Topic area and perimeter worksheets with answers: Discover a variety of engaging area and perimeter worksheets with answers to help students master these fundamental math concepts. These worksheets are designed for different grade levels and include detailed solutions to enhance learning. Perfect for classroom use or home practice, these resources make calculating area and perimeter both fun and educational.
Table of Content
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets with Answers
- Introduction
- Grade-Level Worksheets
- Rectangles and Squares
- Triangles
- Polygons
- Circles
- Compound Shapes
- Practice Problems
- Printable PDFs
- Online Quizzes and Flashcards
- Customizable Worksheet Generators
- Real-World Applications
- Critical Thinking Problems
- Additional Resources
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một hình dạng tổ hợp, với ví dụ về hình L. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính toán các khái niệm này trong hình học.
Area and Perimeter Worksheets with Answers
Explore a variety of worksheets designed to help students master the concepts of area and perimeter. These worksheets are suitable for different grade levels and cover a range of shapes and figures.
Worksheet Types
- Polygons
Example Problems
Here are some example problems included in the worksheets:
- Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 8 cm and a width of 5 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 4 cm.
- Determine the area of a triangle with a base of 6 cm and a height of 3 cm.
- Compute the circumference of a circle with a radius of 7 cm.
Answer Keys
All worksheets come with detailed answer keys to help students check their work and understand the solutions:
- Rectangles and Squares:
Area = \text{length} \times \text{width},Perimeter = 2(\text{length} + \text{width}) - Triangles:
Area = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} - Circles:
Circumference = 2\pi \times \text{radius},Area = \pi \times \text{radius}^2
Interactive Features
Many worksheets offer interactive features such as:
- Printable PDFs
- Customizable worksheet generators
- Online quizzes and flashcards
Sample Worksheet
| Shape | Dimensions | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangle | Length = 8 cm, Width = 5 cm | \(Area = \text{length} \times \text{width}\) | 40 cm2 |
| Square | Side = 4 cm | \(Perimeter = 4 \times \text{side}\) | 16 cm |
| Triangle | Base = 6 cm, Height = 3 cm | \(Area = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}\) | 9 cm2 |
| Circle | Radius = 7 cm | \(Circumference = 2\pi \times \text{radius}\) | 43.98 cm |

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding how to calculate the area and perimeter of various shapes is an essential math skill. Area and perimeter worksheets provide students with the practice needed to master these concepts. These worksheets include exercises on finding the area of rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and circles, as well as compound shapes. By practicing with these worksheets, students can improve their problem-solving skills and gain confidence in their ability to tackle geometry problems.
- Calculating the Area of Basic Shapes
- Perimeter Calculations
- Compound Shapes
- Word Problems and Real-life Applications
- Answer Keys for Self-assessment
Whether for classroom use or home practice, these worksheets are an excellent resource for students at various grade levels. They provide a structured approach to learning, with step-by-step solutions and clearly defined methods to solve area and perimeter problems.
Grade-Level Worksheets
Our collection of grade-level worksheets for area and perimeter is designed to cater to the learning needs of students from elementary to high school. Each worksheet is crafted to provide students with comprehensive practice and understanding of the concepts of area and perimeter. Below are the grade-level details:
Elementary School
- Grade 1-2: Introduction to basic shapes, counting squares to find area, and simple perimeter calculations.
- Grade 3-4: Calculating area and perimeter of rectangles and squares, understanding units of measure, and solving word problems.
Middle School
- Grade 5-6: Advanced problems involving irregular shapes, introduction to triangles, and basic polygons. Incorporating fractional measurements.
- Grade 7-8: Calculating area and perimeter of complex shapes, circles, and composite figures. Application of formulas and solving multi-step problems.
High School
- Grade 9-10: Detailed exploration of polygons, circles, and compound shapes. Using algebraic expressions to find area and perimeter.
- Grade 11-12: Advanced geometric problems, including coordinate geometry, transformations, and real-world applications of area and perimeter in various fields.
Worksheet Features
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Each worksheet comes with detailed step-by-step solutions to ensure students understand the process of solving area and perimeter problems.
- Interactive Components: Some worksheets include interactive elements like drag-and-drop and fill-in-the-blank activities to enhance learning.
- Varied Difficulty Levels: Worksheets are available in varying difficulty levels to cater to different learning paces and abilities.
