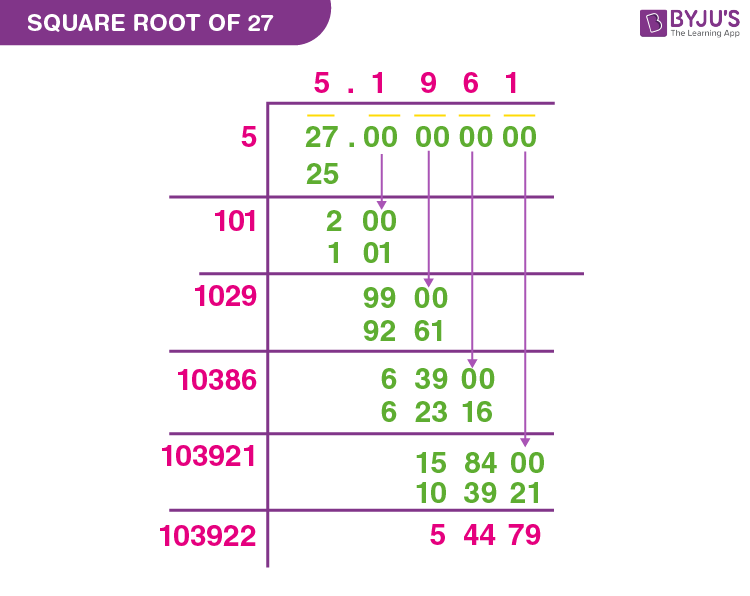
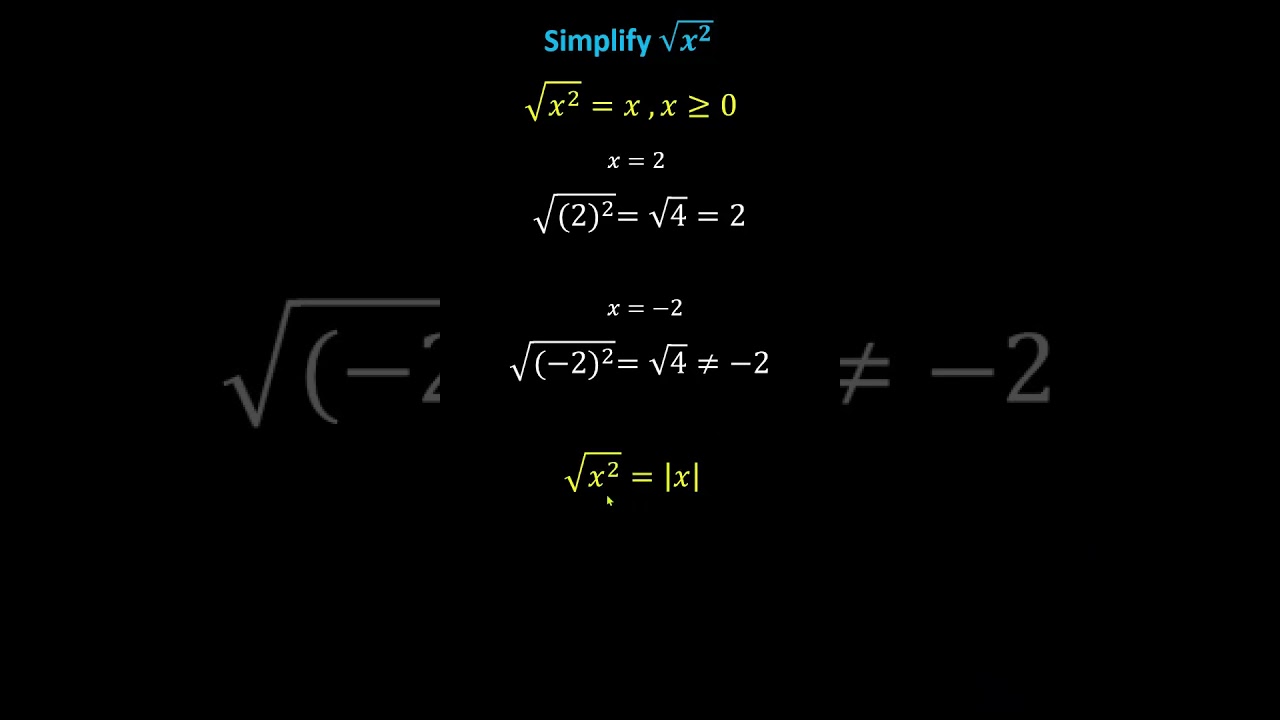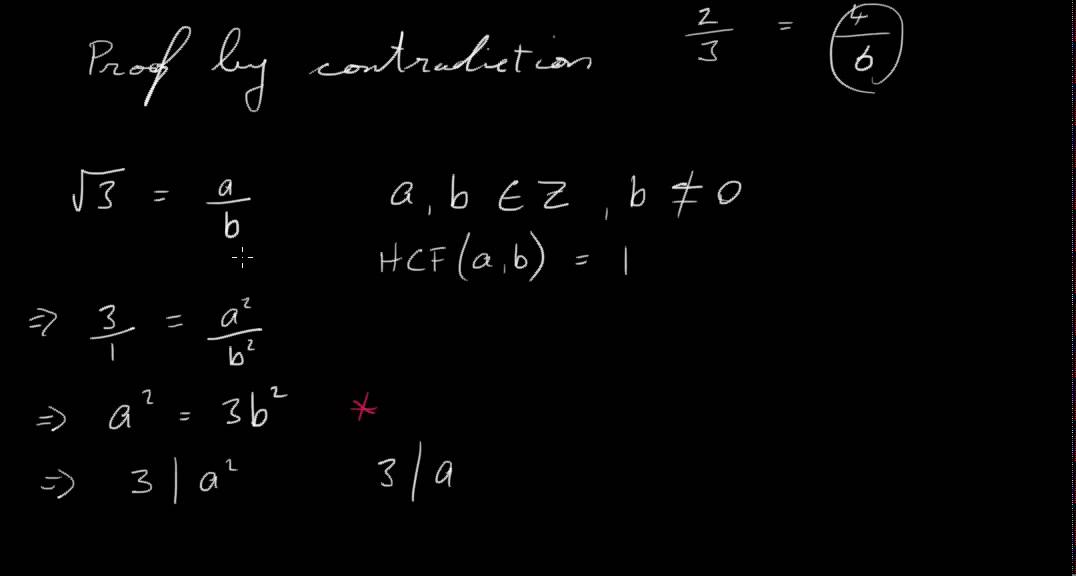Topic square root of 2/3: The square root of 2/3 is a fundamental concept in mathematics with various applications. This article explores the methods to calculate it, its significance, and practical examples. Dive in to understand the intricacies of the square root of 2/3 and how it applies in different mathematical contexts.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 2/3
- Introduction to the Square Root of 2/3
- Mathematical Definition and Properties
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Approximating the Square Root of 2/3
- Applications in Real Life
- Comparing Square Roots of Fractions
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Using Calculators and Tools
- Square Root of 2/3 in Advanced Mathematics
- Visual Representation and Graphical Interpretation
- Practical Examples and Exercises
- FAQs on the Square Root of 2/3
- Additional Resources and Further Reading
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Video 'Rút Gọn Căn Bậc Hai của 2/3' hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách rút gọn và tính toán căn bậc hai của phân số 2/3.
Square Root of 2/3
The square root of a fraction is found by taking the square root of the numerator and the square root of the denominator separately. For the fraction , we calculate the square root as follows:
Calculation
The fraction is:
The square root of the fraction can be expressed as:
Using the property of square roots of fractions, this is equal to:
Approximate Value
Approximating the square roots of the numerator and the denominator individually:
and
Therefore, the square root of is approximately:
Conclusion
The exact value of the square root of is:
Its decimal approximation is approximately 0.816.

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Square Root of 2/3
The square root of is a mathematical expression that represents a value which, when multiplied by itself, gives the fraction . This concept is fundamental in various fields of mathematics, including algebra and calculus, and has practical applications in science and engineering.
To understand the square root of , we can break down the process into several steps:
- Identify the fraction: .
- Apply the square root to both the numerator and the denominator: .
- Approximate the square roots:
- is approximately 1.414.
- is approximately 1.732.
- Calculate the approximate value: .
This step-by-step breakdown helps in understanding the process and the significance of the square root of . It shows that the square root of a fraction is found by taking the square roots of the numerator and the denominator separately.
