Topic finding perimeter of right triangle: Discover how to calculate the perimeter of a right triangle with ease. This comprehensive guide provides step-by-step instructions, formulas, and examples to help you master this essential mathematical concept. Whether you are a student or a math enthusiast, this article will enhance your understanding and skills.
Table of Content
- Finding the Perimeter of a Right Triangle
- Introduction
- Understanding Right Triangles
- Perimeter Formula
- Example Calculations
- Applications and Practice Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để hiểu rõ về cách tính diện tích và chu vi của tam giác vuông, giúp bạn áp dụng kiến thức vào việc tìm chu vi của tam giác vuông trong bài toán thực tế.
Finding the Perimeter of a Right Triangle
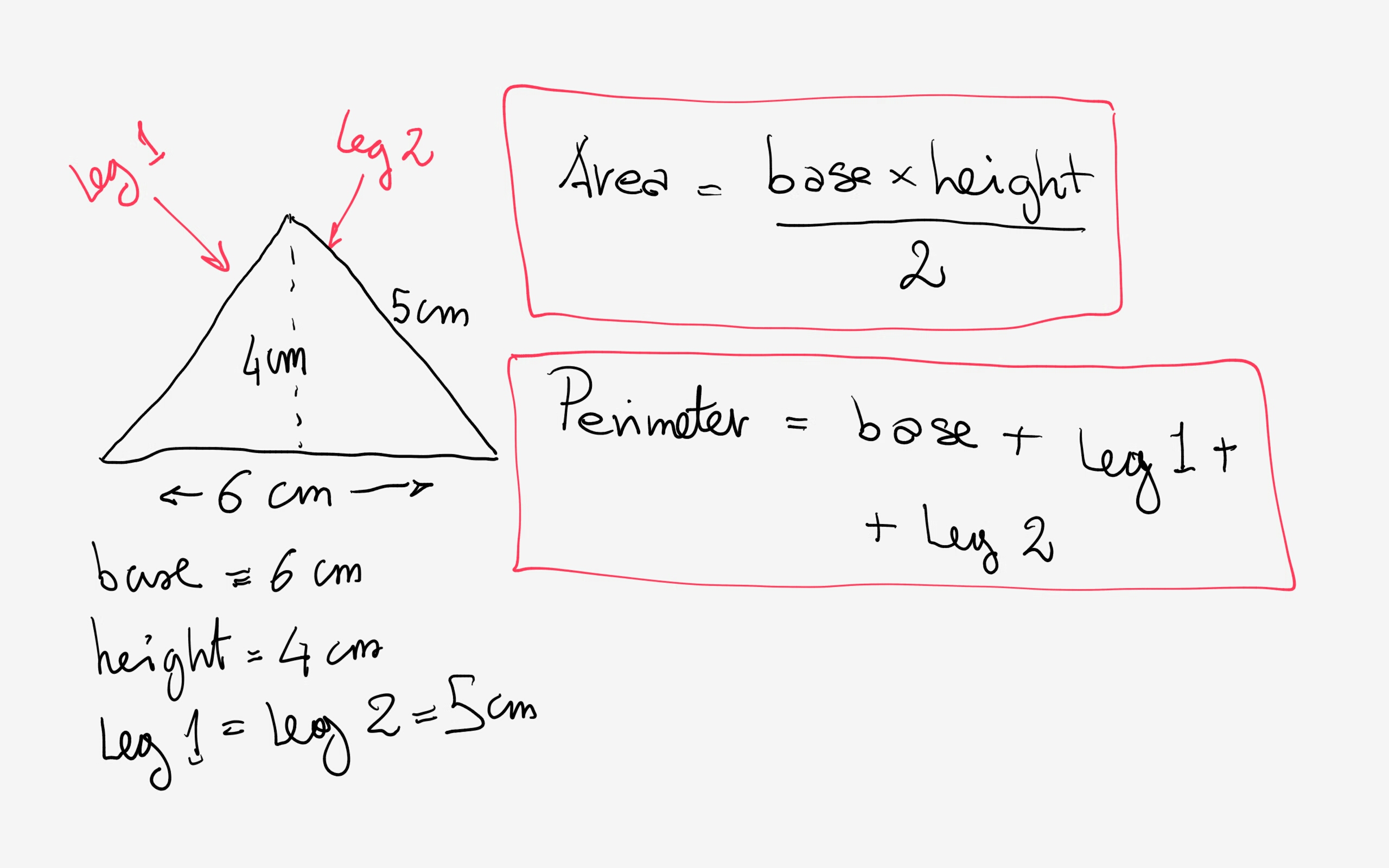
The perimeter of a right triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides: the base, the height, and the hypotenuse. Here are the steps and examples to calculate it:
Using Side Lengths
If the lengths of all three sides (base a, height b, and hypotenuse c) are known, the perimeter P is calculated as:
Using the Pythagorean Theorem
If the hypotenuse is unknown, it can be found using the Pythagorean theorem:
Then, the perimeter is calculated by summing up all sides.
