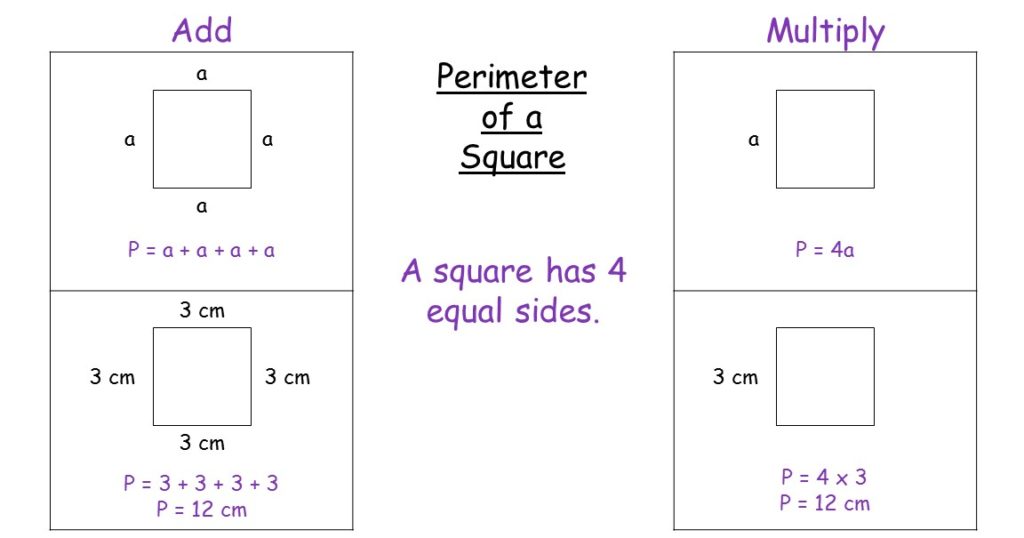
Topic finding perimeter of a semicircle: Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle is essential for various mathematical and practical applications. This guide provides a thorough explanation, formula, step-by-step calculations, examples, and common mistakes to avoid. Whether you are a student or a professional, this article will help you master the concept of finding the perimeter of a semicircle.
Table of Content
- Finding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Introduction to Semicircle
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Formula for Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Examples of Finding Perimeter
- Common Mistakes and Tips
- Applications of Semicircle Perimeter in Real Life
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn tính chu vi của nửa vòng tròn từ Corbettmaths. Xem xét liệu video này có phù hợp với bài viết về tìm chu vi của nửa vòng tròn không.
Finding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle combines the length of the curved edge (half the circumference of a full circle) and the diameter of the semicircle. Here, we will explain how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle and provide examples to illustrate the process.
Formulas
- When the diameter \(d\) is given: \( P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \)
- When the radius \(r\) is given: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
Derivation
The formula for the perimeter of a semicircle is derived by adding the length of the arc (half the circumference of a circle) to the diameter of the semicircle.
The circumference of a full circle is \(2\pi r\). Therefore, the length of the arc of a semicircle is half of that, which is \(\pi r\). Adding the diameter, which is \(2r\), the perimeter formula becomes:
\( P = \pi r + 2r = r(\pi + 2) \)
Examples
Example 1: Finding the Perimeter with Diameter
Given the diameter \(d = 10\) units:
- Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = 5 \) units
- Use the formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) = 5(\pi + 2) \)
- Approximate value: \( P \approx 5(3.14 + 2) = 5 \times 5.14 = 25.7 \) units
Example 2: Finding the Perimeter with Radius
Given the radius \(r = 7\) cm:
- Use the formula: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Approximate value: \( P \approx 7(3.14 + 2) = 7 \times 5.14 = 35.98 \) cm
Practice Problems
- Calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 8 inches. (Use \(\pi = 3.14\))
- Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 46 inches.
- What is the perimeter of a semicircle if the radius is 12 units?
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a semicircle can be useful in various real-world applications, such as construction and design.
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| \( P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \) | Perimeter when the diameter is known |
| \( P = r(\pi + 2) \) | Perimeter when the radius is known |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Semicircle
A semicircle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that represents half of a circle. It is formed by dividing a circle along its diameter, resulting in a shape with a straight edge and a curved edge.
The key characteristics of a semicircle include:
- Diameter: The straight line segment passing through the center, connecting two points on the boundary.
- Radius: The distance from the center to any point on the curved boundary, which is half of the diameter.
- Curved Edge: The arc representing half of the circumference of the original circle.
- Center: The midpoint of the diameter.
In mathematical terms, if the diameter of the original circle is \(d\), then the radius \(r\) is given by:
\[ r = \frac{d}{2} \]
The perimeter of the semicircle consists of the curved edge (half of the circumference of the full circle) and the diameter. If the circumference of a full circle is \(2\pi r\), the curved edge of the semicircle is:
\[ \text{Curved Edge} = \pi r \]
Therefore, the total perimeter \(P\) of the semicircle is:
\[ P = \pi r + d \]
By substituting \(r\) with \(\frac{d}{2}\), we get:
\[ P = \pi \left(\frac{d}{2}\right) + d = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d = d \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right) \]
Understanding these fundamental properties and formulas is essential for accurately calculating the perimeter of a semicircle in various applications.
