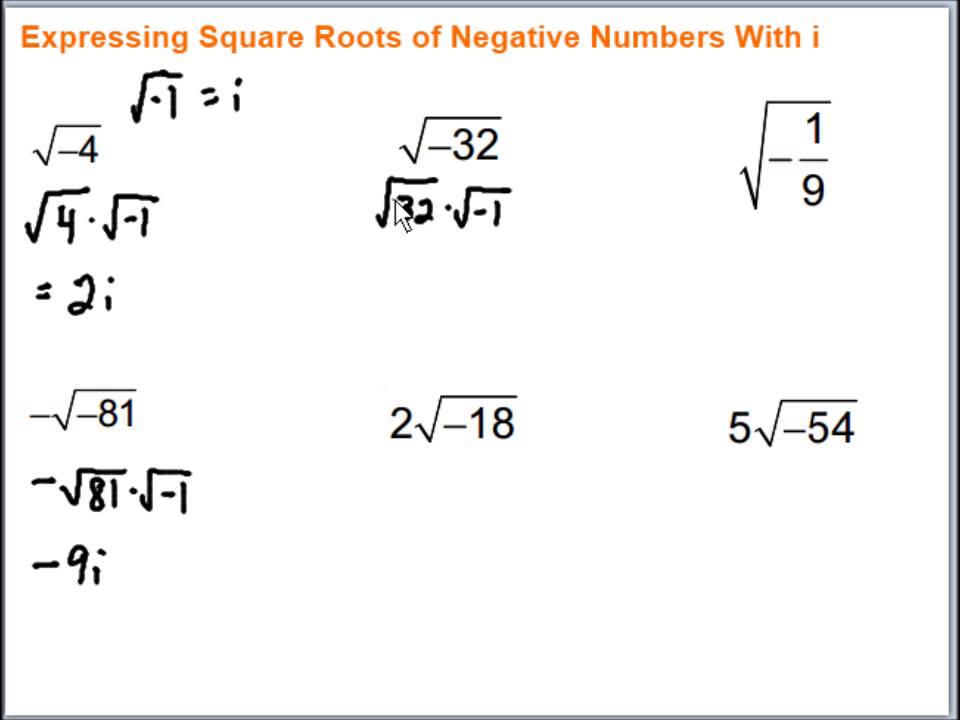
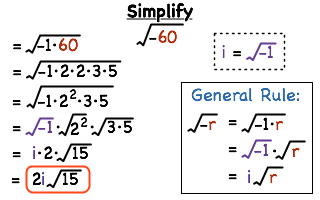
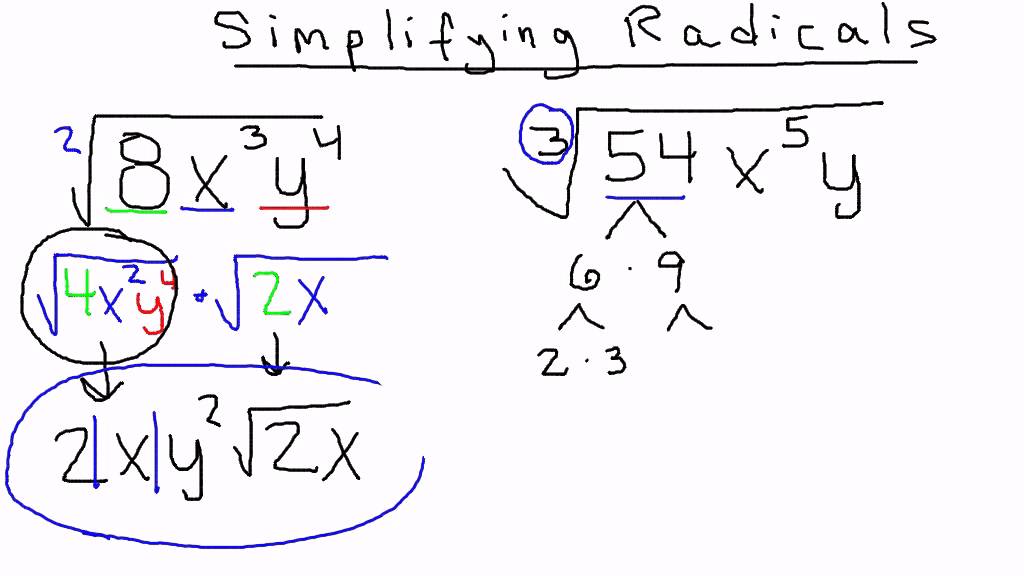Topic solve radical expressions calculator: Discover the power of solving radical expressions with our comprehensive guide. This article covers everything from basic operations to advanced techniques, ensuring you can tackle any radical expression with confidence. Whether you're a student, teacher, or math enthusiast, our step-by-step instructions and online calculators will make solving radicals a breeze.
Table of Content
- Simplify Radical Expressions Calculator
- Introduction to Radical Expressions
- What is a Radical Expression?
