Topic root 2 rectangle: Discover the intriguing concept of the Root 2 Rectangle, where mathematical precision meets architectural elegance. This article delves into its unique properties, construction methods, and practical applications in design. Explore how this geometric form enhances aesthetic appeal and functionality in various artistic and architectural contexts.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Root 2 Rectangle
- Introduction to Root 2 Rectangle
- Mathematical Properties of Root 2 Rectangle
- Construction Methods for Root 2 Rectangle
- Applications of Root 2 Rectangle in Architecture
- Artistic and Aesthetic Considerations of Root 2 Rectangle
- Comparisons with Other Golden Ratio Forms
- Historical Significance of Root 2 Rectangle
- Practical Examples of Root 2 Rectangle in Design
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách vẽ bất kỳ Hình chữ nhật căn bậc 2 nào với các tỷ lệ √2, √3, √4, √5. Video này có phù hợp với bài viết về Hình chữ nhật căn bậc 2 không?
Understanding the Root 2 Rectangle
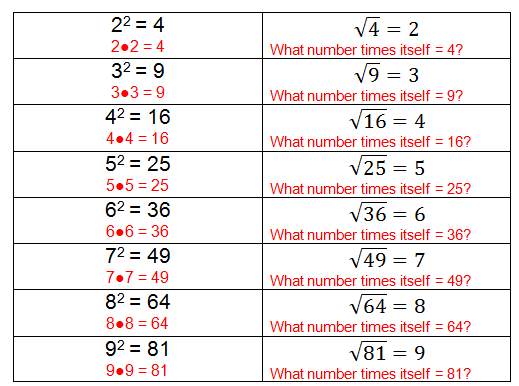
The root 2 rectangle, also known as the A4 or ISO 216 standard paper size ratio, is a geometric figure with unique properties. This rectangle is defined by its aspect ratio of 1:√2, meaning the longer side is √2 times the length of the shorter side.
Properties of the Root 2 Rectangle
- The aspect ratio is 1:√2.
- If a root 2 rectangle is cut or folded in half parallel to its shorter side, the two resulting rectangles will also have the same 1:√2 aspect ratio.
- This self-similarity property makes the root 2 rectangle ideal for paper sizes, allowing consistent scaling without changing the aspect ratio.
Mathematical Definition
The dimensions of a root 2 rectangle can be expressed as follows:
Applications of the Root 2 Rectangle
- Paper Sizes: The most common application is in the ISO 216 standard for paper sizes (A series), where A4 paper has dimensions that conform to the root 2 ratio.
- Design and Architecture: This ratio is often used in design and architecture for its aesthetic properties and ease of scaling.
- Photography: The root 2 rectangle is sometimes used in photography and art to create pleasing compositions.
Deriving the Aspect Ratio
To derive the aspect ratio of a root 2 rectangle, consider the following steps:
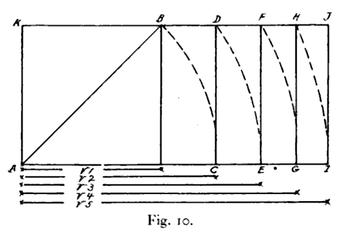
- Start with a square with sides of length 1.
- Cut the square in half along its diagonal to form two right-angle triangles.
- Rearrange these triangles to form a rectangle with sides of 1 and √2.
This process demonstrates that the root 2 rectangle maintains its aspect ratio of 1:√2, regardless of scaling or division.
Conclusion
The root 2 rectangle is a fundamental geometric shape with applications in various fields due to its unique properties and the ease with which it can be scaled and reproduced. Its aspect ratio of 1:√2 makes it especially valuable in standardizing dimensions in paper sizes, design, and art.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Root 2 Rectangle
A Root 2 Rectangle, also known as a silver rectangle or a √2 rectangle, is a unique geometric form defined by its aspect ratio. Unlike the more commonly known golden rectangle (which has an aspect ratio of φ = 1.618...), the Root 2 Rectangle's sides are in the ratio of √2:1, where √2 is approximately 1.414.
This rectangle emerges from the mathematical relationship where dividing a square into two halves along its diagonal results in two rectangles, one of which is a Root 2 Rectangle. It can also be derived geometrically by adding a square to itself, maintaining the rectangle's proportion.
