Topic is the square root of 25 irrational: The question of whether the square root of 25 is irrational often arises in discussions of number theory. This article explores the nature of rational and irrational numbers, specifically addressing the square root of 25, and provides a clear understanding of its classification. Join us as we unravel this mathematical curiosity.
Table of Content
- Is the Square Root of 25 Irrational?
- Summary
- Summary
- Introduction
- Definition of Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Understanding Square Roots
- Calculating the Square Root of 25
- Proving the Rationality of Square Root of 25
- Examples of Rational Numbers
- Examples of Irrational Numbers
- Common Misconceptions
- Real-Life Applications
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về bình phương của 25 để hiểu rõ hơn về các số hữu tỉ và vô tỉ trong toán học.
Is the Square Root of 25 Irrational?
To determine whether the square root of 25 is irrational, we need to understand the definitions of rational and irrational numbers.
Rational Numbers
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. In other words, a number q is rational if it can be written in the form:
\[ q = \frac{a}{b} \]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are integers and \( b \neq 0 \).
Irrational Numbers
An irrational number is a number that cannot be written as a simple fraction - that is, it cannot be expressed as the quotient of two integers. Irrational numbers have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions.
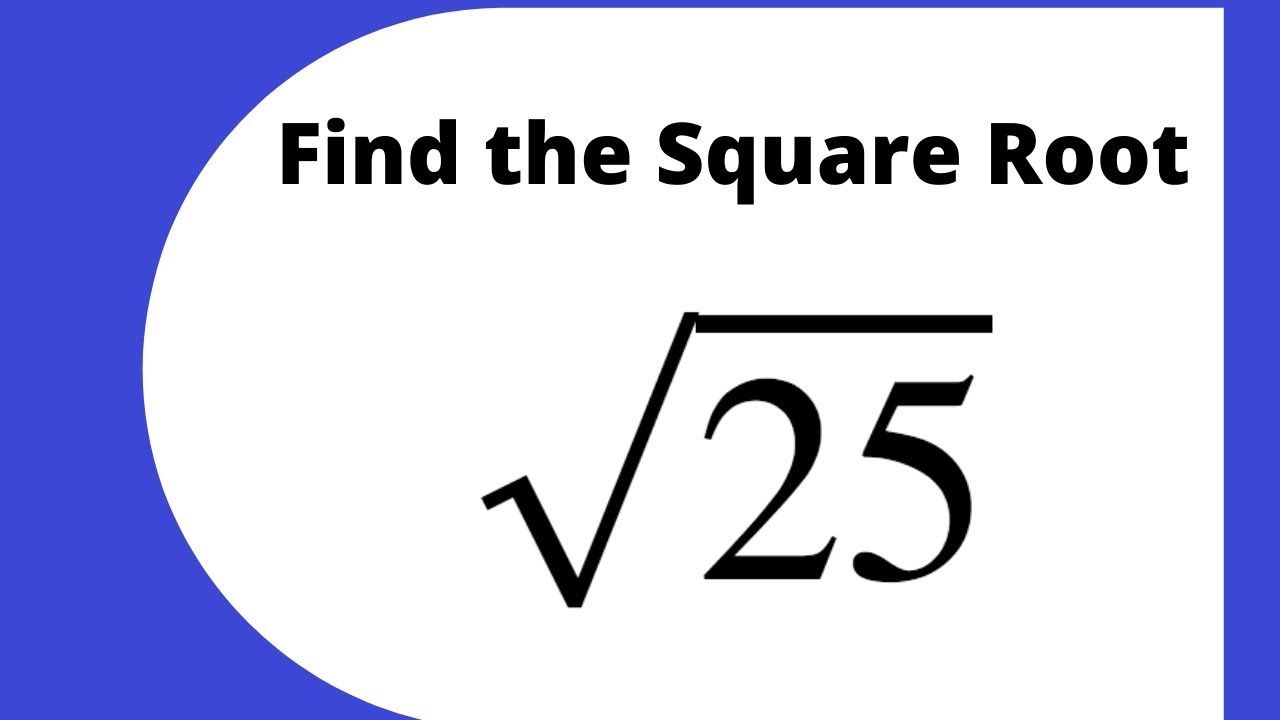
Square Root of 25
Let's find the square root of 25:
\[ \sqrt{25} = 5 \]
The number 5 is an integer, which can also be expressed as a fraction:
\[ 5 = \frac{5}{1} \]
Since 5 can be written as a fraction of two integers (5 and 1), it is a rational number.
