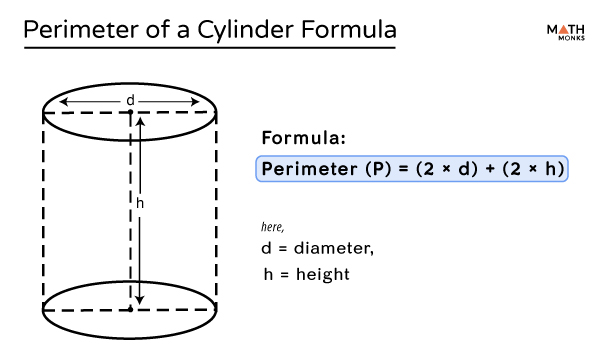
Topic area and perimeter for third graders: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding area and perimeter for third graders! This fun and easy-to-follow resource is designed to help young learners grasp the basics of these important math concepts through interactive activities, real-world examples, and simple explanations. Let's dive in and make learning math enjoyable!
Table of Content
- Understanding Area and Perimeter for Third Graders
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Understanding Area
- Understanding Perimeter
- Formulas for Area and Perimeter
- Measuring Area
- Measuring Perimeter
- Units of Measurement
- Calculating Area of Rectangles and Squares
- Calculating Perimeter of Rectangles and Squares
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Visual Learning with Graph Paper
- Interactive Activities and Games
- Using Real-World Objects to Learn
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Tips for Parents and Teachers
- Resources for Further Learning
- Conclusion and Encouragement
- YOUTUBE:
Understanding Area and Perimeter for Third Graders
Learning about area and perimeter is an important part of third-grade math. These concepts help students understand space and boundaries in everyday life. Here's a simple guide to help third graders learn about area and perimeter.
What is Area?
Area is the amount of space inside a shape. We measure area in square units, like square inches (in²) or square centimeters (cm²).
To find the area of a rectangle or square, we use the formula:
\[ \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \]
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units, the area is:
\[ 5 \times 3 = 15 \, \text{square units} \]
What is Perimeter?
Perimeter is the distance around the outside of a shape. We measure perimeter in linear units, like inches (in) or centimeters (cm).
To find the perimeter of a rectangle or square, we add up the lengths of all the sides. For a rectangle, the formula is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \]
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units, the perimeter is:
\[ 2 \times (5 + 3) = 2 \times 8 = 16 \, \text{units} \]
Activities to Practice Area and Perimeter
- Draw different shapes on graph paper and count the squares inside to find the area.
- Use a ruler to measure the sides of objects around the house and calculate their perimeter.
- Create a small garden plot and use string to measure the perimeter.
Interactive Questions
- If a rectangle has a length of 7 units and a width of 4 units, what is its area?
- If a square has a side length of 6 units, what is its perimeter?
- Draw a rectangle with an area of 20 square units. What could be its length and width?
Learning about area and perimeter can be fun and easy with practice. Keep measuring and calculating to become a math expert!

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding area and perimeter, specially designed for third graders. Let's start by learning what these terms mean and why they are important.
Area is the amount of space inside a shape. Imagine you have a piece of paper; the area is how much of that paper you can cover with a crayon. We measure area in square units, like square centimeters (cm²) or square inches (in²).
Perimeter is the distance around the outside of a shape. Think of it like a fence that goes all around your backyard. We measure perimeter in units like centimeters (cm) or inches (in).
Understanding area and perimeter helps us in many real-life situations, such as knowing how much paint to buy for a wall (area) or how much fencing is needed for a garden (perimeter).
- Area: The space inside a shape.
- Perimeter: The distance around a shape.
We will learn how to calculate the area and perimeter of rectangles and squares, which are common shapes. Let's get started!
Example: If you have a rectangle that is 4 units long and 3 units wide, you can find the area by multiplying the length by the width. The perimeter is found by adding all the sides together.
- To find the area of a rectangle:
- Formula: Area = Length × Width
- Example: If Length = 4 units and Width = 3 units, then Area = 4 × 3 = 12 square units.