These worksheets are an excellent resource for teachers and parents to help students master the concepts of area and perimeter through consistent practice and real-world application problems.
Rectangles and Squares
Rectangles and squares are fundamental shapes in geometry, making them perfect for practicing area and perimeter calculations. The following worksheets cover a range of problems to help students understand and master these concepts.
-
Basic Area and Perimeter
These worksheets focus on calculating the area and perimeter of rectangles and squares given their side lengths. Problems include both straightforward calculations and word problems.
- Find the area of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) using the formula \( A = l \times w \).
- Determine the perimeter of a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \) using the formula \( P = 2(l + w) \).
-
Rectangles with Same Area but Different Perimeters
Students create rectangles that have the same area but different perimeters. This helps in understanding how different dimensions affect the perimeter while keeping the area constant.
- Worksheet includes 5 problems per set.
-
Rectangles with Same Perimeter but Different Areas
This set of worksheets involves creating rectangles that share the same perimeter but have different areas, emphasizing the relationship between side lengths and area.
- Each worksheet contains 5 problems to solve.
-
Finding Missing Side Lengths
These problems require students to find the missing side length of rectangles and squares given the area or perimeter.
- Includes problems with both whole numbers and decimals.
-
Advanced Problems with Decimals
Worksheets designed for more advanced students involve finding the area and perimeter of shapes when side lengths are given in decimal form.
- Each worksheet contains 15 problems.
-
Scale Rectangles
Problems focused on finding the width, height, and area of scaled rectangles, helping students understand how scaling affects dimensions and area.
- Each worksheet includes 8 problems.
Triangles
Understanding the area and perimeter of triangles is crucial in geometry. This section provides a variety of worksheets tailored to help students grasp these concepts through practical exercises.
Area of Triangles
To calculate the area of a triangle, use the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}
\]
- Worksheets include problems with different types of triangles: right, equilateral, isosceles, and scalene.
- Students practice identifying the base and height in various orientations.
- Exercises come with step-by-step solutions to ensure thorough understanding.
Perimeter of Triangles
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
- Problems range from simple calculations with integers to more complex ones involving decimals and fractions.
- Worksheets include a variety of triangle types, enhancing problem-solving skills.
- Real-world applications and word problems are provided to apply concepts in practical scenarios.
Worksheet Features
- Customizable settings: Choose units (inches, feet, yards, centimeters, millimeters).
- Language options: Available in multiple languages including English, Spanish, French, and more.
- Answer keys included: Each worksheet comes with detailed solutions for self-assessment.
Sample Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the area of a triangle with a base of 5 cm and a height of 10 cm. | \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 10 = 25 \, \text{cm}^2 \] |
| Calculate the perimeter of a triangle with sides 7 cm, 9 cm, and 12 cm. | \[ \text{Perimeter} = 7 + 9 + 12 = 28 \, \text{cm} \] |
Interactive Practice
Enhance your learning experience with interactive features:
- Online quizzes to test your knowledge.
- Flashcards for quick review and memorization.
- Dynamic worksheet generators to create customized practice sets.
These worksheets and resources are designed to build a strong foundation in calculating the area and perimeter of triangles, preparing students for more advanced geometric concepts.

Polygons
Understanding the area and perimeter of polygons is a key component of geometry education. Polygons are multi-sided figures with straight sides. This section provides worksheets and explanations to help students master the calculation of both area and perimeter for various types of polygons.
Below is an outline of the concepts covered:
- Definitions and properties of different polygons
- Formulas for calculating the area and perimeter
- Examples and step-by-step problem-solving guides
- Practice worksheets with answers for self-assessment
Types of Polygons
Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides they have. Here are some common types:
- Triangle: A three-sided polygon.
- Quadrilateral: A four-sided polygon, including squares and rectangles.
- Pentagon: A five-sided polygon.
- Hexagon: A six-sided polygon.
- Heptagon: A seven-sided polygon.
- Octagon: An eight-sided polygon.