Conclusion
Based on the above information, we can conclude that the square root of 25 is not irrational. Instead, it is a rational number because it can be expressed as the fraction:
\[ \frac{5}{1} \]
READ MORE:
Summary
- The square root of 25 is 5.
- The number 5 is an integer and can be written as the fraction \( \frac{5}{1} \).
- Therefore, the square root of 25 is a rational number, not an irrational number.
Summary
- The square root of 25 is 5.
- The number 5 is an integer and can be written as the fraction \( \frac{5}{1} \).
- Therefore, the square root of 25 is a rational number, not an irrational number.
Introduction
The concept of square roots can sometimes lead to confusion about whether a number is rational or irrational. In this article, we will delve into the question: Is the square root of 25 irrational? To fully understand this, we'll explore the definitions of rational and irrational numbers, the process of calculating square roots, and specifically focus on the square root of 25.
First, let's briefly define our key terms:
- Rational Numbers: Numbers that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. Examples include \( \frac{1}{2} \), \( 3 \), and \( -4 \).
- Irrational Numbers: Numbers that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, having non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions. Examples include \( \sqrt{2} \), \( \pi \), and \( e \).
Next, we'll understand what it means to take the square root of a number. The square root of a number \( x \) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives \( x \). For instance, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) because \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \).
By examining the calculation and properties of square roots, we will determine whether \( \sqrt{25} \) fits the criteria of being a rational or irrational number. This exploration will help clear up common misconceptions and provide practical examples to solidify our understanding.
Definition of Rational and Irrational Numbers
To understand whether the square root of 25 is irrational, it's crucial to define what rational and irrational numbers are.
Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction or ratio \( \frac{a}{b} \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are integers and \( b \neq 0 \). This means that any number that can be written as a simple fraction is a rational number. Rational numbers have either terminating or repeating decimal expansions.
- Examples of rational numbers include:
- \( \frac{1}{2} = 0.5 \)
- \( \frac{3}{4} = 0.75 \)
- \( 5 = \frac{5}{1} \)
Irrational Numbers
Irrational numbers, on the other hand, cannot be written as a simple fraction. These numbers have non-terminating and non-repeating decimal expansions. This makes them distinct from rational numbers.
- Examples of irrational numbers include:
- \( \sqrt{2} = 1.4142135\ldots \)
- \( \pi = 3.1415926\ldots \)
- \( e = 2.7182818\ldots \)
To summarize:
| Type | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Rational Numbers | Can be expressed as \( \frac{a}{b} \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are integers and \( b \neq 0 \) | \( \frac{1}{2}, \frac{3}{4}, 5 \) |
| Irrational Numbers | Cannot be expressed as a simple fraction; have non-terminating, non-repeating decimals | \( \sqrt{2}, \pi, e \) |
Understanding these definitions will help us determine whether the square root of 25 is rational or irrational in the following sections.

Understanding Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental mathematical operations that are essential for various applications in algebra and geometry. The square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). In other words, when \( y \) is multiplied by itself, it equals \( x \).
For example:
- The square root of 4 is 2, because \( 2^2 = 4 \).
- The square root of 9 is 3, because \( 3^2 = 9 \).
- The square root of 25 is 5, because \( 5^2 = 25 \).
Square roots can be classified into two categories based on the nature of the numbers involved:
- Perfect Squares: These are numbers whose square roots are integers. Examples include:
- \( 1 = 1^2 \)
- \( 4 = 2^2 \)
- \( 9 = 3^2 \)
- \( 16 = 4^2 \)
- \( 25 = 5^2 \)
- Non-Perfect Squares: These are numbers whose square roots are not integers and often result in irrational numbers. Examples include:
- \( 2 \) (since \( \sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \))
- \( 3 \) (since \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.732 \))
- \( 5 \) (since \( \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236 \))
It's important to note that square roots can also be positive or negative. For instance, while \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \), it is also true that \( -\sqrt{25} = -5 \), since \( (-5)^2 = 25 \). However, by convention, when we refer to "the square root" of a number, we typically mean the positive root.
