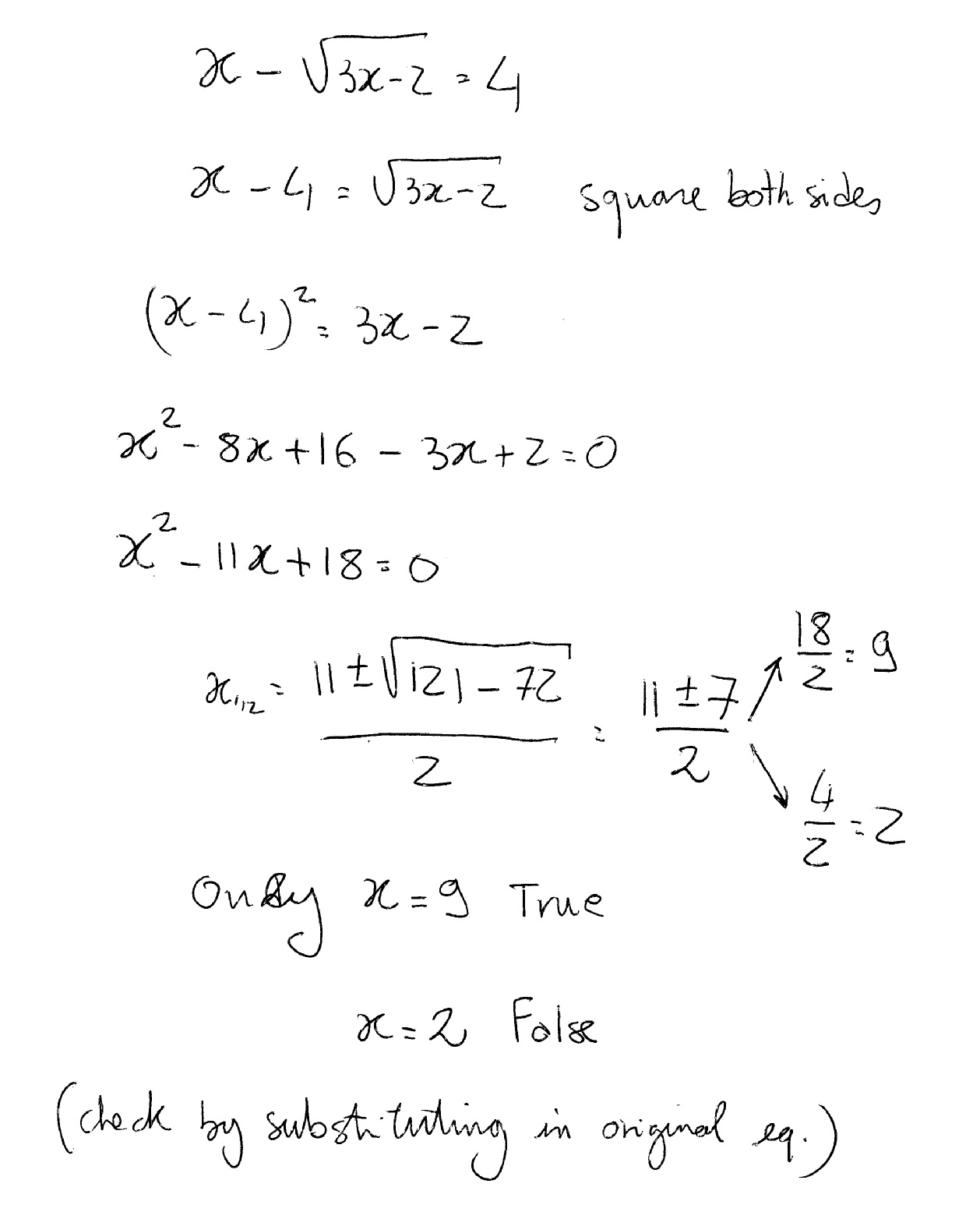Topic 5 square root of x: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the 5 square root of x. This article will help you understand the concept, properties, and applications of square roots. Whether you're simplifying expressions, solving equations, or graphing functions, we've got you covered with detailed explanations and practical examples.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of x
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Definition and Properties of Square Roots
- Simplifying Square Roots
- Methods to Find Square Roots
- Graphing Square Root Functions
- Solving Square Root Equations
- Examples and Applications
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để học cách đơn giản hóa biểu thức căn bậc hai của x^5. Bài hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Understanding the Square Root of x
The square root of a number \(x\) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number \(x\). It is denoted as \(\sqrt{x}\). The square root has two solutions: one positive and one negative.
