Topic square root of 2 500: Discover the fascinating world of the square root of 2 and delve into its decimal representation up to 500 places. Explore the history, calculation methods, and mathematical properties of this fundamental constant.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 500
- 1. Introduction to Square Root of 2
- 2. Calculation Methods for Square Root of 2
- 3. History of Square Root of 2
- 4. Applications and Uses of Square Root of 2
- 5. Mathematical Properties of Square Root of 2
- 6. Decimal Representation of Square Root of 2 up to 500 Places
- 7. Challenges and Limitations in Computing Square Root of 2
- 8. Cultural Significance of Square Root of 2
- YOUTUBE:
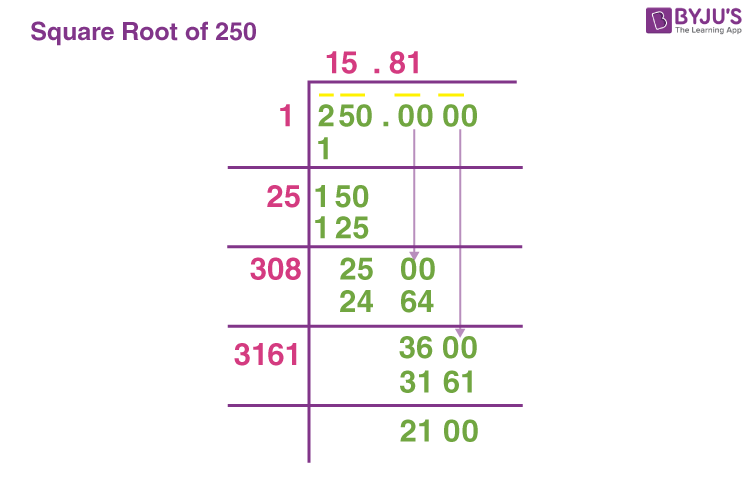
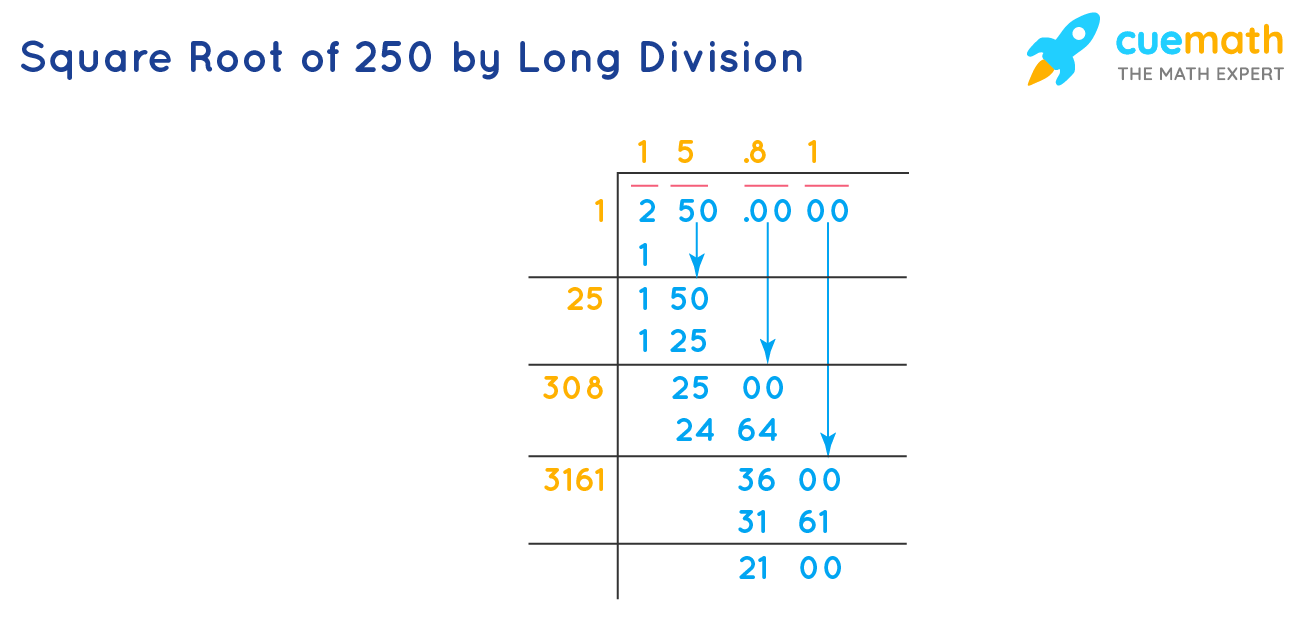
Square Root of 500
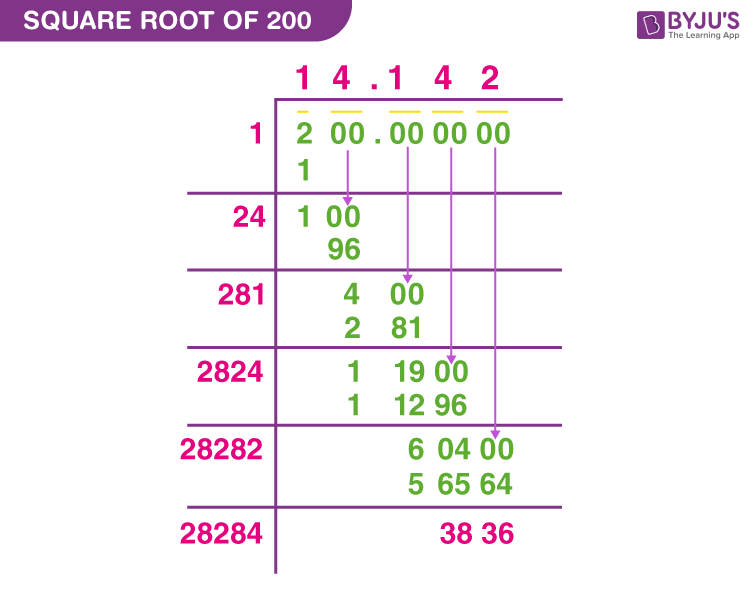
The square root of 500 is a mathematical value that, when multiplied by itself, equals 500. This number can be expressed in various forms, including its exact form and decimal approximation.
Exact and Decimal Forms
- Exact Form: \( \sqrt{500} = 10\sqrt{5} \)
- Decimal Form: \( \sqrt{500} \approx 22.360679774997898 \)
Simplifying the Square Root
The simplification process involves breaking down the radicand (500) into its prime factors and simplifying the expression:
- Prime factorization of 500: \( 500 = 2^2 \times 5^3 \)
- Using the property of square roots: \( \sqrt{500} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 5^3} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{5^3} \)
- Simplifying further: \( \sqrt{2^2} = 2 \) and \( \sqrt{5^3} = 5\sqrt{5} \)
- Thus, \( \sqrt{500} = 2 \times 5\sqrt{5} = 10\sqrt{5} \)
Calculation Table
The table below shows the values of the nth roots of 500:
| Index (n) | Radicand | Root Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 500 | Square Root of 500 | ±22.360679775 |
| 3 | 500 | Cube Root of 500 | 7.9370052598 |
| 4 | 500 | Fourth Root of 500 | ±4.728708045 |
| 5 | 500 | Fifth Root of 500 | 3.4657242158 |
