Topic area and perimeter worksheets 4th grade: Discover our collection of area and perimeter worksheets for 4th grade designed to make learning math fun and engaging. These worksheets provide a variety of activities to help students master calculating area and perimeter, enhancing their problem-solving skills and building a strong mathematical foundation.
Table of Content
- 4th Grade Area and Perimeter Worksheets
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Basic Concepts of Area
- Basic Concepts of Perimeter
- Formulas for Calculating Area and Perimeter
- Worksheets for Calculating Area
- Worksheets for Calculating Perimeter
- Mixed Area and Perimeter Problems
- Real-Life Application Problems
- Interactive Activities and Games
- Word Problems and Scenarios
- Tips and Tricks for Understanding Area and Perimeter
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Answer Keys and Explanations
- Additional Resources and Practice Sheets
- YOUTUBE: Xem bài hát về diện tích và chu vi này để giúp trẻ em lớp 3 - lớp 4 học về các khái niệm toán học một cách vui nhộn và dễ hiểu.
4th Grade Area and Perimeter Worksheets
Explore a variety of worksheets designed to help 4th-grade students understand the concepts of area and perimeter. These worksheets provide engaging activities that involve calculating the area and perimeter of different shapes.
Understanding Area
Area is the measure of the surface inside a shape. It is calculated by multiplying the length and the width of the shape.
- Square: Area = \( side \times side \)
- Rectangle: Area = \( length \times width \)
- Triangle: Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \)
Understanding Perimeter
Perimeter is the distance around the boundary of a shape. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all the sides of the shape.
- Square: Perimeter = \( 4 \times side \)
- Rectangle: Perimeter = \( 2 \times (length + width) \)
- Triangle: Perimeter = \( side1 + side2 + base \)
Worksheet Activities
-
Calculating Area
Students are provided with different shapes and asked to calculate the area using the given dimensions.
Shape Dimensions Area Square Side = 5 units \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \) square units Rectangle Length = 8 units, Width = 3 units \( 8 \times 3 = 24 \) square units -
Calculating Perimeter
Students measure the perimeter of various shapes using the given dimensions.
Shape Dimensions Perimeter Square Side = 5 units \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units Rectangle Length = 8 units, Width = 3 units \( 2 \times (8 + 3) = 22 \) units
Interactive Problems
In addition to the basic calculations, students are given word problems and real-life scenarios to solve, enhancing their understanding and application of area and perimeter.
- Solve for the area of a garden that is 7 units long and 4 units wide.
- Calculate the perimeter of a playground that has a length of 10 units and a width of 6 units.
These worksheets are perfect for classroom use, homework assignments, and additional practice to reinforce the students' understanding of area and perimeter concepts.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is essential for 4th-grade students as they build their mathematical skills. Area refers to the amount of space inside a shape, while perimeter is the distance around the shape. These fundamental concepts are used in various real-life situations and advanced math problems.
Area is measured in square units, and the formula depends on the shape:
- Square: Area = \( side \times side \)
- Rectangle: Area = \( length \times width \)
- Triangle: Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \)
- Circle: Area = \( \pi \times radius^2 \)
Perimeter is the total distance around a shape, calculated by adding the lengths of all sides:
- Square: Perimeter = \( 4 \times side \)
- Rectangle: Perimeter = \( 2 \times (length + width) \)
- Triangle: Perimeter = \( side1 + side2 + base \)
- Circle: Perimeter (Circumference) = \( 2 \times \pi \times radius \)
By practicing with area and perimeter worksheets, students can:
- Enhance their problem-solving skills.
- Understand the practical applications of these concepts.
- Build a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical topics.
These worksheets often include a variety of activities, such as calculating the area and perimeter of different shapes, solving word problems, and engaging in interactive exercises. This comprehensive approach helps students grasp the concepts effectively and enjoyably.
Basic Concepts of Area
Area is a fundamental concept in geometry that measures the amount of space inside a two-dimensional shape. It is expressed in square units, such as square centimeters (cm²), square meters (m²), or square inches (in²). Understanding how to calculate the area of various shapes is crucial for solving real-world problems and advancing in math.