Properties of Square Roots
- A square root of \(x\) is a number \(r\) such that \(r^2 = x\).
- There are two square roots for any positive number: \(\sqrt{x}\) (positive) and \(-\sqrt{x}\) (negative).
- The principal square root is the non-negative root and is often the default when using the square root symbol \(\sqrt{}\).
Example: Simplifying Square Roots
Consider the square root of 45:
\(\sqrt{45} = \sqrt{9 \times 5} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{5} = 3\sqrt{5}\)
This shows that simplifying the square root involves breaking it down into its factors, including perfect squares.
Graphing the Function \(y = 5\sqrt{x}\)
To graph the function \(y = 5\sqrt{x}\), follow these steps:
- Find the domain where the expression is defined. For \(y = 5\sqrt{x}\), \(x\) must be greater than or equal to 0.
- Select values of \(x\) from the domain and calculate corresponding \(y\) values.
- Plot the points \((x, y)\) and draw the curve.
Examples of Square Roots
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 81 | \(\pm 9\) |
| 25 | \(\pm 5\) |
| 100 | \(\pm 10\) |
| 10 | \(\pm 3.162\) |
Square Root Symbol
To type the square root symbol, you can use the following methods:
- Copy the symbol: √
- On Windows, use the character map to find and copy the symbol.
- On Mac, press Option + V to type the symbol.
Square roots are essential in mathematics for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding geometric properties.
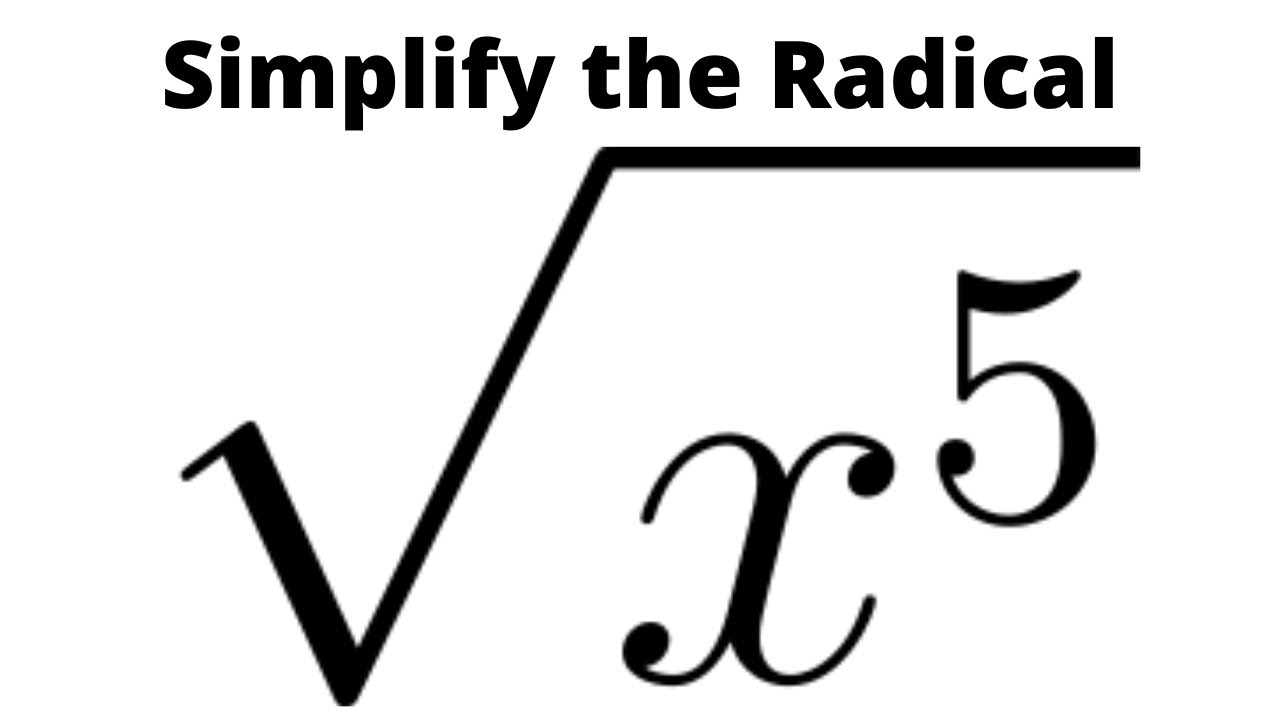
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical notation, the square root of x is denoted as √x. For instance, the square root of 25 is 5 because 5 × 5 = 25.