- Basic Radical Operations
- Types of Radical Expressions
- How to Simplify Radical Expressions
- Methods for Solving Radical Equations
- Step-by-Step Examples
- Common Problems and Solutions
- Online Calculators for Radical Expressions
- Using Mathway's Radical Expression Calculator
- Using CalculatorSoup's Simplify Radical Expressions Calculator
- Using Symbolab's Exponents and Radicals Calculator
- Using SnapXam's Radicals Calculator
- Using MathPortal's Radical Simplification Tool
- Additional Resources and Tools
- Practice Problems and Exercises
- FAQs about Radical Expressions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz để đơn giản hóa các biểu thức căn bậc hai.
Simplify Radical Expressions Calculator
Solving radical expressions can be simplified using specialized calculators. These calculators provide step-by-step solutions to help understand and solve various radical expressions. Here are some features and examples of popular calculators:
Features of Radical Expressions Calculators
- Simplify radicals
- Perform arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) on radical expressions
- Show step-by-step solutions
- Handle complex radical expressions
- Provide explanations and rules for simplifying radicals
Examples of Simplifying Radical Expressions
Here are a few examples of how to simplify radical expressions:
-
Add the following radical expressions:
\(\sqrt{75} + \sqrt{12}\)
Simplified:
\(\sqrt{25 \cdot 3} + \sqrt{4 \cdot 3} = 5\sqrt{3} + 2\sqrt{3} = 7\sqrt{3}\)
-
Find the product of the following radical expressions:
\(\sqrt{18} \cdot \sqrt{14}\)
\(\sqrt{9 \cdot 2} \cdot \sqrt{14} = 3\sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{14} = 3\sqrt{28} = 3 \cdot 2\sqrt{7} = 6\sqrt{7}\)
How to Use a Simplify Radical Expressions Calculator
Using a radical expressions calculator is straightforward. Here’s a general guide:
- Select the operation you want to perform (simplify, add, multiply, etc.) from the drop-down menu.
- Enter the values in the appropriate fields.
- Click the "Calculate" button to see the simplified form.
Common Questions
- What is the square root of 288 in radical form?
The square root of 288 in simplified radical form is \(12\sqrt{2}\).

READ MORE:
Introduction to Radical Expressions
Radical expressions are mathematical expressions that involve roots, such as square roots or cube roots. These expressions are fundamental in algebra and calculus, and understanding how to manipulate them is crucial for solving various mathematical problems.
A radical expression is typically written in the form \( \sqrt[n]{x} \), where \( n \) is the index of the root and \( x \) is the radicand. When \( n \) is not specified, it is assumed to be 2, which denotes a square root. Here are the steps to work with radical expressions:
- Simplifying Radical Expressions:
- Identify and factor the radicand into its prime factors.
- Group the factors according to the index of the root.
- Move the grouped factors outside the radical symbol.
- Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions:
- Ensure the radicals have the same index and radicand.
- Combine the coefficients of the radicals.
- Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions:
- Multiply/divide the coefficients and the radicands separately.
- Simplify the resulting radical if possible.
Understanding these steps helps in efficiently solving more complex problems involving radical expressions. Calculators such as those provided by Symbolab, SnapXam, CalculatorSoup, and Mathway offer step-by-step solutions to aid in learning and verifying your work.
What is a Radical Expression?
A radical expression is any mathematical expression containing a radical symbol (√), which indicates the root of a number. The most common type is the square root, but there are other types such as cube roots and fourth roots.
Radical expressions can be used in various mathematical contexts, including algebra, geometry, and calculus. They are particularly useful for solving equations that involve roots and for simplifying complex mathematical expressions.
Here are some key concepts related to radical expressions:
- Radicand: The number inside the radical symbol. For example, in √x, x is the radicand.
- Index: The small number outside and to the left of the radical symbol, indicating the degree of the root. If no number is present, the index is assumed to be 2 (square root).
- Radical: The entire expression, including the radical symbol, radicand, and index.
To simplify a radical expression, follow these steps:
- Factor the radicand into its prime factors.
- Group the factors into pairs (for square roots) or other groupings based on the index.
- Move each pair (or group) of factors outside the radical, leaving the unpaired factors inside.