Formulas
The following formulas are essential for calculating the area and perimeter of regular polygons (where all sides and angles are equal):
- Perimeter: \( P = n \cdot s \)
- \( n \) = number of sides
- \( s \) = length of one side
- Area: For regular polygons, the area can often be found using the apothem (a line from the center to the midpoint of a side):
- \( A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot P \cdot a \)
- \( P \) = perimeter
- \( a \) = apothem
Example Problems
Here are examples to help illustrate the application of these formulas:
| Polygon | Sides | Length (s) | Perimeter | Apothem (a) | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hexagon | 6 | 4 cm | \( P = 6 \cdot 4 = 24 \, \text{cm} \) | 3.46 cm | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot 24 \cdot 3.46 \approx 41.52 \, \text{cm}^2 \) |
| Pentagon | 5 | 3 cm | \( P = 5 \cdot 3 = 15 \, \text{cm} \) | 2.88 cm | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot 15 \cdot 2.88 \approx 21.6 \, \text{cm}^2 \) |
Practice Worksheets
To reinforce learning, students can use the following worksheets:
These worksheets include detailed answer keys to help students check their work and understand any mistakes.
Additional Resources
For more interactive learning, consider using online tools and apps that provide real-time feedback and additional practice problems. These resources can greatly enhance a student's understanding and proficiency in calculating the area and perimeter of polygons.
Circles
Understanding the area and circumference of circles is fundamental in geometry. Below are detailed steps and example problems to help students grasp these concepts.
Key Formulas
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Circumference: \( C = 2 \pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \)
Steps to Calculate Area and Circumference
- Identify the radius (r) or diameter (d): The radius is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge, while the diameter is twice the radius.
- Apply the formulas:
- For the area, use \( A = \pi r^2 \).
- For the circumference, use \( C = 2 \pi r \) or \( C = \pi d \).
- Solve and simplify: Use \( \pi \approx 3.14 \) or leave \( \pi \) in the answer for exact values.
Example Problems
Example 1: Find the area of a circle with a radius of 7 cm.
Using the formula \( A = \pi r^2 \):
\( A = \pi (7)^2 = 49\pi \approx 153.94 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
Example 2: Calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm.
Using the formula \( C = \pi d \):
\( C = \pi \times 10 = 10\pi \approx 31.4 \, \text{cm} \)
Practice Problems
Try solving the following problems to test your understanding:
- 1. Find the area of a circle with a radius of 5 cm.
- 2. Determine the circumference of a circle with a radius of 12 cm.
- 3. If the diameter of a circle is 15 cm, what is its area?
- 4. A circle has a circumference of 25.12 cm. What is its radius?
Worksheet Downloads
Compound Shapes
Understanding the area and perimeter of compound shapes involves breaking down complex figures into simpler geometric shapes such as rectangles, triangles, circles, and trapezoids. The worksheets provided help students practice calculating these areas and perimeters through various methods and techniques.
Types of Compound Shapes
- Shapes formed by adding areas of non-overlapping figures.
- Shapes formed by subtracting areas of overlapping figures.
Steps to Calculate Area and Perimeter
- Identify Simple Shapes: Break down the compound shape into recognizable simple shapes (e.g., rectangles, triangles, circles).
- Calculate Individual Areas: Use the appropriate formulas to calculate the area of each simple shape. For example:
- Rectangle: \( \text{Area} = l \times w \)
- Triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \)
- Circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \)
- Add or Subtract Areas: Depending on whether the shapes are overlapping or non-overlapping, add or subtract the areas to get the total area of the compound shape.
- Calculate Perimeter: Sum up the outer side lengths of the entire compound shape to find the perimeter.
Example Problem
Consider a compound shape consisting of a rectangle and a semicircle attached to one of its sides:
- Rectangle length \( l = 10 \) units and width \( w = 4 \) units.
- Semicircle radius \( r = 2 \) units.
Steps:
- Calculate the area of the rectangle: \( \text{Area}_{\text{rect}} = l \times w = 10 \times 4 = 40 \) square units.
- Calculate the area of the semicircle: \( \text{Area}_{\text{semi}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi r^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi (2)^2 = 2\pi \) square units.
- Add the areas: \( \text{Total Area} = 40 + 2\pi \) square units.
- Calculate the perimeter, including the curved part of the semicircle and the three sides of the rectangle: \( \text{Perimeter} = 10 + 4 + 10 + \pi(2) = 24 + 2\pi \) units.
Practice Worksheets
These worksheets provide practice problems with a variety of compound shapes. Students can select the type of shapes they wish to work with and the units of measurement (inches, feet, yards, centimeters, meters). They can also choose the level of difficulty by selecting shapes with whole numbers or decimal dimensions.