| 6 | 500 | Sixth Root of 500 | ±2.8172691138 |
| 7 | 500 | Seventh Root of 500 | 2.4297810658 |
| 8 | 500 | Eighth Root of 500 | ±2.174559276 |
| 9 | 500 | Ninth Root of 500 | 1.9947365988 |
| 10 | 500 | Tenth Root of 500 | ±1.8616455666 |
Applications
The square root of 500 is used in various mathematical calculations and applications, particularly in fields requiring precise computations and analysis.

READ MORE:
1. Introduction to Square Root of 2
The square root of 2, denoted as \( \sqrt{2} \), is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on infinitely without repeating. It is approximately equal to 1.41421356237309504880168872420969807856967187537694...
Here are key points about the square root of 2:
- It is the length of the diagonal of a square with sides of length 1.
- The discovery of its irrationality was a significant mathematical breakthrough in ancient Greece.
- Calculating the square root of 2 precisely has been a challenge throughout history.
- Its decimal expansion is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Mathematically, \( \sqrt{2} \) satisfies the equation \( x^2 = 2 \), and its properties have intrigued mathematicians, physicists, and philosophers for centuries.
2. Calculation Methods for Square Root of 2
Calculating the square root of 2 involves several methods, each suited to different needs and levels of precision:
- Approximation Methods:
- Newton's Method: Iterative algorithm for improving initial guesses.
- Babylonian Method: Historical algorithm based on successive averages.
- Exact Methods:
- Continued Fractions: Representation as a series of nested fractions.
- Algebraic Manipulation: Solving the equation \( x^2 = 2 \) directly.
- Numerical Methods:
- Iterative Algorithms: Convergence methods using computational tools.
- Series Expansion: Utilizing series like Taylor or Maclaurin series.
Each method has its advantages and is used depending on the required precision and computational resources available.