Understanding this concept is crucial for solving more complex mathematical problems and for its applications in real-world scenarios where precise calculations are needed.
Mathematical Definition and Properties
The square root of a fraction, such as , involves finding a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original fraction. This can be expressed as:
Here are the steps to understand the definition and properties of this expression:
- Identify the fraction: .
- Express the square root of the fraction as the fraction of the square roots: .
Properties of Square Roots
- Non-negative: The square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative. Hence, both and are positive.
- Multiplicative Property: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots: .
- Rational and Irrational Numbers: Since both and are not perfect squares, their square roots are irrational numbers.
By understanding these properties, we can accurately compute and utilize the square root of in various mathematical contexts.
These principles are essential for more advanced topics in mathematics, providing a foundation for solving equations and analyzing functions where the square root of a fraction is involved.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculating the square root of involves breaking down the process into manageable steps. Here is a detailed guide:
-
Identify the fraction:
The given fraction is .
-
Apply the square root to both the numerator and the denominator:
This step involves taking the square root of the numerator (2) and the denominator (3) separately:
-
Calculate the square roots:
- is approximately 1.414.
- is approximately 1.732.
-
Form the fraction with these approximations:
Now, we create the fraction using the square root values obtained:
-
Simplify the fraction:
Divide the numerator by the denominator to find the decimal approximation:
Thus, the square root of is approximately 0.816 when calculated step-by-step. This method ensures accuracy and clarity in understanding how the value is derived.
Approximating the Square Root of 2/3
Approximating the square root of involves finding a close numerical value to the actual square root. Here’s a step-by-step method to approximate this value:
-
Understand the exact form:
The exact form of the square root of is expressed as:
-
Approximate the square root of the numerator:
The square root of 2 is approximately:
-
Approximate the square root of the denominator:
The square root of 3 is approximately:
-
Form the fraction:
Using these approximations, we form the fraction:
-
Perform the division:
Divide the numerator by the denominator to get the decimal approximation:
This method provides an approximate value for the square root of . Approximations are particularly useful in practical applications where exact values are not required, and a high degree of precision is sufficient.
By following these steps, one can quickly estimate the square root of fractions and apply these values in various mathematical and real-world problems.
Applications in Real Life
The square root of is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical applications in various real-life scenarios. Understanding and using this value can be crucial in fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. Here are some key applications:
-
Engineering:
In engineering, precise calculations are essential for designing structures and systems. The square root of can be used in formulas involving proportions and ratios, ensuring accurate measurements and safe designs.
-
Physics:
Physics often involves calculations of forces, velocities, and other quantities where square roots of fractions are used. For instance, when dealing with equations of motion or wave functions, the square root of might appear in derivations and solutions.
-
Finance:
In finance, the square root of fractions can be useful in risk assessment and portfolio management. For example, when calculating the standard deviation or volatility of returns, which involves square root operations, an understanding of these values helps in making informed investment decisions.
-
Computer Science:
Algorithms in computer science, particularly those involving graphics and simulations, often require calculations of square roots of fractions. Efficiently computing these values ensures smoother and more accurate rendering and processing.
-
Everyday Problem Solving:
In daily life, we encounter various situations where understanding fractions and their roots is beneficial. Whether it’s mixing ingredients in a recipe or determining proportions in a DIY project, the square root of can play a role in achieving desired results.
These applications demonstrate the practical importance of understanding and calculating the square root of . Mastery of this concept aids in solving complex problems and enhances precision in various professional and everyday contexts.
Comparing Square Roots of Fractions
Comparing the square roots of fractions is a valuable skill in mathematics, helping to understand the relative sizes and relationships between different fractions. Let’s explore how to compare the square root of with the square roots of other fractions step by step:
-
Identify the fractions:
We’ll compare the square root of with the square roots of and .
-
Calculate the square roots:
-
Compare the values:
We now compare the approximate values:
- The square root of is approximately 0.816.
- The square root of is approximately 0.707.
- The square root of is approximately 0.866.
-
Analyze the comparisons:
Based on these approximations:
- The square root of (0.816) is greater than the square root of (0.707).
- The square root of (0.816) is less than the square root of (0.866).