Additional Features
- Interactive problems to enhance understanding.
- Printable PDFs for offline practice.
- Answer keys to help verify solutions.
These resources are designed to help students build a solid understanding of how to calculate the area and perimeter of compound shapes by breaking them down into simpler parts and applying fundamental geometric principles.
Practice Problems
Practice problems are an essential part of mastering the concepts of area and perimeter. Here, we provide a variety of worksheets tailored to different skill levels and types of shapes. Each worksheet includes detailed answers to help students learn from their mistakes and improve their understanding.
-
Rectangles and Squares
-
Basic Problems: Calculate the area and perimeter of given rectangles and squares.
- Find the area and perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 cm and a width of 5 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of a square with each side measuring 6 cm.
-
Advanced Problems: Solve for missing dimensions using area and perimeter formulas.
- If the area of a square is 64 cm², what is the length of one side?
- A rectangle has a perimeter of 24 cm and a width of 4 cm. What is its length?
-
-
Triangles
-
Basic Problems: Calculate the area and perimeter of given triangles.
- Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 5 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 7 cm.
-
Advanced Problems: Solve for missing dimensions using area and perimeter formulas.
- If the area of a triangle is 30 cm² and its base is 6 cm, what is its height?
- A right triangle has legs of 3 cm and 4 cm. What is its perimeter?
-
-
Polygons
-
Basic Problems: Calculate the area and perimeter of regular polygons.
- Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon with each side measuring 6 cm.
- Calculate the area of a regular pentagon with a side length of 5 cm.
-
Advanced Problems: Solve for missing dimensions using area and perimeter formulas.
- A regular octagon has a perimeter of 80 cm. What is the length of one side?
- Find the area of a regular hexagon with a side length of 4 cm.
-
-
Circles
-
Basic Problems: Calculate the area and circumference of given circles.
- Find the area of a circle with a radius of 7 cm.
- Calculate the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 10 cm.
-
Advanced Problems: Solve for missing dimensions using area and circumference formulas.
- If the circumference of a circle is 31.4 cm, what is its radius?
- A circle has an area of 50.24 cm². What is its diameter?
-
-
Compound Shapes
-
Basic Problems: Calculate the area and perimeter of compound shapes.
- Find the area of an L-shaped figure made of two rectangles, each with dimensions 4 cm by 3 cm and 6 cm by 2 cm.
- Calculate the perimeter of a T-shaped figure made of three rectangles.
-
Advanced Problems: Solve for missing dimensions using area and perimeter formulas.
- An L-shaped figure is made of two rectangles. The total area is 34 cm². If one rectangle is 4 cm by 3 cm, what are the dimensions of the other rectangle?
- Find the perimeter of a compound shape made of a rectangle and a semicircle.
-
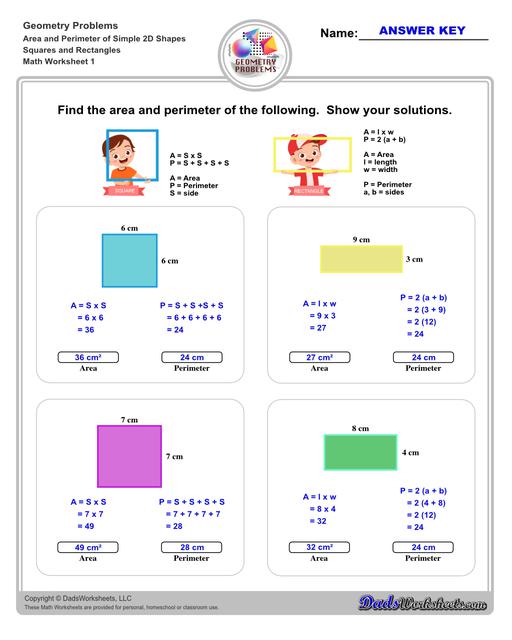
Printable PDFs
Enhance your learning experience with our comprehensive collection of printable PDFs focused on area and perimeter worksheets. These resources are designed to help students master the concepts of area and perimeter through a variety of engaging and interactive exercises.
- Area and Perimeter Worksheets for Different Grades:
- Specialized Worksheets:
- Real-World Applications: Worksheets that incorporate real-life problems to help students understand the practical uses of area and perimeter calculations.
- Answer Keys: Each worksheet comes with a detailed answer key to facilitate self-paced learning and easy grading.