Here’s an example of simplifying a radical expression:
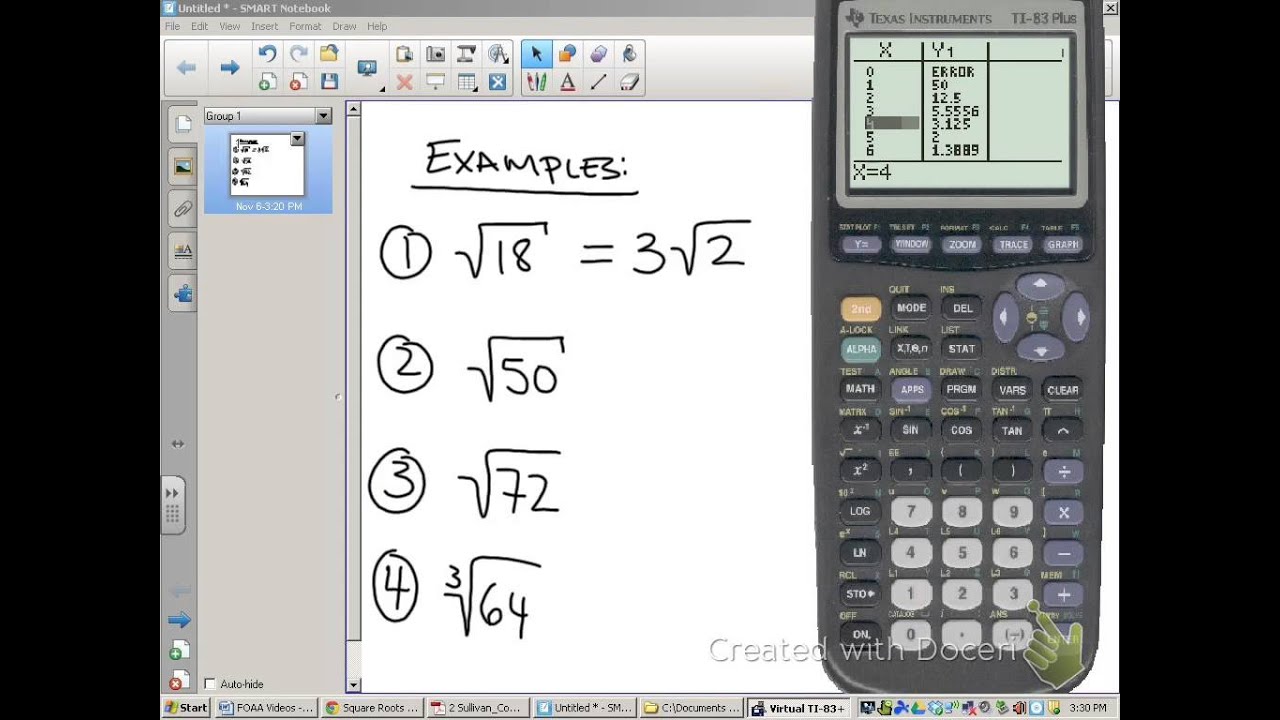
Consider the expression √18:
- Factor 18 into its prime factors: 18 = 2 × 3 × 3
- Group the factors into pairs: √(2 × 32)
- Move the pair of 3s outside the radical: 3√2
So, √18 simplifies to 3√2.
Understanding radical expressions is fundamental to higher-level mathematics, and tools such as a radical expression calculator can be extremely helpful in solving and simplifying these expressions efficiently.
Basic Radical Operations
Understanding basic radical operations is essential for solving and simplifying radical expressions. Here we cover the foundational operations involving radicals, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Addition and Subtraction of Radicals
To add or subtract radical expressions, the radicands (the numbers under the radical sign) must be the same. If they are not, you must first simplify the radicals to make the radicands identical.
- Simplify each radical expression to its simplest form.
- If the radicands are the same, combine the coefficients.
- If the radicands are different, look for a common factor to simplify further.
For example:
- \(\sqrt{75} + \sqrt{12}\) becomes \(5\sqrt{3} + 2\sqrt{3} = 7\sqrt{3}\)
- \(3\sqrt{18} - 2\sqrt{8}\) becomes \(3 \cdot 3\sqrt{2} - 2 \cdot 2\sqrt{2} = 9\sqrt{2} - 4\sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2}\)
Multiplication and Division of Radicals
Multiplying and dividing radicals follows specific rules. When multiplying, multiply the coefficients and the radicands separately. For division, divide the coefficients and the radicands.
- Multiply the coefficients together and the radicands together.
- Simplify the resulting radical expression.
For example:
- \(\sqrt{3} \cdot \sqrt{12}\) becomes \(\sqrt{3 \cdot 12} = \sqrt{36} = 6\)
- \(\frac{\sqrt{50}}{\sqrt{2}}\) becomes \(\sqrt{\frac{50}{2}} = \sqrt{25} = 5\)
Rationalizing the Denominator
Rationalizing the denominator involves eliminating the radical from the denominator of a fraction.
- Multiply the numerator and the denominator by the radical in the denominator.
- Simplify the resulting expression.
For example:
- \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{2}}\) becomes \(\frac{5 \cdot \sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2} \cdot \sqrt{2}} = \frac{5\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
- \(\frac{3}{2+\sqrt{5}}\) becomes \(\frac{3(2-\sqrt{5})}{(2+\sqrt{5})(2-\sqrt{5})} = \frac{3(2-\sqrt{5})}{4-5} = \frac{3(2-\sqrt{5})}{-1} = -3(2-\sqrt{5})\)
These basic operations form the foundation for more complex manipulations of radical expressions. Practice these steps to gain confidence in handling radicals.
Types of Radical Expressions
Radical expressions come in various forms, each with unique characteristics and rules for simplification. Understanding these types is essential for mastering operations involving radicals. Below are the main types of radical expressions:
- Square Roots: The most common type, represented as \(\sqrt{x}\). Example: \(\sqrt{25} = 5\).