- To find the perimeter of a rectangle:
- Formula: Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width)
- Example: If Length = 4 units and Width = 3 units, then Perimeter = 2 × (4 + 3) = 14 units.
Now that we have a basic understanding of what area and perimeter are, let's dive deeper into how to measure and calculate them!
Understanding Area
Area is an important concept in mathematics, especially for third graders who are starting to explore geometry. It refers to the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape. Let's break down the concept of area step by step.
What is Area?
Area is the measure of how much surface a shape covers. Imagine you have a piece of paper, and you want to know how much space it takes up on your desk. The area tells you that.
Units of Area
Area is measured in square units. These could be square centimeters (cm²), square inches (in²), square feet (ft²), or any other unit squared. The "squared" part means you're measuring both the length and the width of the shape.
Calculating Area
To find the area of a rectangle or square, you multiply the length by the width. This is because a rectangle or square is made up of rows and columns of unit squares.
- Identify the length and the width of the shape.
- Length: The longer side of the rectangle.
- Width: The shorter side of the rectangle.
- Multiply the length by the width to get the area.
- Formula: Area = Length × Width
- Example: If a rectangle has a length of 5 units and a width of 3 units, the area is \( 5 \times 3 = 15 \) square units.
Here is a visual example:
| 1 unit | 1 unit | 1 unit | ||||
| 1 unit | 1 unit | 1 unit | ||||
| 1 unit | 1 unit | 1 unit | ||||
| 1 unit | 1 unit | 1 unit | ||||
| 1 unit | 1 unit | 1 unit |
In the table above, each small square represents 1 square unit. The entire shape is a rectangle that covers 15 square units, which matches our calculation.
Understanding area helps us in many ways, such as finding out how much carpet we need for a room or how much wrapping paper is needed to cover a gift. Keep practicing to become more confident in measuring and calculating area!
Understanding Perimeter
Perimeter is another key concept in geometry that third graders need to understand. It refers to the total distance around the outside of a shape. Let's explore perimeter step by step.
What is Perimeter?
Perimeter is the distance you would travel if you walked all the way around the edge of a shape. Think of it as the length of a fence that surrounds a garden.
Units of Perimeter
Perimeter is measured in linear units, such as centimeters (cm), meters (m), inches (in), or feet (ft). Unlike area, we are only measuring distance, not space.
Calculating Perimeter
To find the perimeter of a rectangle or square, you add up the lengths of all the sides. Let's look at how to do this:
- Identify the length and width of the rectangle or square.
- Length: The longer side of the rectangle.
- Width: The shorter side of the rectangle.
- Use the formula to calculate the perimeter.
- For a rectangle: Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width)
- For a square: Perimeter = 4 × Side
Example for a Rectangle:
- Let's say a rectangle has a length of 6 units and a width of 4 units.
- Using the formula: Perimeter = 2 × (6 + 4) = 2 × 10 = 20 units
Example for a Square:
- If a square has a side length of 5 units:
- Using the formula: Perimeter = 4 × 5 = 20 units
Here is a visual example to help you understand:
| Length | 6 units | |||
| Width | 4 units | |||
| Perimeter = 2 × (6 + 4) = 20 units | ||||
Calculating the perimeter is helpful in many real-life situations, like figuring out how much ribbon you need to go around a gift box or how much trim you need to go around a picture frame.
Keep practicing to become more comfortable with measuring and calculating perimeter!
Formulas for Area and Perimeter
Understanding the formulas for calculating area and perimeter is essential for solving many geometry problems. Let's explore the key formulas step by step.
Formulas for Area
The area of a shape tells us how much space is inside it. Here are the formulas for finding the area of some common shapes:
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is found by multiplying the length by the width.
- Formula: Area = Length × Width
- Example: If the length is 7 units and the width is 3 units, then Area = 7 × 3 = 21 square units.
- Square: The area of a square is found by multiplying one side by itself, because all sides of a square are equal.
- Formula: Area = Side × Side or Area = Side²
- Example: If one side of the square is 4 units, then Area = 4 × 4 = 16 square units.