These worksheets are available for free download and can be used in the classroom or at home to provide additional practice. Click on the links above to access the printable PDFs and start mastering area and perimeter today!
| Worksheet Title | Download Link |
|---|---|
| Area and Perimeter Worksheet - 1 | |
| Area and Perimeter Worksheet - 2 | |
| Area and Perimeter Worksheet - 3 | |
| Area and Perimeter Worksheet - 4 |
For more practice, explore our interactive worksheets that adapt to your learning pace and provide instant feedback.
Online Quizzes and Flashcards
Online quizzes and flashcards are excellent tools for reinforcing students' understanding of area and perimeter concepts. These interactive features help students practice calculations in an engaging and efficient manner.
- Interactive Quizzes:
Students can take timed quizzes that challenge their knowledge of area and perimeter. These quizzes provide instant feedback and explanations for each answer, helping students learn from their mistakes.
- Quizzes covering various shapes such as rectangles, triangles, circles, and polygons.
- Difficulty levels range from basic to advanced to cater to different learning stages.
- Detailed score reports to track progress over time.
- Flashcards:
Flashcards are a great way to memorize key formulas and properties related to area and perimeter.
- Flashcards include formulas for calculating the area and perimeter of different shapes.
- Interactive elements such as multiple-choice questions to reinforce learning.
- Customizable flashcards to focus on specific areas of difficulty.
Here are a few examples of online quiz questions and flashcard content:
| Question Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Quiz Question | |
| Flashcard |
By regularly using online quizzes and flashcards, students can strengthen their understanding and become more confident in solving area and perimeter problems.
Customizable Worksheet Generators
Customizable worksheet generators are a fantastic tool for educators and students to create personalized learning materials. These tools allow users to tailor worksheets to meet specific learning objectives, making them ideal for practicing concepts like area and perimeter. Below, we'll explore some of the features and benefits of these generators and provide a step-by-step guide on how to use them effectively.
Features of Customizable Worksheet Generators
- Versatile Templates: Choose from a variety of templates including simple shapes, complex polygons, and mixed geometry problems. This ensures that you can generate worksheets suited to different grade levels and learning needs.
- Adjustable Difficulty Levels: Set the complexity of the problems to match the student's proficiency. This could involve varying the dimensions of shapes, including decimal values, or introducing word problems.
- Automatic Answer Keys: Generate worksheets with or without answer keys. This feature is especially useful for self-study or homework assignments.
- Interactive Elements: Some platforms offer interactive features, allowing students to complete worksheets online and receive instant feedback.
- Printable and Digital Options: Worksheets can be downloaded in PDF format for printing or saved as digital files for online use, catering to both traditional and modern classroom environments.
Steps to Create a Custom Worksheet
- Select a Template: Start by choosing a worksheet template that matches the topic you want to cover. Templates may range from basic shapes (like rectangles and circles) to compound figures.
- Define Parameters: Specify the parameters for each problem, such as the shape dimensions, units of measurement, and whether to include perimeter, area calculations, or both.
- Adjust Difficulty: Use the settings to adjust the difficulty level. This might include setting the range for dimensions, adding decimal places, or mixing various shapes.
- Generate and Preview: Click the generate button to create your worksheet. Preview the problems to ensure they meet your expectations.
- Download and Print: Once satisfied with the generated worksheet, download it as a PDF for printing or save it for digital distribution. Ensure to download the answer key if needed.
Popular Platforms for Worksheet Generation
- - Offers a variety of customizable geometry worksheets.
- - Provides comprehensive worksheets that can be adjusted for different learning levels.
- - Allows for interactive worksheet creation and online completion.
- - Features extensive resources for creating and downloading math worksheets.
Using these customizable worksheet generators, teachers can craft precise and effective practice materials, enhancing students' understanding and proficiency in calculating area and perimeter.
Real-World Applications
Understanding how to calculate the area and perimeter of shapes is not just a theoretical exercise confined to the classroom. These mathematical concepts have numerous practical applications in daily life and various professions. Here, we explore several real-world scenarios where knowledge of area and perimeter is essential.
Everyday Life
- Home Improvement: When planning to paint a room, knowing the area of the walls helps in estimating the amount of paint required. Similarly, understanding the perimeter is crucial when adding baseboards or crown molding.