- Cubic Roots: These involve the cube root of a number, represented as \(\sqrt[3]{x}\). Example: \(\sqrt[3]{27} = 3\).
- Higher-Order Roots: These include fourth roots, fifth roots, etc., represented as \(\sqrt[n]{x}\). Example: \(\sqrt[4]{16} = 2\).
Each type of radical expression follows specific rules for simplification and manipulation:
- Simplifying Radicals:
- Identify and factor out perfect squares (or cubes, etc.) from under the radical sign.
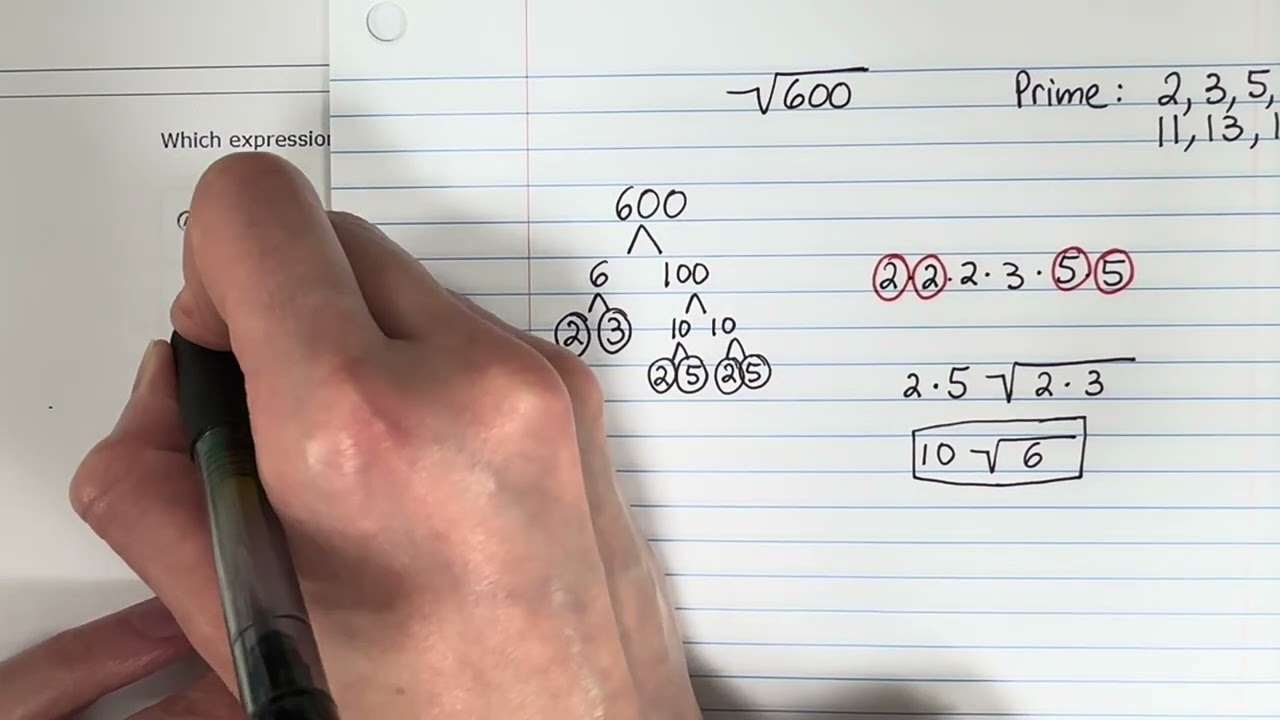
- Example: Simplify \(\sqrt{50}\): \[ \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{25 \times 2} = \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} = 5\sqrt{2} \]
- Adding and Subtracting Radicals:
- Combine like terms (radicals with the same radicand). Example: \(\sqrt{2} + 3\sqrt{2} = 4\sqrt{2}\).
- Multiplying and Dividing Radicals:
- Use the property \(\sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} = \sqrt{a \times b}\). Example: \(\sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{36} = 6\).
- For division, apply \(\frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} = \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}}\). Example: \(\frac{\sqrt{8}}{\sqrt{2}} = \sqrt{4} = 2\).
- Rationalizing Denominators:
- Remove radicals from the denominator by multiplying by a conjugate or using appropriate algebraic methods. Example: \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \times \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\).
By mastering these basic types and operations, you can confidently handle more complex radical expressions and equations.
How to Simplify Radical Expressions
Simplifying radical expressions involves rewriting the expression in its simplest form. Here is a step-by-step guide to simplify radical expressions:
- Identify the radicand, which is the number or expression inside the radical sign.
- Factor the radicand into its prime factors. For example, if the radicand is 72, you would factor it as \( 72 = 2^3 \times 3^2 \).
- Group the prime factors into pairs. Each pair of identical factors can be taken out of the radical sign as a single factor. For example, \( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^2} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 3^2) \times 2} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Multiply the factors outside the radical sign. In the example above, this would result in \( 2 \times 3 = 6 \), so \( \sqrt{72} = 6\sqrt{2} \).