Understanding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is the total length around the shape, combining both its curved and straight edges. To understand how to find the perimeter, it's important to recognize the components that make up the semicircle's boundary.
A semicircle consists of two main parts:
- The Curved Edge: This is the arc that represents half of the circumference of a full circle.
- The Straight Edge: This is the diameter of the original circle.
Given the radius \( r \) of the semicircle, the circumference of the full circle is \( 2\pi r \). Therefore, the length of the curved edge of the semicircle is:
\[ \text{Curved Edge} = \pi r \]
The straight edge, which is the diameter, is:
\[ \text{Diameter} = 2r \]
To find the total perimeter \( P \) of the semicircle, you sum the lengths of the curved edge and the straight edge:
\[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
To put this in a more general formula, if the diameter \( d \) of the semicircle is given, the radius can be expressed as \( r = \frac{d}{2} \). Substituting \( r \) into the perimeter formula gives:
\[ P = \pi \left( \frac{d}{2} \right) + d = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d = d \left( \frac{\pi}{2} + 1 \right) \]
This formula shows that the perimeter of a semicircle depends on the diameter of the original circle. Understanding this relationship is crucial for accurately calculating the perimeter in various mathematical and practical scenarios.
To summarize the steps:
- Identify the radius \( r \) or the diameter \( d \) of the semicircle.
- Calculate the curved edge using \( \pi r \).
- Add the diameter to the curved edge to get the total perimeter.
By following these steps, you can easily determine the perimeter of any semicircle.
Formula for Perimeter of a Semicircle
To accurately find the perimeter of a semicircle, it's essential to understand the formula that combines the lengths of both the curved and straight edges. Here is the detailed explanation of the formula used:
The perimeter \( P \) of a semicircle is given by the sum of the length of the curved edge (half the circumference of the full circle) and the diameter.
Let's break down the steps to derive this formula:
- First, recall the formula for the circumference \( C \) of a full circle, which is: \[ C = 2\pi r \]
- Since a semicircle is half of a full circle, the length of the curved edge is half of the circumference: \[ \text{Curved Edge} = \frac{C}{2} = \frac{2\pi r}{2} = \pi r \]
- The straight edge of the semicircle is simply the diameter \( d \) of the original circle. Since the diameter is twice the radius, we have: \[ d = 2r \]
- To find the total perimeter \( P \), add the length of the curved edge to the diameter: \[ P = \pi r + d \]
- Substitute \( d = 2r \) into the formula: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \]
- Factor out \( r \) to simplify: \[ P = r(\pi + 2) \]
- If the diameter \( d \) is given instead of the radius, you can express the formula in terms of \( d \): \[ r = \frac{d}{2} \] \[ P = \pi \left(\frac{d}{2}\right) + d = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \] \[ P = d \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right) \]
Therefore, the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle is:
\[ P = r(\pi + 2) \] or \[ P = d \left(\frac{\pi}{2} + 1\right) \]
Understanding and applying this formula allows you to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle efficiently and accurately.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To find the perimeter of a semicircle, follow these detailed steps:
- Understand the formula: The perimeter \( P \) of a semicircle is given by the formula: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \] where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle. The formula combines the curved part (half the circumference of a circle) and the straight diameter.
- Identify the radius: Determine the radius \( r \) of the semicircle. For example, if the diameter \( d \) is given, the radius is half of the diameter: \[ r = \frac{d}{2} \]
- Calculate the curved part: Compute the curved part of the perimeter, which is half the circumference of a full circle: \[ \text{Curved part} = \pi r \]
- Calculate the straight part: The straight part of the perimeter is simply the diameter of the semicircle: \[ \text{Straight part} = 2r \]
- Add the parts together: Combine the curved and straight parts to find the total perimeter: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \] This can also be factored to: \[ P = r(\pi + 2) \]
- Example calculation: For a semicircle with a radius of 5 units:
- Curved part: \( \pi \times 5 = 15.71 \) units (using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \))
- Straight part: \( 2 \times 5 = 10 \) units
- Total perimeter: \( 15.71 + 10 = 25.71 \) units
By following these steps, you can accurately find the perimeter of any semicircle.

Examples of Finding Perimeter
Here are some detailed examples to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle:
Example 1: Semicircle with a Given Diameter
- Given: Diameter (d) = 10 units
- Calculate the radius (r):
- \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \) units
- Use the formula for the perimeter (P) of a semicircle:
- \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Substitute the radius into the formula:
- \( P = 5(\pi + 2) \approx 5(3.14 + 2) = 5 \times 5.14 = 25.7 \) units
- Result: The perimeter of the semicircle is approximately 25.7 units.