Here are the basic formulas for calculating the area of common shapes:
- Square: The area of a square is found by multiplying the length of one side by itself.
- Area = \( side \times side \)
- Example: If the side length is 4 units, then Area = \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \) square units.
- Rectangle: The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying the length by the width.
- Area = \( length \times width \)
- Example: If the length is 5 units and the width is 3 units, then Area = \( 5 \times 3 = 15 \) square units.
- Triangle: The area of a triangle is found using the base and the height. The formula is:
- Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \)
- Example: If the base is 6 units and the height is 4 units, then Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4 = 12 \) square units.
- Circle: The area of a circle is determined using the radius and the constant π (pi, approximately 3.14).
- Area = \( \pi \times radius^2 \)
- Example: If the radius is 3 units, then Area = \( \pi \times 3^2 = \pi \times 9 \approx 28.26 \) square units.
To help students understand and practice these concepts, area worksheets often include exercises such as:
- Identifying the shape and its dimensions.
- Applying the correct formula to calculate the area.
- Solving word problems that require area calculations.
- Comparing areas of different shapes to build a deeper understanding.
By regularly practicing with these worksheets, students can improve their ability to calculate area accurately and efficiently, laying a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Basic Concepts of Perimeter
Perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is measured in linear units such as centimeters (cm), meters (m), or inches (in). Calculating the perimeter of various shapes helps in understanding how to measure boundaries and is useful in many real-life situations.
Here are the basic formulas for calculating the perimeter of common shapes:
- Square: The perimeter of a square is found by adding the lengths of all four sides.
- Perimeter = \( 4 \times side \)
- Example: If the side length is 5 units, then Perimeter = \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units.
- Rectangle: The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides or using the formula:
- Perimeter = \( 2 \times (length + width) \)
- Example: If the length is 8 units and the width is 3 units, then Perimeter = \( 2 \times (8 + 3) = 2 \times 11 = 22 \) units.
- Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is found by adding the lengths of its three sides.
- Perimeter = \( side1 + side2 + base \)
- Example: If the sides are 4 units, 6 units, and 7 units, then Perimeter = \( 4 + 6 + 7 = 17 \) units.
- Circle: The perimeter of a circle, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius and the constant π (pi, approximately 3.14).
- Perimeter (Circumference) = \( 2 \times \pi \times radius \)
- Example: If the radius is 3 units, then Perimeter = \( 2 \times \pi \times 3 = 6 \pi \approx 18.84 \) units.
To help students grasp these concepts, perimeter worksheets often include activities such as:
- Identifying the shape and its side lengths.
- Applying the correct formula to calculate the perimeter.
- Solving word problems that involve perimeter calculations.
- Comparing perimeters of different shapes to understand the relationship between side lengths and perimeter.
Regular practice with these worksheets helps students improve their ability to calculate perimeters accurately and develop a strong understanding of measuring boundaries, which is essential for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Formulas for Calculating Area and Perimeter
Knowing the formulas for calculating area and perimeter is essential for solving geometry problems effectively. Below are the formulas for various common shapes, with detailed steps and examples.
Formulas for Area
- Square: The area is found by multiplying the length of one side by itself.
- Formula: \( Area = side \times side \)
- Example: If the side length is 4 units, then Area = \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \) square units.
- Rectangle: The area is calculated by multiplying the length by the width.
- Formula: \( Area = length \times width \)
- Example: If the length is 5 units and the width is 3 units, then Area = \( 5 \times 3 = 15 \) square units.
- Triangle: The area is found using the base and the height.
- Formula: \( Area = \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \)
- Example: If the base is 6 units and the height is 4 units, then Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 4 = 12 \) square units.
- Circle: The area is determined using the radius and the constant π (pi, approximately 3.14).
- Formula: \( Area = \pi \times radius^2 \)
- Example: If the radius is 3 units, then Area = \( \pi \times 3^2 = \pi \times 9 \approx 28.26 \) square units.
Formulas for Perimeter
- Square: The perimeter is found by adding the lengths of all four sides.
- Formula: \( Perimeter = 4 \times side \)
- Example: If the side length is 5 units, then Perimeter = \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units.