By following these steps, we can accurately compare the square roots of different fractions. Understanding these comparisons is useful in various mathematical contexts, helping to simplify problems and providing deeper insights into the relationships between numbers.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Understanding the square root of is essential for avoiding common mistakes and misconceptions. Here are some frequent errors and misunderstandings, along with explanations to clarify them:
-
Mistaking the Fraction:
Some may mistakenly consider the fraction as . It is crucial to identify the correct numerator and denominator.
-
Incorrect Square Root Application:
Applying the square root separately to the numerator and the denominator can be confusing. The correct approach is:
-
Ignoring the Simplification:
After finding the square root values, some may neglect to simplify the fraction. Simplifying ensures accuracy and understanding.
-
Forgetting Approximation Accuracy:
When approximating, it’s important to maintain accuracy. For instance, the square root of 2 is approximately 1.414, and the square root of 3 is approximately 1.732. Incorrect approximations lead to errors in the final result.
-
Misinterpreting the Result:
Interpreting the result as a fraction or decimal incorrectly is a common mistake. The approximate value of the square root of is 0.816, and understanding this helps in applying it correctly in various contexts.
By recognizing these common mistakes and misconceptions, students and practitioners can better understand the square root of and apply it more effectively in mathematical problems and real-life situations.
Using Calculators and Tools
Calculating the square root of a fraction like \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) can be easily done using various online calculators and tools. Here, we will explore how to use some of the popular calculators to find this square root.
Using Mathway
- Go to the .
- Enter the expression
sqrt(2/3)into the input field. - Click the blue arrow button to calculate.
- Mathway will provide the result in both exact and decimal forms.
Using Symbolab
- Visit the .
- Type
\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}in the input box. - Press Enter or click on the "Go" button to see the result.
- Symbolab will display the simplified radical form as well as the decimal approximation.
Using Omni Calculator
- Navigate to the .
- Input
2/3under the square root symbol. - Click the calculate button to obtain the result.
- Omni Calculator will show both the simplified radical form and the approximate decimal value.
Using MathCracker
- Access the .
- Enter
sqrt(2/3)into the calculator. - Click the "Calculate" button.
- MathCracker provides step-by-step calculations and simplifies the expression if possible.
Steps to Manually Calculate \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\)
- Express the fraction under the square root: \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}}\).
- Rationalize the denominator by multiplying by \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\): \[ \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}} \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}. \]
- The simplified form is \(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}\), which can be further approximated using a calculator for a decimal value.
Using these online tools not only provides the result but also helps in understanding the step-by-step process of simplifying and calculating square roots of fractions.

Square Root of 2/3 in Advanced Mathematics
The square root of \(\frac{2}{3}\) plays a significant role in various advanced mathematical contexts. This section explores its applications and properties in detail.
Firstly, let's denote the square root of \(\frac{2}{3}\) as \( \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} \). This can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}}
\]
Simplifying further using rationalization:
\[
\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}
\]
Thus,
\[
\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}
\]
Properties and Applications
- Algebraic Manipulations: The expression \(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}\) can be used in algebraic equations where rationalizing the denominator is necessary.
- Calculus: The square root of fractions, including \(\frac{2}{3}\), is frequently encountered in limits, integrals, and differential equations. For example, when dealing with integrals that involve radicals, \(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}\) can simplify the process.
- Complex Numbers: In the context of complex numbers, particularly when expressing roots in polar form, \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) is useful. The polar form representation involves magnitudes and angles, where roots of fractions like \(\frac{2}{3}\) appear.
Numerical Approximations
Using numerical methods or tools like scientific calculators, we can approximate \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) to a decimal value for practical applications. For instance,
\[
\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} \approx 0.81649658
\]
This approximation is useful in engineering and physics problems where precise decimal values are required.
Graphical Interpretation
In graphing contexts, \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) may appear in function transformations. Consider a function \(f(x) = \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}x}\). Understanding its graphical behavior is crucial in advanced studies:
1. **Scaling Factor:** The factor \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) scales the input \(x\) values, effectively compressing the graph horizontally by a factor of \(\frac{3}{\sqrt{6}}\).
2. **Derivative and Integral Analysis:** The derivative of \(f(x)\) with respect to \(x\) involves the constant \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\), impacting the slope and area under the curve.