Formulas for Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around the outside of it. Here are the formulas for finding the perimeter of some common shapes:
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is found by adding together the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides are equal, you can use the formula:
- Formula: Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width)
- Example: If the length is 7 units and the width is 3 units, then Perimeter = 2 × (7 + 3) = 2 × 10 = 20 units.
- Square: The perimeter of a square is found by adding together the lengths of all four sides. Since all sides are equal, you can use the formula:
- Formula: Perimeter = 4 × Side
- Example: If one side of the square is 4 units, then Perimeter = 4 × 4 = 16 units.
Let's summarize the formulas in a table for quick reference:
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | Area = Length × Width | Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width) | ||||
| Square | Area = Side × Side | Perimeter = 4 × Side |
By using these formulas, you can easily find the area and perimeter of rectangles and squares. Practice using these formulas with different shapes to become confident in your skills!
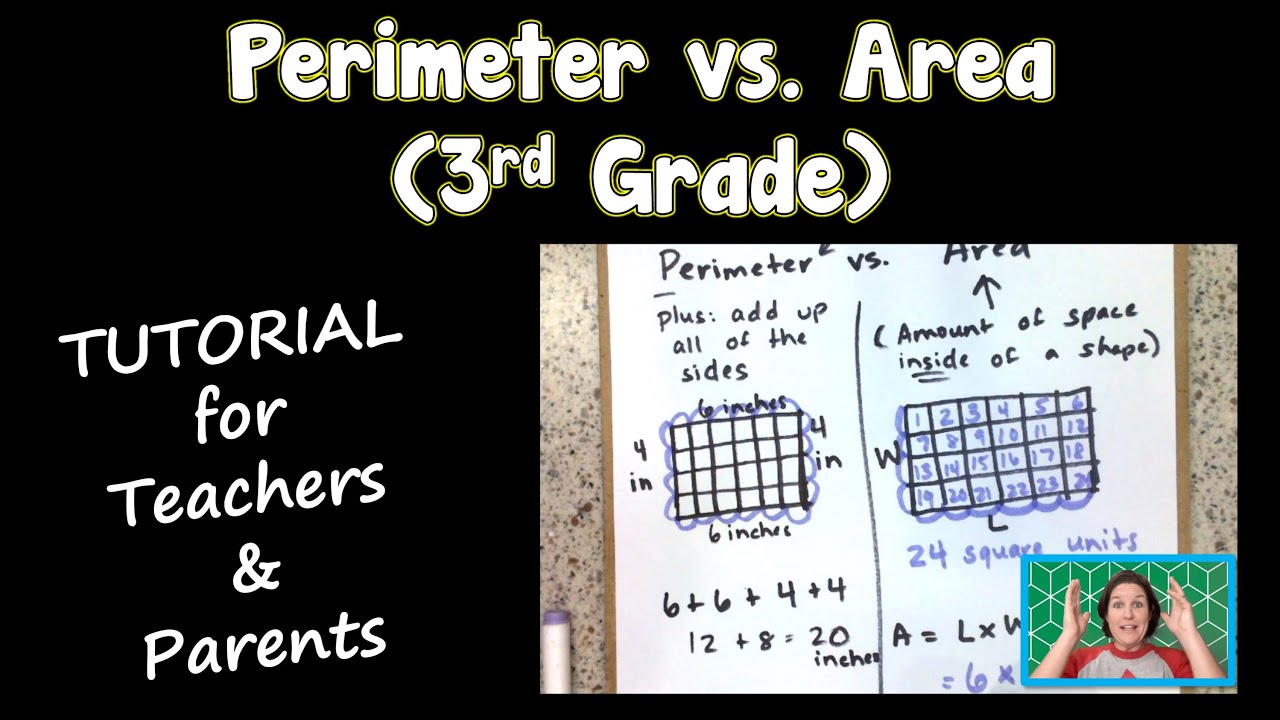
Measuring Area
Measuring area is a fun and important skill that helps us understand how much space a shape covers. Let's learn how to measure area step by step.