Examples
- Example 1: If the base is 3 units, the height is 4 units, and the hypotenuse is 5 units, the perimeter is:
- Example 2: If the base is 6 units, the height is 8 units, find the hypotenuse using:
Therefore, . The perimeter is:
Special Right Triangles
- For a 30°-60°-90° triangle, the sides follow the ratio 1:√3:2. Knowing one side allows you to determine the others.
- For a 45°-45°-90° triangle, the sides follow the ratio 1:1:√2. Again, knowing one side lets you calculate the others.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a right triangle with base 7 units, height 24 units, and hypotenuse 25 units.
- Calculate the perimeter of a right triangle if the base is 9 units and the height is 12 units.

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the perimeter of a right triangle is fundamental in geometry and trigonometry. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all three sides of the triangle, which include the base, height, and hypotenuse. This section introduces the concepts and methods required to calculate the perimeter, using the Pythagorean theorem and basic arithmetic operations.
To find the perimeter of a right triangle:
- Identify the lengths of the two legs (base and height) and the hypotenuse.
- Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse if it is not given:
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}
\]
- Add the lengths of the three sides to find the perimeter:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
Let's consider an example:
Given a right triangle with a base of 6 units and a height of 8 units:
- Calculate the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c = \sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} = \sqrt{36 + 64} = \sqrt{100} = 10 \, \text{units}
\]
- Find the perimeter by adding all sides:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 \, \text{units}
\]
This method ensures you can accurately determine the perimeter of any right triangle, enhancing your geometric problem-solving skills.
Understanding Right Triangles
A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle measuring 90 degrees. This 90-degree angle is called the right angle, and the side opposite this angle is known as the hypotenuse. The other two sides of the triangle are referred to as the legs. Right triangles have unique properties that make them fundamental in trigonometry and geometry.
Key Characteristics of Right Triangles:
- Right Angle: One of the angles is exactly 90 degrees.
- Hypotenuse: The side opposite the right angle, and the longest side of the triangle.
- Legs: The two sides that form the right angle.
To identify a right triangle, look for the following features:
- Check if one angle is 90 degrees. This is the defining property of a right triangle.
- Measure the lengths of the sides. The hypotenuse will always be the longest side.
- Verify using the Pythagorean Theorem: \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \), where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the legs and \( c \) is the length of the hypotenuse.