- Gardening and Landscaping: Calculating the area of a garden bed ensures the right amount of soil, fertilizer, or mulch is used. Measuring the perimeter is important for fencing or outlining garden borders.
- Flooring: To install tiles, carpets, or hardwood floors, the area of the floor space must be measured to determine how much material is needed.
Professional Use
- Construction and Architecture: Architects and builders use area and perimeter calculations to design blueprints and determine the materials needed for buildings and structures. For example, they calculate the area of a roof to estimate roofing materials or the perimeter of a plot to plan the layout of a building.
- Engineering: Engineers apply these concepts in designing and analyzing various systems, such as calculating the area of land for infrastructure projects or the perimeter of components in machinery.
- Interior Design: Interior designers need to measure the area of rooms to plan layouts and select furnishings that fit within the space constraints.
Business and Commerce
- Real Estate: Real estate agents use area and perimeter to describe the size of properties, whether it's the total floor space of a house or the perimeter of a lot.
- Retail: Store managers might use area calculations to plan the layout of merchandise within a retail space efficiently or to determine the shelf space needed for products.
- Advertising: For billboards and signs, advertisers need to calculate the area to understand the available space for their advertisements and to price the advertising space appropriately.
Educational Projects
- School Projects: Students can apply these concepts in various projects, such as designing a park, creating a model city, or planning a sports field, integrating their mathematical knowledge with creative and practical thinking.
- Competitions and Fairs: In events like science fairs or design contests, accurate area and perimeter calculations are often essential for creating functional and aesthetically pleasing displays and models.
Mastering area and perimeter is not just about solving problems on paper; it equips individuals with the skills needed to tackle real-world challenges effectively. Whether at home, at work, or in the community, these measurements help in making informed decisions and achieving successful outcomes.

Critical Thinking Problems
Critical thinking problems help students apply their knowledge of area and perimeter to real-world scenarios, promoting deeper understanding and problem-solving skills. Below are a few challenging problems designed to enhance critical thinking abilities:
-
Problem 1: A garden has a rectangular section that measures 8 meters by 6 meters. Attached to this section is a semicircular section with a diameter of 6 meters. Calculate the total area of the garden.
Solution:
- Calculate the area of the rectangular section: \(A_{\text{rectangle}} = 8 \times 6 = 48 \, \text{m}^2\)
- Calculate the area of the semicircular section: \(A_{\text{semicircle}} = \frac{1}{2} \pi \left(\frac{6}{2}\right)^2 = \frac{1}{2} \pi \cdot 3^2 = \frac{9\pi}{2} \, \text{m}^2\)
- Add the two areas together to find the total area: \(A_{\text{total}} = 48 + \frac{9\pi}{2} \, \text{m}^2\)
-
Problem 2: A composite shape is made up of a square and an equilateral triangle on one of its sides. If the side length of the square is 4 cm, find the perimeter of the composite shape.
Solution:
- Calculate the perimeter of the square: \(P_{\text{square}} = 4 \times 4 = 16 \, \text{cm}\)
- Since one side of the square is shared with the triangle, only the remaining two sides of the triangle add to the perimeter.