In terms of construction, the Root 2 Rectangle's proportions have notable properties in design and architecture. Its unique aspect ratio lends itself to practical applications in areas requiring specific spatial relationships, such as in paper sizes (ISO sizes), where A0 is defined as having an area of 1 square meter with sides in the Root 2 ratio.
Mathematically, the Root 2 Rectangle has connections to various areas of study, including number theory and geometric constructions. Its properties make it a subject of interest in both artistic compositions and technical drawings, where its harmonious proportions offer an alternative to the more widely recognized golden ratio.
Mathematical Properties of Root 2 Rectangle
The Root 2 Rectangle exhibits several notable mathematical properties:
- Aspect Ratio: The sides of a Root 2 Rectangle are in the ratio of √2:1, which approximates to 1.414:1.
- Geometric Construction: It can be constructed by adding a square to itself or by dividing a square along its diagonal.
- Area Relationship: When a square of side length 1 is divided into two rectangles along its diagonal, one of these rectangles is a Root 2 Rectangle.
- Connection to Squares and Proportions: The Root 2 Rectangle maintains its proportion when scaled, making it useful in applications such as paper sizes (ISO standards).
- Mathematical Representation: In terms of mathematics, the Root 2 Rectangle's dimensions can be represented as x × √2x, where x is a positive real number.
These properties make the Root 2 Rectangle a subject of interest in various mathematical fields, including geometry, number theory, and applications in design and architecture.
Construction Methods for Root 2 Rectangle
There are several methods to construct a Root 2 Rectangle:
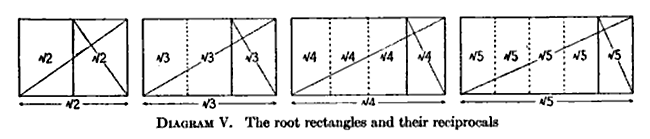
- Geometric Construction: Start with a square of side length 1. Divide the square into two rectangles by drawing a diagonal. One of these rectangles will be a Root 2 Rectangle.
- Algebraic Construction: Consider a square with side length 1. The Root 2 Rectangle can be formed by adding a square of side length 1 adjacent to it, resulting in a rectangle with sides in the ratio of √2:1.
- Iterative Construction: Begin with a square of any size. To create a Root 2 Rectangle, repeatedly add squares of the same size to the existing rectangle, maintaining the aspect ratio of √2:1.
- Mathematical Representation: The Root 2 Rectangle can be described as having dimensions x × √2x, where x is a positive real number. This representation helps in scaling the rectangle while maintaining its proportional characteristics.
These construction methods illustrate the versatility of the Root 2 Rectangle in geometric and mathematical contexts, demonstrating its applicability in various fields including design, architecture, and engineering.
Applications of Root 2 Rectangle in Architecture
The Root 2 Rectangle finds diverse applications in architecture due to its unique geometric properties:
- Proportional Harmony: Architects utilize Root 2 Rectangles to create aesthetically pleasing proportions in building facades, room dimensions, and structural elements.
- Space Efficiency: The rectangle's aspect ratio optimizes space utilization in floor plans and interior layouts, providing efficient use of area while maintaining visual balance.
- Facade Design: Facades designed using Root 2 Rectangles often convey a sense of symmetry and harmony, contributing to the overall visual appeal of architectural compositions.
- Structural Integration: In structural design, the rectangle's proportions aid in distributing loads effectively, enhancing stability and structural integrity.
- Historical Adaptation: Historical buildings and monuments incorporate Root 2 Rectangles in their designs, reflecting the enduring appeal and practical utility of this geometric form.
These architectural applications demonstrate how the Root 2 Rectangle serves as a versatile tool for architects, balancing mathematical precision with aesthetic considerations in various building projects.
Artistic and Aesthetic Considerations of Root 2 Rectangle
The Root 2 Rectangle holds significant artistic and aesthetic appeal:
- Harmonious Proportions: Artists and designers appreciate the rectangle's √2:1 ratio for its harmonious and balanced proportions, which can evoke a sense of stability and order in compositions.
- Visual Balance: Its proportions offer a visually pleasing alternative to other geometric forms, contributing to the overall balance and coherence of artistic creations.
- Historical Significance: Throughout history, the Root 2 Rectangle has been utilized in art and architecture, reflecting its enduring appeal and timeless aesthetic qualities.