Here are some important points about square roots:
- Every positive real number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- The principal square root is the non-negative root, denoted as √x.
- Square roots of negative numbers are not real numbers but are instead complex numbers.
Let's consider an example: the square root of 16.
- Identify the number: 16
- Determine the square roots: 4 and -4 (since 4 × 4 = 16 and -4 × -4 = 16)
- The principal square root is 4.
Square roots have various applications in different fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. Understanding how to compute and simplify square roots is fundamental in solving many mathematical problems.
| Number | Square Root |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
Definition and Properties of Square Roots
The square root of a number x, denoted as √x or \( \sqrt{x} \), is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields x. For example, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) because \( 5^2 = 25 \).
Here are the fundamental properties of square roots:
- Non-Negative Principal Root: The principal square root is always non-negative. For any non-negative number x, \( \sqrt{x} \geq 0 \).
- Two Roots: Every positive number x has two square roots: \( \sqrt{x} \) (positive) and \( -\sqrt{x} \) (negative). For example, the square roots of 9 are 3 and -3.
- Zero: The square root of zero is zero, \( \sqrt{0} = 0 \).
- Product Property: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots, \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \).
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots, \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \), for \( b \neq 0 \).
- Powers of Square Roots: The square root of a number squared returns the absolute value of the number, \( \sqrt{x^2} = |x| \).
Let's explore these properties with some examples:
- \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \) and \( \sqrt{49} = 7 \)
- \( \sqrt{9 \times 16} = \sqrt{144} = 12 \) and \( \sqrt{9} \cdot \sqrt{16} = 3 \cdot 4 = 12 \)
- \( \sqrt{\frac{25}{4}} = \frac{\sqrt{25}}{\sqrt{4}} = \frac{5}{2} \)
- \( \sqrt{(-5)^2} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
These properties are crucial for simplifying expressions and solving equations involving square roots. The following table provides some common values of square roots:
| Number | Square Root |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves expressing a square root in its simplest form. This often requires factoring the number inside the square root into its prime factors and then applying the properties of square roots. Here’s a step-by-step guide to simplifying square roots:
- Factor the Number: Break down the number inside the square root into its prime factors. For example, for \( \sqrt{72} \):
- 72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
- Pair the Factors: Group the prime factors into pairs of the same number.
- \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3} \)
- Take One Factor Out of Each Pair: For each pair of the same number, take one factor out of the square root.
- \( \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
Let’s consider another example:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \):
- Factorize 50: 50 = 2 × 5 × 5
- Pair the factors: \( \sqrt{2 \times 5 \times 5} \)
- Simplify: \( 5\sqrt{2} \)
Using these steps, you can simplify any square root. Here are some additional examples:
| Original Square Root | Simplified Form |
| \( \sqrt{18} \) | 3\sqrt{2} |
| \( \sqrt{45} \) | 3\sqrt{5} |
| \( \sqrt{75} \) | 5\sqrt{3} |
| \( \sqrt{98} \) | 7\sqrt{2} |
Simplifying square roots is a valuable skill in algebra that helps in solving equations and understanding mathematical relationships more clearly.