- Calculate the perimeter of the equilateral triangle (without the shared side): \(P_{\text{triangle}} = 2 \times 4 = 8 \, \text{cm}\)
- Add the two perimeters together: \(P_{\text{total}} = 16 + 8 = 24 \, \text{cm}\)
-
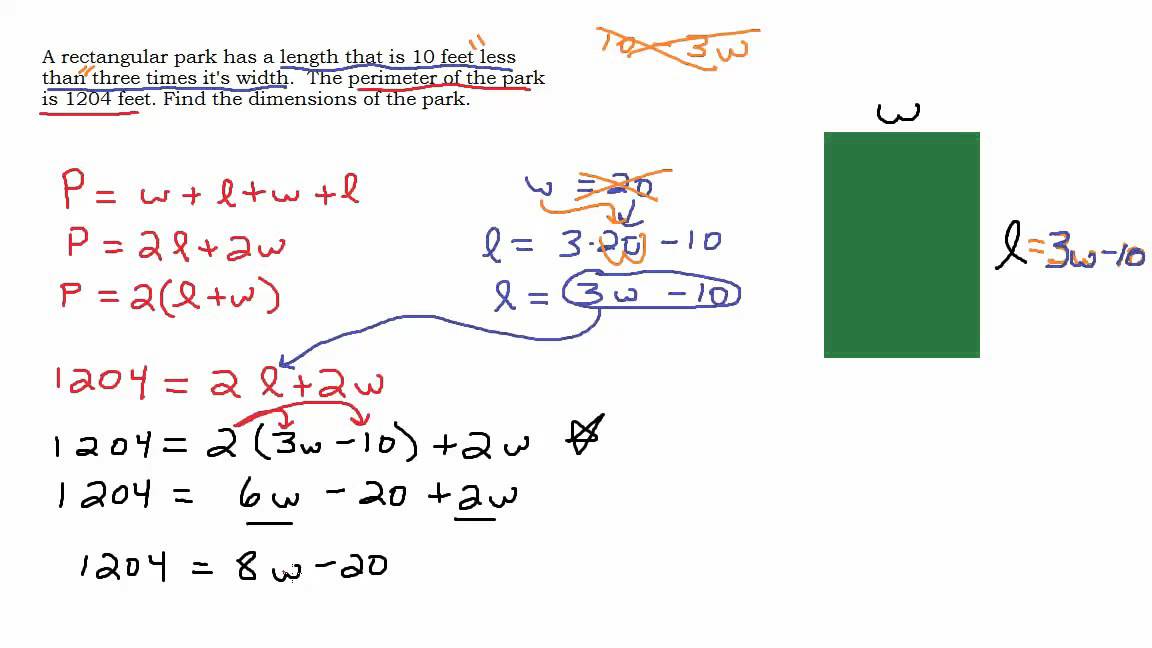
Problem 3: A playground is in the shape of an L. It consists of two rectangles, one measuring 10 meters by 4 meters and the other measuring 6 meters by 4 meters. Calculate the total perimeter of the playground.
Solution:
- Draw the L-shaped playground and label the dimensions.
- Identify the external sides to calculate the perimeter.
- Sum the lengths of the external sides: \(P_{\text{playground}} = 10 + 4 + 6 + 4 + 6 + 4 = 34 \, \text{m}\)
Additional Resources
To further support your learning and practice in calculating area and perimeter, we have compiled a list of valuable resources. These resources include educational websites, interactive tools, printable materials, and video tutorials.
-
Educational Websites:
- - Offers comprehensive lessons and practice exercises on area and perimeter for various grade levels.
- - Provides a wide range of printable worksheets on area and perimeter with answer keys.
- - Features interactive questions and immediate feedback to help students master area and perimeter concepts.
-
Interactive Tools:
- - An interactive geometry, algebra, statistics, and calculus application that includes tools for exploring area and perimeter.
- - Engaging games and puzzles focused on area and perimeter, suitable for elementary and middle school students.
-
Printable Materials:
- - Printable area and perimeter worksheets that come with detailed answer keys.
- - A marketplace with a variety of teacher-created worksheets on area and perimeter.
-
Video Tutorials:
- - YouTube channel offering clear and engaging videos explaining area and perimeter concepts.
- - A vast collection of educational videos covering a wide range of math topics, including area and perimeter.
We encourage you to explore these resources to enhance your understanding and proficiency in solving area and perimeter problems. Happy learning!
Conclusion
After exploring various grade-level worksheets covering different geometric shapes and concepts such as area and perimeter, it's evident that there are ample resources available to enhance students' understanding and proficiency in these topics.
By providing comprehensive worksheets with answers, interactive features, printable PDFs, online quizzes, and customizable worksheet generators, educators can effectively cater to diverse learning needs and preferences.
Furthermore, real-world applications and critical thinking problems included in the materials encourage students to apply their knowledge in practical scenarios and develop problem-solving skills.
With the abundance of additional resources and engaging content, both teachers and students can enjoy a stimulating learning experience that fosters mathematical proficiency and conceptual clarity.
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi và diện tích của một hình dạng tổ hợp, với ví dụ về hình L. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về cách tính toán các khái niệm này trong hình học.
Tìm Chu Vi và Diện Tích Hình Dạng Tổ Hợp | Ví dụ Hình L | Hình Học | Toán cùng thầy J
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi và diện tích của các hình không đều cho học sinh lớp 3. Video này sẽ giúp các em hiểu cách tính toán những khái niệm này một cách dễ dàng và thú vị.
Chu vi & Diện tích của Hình Không Đều cho Lớp 3