Understanding Square Units
To measure area, we use square units. A square unit is a square with sides that are one unit long. For example, if we use centimeters, a square unit would be a square with each side measuring 1 centimeter.
Using a Grid to Measure Area
One of the easiest ways to measure area is by using a grid. Let's see how this works:
- Draw the shape on graph paper: This helps us see the individual square units inside the shape.
- Count the number of complete square units: Each complete square inside the shape counts as one square unit of area.
- Estimate partial squares: If the shape includes partial squares, estimate how many whole squares they add up to.
Here is an example of measuring the area of a rectangle using a grid:
| 1 cm | 1 cm | 1 cm | ||||
| 1 cm | 1 cm | 1 cm | ||||
| 1 cm | 1 cm | 1 cm |
In this example, the rectangle covers 3 rows and 3 columns of square units. So, the area is:
Area = 3 rows × 3 columns = 9 square centimeters
Using the Formula to Measure Area
We can also use formulas to measure area, especially for rectangles and squares:
- Rectangle: Area = Length × Width
- Square: Area = Side × Side or Side²
Let's practice with an example:
- If a rectangle has a length of 5 cm and a width of 4 cm:
- Using the formula: Area = 5 × 4 = 20 square centimeters
Measuring area helps us in many real-life situations, such as finding out how much space we have in a room or how much fabric we need for a project. Keep practicing, and soon you'll be an expert at measuring area!
Measuring Perimeter
Measuring perimeter is an essential skill that helps us understand the total length of the boundary of a shape. Third graders can learn to measure perimeter using simple techniques and tools.
To measure the perimeter of a shape:
- Identify the shape: Determine whether the shape is a rectangle, square, or any other polygon.
- Understand the concept: Perimeter is the sum of all the sides of a shape.
- Use a ruler or measuring tape: Measure each side of the shape in the same unit of measurement.
- Add the measurements: Sum up all the measurements to find the total perimeter of the shape.
For example, let's consider a rectangle with sides measuring 5 cm and 3 cm. To find the perimeter:
| Side 1 | Side 2 | Side 3 | Side 4 | Total Perimeter |
| 5 cm | 3 cm | 5 cm | 3 cm | 5 cm + 3 cm + 5 cm + 3 cm = 16 cm |
So, the perimeter of the rectangle is 16 cm.
Practicing measuring perimeter with different shapes and sizes helps third graders develop a strong understanding of geometric concepts.
Units of Measurement
Understanding units of measurement is important when working with area and perimeter. Third graders can explore various units to measure length, width, area, and perimeter.
Common units of measurement for length include:
- Centimeters (cm)
- Meters (m)
- Inches (in)
- Feet (ft)
When measuring area, these units are squared, such as square centimeters (cm2), square meters (m2), square inches (in2), and square feet (ft2).
Similarly, units for perimeter are the same as units for length, such as centimeters, meters, inches, and feet.
It's essential to use the appropriate unit of measurement depending on the size of the shape being measured. For smaller shapes, centimeters or inches may be suitable, while larger shapes may require meters or feet.
Calculating Area of Rectangles and Squares
Calculating the area of rectangles and squares is a fundamental concept in geometry that third graders can easily grasp with the right guidance. Here's how to calculate the area of these shapes:
- Rectangle:
To find the area of a rectangle, multiply its length by its width.
Area = Length × Width
- Square:
For a square, since all sides are equal, you can simply square the length of one side.
Area = Side Length × Side Length (or Side Length2)
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 6 units and a width of 4 units:
| Length | Width | Area |
| 6 units | 4 units | 6 units × 4 units = 24 square units |
So, the area of the rectangle is 24 square units.
Similarly, if a square has a side length of 5 units:
| Side Length | Area |
| 5 units | 5 units × 5 units = 25 square units |
Therefore, the area of the square is 25 square units.