- Rectangle: The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides or using the formula:
- Formula: \( Perimeter = 2 \times (length + width) \)
- Example: If the length is 8 units and the width is 3 units, then Perimeter = \( 2 \times (8 + 3) = 2 \times 11 = 22 \) units.
- Triangle: The perimeter is found by adding the lengths of its three sides.
- Formula: \( Perimeter = side1 + side2 + base \)
- Example: If the sides are 4 units, 6 units, and 7 units, then Perimeter = \( 4 + 6 + 7 = 17 \) units.
- Circle: The perimeter, also known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius and the constant π (pi).
- Formula: \( Perimeter = 2 \times \pi \times radius \)
- Example: If the radius is 3 units, then Perimeter = \( 2 \times \pi \times 3 = 6 \pi \approx 18.84 \) units.
Using these formulas, students can solve a variety of geometry problems related to area and perimeter, building a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.

Worksheets for Calculating Area
Worksheets for calculating area are essential tools to help 4th-grade students understand and practice finding the area of various shapes. These worksheets provide a structured approach to learning, offering step-by-step problems and real-world applications.
Here are some typical activities and problems included in these worksheets:
Basic Area Calculations
Students start by calculating the area of simple shapes using provided formulas.
| Shape | Dimensions | Formula | Example Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Square | Side = 4 units | Area = \( side \times side \) | Area = \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \) square units |
| Rectangle | Length = 6 units, Width = 3 units | Area = \( length \times width \) | Area = \( 6 \times 3 = 18 \) square units |
| Triangle | Base = 5 units, Height = 2 units | Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height \) | Area = \( \frac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 2 = 5 \) square units |
Complex Shapes and Composite Figures
Worksheets may include problems that involve finding the area of composite figures by breaking them down into simpler shapes.
- Divide the composite shape into known shapes (e.g., rectangles, triangles).
- Calculate the area of each individual shape.
- Add the areas together to find the total area.
Word Problems
Students apply their knowledge to solve word problems that require area calculations. These problems help them understand the practical applications of finding area.
- A rectangular garden has a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters. What is the area of the garden?
- Solution: \( Area = 8 \times 5 = 40 \) square meters.
- A triangular plot of land has a base of 10 meters and a height of 6 meters. Calculate the area of the plot.
- Solution: \( Area = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 6 = 30 \) square meters.
Real-Life Applications
Worksheets often include scenarios where students must use their area calculation skills in real-life contexts, such as determining the amount of paint needed for a wall or the size of a piece of fabric.
- Calculate the area of a room to determine how much carpeting is needed.
- Find the area of a garden to decide how many plants can be planted.
These comprehensive worksheets are designed to build confidence and proficiency in calculating area, ensuring students are well-prepared for more advanced math challenges.
Worksheets for Calculating Perimeter
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of various shapes is a crucial skill for 4th-grade students. These worksheets are designed to help students practice and master perimeter calculations through a variety of problems and activities.
Basic Perimeter Calculations
Start with simple shapes such as squares and rectangles. Ensure students understand the formula for perimeter:
\[ P = 2 \times (length + width) \]
- Worksheet 1: Calculate the perimeter of squares and rectangles with given side lengths.
- Worksheet 2: Word problems involving perimeter calculations of rectangles.
Advanced Perimeter Problems
Progress to more complex shapes and scenarios:
- Worksheet 3: Calculate the perimeter of polygons including triangles, pentagons, and hexagons.
- Worksheet 4: Real-life application problems where students find the perimeter of composite shapes.
Interactive and Visual Activities
Engage students with hands-on activities and visual aids:
- Worksheet 5: Draw shapes on graph paper and calculate their perimeters.
- Worksheet 6: Use interactive online tools to manipulate shapes and measure their perimeters.
Challenging Perimeter Word Problems
Enhance critical thinking skills with challenging word problems:
- Worksheet 7: Multi-step word problems involving the perimeter of irregular shapes.
- Worksheet 8: Perimeter puzzles where students need to find missing side lengths.