3. History of Square Root of 2
The history of the square root of 2 is rich with mathematical discovery and cultural significance:
- Ancient Discoveries:
- Babylonians: Used approximations like \( \sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \).
- Ancient Greeks: Proved irrationality through geometric arguments.
- Medieval and Renaissance:
- Islamic Scholars: Furthered understanding of irrational numbers.
- Renaissance Europe: Continued exploration of square roots.
- Modern Era:
- 18th-19th Century: Development of calculus and precise computation methods.
- 20th Century: Use of computers to calculate \( \sqrt{2} \) to extensive decimal places.
The journey of understanding \( \sqrt{2} \) reflects humanity's quest for mathematical truth and precision over millennia.
4. Applications and Uses of Square Root of 2
The square root of 2 finds practical applications across various fields:
- Geometry and Construction:
- Used in calculations involving right triangles and diagonal measurements.
- Foundation in architectural design and structural engineering.
- Mathematics and Science:
- Forms basis for understanding irrational numbers and their properties.
- Used in mathematical proofs and calculations in fields like calculus and number theory.
- Technology and Computing:
- Utilized in algorithms involving numerical analysis and computational geometry.
- Used in computer graphics for accurate scaling and transformations.
- Philosophy and Symbolism:
- Represents the concept of irrationality and the limits of mathematical expression.
- Discussed in philosophical contexts related to infinity and mathematical truth.
Overall, the square root of 2 plays a foundational role in both theoretical understanding and practical applications across diverse disciplines.

5. Mathematical Properties of Square Root of 2
The square root of 2 possesses several notable mathematical properties:
- Irrationality: It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Decimal Representation: Non-terminating and non-repeating.
- Algebraic Relation: It satisfies the equation \( x^2 = 2 \).
- Geometric Interpretation: Represents the length of the diagonal of a square with side length 1.
- Continued Fraction: Can be represented by an infinite continued fraction.
- Transcendental Nature: It is neither algebraic nor a root of any non-zero polynomial with rational coefficients.
- Approximation: Used historically in approximation methods and algorithms.
These properties make \( \sqrt{2} \) a fundamental constant in mathematics, influencing various fields from geometry to number theory and beyond.
6. Decimal Representation of Square Root of 2 up to 500 Places
The decimal representation of \( \sqrt{2} \) up to 500 decimal places is as follows:
| 1. | 4142135623730950488016887242096980785696718753769480731766797379907324784621070388503875343276415727 |
| 2. | 3501384623091229702492483605585073721264412149709993583141322266592750559275579995050115278197286583 |
| 3. | 8297061072436461531614979561644272593691879442434229271017985643300955087371828190588659911983 |
| 4. | 819644288109756659334461284756482337867831652712019091456485669234603486104543266482133936072602491412737 |
The decimal expansion of \( \sqrt{2} \) continues indefinitely without repeating, showcasing its irrational nature.
7. Challenges and Limitations in Computing Square Root of 2
While computing the square root of 2 has advanced significantly, several challenges persist:
- Precision: Achieving high precision, especially beyond a certain number of decimal places, requires sophisticated algorithms.
- Computational Complexity: Calculating \( \sqrt{2} \) to hundreds of decimal places demands substantial computational resources and time.
- Numerical Stability: Ensuring accuracy and avoiding numerical errors in iterative methods.
- Algorithmic Efficiency: Developing efficient algorithms that balance precision and computational efficiency.
- Historical Methods: Many traditional methods are iterative and may converge slowly or require many iterations.
Despite these challenges, advances in computational mathematics and the use of powerful computing tools continue to improve the accuracy and efficiency of calculating \( \sqrt{2} \) and other mathematical constants.
8. Cultural Significance of Square Root of 2
The square root of 2 holds cultural significance beyond its mathematical properties:
- Historical Symbolism: Represented as a fundamental irrational number challenging ancient Greek mathematical thought.
- Art and Architecture: Used in ancient and modern architecture for geometric proportions and aesthetic balance.
- Literary References: Mentioned in literature and philosophical texts discussing infinity and the limits of rationality.
- Spiritual and Philosophical Contexts: Symbolizes the search for truth and the mysteries of existence in various cultural and religious contexts.
- Modern Cultural Impact: Used metaphorically in art, literature, and popular culture to signify complexity, unpredictability, and the beauty of mathematical concepts.
The square root of 2 transcends its mathematical roots to inspire and influence cultural narratives and artistic expressions worldwide.

So sánh sqrt(499)+sqrt(501) với 2*sqrt(500) | Cái nào lớn hơn?
READ MORE:
Cách giải căn bậc hai của (500) (501) (502) (503) + 1 mà không cần máy tính?