- Simplify any remaining expressions inside the radical sign if possible.
Let's consider another example to illustrate these steps:
- Example: Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \)
- Step 1: Factor 50 into its prime factors: \( 50 = 2 \times 5^2 \)
- Step 2: Group the prime factors: \( \sqrt{50} = \sqrt{2 \times 5^2} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
- Step 3: The simplified form is \( 5\sqrt{2} \).
Using these steps, you can simplify any radical expression. Practice with different examples to become proficient in this technique.
| Original Expression | Simplified Form |
|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{75} \) | \( 5\sqrt{3} \) |
| \( \sqrt{128} \) | \( 8\sqrt{2} \) |
| \( \sqrt{200} \) | \( 10\sqrt{2} \) |
Remember, the key to simplifying radical expressions is to look for perfect squares (or cubes, etc., depending on the root) within the radicand and factor them out.
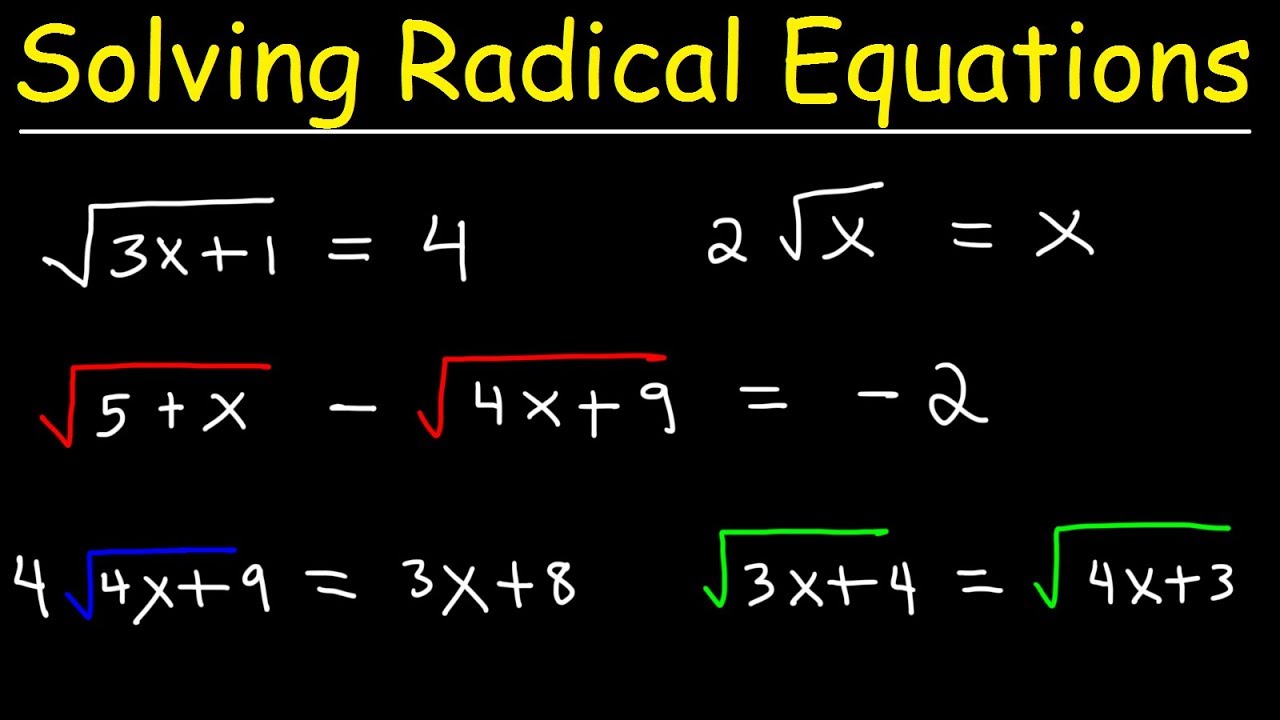
Methods for Solving Radical Equations
Solving radical equations involves isolating the radical expression and then eliminating the radical by raising both sides of the equation to the power that corresponds to the index of the radical. Below are some common methods:
- Isolate the Radical: Ensure the radical expression is by itself on one side of the equation.
- Eliminate the Radical: Raise both sides of the equation to the power of the radical’s index to remove the radical.
- Simplify: Simplify the resulting equation, which should now be a polynomial or simpler algebraic equation.
- Solve the Equation: Solve for the variable using appropriate algebraic methods.
- Check Solutions: Substitute the solutions back into the original equation to verify that they do not produce any extraneous solutions.
Step-by-Step Example
Original Equation: Solve the equation \( \sqrt{x + 3} = x - 1 \).
Isolate the Radical: The radical expression \( \sqrt{x + 3} \) is already isolated.