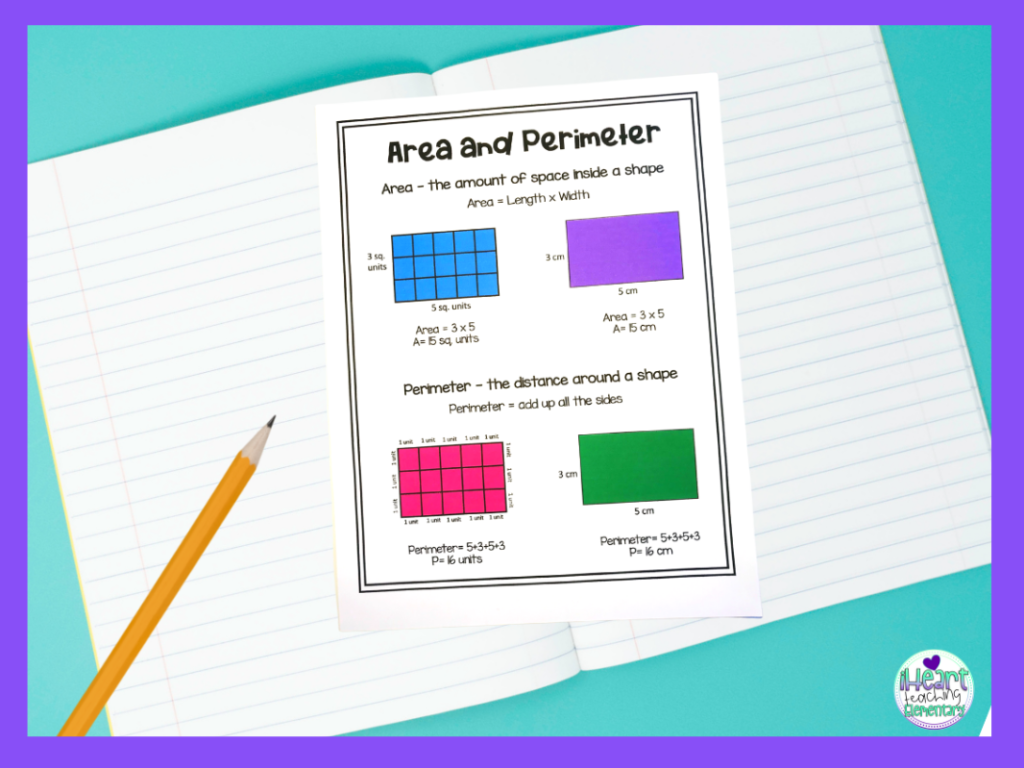
Calculating Perimeter of Rectangles and Squares
Calculating the perimeter of rectangles and squares is a fundamental skill that third graders can easily learn and apply. Here's how to calculate the perimeter of these shapes:
- Rectangle:
To find the perimeter of a rectangle, add the lengths of all four sides.
Perimeter = 2 × (Length + Width)
- Square:
For a square, since all sides are equal, you can simply multiply the length of one side by 4.
Perimeter = 4 × Side Length
For example, if a rectangle has a length of 6 units and a width of 4 units:
| Length | Width | Perimeter |
| 6 units | 4 units | 2 × (6 units + 4 units) = 2 × 10 units = 20 units |
So, the perimeter of the rectangle is 20 units.
Similarly, if a square has a side length of 5 units:
| Side Length | Perimeter |
| 5 units | 4 × 5 units = 20 units |
Therefore, the perimeter of the square is 20 units.
Examples and Practice Problems
Examples and practice problems are excellent ways for third graders to reinforce their understanding of area and perimeter concepts. Let's explore some:
- Example 1: Rectangle
- Example 2: Square
Consider a rectangle with a length of 8 units and a width of 3 units. Calculate its area and perimeter.
| Length | Width | Area | Perimeter |
| 8 units | 3 units | 8 units × 3 units = 24 square units | 2 × (8 units + 3 units) = 2 × 11 units = 22 units |
Suppose a square has a side length of 5 units. Find its area and perimeter.
| Side Length | Area | Perimeter |
| 5 units | 5 units × 5 units = 25 square units | 4 × 5 units = 20 units |
Encourage third graders to practice similar problems to strengthen their skills in calculating area and perimeter.