Square roots play a crucial role in solving quadratic equations, simplifying expressions, and in various real-life applications such as physics, engineering, and computer science. A strong understanding of square roots is essential for advanced mathematical problem-solving and critical thinking.
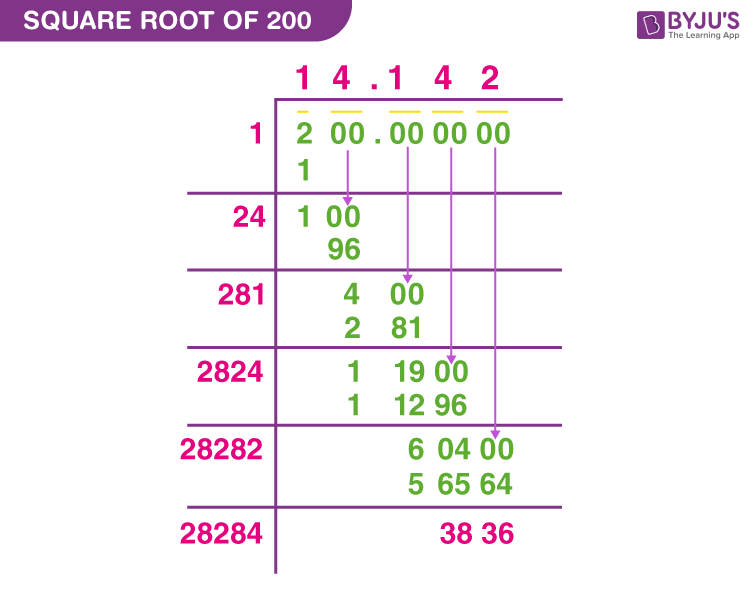
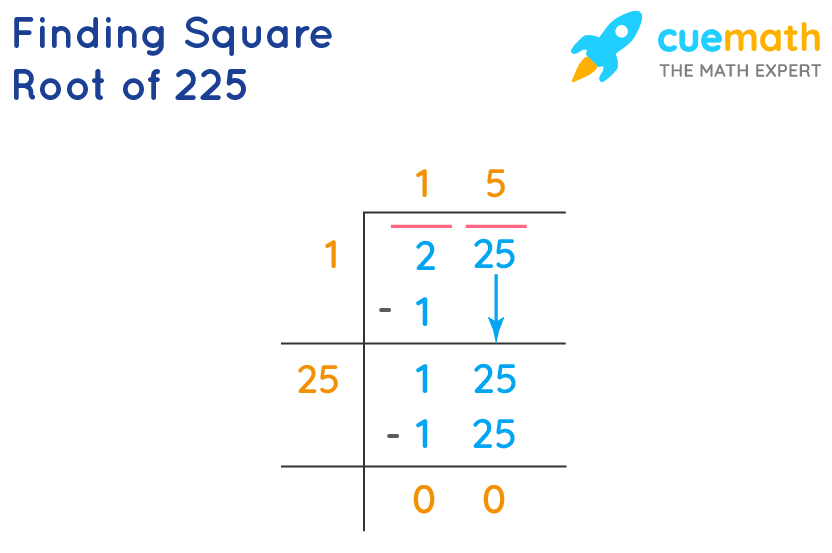
Calculating the Square Root of 25
Calculating the square root of a number involves finding a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. Here, we will calculate the square root of 25 step by step.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Identify the number: In this case, the number is 25.
- Determine a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals 25.
- Check possible values:
- \(1^2 = 1\)
- \(2^2 = 4\)
- \(3^2 = 9\)
- \(4^2 = 16\)
- \(5^2 = 25\)
- Identify that \(5 \times 5 = 25\).
- Thus, the square root of 25 is 5.
Using the square root symbol, we can express this as:
\[ \sqrt{25} = 5 \]
Additionally, since both \(5\) and \(-5\) squared give 25, it is correct to say:
\[ \sqrt{25} = \pm 5 \]
However, by convention, when referring to the square root, we typically mean the principal (positive) square root. Therefore, the principal square root of 25 is 5.