Example 2: Semicircle with a Given Radius
- Given: Radius (r) = 8 units
- Use the formula for the perimeter (P) of a semicircle:
- \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Substitute the radius into the formula:
- \( P = 8(\pi + 2) \approx 8(3.14 + 2) = 8 \times 5.14 = 41.12 \) units
- Result: The perimeter of the semicircle is approximately 41.12 units.
Example 3: Finding Radius from Perimeter
- Given: Perimeter (P) = 27 units
- Use the formula for the perimeter (P) of a semicircle:
- \( P = r(\pi + 2) \)
- Rearrange the formula to solve for the radius (r):
- \( r = \frac{P}{\pi + 2} \)
- Substitute the perimeter into the formula:
- \( r = \frac{27}{3.14 + 2} \approx \frac{27}{5.14} = 5.25 \) units
- Result: The radius of the semicircle is approximately 5.25 units.
These examples demonstrate how to use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle, \( P = r(\pi + 2) \), whether you start with the diameter, the radius, or the perimeter itself.
Common Mistakes and Tips
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle can sometimes lead to errors. Here are some common mistakes and tips to avoid them:
- Ignoring the Diameter: One common mistake is calculating only the arc length of the semicircle and forgetting to add the diameter. Remember, the perimeter includes both the arc length and the straight line through the semicircle's base.
- Confusing Radius and Diameter: Another frequent error is mixing up the radius and diameter when applying the formula. The radius is half the diameter, and this distinction is crucial for accurate calculations.
- Incorrect Pi Value: Using an inaccurate value for π (pi) can significantly affect the result. While approximations like 3.14 or 22/7 are common, using a more precise value (e.g., 3.14159) when needed can improve accuracy.
- Misapplication of Formula: Some may attempt to apply the full circle's perimeter formula (2πr) without adjusting for the semicircle's unique characteristics. The correct formula is \( P = r(\pi + 2) \), specifically tailored for semicircles.
- Unit Conversion Errors: Failing to consistently use units throughout the calculation can lead to incorrect perimeter measurements. Always ensure that the radius and the resulting perimeter are in the same unit system.
By being mindful of these common pitfalls, one can more reliably compute the perimeter of a semicircle, enhancing both learning and practical application in geometry.
Applications of Semicircle Perimeter in Real Life
Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle is not just a theoretical exercise but has many practical applications across various fields. Here are some key areas where the calculation of the perimeter of a semicircle is utilized:
-
Architecture and Design:
Architects use semicircular designs in structures such as archways, windows, and domes. Calculating the perimeter helps ensure the correct amount of materials and structural integrity for these elements.
-
Engineering:
In engineering, the perimeter of semicircular shapes is crucial for projects involving tunnels, bridges, and roads. Accurate perimeter calculations are essential for material estimation and construction planning.
-
Landscaping and Garden Design:
Landscapers design curved pathways, flower beds, and other garden features using semicircular shapes. Knowing the perimeter allows for precise planning and placement, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of outdoor spaces.
-
Art and Craft:
Artists and crafters use semicircles in their designs. Calculating the perimeter is important for cutting materials accurately and assembling pieces correctly.
-
Sports Field Design:
In sports, the design of tracks and fields often includes semicircular sections. Calculating the perimeter helps in accurately marking these areas, ensuring fair play and proper field dimensions.
These applications highlight the importance of understanding geometric principles and how they are applied in real-world scenarios, from building structures to creating beautiful gardens and ensuring accurate sports field designs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about finding the perimeter of a semicircle:
- What is the perimeter of a semicircle?
- What is the formula to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle?
- How do I find the perimeter of a semicircle if only the diameter is given?
- Can the perimeter of a semicircle be negative?
- What are some real-life applications of finding the perimeter of a semicircle?
The perimeter of a semicircle is the total length of its curved boundary plus the straight diameter line that forms its base.
The formula for the perimeter of a semicircle is: \( P = \pi r + 2r \), where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle.
If only the diameter \( d \) is given, you can find the radius \( r \) by dividing the diameter by 2. Then, you can use the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \) to calculate the perimeter.
No, the perimeter of a semicircle cannot be negative. It represents a physical length and is always positive or zero.
Real-life applications include calculating the length of half-circular paths, such as the boundary of a garden or the circumference of a semicircular pond.
Hướng dẫn tính chu vi của nửa vòng tròn từ Corbettmaths. Xem xét liệu video này có phù hợp với bài viết về tìm chu vi của nửa vòng tròn không.
Chu Vi của Nửa Vòng Tròn - Corbettmaths
READ MORE:
Xem video này để học cách tính chu vi của nửa vòng tròn. Video này có phù hợp với bài viết về tìm chu vi của nửa vòng tròn không?
Chu Vi của Nửa Vòng Tròn