Visual Learning with Graph Paper
Using graph paper is a fantastic way to help third graders visualize and understand the concepts of area and perimeter. Here are some step-by-step activities and tips for using graph paper effectively:
Step-by-Step Activities
-
Introduction to Graph Paper: Start by explaining what graph paper is and how the squares on the paper can represent units of measurement. Each square can be 1 unit by 1 unit.
-
Drawing Shapes: Have students draw rectangles and squares on the graph paper. For example, draw a rectangle that is 4 squares wide and 3 squares high.
-
Counting Squares for Area: Teach students to count the number of squares inside the shape to find the area. In the example, the rectangle has an area of 12 square units.
\[
\text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 4 \times 3 = 12 \text{ square units}
\] -
Measuring Perimeter: Show students how to count the squares along the edges of the shape to find the perimeter. In the rectangle example, count 4 squares on the top, 4 on the bottom, and 3 on each side.
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) = 2 \times (4 + 3) = 14 \text{ units}
\] -
Shading Areas: Let students shade the squares inside the shapes to visually confirm their area calculations. This reinforces the concept of area being the amount of space inside a shape.
Practical Tips
Use Different Colors: Encourage the use of different colored pencils or markers to differentiate between various shapes and their measurements.
Label Dimensions: Have students label the length and width of each shape on the graph paper to help them remember the dimensions.
Interactive Activities: Create challenges where students have to find shapes with specific areas or perimeters on their graph paper.
Group Work: Allow students to work in pairs or small groups to discuss their findings and verify each other's work.
Example Table of Measurements
| Shape | Length (units) | Width (units) | Area (square units) | Perimeter (units) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangle 1 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 14 |
| Square 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
Conclusion
Graph paper is an excellent tool for making the abstract concepts of area and perimeter more concrete. By engaging in these visual and hands-on activities, third graders can develop a stronger understanding and enjoy learning math in a fun and interactive way.
Interactive Activities and Games
Engaging students in learning area and perimeter can be both fun and educational with interactive activities and games. Here are some exciting ways to help third graders understand these concepts:
-
Area and Perimeter Builder Game
This online activity allows students to create their own shapes using colorful blocks and explore the relationship between area and perimeter. They can compare the area and perimeter of different shapes side-by-side and build figures with given dimensions. This interactive game helps students understand these concepts through hands-on practice.
-
Digital Pattern Blocks
Students can use digital pattern blocks to create various shapes, such as houses or boats, and calculate the perimeter of their creations. Each side of the pattern block represents one unit, making it easier for students to visualize and measure the perimeter. Recording their designs on graph paper helps reinforce their learning.
-
Connect Four Using Area & Perimeter
This twist on the classic game involves students solving area and perimeter problems to place their game pieces. Each correct answer allows them to cover a spot on the board, and the goal is to get four in a row. This competitive game makes learning math concepts exciting and interactive.
-
Area and Perimeter Scavenger Hunt
In this activity, students solve area and perimeter problems to find clues that lead them to a secret phrase. This engaging scavenger hunt keeps students motivated and helps them practice their math skills in a fun way.
-
Area and Perimeter Bingo
Just like traditional bingo, this game involves students solving area and perimeter problems to mark off spots on their bingo cards. The first to get five in a row wins, making it a fun and interactive way to review these concepts.
-
Build a Farm Activity
Students use area and perimeter to design their own farm. They draw each space on a map according to the given dimensions, helping them apply their knowledge in a real-world context. This activity can be differentiated by providing catalogs focused on either perimeter or area.
-
Digital Mystery Pictures
As students answer questions about area and perimeter, a mystery picture gradually appears. This self-checking activity not only makes learning fun but also provides immediate feedback, reinforcing correct answers.
These interactive activities and games are designed to make learning area and perimeter enjoyable and memorable for third graders. By incorporating hands-on practice and engaging challenges, students can develop a deeper understanding of these important math concepts.