Eliminate the Radical: Square both sides to remove the square root:
\( (\sqrt{x + 3})^2 = (x - 1)^2 \)
This simplifies to:
\( x + 3 = x^2 - 2x + 1 \)
Simplify: Rearrange the equation to form a quadratic equation:
\( x^2 - 3x - 2 = 0 \)
Solve the Quadratic Equation: Factorize or use the quadratic formula:
\( x^2 - 3x - 2 = (x - 2)(x + 1) \)
So, \( x = 2 \) or \( x = -1 \).
Check Solutions: Substitute back into the original equation:
- For \( x = 2 \): \( \sqrt{2 + 3} = 2 - 1 \) ⟹ \( \sqrt{5} \neq 1 \), so \( x = 2 \) is not a solution.
- For \( x = -1 \): \( \sqrt{-1 + 3} = -1 - 1 \) ⟹ \( \sqrt{2} \neq -2 \), so \( x = -1 \) is not a solution.
Hence, there is no solution to \( \sqrt{x + 3} = x - 1 \).
Step-by-Step Examples
Radical expressions can be simplified and solved using various techniques. Here are some detailed, step-by-step examples to help you understand how to work with radical expressions:
Example 1: Simplifying a Radical Expression
Consider the expression:
- First, factor the numbers under the radicals:
- Add the simplified terms:
- Combine like terms:
- Combine like terms:
Example 2: Multiplying Radical Expressions
Consider the expression:
- Factor the numbers under the radicals:
- Multiply the simplified terms:
- Simplify the radicand if possible:
- Simplify the radicand if possible:
Example 3: Dividing Radical Expressions
Consider the expression:
- Simplify the radicands:
- Divide the radicals:
Common Problems and Solutions
Understanding how to solve radical equations can be challenging. Here are some common problems and solutions to help you master these concepts:
Problem 1: Simplifying Radical Expressions
Problem: Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \).
Solution:
\[
\begin{aligned}
\sqrt{50} &= \sqrt{25 \times 2} \\
&= \sqrt{25} \times \sqrt{2} \\
&= 5\sqrt{2}
\end{aligned}
\]
Problem 2: Adding and Subtracting Radical Expressions
Problem: Simplify \( 3\sqrt{2} + 4\sqrt{2} \).
Solution:
\[
3\sqrt{2} + 4\sqrt{2} = (3 + 4)\sqrt{2} = 7\sqrt{2}
\]
Problem 3: Multiplying Radical Expressions
Problem: Simplify \( (\sqrt{3} + 2)(\sqrt{3} - 2) \).
Solution:
\[
\begin{aligned}
(\sqrt{3} + 2)(\sqrt{3} - 2) &= (\sqrt{3})^2 - (2)^2 \\
&= 3 - 4 \\
&= -1
\end{aligned}
\]
Problem 4: Solving Radical Equations
Problem: Solve \( \sqrt{5x + 11} - 1 = x \).
Solution:
- Isolate the radical expression: \[ \sqrt{5x + 11} = x + 1
- Square both sides: \[ (\sqrt{5x + 11})^2 = (x + 1)^2 \\ 5x + 11 = x^2 + 2x + 1
- Rearrange the equation: \[ x^2 - 3x - 10 = 0
- Factorize: \[ (x - 5)(x + 2) = 0
- Find the solutions: \[ x = 5 \text{ or } x = -2
- Verify the solutions:
\[
\begin{aligned}
\text{For } x = 5: & \quad \sqrt{5(5) + 11} - 1 = 5 \implies \sqrt{25 + 11} - 1 = 5 \implies \sqrt{36} - 1 = 5 \implies 6 - 1 = 5 \\
\text{For } x = -2: & \quad \sqrt{5(-2) + 11} - 1 = -2 \implies \sqrt{-10 + 11} - 1 = -2 \implies \sqrt{1} - 1 = -2 \implies 1 - 1 = -2 \text{ (False)}
\end{aligned}
\]
\endol
So, the solution is \( x = 5 \).
Problem 5: Solving Radical Equations with Two Radicals
Problem: Solve \( \sqrt{x-4} - \sqrt{x} = -2 \).
Solution:
- Isolate one of the radicals:
\[
\sqrt{x-4} = \sqrt{x} - 2
- Square both sides:
\[
(\sqrt{x-4})^2 = (\sqrt{x} - 2)^2 \\
x - 4 = x - 4\sqrt{x} + 4
- Simplify and solve for \( x \):
\[
0 = -4\sqrt{x} + 8 \implies 4\sqrt{x} = 8 \implies \sqrt{x} = 2 \implies x = 4
\endol
Verify the solution by substituting \( x = 4 \) back into the original equation:
\[
\sqrt{4-4} - \sqrt{4} = -2 \implies 0 - 2 = -2 \implies -2 = -2 \text{ (True)}
\]
```
- Isolate one of the radicals:
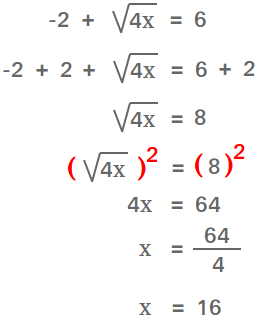
Online Calculators for Radical Expressions
Using online calculators can greatly simplify the process of solving radical expressions. Here are some recommended calculators that can help:
-
Mathway's Evaluate Radicals Calculator:
This tool allows you to enter the radical expression you need to solve. Simply input the expression and click "Evaluate" to get the solution. It's available both online and as a mobile app, which makes it very convenient for on-the-go calculations.