The Pythagorean Theorem is a critical tool for working with right triangles. It states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (\( c \)) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides (\( a \) and \( b \)). This can be written as:
\( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \)
Right triangles are not only important in theoretical mathematics but also have practical applications in various fields such as architecture, engineering, and physics. Understanding their properties and how to work with them is essential for solving many geometric problems.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Right Angle | An angle that measures 90 degrees. |
| Hypotenuse | The side opposite the right angle and the longest side of the triangle. |
| Legs | The two sides that form the right angle. |
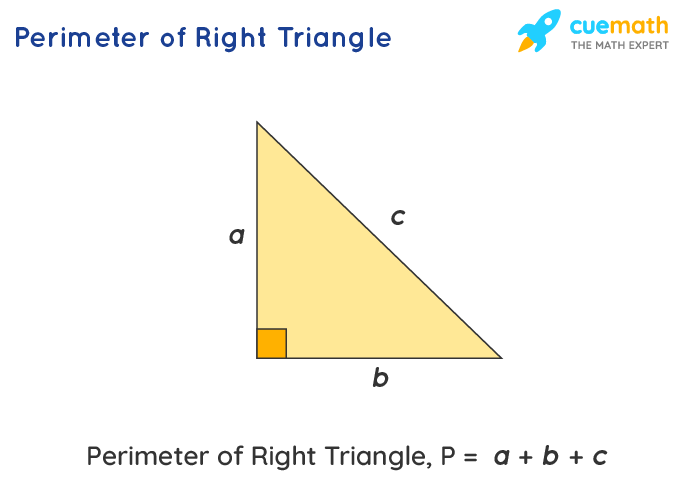
Perimeter Formula
The perimeter of a right triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides: the two legs and the hypotenuse. The formula to find the perimeter (P) is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\]
Where:
- \(a\) is the length of one leg
- \(b\) is the length of the other leg
- \(c\) is the length of the hypotenuse
If you only know the lengths of the two legs, you can find the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}
\]
Once you have all three side lengths, you can use the perimeter formula above.
Examples
Here are some examples to illustrate how to calculate the perimeter of a right triangle:
-
Example 1: Given a right triangle with legs \(a = 3\) units and \(b = 4\) units.
First, find the hypotenuse \(c\) using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5
\]Then, calculate the perimeter:
\[
P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ units}
\] -
Example 2: Given a right triangle with legs \(a = 5\) units and \(b = 12\) units.
First, find the hypotenuse \(c\) using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c = \sqrt{5^2 + 12^2} = \sqrt{25 + 144} = \sqrt{169} = 13
\]Then, calculate the perimeter:
\[
P = 5 + 12 + 13 = 30 \text{ units}
\] -
Example 3: Given a right triangle with legs \(a = 7\) units and \(b = 24\) units.
First, find the hypotenuse \(c\) using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c = \sqrt{7^2 + 24^2} = \sqrt{49 + 576} = \sqrt{625} = 25
\]Then, calculate the perimeter:
\[
P = 7 + 24 + 25 = 56 \text{ units}
\]
By following these steps and using the formulas provided, you can easily calculate the perimeter of any right triangle.
Example Calculations
In this section, we will go through detailed examples to illustrate how to find the perimeter of a right triangle. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
Example 1
What is the perimeter of a triangle with sides of length 8 m, 9 m, and 12.4 m?
Solution:
- Side 1, \( a = 8 \) m
- Side 2, \( b = 9 \) m
- Side 3, \( c = 12.4 \) m
Using the perimeter formula:
\( p = a + b + c \)
Calculating the perimeter:
\( p = 8 + 9 + 12.4 = 29.4 \) m
The perimeter of the triangle is 29.4 m.
Example 2
We have a triangle with sides of length 10 m, 24 m, and 26 m. What is the perimeter?
Solution:
- Side 1, \( a = 10 \) m
- Side 2, \( b = 24 \) m
- Side 3, \( c = 26 \) m
Using the perimeter formula:
\( p = a + b + c \)
Calculating the perimeter:
\( p = 10 + 24 + 26 = 60 \) m
The perimeter of the triangle is 60 m.
Example 3
What is the perimeter of a right triangle that has sides of length 11 cm, 12 cm, and 16.28 cm?