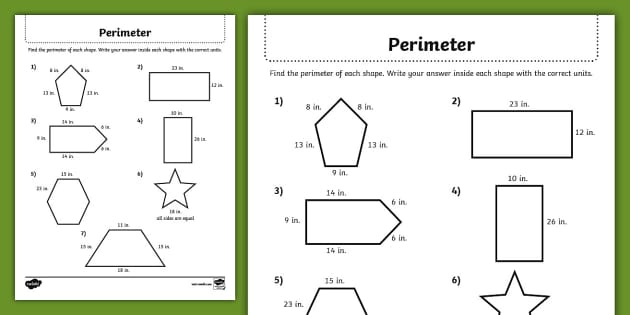
Using Real-World Objects to Learn
Learning about area and perimeter becomes more engaging and meaningful for third graders when they can connect these concepts to real-world objects. Here are some effective activities and games that use everyday items to teach area and perimeter:
-
Floor Tiles and Tape:
Use square floor tiles and tape to create shapes on the floor. Have students measure the perimeter and area of these shapes. This activity helps students visualize and understand the concepts as they physically measure the space.
-
Post-it Notes:
Provide students with square Post-it notes to form different shapes. Students can then calculate the area and perimeter of these shapes by counting the number of Post-it notes used and measuring the sides.
-
Building a Kite:
Give students materials to build their own kites. After constructing their kites, have them measure and calculate the area and perimeter. This activity combines creativity with practical application of math skills.
-
Interior Design Project:
Ask students to design a room layout using cut-out furniture pieces. They will measure the perimeter of the room and the area of each piece of furniture to ensure everything fits. This real-life application helps them understand the importance of area and perimeter.
-
Scavenger Hunt:
Organize a scavenger hunt where students find and measure various objects around the classroom or school. They can calculate the area and perimeter of these objects, reinforcing their understanding through hands-on practice.
Using real-world objects to teach area and perimeter makes learning interactive and enjoyable. It helps students see the relevance of math in their everyday lives and enhances their problem-solving skills.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Learning to calculate area and perimeter can be challenging for third graders. Here are some common mistakes and tips on how to avoid them:
- Confusing Area and Perimeter:
Students often mix up the concepts of area and perimeter. Remember:
- Area: The amount of space inside a shape.
- Perimeter: The distance around the outside of a shape.
Tip: Use visual aids like colored shapes and border lines to highlight the difference. Practice with real-world objects, such as measuring the area of a book cover and the perimeter of a classroom.
- Incorrect Formula Application:
Ensure that students use the correct formulas for different shapes:
- Rectangles and Squares:
- Area = length × width
- Perimeter = 2 × (length + width)
Tip: Practice with simple, clear examples and gradually increase difficulty. Encourage students to write down the formula before calculating.
- Unit Confusion:
Students may forget to use consistent units or confuse square units (for area) with linear units (for perimeter).
Tip: Emphasize the importance of units by always including them in calculations. Use activities that involve measuring objects with a ruler and counting unit squares on graph paper.
- Errors in Multiplication and Addition:
Basic arithmetic errors can lead to incorrect results.
Tip: Practice multiplication and addition separately. Use checklists to ensure each step is followed correctly.
- Forgetting to Double Check Work:
Students may rush through problems without verifying their answers.
Tip: Teach students to always double-check their work. Pair them up to review each other’s calculations and provide feedback.
By addressing these common mistakes, students can improve their understanding and accuracy in calculating area and perimeter.
Tips for Parents and Teachers
Supporting third graders in learning area and perimeter can be rewarding and fun. Here are some tips to help parents and teachers guide their students effectively:
- Use Real-World Examples:
Relate area and perimeter to everyday objects and activities:
- Measure the area of a tabletop or a book cover.
- Calculate the perimeter of a garden or a playground.
- Incorporate Visual Aids:
Visual aids can help students understand and remember concepts better:
- Use graph paper to draw shapes and count squares for area.
- Highlight the boundaries of shapes to emphasize perimeter.
- Interactive Activities and Games:
Engage students with fun and interactive learning tools:
- Play online games that involve calculating area and perimeter.