-
CalculatorSoup's Radicals and Roots Calculator:
This calculator can find roots of both positive and negative real numbers. It is particularly useful for calculating the square root, cube root, or any higher-order root of a number. The user-friendly interface makes it easy to enter values and get immediate results.
-
SnapXam's Radicals Calculator:
SnapXam offers a step-by-step calculator for solving radical expressions. It provides detailed solutions and is ideal for students looking to understand the steps involved in simplifying or solving radical equations.
-
Calculator-Online's Simplify Radicals Calculator:
This tool helps in simplifying radical expressions by performing arithmetic operations on them. It's designed to handle various types of radical expressions and can provide quick, simplified results.
These online calculators can help you solve and simplify radical expressions with ease, offering step-by-step solutions and user-friendly interfaces.
Using Mathway's Radical Expression Calculator
Mathway offers a powerful online tool for solving radical expressions quickly and accurately. Follow these steps to use Mathway's Radical Expression Calculator:
- Go to Mathway's website or use their mobile app.
- Locate the search bar and type in your radical expression to simplify or solve.
- Choose the appropriate operation (simplify, solve, etc.) from the options provided.
- Enter the details of your radical expression, including the specific variables or constants involved.
- Click the "Calculate" or "Solve" button to see the step-by-step solution and simplified form of your expression.
- Review the solution provided, which includes detailed steps and explanations, ensuring clarity and understanding.
Using CalculatorSoup's Simplify Radical Expressions Calculator
CalculatorSoup provides a user-friendly tool for simplifying radical expressions effortlessly. Follow these steps to utilize CalculatorSoup's Simplify Radical Expressions Calculator:
- Visit CalculatorSoup's website and navigate to the radical expressions calculator section.
- Enter your radical expression in the designated input box.
- Select the "Simplify" option to simplify the radical expression.
- Input the necessary variables or constants involved in your expression.
- Click the "Calculate" button to instantly generate the simplified form of your radical expression.
- Review the simplified result displayed, ensuring accuracy and understanding of the solution provided.
Using Symbolab's Exponents and Radicals Calculator
Symbolab offers a robust tool for handling exponents and radicals efficiently. Follow these steps to utilize Symbolab's Exponents and Radicals Calculator:
- Go to Symbolab's website or use their mobile app.
- Find the Exponents and Radicals Calculator section.
- Enter your radical expression into the input field.
- Select the operation you want to perform (simplify, solve, etc.).
- Specify any variables or constants included in the expression.
- Click the "Calculate" button to obtain the simplified or solved result.
- Review the step-by-step solution provided by Symbolab, ensuring clarity and correctness.
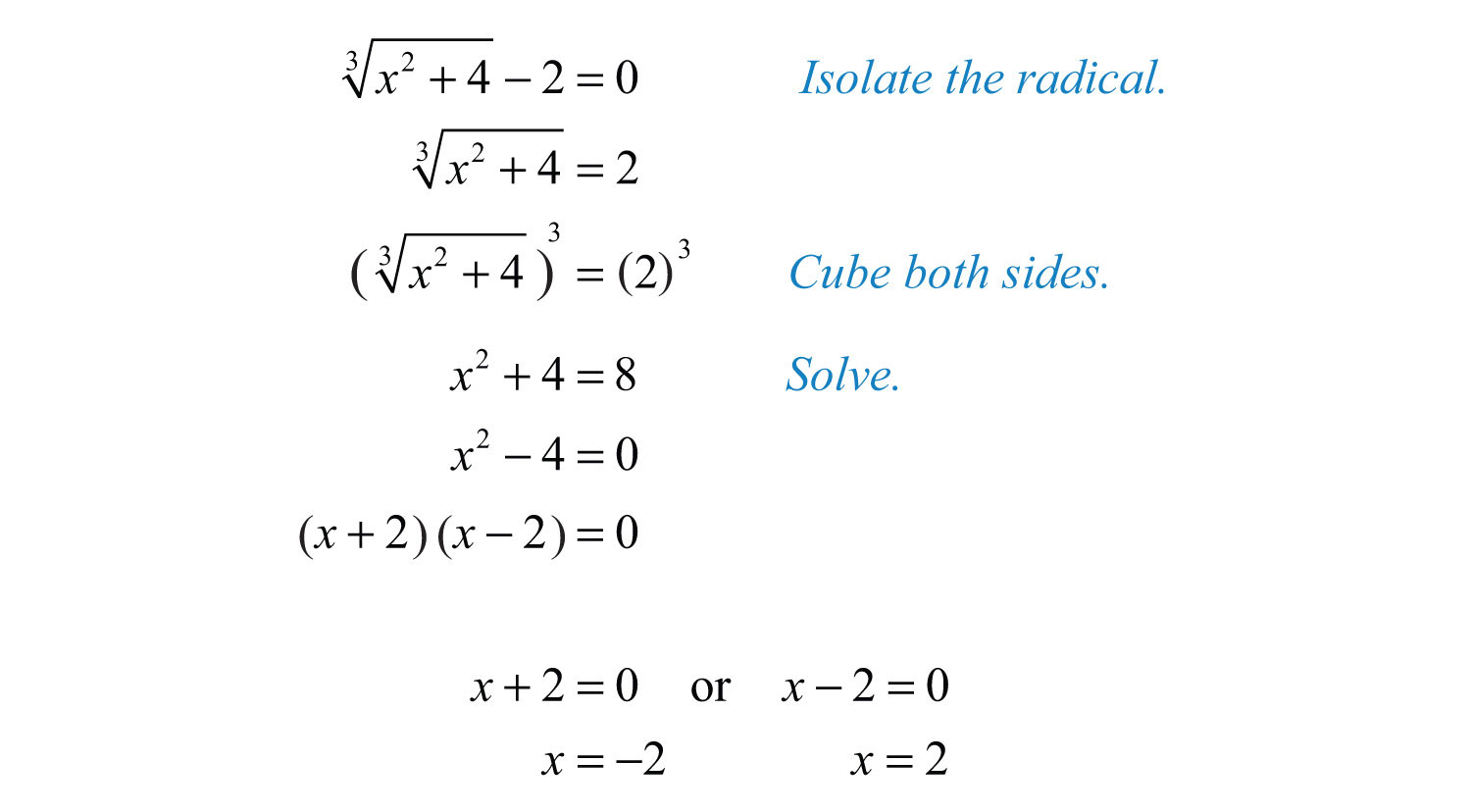
Using SnapXam's Radicals Calculator
SnapXam provides a convenient tool for working with radical expressions effectively. Follow these steps to utilize SnapXam's Radicals Calculator:
- Visit SnapXam's website and navigate to the Radicals Calculator section.
- Enter your radical expression in the input field.