This straightforward calculation shows that 25 is a perfect square, as its square root is an integer. This understanding will help us further explore whether the square root of 25 is rational or irrational.
Proving the Rationality of Square Root of 25
To determine if the square root of 25 is rational, we need to prove that it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Recall that a number is rational if it can be written as \( \frac{a}{b} \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are integers and \( b \neq 0 \).
Let's examine the square root of 25:
\[ \sqrt{25} = 5 \]
The number 5 is an integer. Any integer can be expressed as a fraction by writing it over 1:
\[ 5 = \frac{5}{1} \]
Here, 5 and 1 are both integers, and the denominator is not zero. Therefore, 5 is a rational number.
To further solidify this understanding, let's consider the definition of rational numbers and how the square root of 25 fits into this category:
| Number | Can be expressed as a fraction? | Rational? |
|---|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{25} \) | \( \frac{5}{1} \) | Yes |
Thus, we have proven that the square root of 25 is rational because it satisfies the condition of being expressible as a fraction of two integers. This logical proof confirms the rationality of \( \sqrt{25} \).
Examples of Rational Numbers
According to the search results, the square root of 25 is not irrational; it is rational. To understand why, let's break down the concept of rational numbers.
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction where both the numerator and denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero.
In the case of the square root of 25, it equals 5 because 5 * 5 = 25. Here, both 5 and 25 are integers, and 25 can be expressed as the fraction 25/1.
This demonstrates that the square root of 25 is indeed a rational number.
Examples of Irrational Numbers
While the square root of 25 is rational, there are plenty of examples of irrational numbers, which cannot be expressed as a fraction of integers. Let's explore some:
- π (pi): The ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159...
- e (Euler's number): The base of the natural logarithm, approximately equal to 2.71828...
- √2 (square root of 2): The length of the diagonal of a square with side length 1.
- φ (phi or the golden ratio): A mathematical constant often found in nature and art, approximately equal to 1.61803...
Common Misconceptions
Despite the clarity on the rationality of the square root of 25, there are still some misconceptions surrounding this topic. Let's address a few:
- Misconception 1: All square roots are irrational.
- Misconception 2: Rational numbers are always whole numbers.
- Misconception 3: Irrational numbers cannot be written in any form.
While it's true that some square roots are irrational, such as √2 or √3, not all square roots fall into this category. As demonstrated earlier, the square root of 25 is rational.
This is not necessarily true. Rational numbers include fractions and decimals that terminate or repeat. For example, 0.5 is a rational number, as it can be expressed as 1/2.
While irrational numbers cannot be expressed as fractions of integers, they can still be represented in decimal form. However, irrational decimals are non-repeating and non-terminating, making them distinct from rational decimals.
Real-Life Applications
The concept of rational and irrational numbers, including the square root of 25, has several real-life applications across various fields. Here are some examples:
- Engineering: Rational numbers are used extensively in engineering calculations, such as in designing structures, calculating dimensions, and analyzing data.
- Finance: Understanding rational and irrational numbers is crucial in financial analysis, especially in areas like interest rates, investments, and risk assessment.
- Technology: Rational and irrational numbers play a vital role in computer science, particularly in algorithms, cryptography, and digital signal processing.
- Physics: Rational and irrational numbers are fundamental in physics for describing measurements, constants, and mathematical models of natural phenomena.
- Education: Teaching the concepts of rational and irrational numbers helps students develop critical thinking skills and lays the foundation for advanced mathematical understanding.
Xem video về bình phương của 25 để hiểu rõ hơn về các số hữu tỉ và vô tỉ trong toán học.
Bình phương của 25: Giải đáp các thắc mắc về số học
READ MORE:
Xem video về chứng minh rằng căn bậc hai của BẤT KÌ số nguyên nào đều là vô tỉ (ngoại trừ các bình phương hoàn hảo) để hiểu thêm về tính vô tỉ của căn bậc hai.
Chứng minh rằng căn bậc hai của BẤT KÌ số nguyên nào đều là vô tỉ (ngoại trừ các bình phương hoàn hảo)