- Set up scavenger hunts where students measure objects around the house or classroom.
- Practice with Worksheets:
Provide plenty of practice with a variety of problems:
- Use worksheets that mix different types of questions.
- Include word problems to develop critical thinking skills.
- Encourage Group Work:
Learning with peers can enhance understanding and make learning more enjoyable:
- Organize group activities where students work together to solve problems.
- Encourage students to explain concepts to each other.
- Provide Clear Instructions and Examples:
Ensure that instructions and examples are easy to understand:
- Break down steps clearly and sequentially.
- Show multiple examples with different shapes and scenarios.
- Regular Review and Reinforcement:
Regularly review concepts to reinforce learning:
- Set aside time each week for a quick review session.
- Use flashcards or quick quizzes to reinforce key concepts.
By following these tips, parents and teachers can create a supportive and effective learning environment for their third graders, helping them master the concepts of area and perimeter with confidence.
Resources for Further Learning
Here are some excellent resources for parents, teachers, and students to explore and deepen their understanding of area and perimeter:
- Online Educational Platforms:
Websites and apps can provide interactive and engaging learning experiences:
- : Offers comprehensive lessons and practice problems on area and perimeter.
- : Features fun games and activities focused on math concepts including area and perimeter.
- : Provides targeted practice questions and detailed explanations.
- Printable Worksheets and Workbooks:
These resources can offer additional practice and review:
- : A vast collection of printable worksheets for various grade levels.
- : Free printable worksheets for extra practice on area and perimeter.
- : Find and purchase workbooks and activities created by teachers.
- Interactive Tools and Games:
Interactive tools can make learning more engaging and effective:
- : Animated educational videos and quizzes on math topics.
- : Math games and activities designed for young learners.
- : Games and books that cover a wide range of math skills, including area and perimeter.
- Books and Educational Materials:
Books can provide structured learning and additional practice:
- Math Adventures with Area and Perimeter by Cindy Neuschwander: A storybook approach to learning area and perimeter.
- Everything You Need to Ace Math in One Big Fat Notebook by Workman Publishing: Comprehensive guide covering many math topics.
- Hands-On Math Projects with Real-Life Applications by Judith A. Muschla and Gary R. Muschla: Practical activities that make math concepts tangible.
- Videos and Tutorials:
Visual learners can benefit from watching instructional videos:
- : Clear and entertaining math tutorials on YouTube.
- : Detailed video lessons on a wide range of math topics.
- : Engaging videos that explore fascinating math concepts.
These resources can help students practice, understand, and excel in calculating area and perimeter, making math a fun and rewarding subject.

Conclusion and Encouragement
Learning about area and perimeter is an exciting journey that builds a strong foundation in math for third graders. As students progress through these concepts, it's important to remember that practice, patience, and a positive mindset are key to success.
Here are some encouraging thoughts and tips to keep students motivated:
- Celebrate Small Wins:
Every step forward is a success. Celebrate each correct calculation and understanding of a new concept.
- Practice Regularly:
Consistent practice helps reinforce learning. Set aside a few minutes each day to work on area and perimeter problems.
- Ask for Help:
Encourage students to ask questions whenever they are unsure. Parents, teachers, and peers are all valuable resources for learning.
- Stay Positive:
Maintaining a positive attitude towards math can make a big difference. Remind students that making mistakes is a part of learning and improvement.
- Use Fun Learning Tools:
Incorporate games, interactive activities, and real-world examples to make learning more enjoyable and relatable.
- Reflect on Progress:
Take time to review what has been learned and acknowledge the progress made. This helps build confidence and motivation.
Remember, learning math is a journey, and every student moves at their own pace. With the right support and encouragement, third graders can master area and perimeter and develop a lifelong love for math.
Keep up the great work, and don't forget to have fun along the way!
Diện Tích vs. Chu Vi | Toán MightyOwl | Lớp 3
READ MORE:
Lớp 3: Chu Vi & Diện Tích Các Hình Bất Quy Tắc