- Cultural Adaptation: Across different cultures, artists have integrated the rectangle into various art forms, from paintings and sculptures to decorative motifs, showcasing its versatility and aesthetic adaptability.
- Mathematical Inspiration: The rectangle's mathematical basis provides artists with a structured framework for exploring geometric relationships and spatial compositions, enriching their creative expressions.
These artistic and aesthetic considerations highlight the Root 2 Rectangle as a versatile element that enhances visual harmony and cultural significance in artistic endeavors.
Comparisons with Other Golden Ratio Forms
When comparing the Root 2 Rectangle with other golden ratio forms, several distinctions and similarities arise:
- Aspect Ratio: The Root 2 Rectangle has an aspect ratio of √2:1 (approximately 1.414:1), whereas the golden ratio (φ) is approximately 1.618:1.
- Geometric Construction: Unlike the golden rectangle, which is constructed by dividing a square based on the golden ratio, the Root 2 Rectangle emerges from dividing a square along its diagonal.
- Mathematical Properties: Both rectangles exhibit unique mathematical properties, influencing their applications in art, architecture, and design.
- Aesthetic Appeal: While the golden rectangle is celebrated for its aesthetic balance and appearance in nature, the Root 2 Rectangle offers a different aesthetic appeal with its distinctive proportions.
- Cultural Significance: Each rectangle form has cultural significance and historical use in various civilizations, showcasing their enduring impact on artistic and architectural practices.
These comparisons illustrate how different geometric ratios and forms contribute to diverse artistic expressions and functional applications in different contexts.
Historical Significance of Root 2 Rectangle
The Root 2 Rectangle holds historical significance across various cultures and periods:
- Ancient Civilizations: In ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, rectangles with proportions close to √2:1 were used in architectural designs and artistic compositions.
- Greek Influence: Greek mathematicians and architects explored geometric forms, including rectangles with √2 proportions, as seen in their architectural achievements.
- Renaissance Era: During the Renaissance, artists and architects revisited classical geometries, including the Root 2 Rectangle, integrating it into their works to achieve ideal proportions and aesthetic harmony.
- Modern Applications: In modern times, the Root 2 Rectangle's mathematical properties continue to inspire architects, designers, and artists, influencing contemporary architectural styles and artistic expressions.
- Cultural Symbolism: Beyond its mathematical significance, the rectangle embodies cultural symbolism and aesthetic ideals, reflecting human endeavors to achieve balance and beauty in creative endeavors.
This historical perspective underscores the enduring legacy and cultural relevance of the Root 2 Rectangle in shaping architectural, artistic, and mathematical developments throughout history.
Practical Examples of Root 2 Rectangle in Design
The Root 2 Rectangle is utilized in various practical applications across different design disciplines:
- Paper Sizes: ISO paper sizes, such as A0, A1, A2, etc., are based on Root 2 Rectangle proportions, ensuring consistent aspect ratios for easy scaling and compatibility.
- Architectural Floor Plans: Architects use Root 2 Rectangles to design floor plans that optimize space efficiency while maintaining proportional harmony in room dimensions and layout.
- Artistic Compositions: Artists integrate Root 2 Rectangle proportions into paintings, sculptures, and other art forms to achieve balanced compositions and visual appeal.
- Graphic Design: Graphic designers utilize Root 2 Rectangle proportions in layout design, ensuring balanced and aesthetically pleasing arrangements of text and images.
- Engineering Applications: Engineers apply Root 2 Rectangle principles in structural design to achieve optimal load distribution and stability in buildings and infrastructure.
These practical examples highlight the versatility and functional advantages of the Root 2 Rectangle in design, where its mathematical properties contribute to both aesthetic appeal and operational efficiency.

Hướng dẫn cách vẽ bất kỳ Hình chữ nhật căn bậc 2 nào với các tỷ lệ √2, √3, √4, √5. Video này có phù hợp với bài viết về Hình chữ nhật căn bậc 2 không?
Hướng dẫn vẽ bất kỳ Hình chữ nhật căn bậc 2 nào ▭ √2 √3 √4 √5 Tỷ lệ
READ MORE:
New Forms of Togetherness - Resident Artist Siri Black: Square Root 2 Rectangle (Work in Progress)
New Forms of Togetherness - Nghệ sĩ cư dân Siri Black: Hình chữ nhật căn bậc 2 (Đang phát triển)