Further Reading
By understanding the square root of \(\frac{2}{3}\) in these advanced contexts, one can appreciate its significance and versatility in higher mathematics.
Visual Representation and Graphical Interpretation
Visualizing the square root of \(\frac{2}{3}\) helps in understanding its properties and applications better. Here, we will explore how to graph and interpret the square root function, particularly focusing on \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\).
Graphing the Square Root Function
To graph the function \(y = \sqrt{x}\), we need to understand its domain and range:
- Domain: \(x \geq 0\)
- Range: \(y \geq 0\)
Since the square root function is defined for non-negative values of \(x\), its graph starts at the origin \((0,0)\) and rises gradually, forming a curve that increases slower as \(x\) becomes larger.
Graphing \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\)
To graph \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\), we plot it on the same axis to compare it with other square roots. Here's how we can visualize it:
- Calculate the value: \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} \approx 0.816\).
- Plot this value on the y-axis when \(x = \frac{2}{3}\).
Using graphing tools like Desmos or GeoGebra can simplify this process. For example, on Desmos:
- Go to .
- Enter the function \(y = \sqrt{x}\).
- Add a point at \(x = \frac{2}{3}\), \(y = \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\).
Graphical Interpretation
Graphing \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) alongside the parent function \(y = \sqrt{x}\) allows us to see how this value fits into the broader context of square roots. This value lies between \(\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}}\) and \(\sqrt{1}\), reflecting its position in the continuous, increasing nature of the square root function.
Understanding Transformations
To better understand graphical interpretations, consider transforming the square root function. For instance, translating the graph horizontally or vertically, scaling it, or reflecting it can provide insights into how \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) behaves under different conditions:
- Horizontal Shift: \(y = \sqrt{x - h}\) shifts the graph to the right by \(h\).
- Vertical Shift: \(y = \sqrt{x} + k\) shifts the graph up by \(k\).
- Scaling: \(y = a\sqrt{x}\) stretches or compresses the graph vertically by a factor of \(a\).
These transformations can be easily visualized using tools like GeoGebra or Desmos, aiding in a deeper understanding of the square root function's behavior.
Example Visualization
Consider plotting the function \(y = \sqrt{x}\) with specific points for different values of \(x\), including \(\frac{2}{3}\):
| x | y = \sqrt{x} |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| \(\frac{2}{3}\) | \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} \approx 0.816\) |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | \(\sqrt{2} \approx 1.414\) |
| 4 | 2 |
By plotting these points, we get a clearer visual representation of how \(\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}\) fits into the square root function. This approach helps in comprehending the gradual increase and the nature of square roots.
Practical Examples and Exercises
Understanding the square root of can be deepened through practical examples and exercises. Below are several examples and exercises to help you grasp the concept:
Example 1: Simplifying the Square Root
To simplify , you can multiply both the numerator and the denominator by 3:
Exercise 1: Simplify
Simplify the expression .
- Rewrite the fraction inside the square root as .
- Apply the square root to both the numerator and the denominator.
- The simplified form is .
Example 2: Approximating the Square Root
To approximate the square root of using a calculator:
Exercise 2: Approximate
Use a calculator to approximate .
- Enter 5 divided by 8 to get the decimal form: 0.625.
- Find the square root of 0.625, which is approximately 0.7906.
Example 3: Real-World Application
Consider a scenario where you need to find the length of the diagonal of a rectangle with sides of lengths 2 and 3. The length of the diagonal can be found using the Pythagorean theorem:
Exercise 3: Real-World Problem
Find the diagonal of a rectangle with side lengths of 5 and 6.
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem: .
- Calculate: .
- The diagonal is .
Practice Problems
- Simplify:
- Approximate:
- Find the diagonal of a rectangle with side lengths of 8 and 15.
FAQs on the Square Root of 2/3
Below are some frequently asked questions about the square root of 2/3, along with detailed answers to help you understand this concept better.
-
What is the square root of 2/3?
The square root of 2/3 can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{3}} = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}
\] -
Is the square root of 2/3 a rational number?
No, the square root of 2/3 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion.
-
How can I approximate the square root of 2/3?
To approximate the square root of 2/3, you can use a calculator or follow these steps:
- Find the square root of 2, which is approximately 1.414.
- Find the square root of 3, which is approximately 1.732.