Solution:
- Side 1, \( a = 11 \) cm
- Side 2, \( b = 12 \) cm
- Side 3, \( c = 16.28 \) cm
Using the perimeter formula:
\( p = a + b + c \)
Calculating the perimeter:
\( p = 11 + 12 + 16.28 = 39.28 \) cm
The perimeter of the triangle is 39.28 cm.
Example 4
What is the perimeter of a right triangle that has sides of length 5 m and 12 m?
Solution:
- Side 1, \( a = 5 \) m
- Side 2, \( b = 12 \) m
First, we find the length of the third side using the Pythagorean theorem:
\( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \)
\( c^2 = 5^2 + 12^2 \)
\( c^2 = 25 + 144 \)
\( c = \sqrt{169} = 13 \) m
Now, using the perimeter formula:
\( p = a + b + c \)
Calculating the perimeter:
\( p = 5 + 12 + 13 = 30 \) m
The perimeter of the triangle is 30 m.
Example 5
A right triangle has sides of lengths 8 m and 11 m. What is the perimeter?
Solution:
- Side 1, \( a = 8 \) m
- Side 2, \( b = 11 \) m
First, we find the length of the third side using the Pythagorean theorem:
\( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \)
\( c^2 = 8^2 + 11^2 \)
\( c^2 = 64 + 121 \)
\( c = \sqrt{185} = 13.6 \) m
Now, using the perimeter formula:
\( p = a + b + c \)
Calculating the perimeter:
\( p = 8 + 11 + 13.6 = 32.6 \) m
The perimeter of the triangle is 32.6 m.
Applications and Practice Problems
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a right triangle is crucial in various real-world scenarios, such as:
- Construction: Builders often need to calculate the total length of fencing required for triangular areas.
- Surveying: Surveyors use perimeter calculations to determine the boundaries of land parcels.
- Engineering: Engineers employ perimeter calculations in structural designs, like determining the length of diagonal braces in trusses.
- Navigation: Navigators use similar principles to measure distances on maps or to calculate travel distances between points.
Let's delve into some practice problems to reinforce our understanding:
- Calculate the perimeter of a right triangle with legs of lengths 3 cm and 4 cm.
- A right triangle has one leg measuring 6 inches and a hypotenuse of length 10 inches. Determine the perimeter of the triangle.
- Given a right triangle with a hypotenuse of 15 meters and one leg of length 9 meters, find the perimeter.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about finding the perimeter of a right triangle:
- What is the perimeter of a right triangle?
- How do you find the perimeter of a right triangle?
- Can you find the perimeter of a right triangle if you only know the lengths of two sides?
- What are some real-world applications of finding the perimeter of a right triangle?
The perimeter of a right triangle is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. In a right triangle, the perimeter can be found by adding the lengths of the two legs and the hypotenuse.
To find the perimeter of a right triangle, simply add the lengths of all three sides together. If you know the lengths of the two legs and the hypotenuse, you can use the formula: perimeter = leg₁ + leg₂ + hypotenuse.
Yes, if you know the lengths of two sides of a right triangle, you can still find the perimeter. To do this, you would add the lengths of the known sides together and then use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the third side. Once you have all three side lengths, you can calculate the perimeter as usual.
Finding the perimeter of a right triangle is essential in various fields such as construction, engineering, surveying, and navigation. Builders use it to determine the amount of fencing needed for triangular areas, while engineers employ it in structural designs. Surveyors rely on perimeter calculations to define land boundaries, and navigators use similar principles for map distances and travel calculations.
Xem video này để hiểu rõ về cách tính diện tích và chu vi của tam giác vuông, giúp bạn áp dụng kiến thức vào việc tìm chu vi của tam giác vuông trong bài toán thực tế.
Diện Tích và Chu Vi của Tam Giác Vuông | Toán cùng Thầy J
READ MORE:
Xem video này để tìm hiểu cách thời trang để tìm chu vi của tam giác vuông, với giải thích từng bước dễ hiểu.
Cách Thời Trang để Tìm Chu Vi của Tam Giác Vuông | (giải thích từng bước) | #toán #toán học