- Select the operation you wish to perform (simplify, solve, etc.).
- Input any variables or constants relevant to your expression.
- Click on the "Calculate" button to see the simplified or solved result.
- Review the detailed solution provided by SnapXam, ensuring clarity and understanding.
Using MathPortal's Radical Simplification Tool
MathPortal offers an intuitive tool for simplifying radical expressions efficiently. Follow these steps to use MathPortal's Radical Simplification Tool:
- Go to MathPortal's website or access their tool through their designated section.
- Enter your radical expression into the provided input box.
- Select the "Simplify" option to simplify the radical expression.
- Specify any variables or constants involved in your expression.
- Click the "Simplify" button to see the simplified form of your radical expression.
- Review the simplified result displayed, ensuring accuracy and understanding.
Additional Resources and Tools
Explore more resources and tools to enhance your understanding and proficiency in solving radical expressions:
- : Offers comprehensive explanations and practice problems.
- : Provides video tutorials and exercises.
- : Helps in solving complex radical equations step-by-step.
- : Includes tools for simplifying radicals and solving equations.
- : Offers a straightforward tool for simplifying radicals.
Practice Problems and Exercises
Enhance your skills in solving radical expressions with these practice problems and exercises:
- Simplify the following radical expression: \( \sqrt{18} \).
- Solve the equation: \( \sqrt{x+7} = 5 \).
- Find the value of \( x \) that satisfies \( \sqrt{x} = 3 \).
- Simplify \( \sqrt{75} \) to its simplest radical form.
- Solve the equation: \( \sqrt{2x+1} = 4 \).

FAQs about Radical Expressions
Get answers to commonly asked questions about radical expressions:
- What is a radical expression?
- How do you simplify radical expressions?
- What are the basic operations involving radicals?
- How do you solve radical equations?
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when simplifying radicals?
- Where can I find online calculators for solving radical expressions?
- What are some real-world applications of radical expressions?
- Can radical expressions have negative solutions?
- How do you rationalize the denominator of a radical expression?
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering radical expressions enhances your algebraic problem-solving skills significantly. By understanding how to simplify, solve, and manipulate radical equations, you gain valuable tools for tackling more complex mathematical problems. Utilizing online calculators and resources discussed in this guide can further streamline your learning process and provide immediate assistance when needed. Continuously practicing with various exercises and exploring additional tools ensures a deeper comprehension and application of radical expressions in both academic and real-world contexts.
Video hướng dẫn cách sử dụng máy tính ClassWiz để đơn giản hóa các biểu thức căn bậc hai.
Hướng Dẫn Sử Dụng Máy Tính ClassWiz - Đại Số 4-1 Đơn Giản Hóa Biểu Thức Căn Bậc Hai
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn sử dụng máy tính TI-84 Plus để đơn giản hóa căn thức trong đại số. Hãy xem video này để biết thêm chi tiết và cải thiện kỹ năng toán học của bạn!
Mẹo Toán Học - Đại Số Với TI-84 Plus - Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Thức