- Divide the square root of 2 by the square root of 3:
\[
\frac{1.414}{1.732} \approx 0.816
\]
-
Can I use a calculator to find the square root of 2/3?Yes, you can use a scientific calculator to find the square root of 2/3. Enter 2 divided by 3, then press the square root button to get the result, which should be approximately 0.816.
-
How is the square root of 2/3 used in advanced mathematics?
The square root of 2/3 is used in various fields of advanced mathematics, including algebra, calculus, and trigonometry. It appears in problems involving ratios, proportions, and when solving quadratic equations.
-
What are the properties of the square root of 2/3?
The properties of the square root of 2/3 include:
- It is an irrational number.
- It lies between 0 and 1 on the number line.
- It can be simplified to \(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{3}\).
- It is the geometric mean of 2 and 3.
-
What is the decimal expansion of the square root of 2/3?The decimal expansion of the square root of 2/3 is approximately 0.8164965809...
-
How can I verify the value of the square root of 2/3?
You can verify the value by squaring it:
\[
\left( \frac{\sqrt{6}}{3} \right)^2 = \frac{6}{9} = \frac{2}{3}
\]

Additional Resources and Further Reading
For those interested in delving deeper into the topic of square roots, particularly the square root of , here are some additional resources and further reading materials that can enhance your understanding:
-
Math is Fun - Simplifying Square Roots
This website offers a comprehensive guide on how to simplify square roots, including step-by-step examples and rules for combining and simplifying roots.
-
Mathematics LibreTexts - Radicals and Rational Expressions
This resource covers the evaluation of square roots, the product and quotient rules for simplifying square roots, and rationalizing denominators with radicals. It includes numerous examples and exercises to practice.
-
MadforMath - Square Root of Fractions Calculator
This tool simplifies the square root of fractions and provides detailed solution steps. It allows users to enter their own fractions or generate random examples for practice.
-
Khan Academy - Simplifying square roots
Khan Academy offers video tutorials and practice exercises on simplifying square roots, including complex examples involving rational and irrational numbers.
-
Paul's Online Math Notes - Rationalizing the Denominator
This resource provides an in-depth look at the techniques used to rationalize denominators in fractions involving square roots, with numerous examples and practice problems.
These resources will provide a robust foundation in understanding and working with square roots, including the specific case of the square root of . Whether you're looking for detailed explanations, calculators, or practice problems, these links offer valuable tools and information.
Conclusion and Summary
The square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \) is a fascinating mathematical concept that appears in various mathematical and real-world applications. In this guide, we explored its definition, calculation methods, properties, and significance.
We started by understanding the mathematical definition and properties of the square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \). This involved expressing it in radical form and simplifying it to \( \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} \) or \( \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{3}} \). We also looked at its decimal approximation, which is approximately 0.8165.
Detailed step-by-step calculations helped in grasping the exact process of deriving the square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \). Various methods of approximation, including the use of calculators and tools, were discussed to make this process more accessible.
The practical applications of the square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \) in fields such as physics, engineering, and statistics highlight its importance. We saw how this value is used in solving real-life problems and in advanced mathematical theories.
By comparing the square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \) with other fractional square roots, we gained a deeper insight into its unique properties and how it stands in relation to other similar values.
Common mistakes and misconceptions about the square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \) were clarified, ensuring a clear and accurate understanding. We also learned about the importance of using appropriate calculators and tools to find this value accurately.
Visual representation and graphical interpretation provided a more intuitive understanding of \( \sqrt{\frac{2}{3}} \), making it easier to visualize and apply in various contexts.
Finally, through practical examples and exercises, we reinforced our knowledge and ability to work with the square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \) effectively.
This comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in the intricacies of square roots and their applications. We hope this detailed exploration enhances your understanding and appreciation of the square root of \( \frac{2}{3} \).
Video 'Rút Gọn Căn Bậc Hai của 2/3' hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách rút gọn và tính toán căn bậc hai của phân số 2/3.
Rút Gọn Căn Bậc Hai của 2/3
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách cộng 2 căn 3 và căn 3. Xem video để biết cách thực hiện phép tính này một cách dễ dàng và chính xác.
2 căn(3) + căn(3) || Cách cộng 2 căn 3 và căn 3