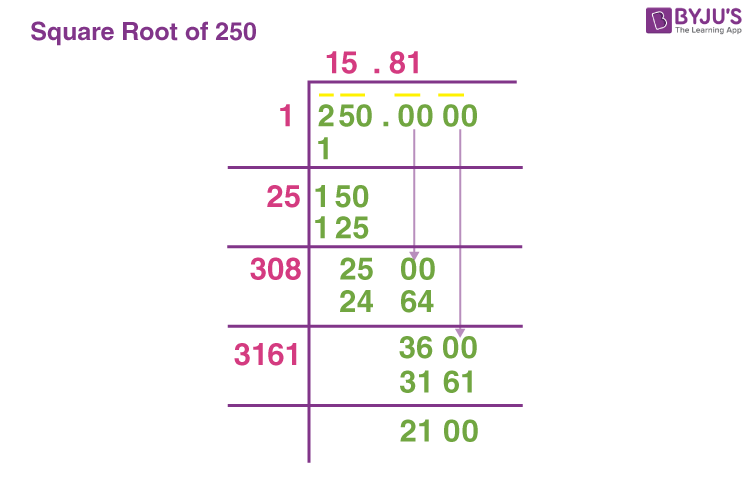
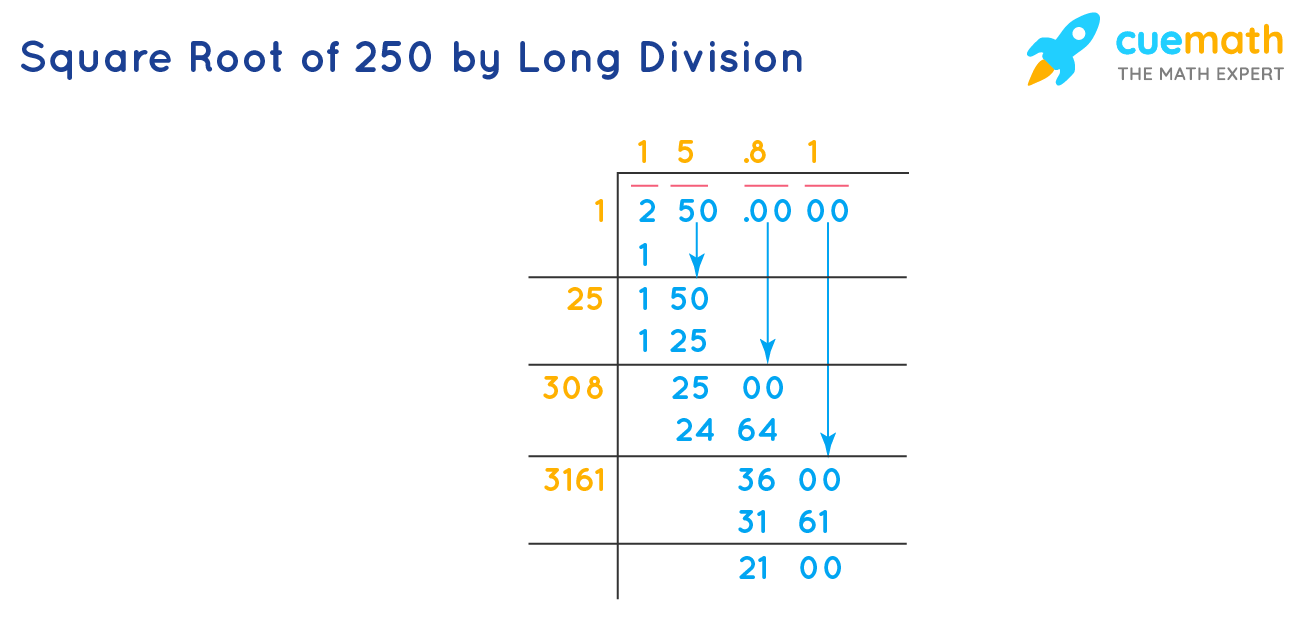
Methods to Find Square Roots
There are several methods to find the square root of a number, including:
- Estimation Method: Approximating the square root by identifying the nearest perfect squares.
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down the number into its prime factors and extracting square roots.
- Newton's Method: Iteratively improving a guess until it converges to the square root.
- Using a Calculator: Modern calculators and software can directly compute square roots.
Each method has its advantages depending on the context and precision required.
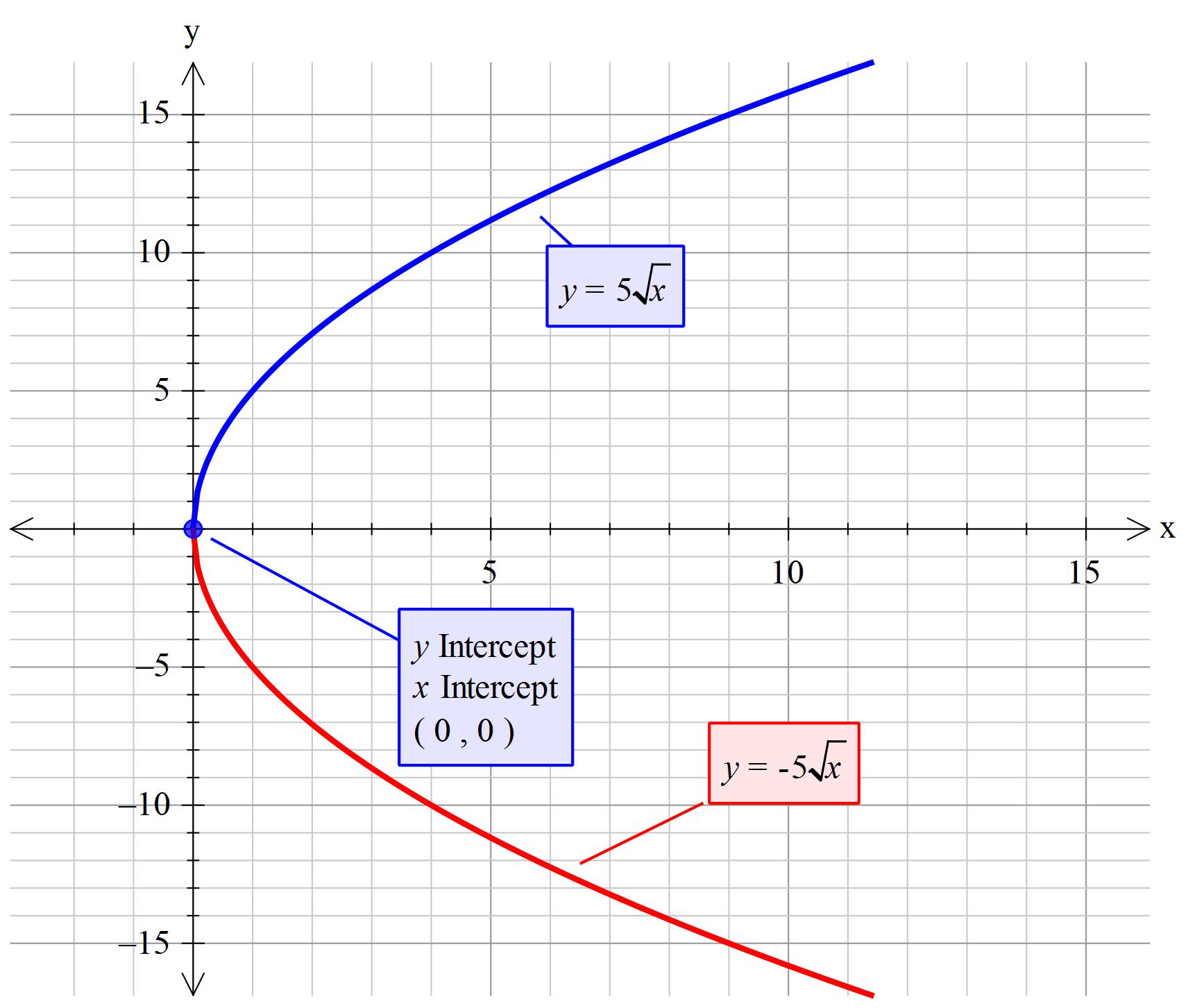
Graphing Square Root Functions
Graphing square root functions involves understanding their basic shape and characteristics:
- Domain and Range: The domain (x-values) of a square root function is typically non-negative real numbers (x ≥ 0), and the range (y-values) includes non-negative real numbers (y ≥ 0).
- Basic Graph: The graph of y = √x starts at the origin (0, 0) and extends to the right, showing a curve that increases slowly at first and then more steeply.
- Transformations: Like other functions, square root functions can undergo transformations such as shifts, stretches, and reflections.
- Graphical Properties: Key points include the vertex at (0, 0) and the behavior as x approaches infinity.
Understanding these aspects helps in accurately graphing and interpreting square root functions.
Solving Square Root Equations
Solving square root equations involves several steps to isolate the variable under the square root:
- Isolate the Square Root: Move any constants to the other side of the equation.
- Square Both Sides: Eliminate the square root by squaring both sides of the equation.
- Solve the Resulting Equation: Solve the resulting equation obtained after squaring both sides.
- Check for Extraneous Solutions: Verify solutions by substituting them back into the original equation to ensure they are valid.
It's important to follow these steps carefully to find accurate solutions to square root equations.
Examples and Applications
Square roots have numerous practical examples and applications:
- Geometry: Calculating side lengths in geometric figures like squares, rectangles, and triangles.
- Physics: Determining velocities, forces, and energies involving quadratic relationships.
- Engineering: Designing structures and machinery where understanding dimensions and forces is crucial.
- Finance: Estimating growth rates and understanding financial models.
- Technology: Digital signal processing, image processing, and data compression rely on mathematical foundations that include square roots.
These examples demonstrate the wide-ranging utility of square roots in various fields.
Xem video này để học cách đơn giản hóa biểu thức căn bậc hai của x^5. Bài hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Đơn giản hóa biểu thức căn bậc hai của x^5 | Video hướng dẫn
READ MORE:
Xem video này để học cách đơn giản hóa toán căn bậc hai và tìm giá trị của X. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu về bài toán.
Đơn giản hóa toán căn bậc hai | Tìm giá trị của X