Assessment and Review
Use these worksheets to assess student understanding and provide comprehensive review:
- Worksheet 9: Mixed problems involving perimeter and area to test overall understanding.
- Worksheet 10: Timed quizzes to enhance speed and accuracy in perimeter calculations.
Download and Print
All worksheets are available for download and print in PDF format:
Mixed Area and Perimeter Problems
Mixed area and perimeter problems help students apply their understanding of both concepts in various contexts. Below are some worksheets that combine both area and perimeter calculations for different shapes and scenarios.
-
Problem Set 1: Rectangles and Squares
- Find the area and perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 cm and a width of 5 cm.
- Calculate the area and perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 cm.
-
Problem Set 2: Triangles
- A right triangle has legs of 6 cm and 8 cm. Find its area and perimeter.
- Calculate the area of an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 9 cm.
-
Problem Set 3: Complex Shapes
- Find the area and perimeter of a composite shape made up of a rectangle (10 cm by 4 cm) and a semicircle with a diameter of 4 cm.
- A garden is in the shape of a right triangle with legs of 12 m and 16 m, and a semicircular flower bed with a diameter of 12 m is added to one of the legs. Calculate the total area and perimeter of the garden.
-
Problem Set 4: Real-Life Scenarios
- A rectangular playground measures 30 m by 20 m. A pathway 2 m wide surrounds the playground. Find the area of the pathway and the total perimeter.
- You are tiling a rectangular floor that is 15 ft by 10 ft with square tiles that are 1 ft by 1 ft. Calculate the number of tiles needed and the perimeter of the tiled floor.
Use the formulas for area and perimeter to solve these problems:
- Area of a rectangle: \( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Perimeter of a rectangle: \( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
- Area of a triangle: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Perimeter of a triangle: Sum of all sides
- Area of a circle: \( \text{Area} = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
- Circumference of a circle: \( \text{Circumference} = 2 \times \pi \times \text{radius} \)
Real-Life Application Problems
Understanding how to calculate area and perimeter is not just for worksheets but also for solving real-world problems. Here are some practical examples where you can apply these concepts:
-
1. Designing a Garden
You are planning to create a rectangular flower garden in your backyard. The length of the garden is 8 meters, and the width is 5 meters.
- Calculate the area of the garden.
- Determine the amount of fencing needed to enclose the garden.
Solution:
Area: The area is calculated as
\( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 8 \, \text{m} \times 5 \, \text{m} = 40 \, \text{m}^2 \).
Perimeter: The perimeter is calculated as
\( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) = 2 \times (8 \, \text{m} + 5 \, \text{m}) = 26 \, \text{m} \). -
2. Painting a Room
You need to paint the four walls of a room that is 12 feet long, 10 feet wide, and 8 feet high. Assume there are no doors or windows.
- Calculate the total wall area to be painted.
- Estimate the amount of paint needed if one gallon covers 350 square feet.
Solution:
Total Wall Area: Calculate the area of each wall and add them together.
\( \text{Area} = 2 \times (\text{length} \times \text{height}) + 2 \times (\text{width} \times \text{height}) \)
\( = 2 \times (12 \, \text{ft} \times 8 \, \text{ft}) + 2 \times (10 \, \text{ft} \times 8 \, \text{ft}) \)
\( = 2 \times 96 \, \text{ft}^2 + 2 \times 80 \, \text{ft}^2 = 352 \, \text{ft}^2 \).
Paint Needed: Divide the total area by the coverage per gallon.
\( \text{Paint needed} = \frac{\text{Total Wall Area}}{\text{Coverage per Gallon}} = \frac{352 \, \text{ft}^2}{350 \, \text{ft}^2/\text{gallon}} \approx 1.01 \, \text{gallons} \).
You will need approximately 1 gallon of paint. -
3. Tiling a Floor
You want to tile a rectangular kitchen floor that measures 6 meters by 4 meters. Each tile is a square with a side length of 0.5 meters.
- Calculate the total number of tiles needed.
- Determine the perimeter of the kitchen floor.
Solution:
Total Number of Tiles: Calculate the area of the floor and the area of one tile.
\( \text{Floor Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 6 \, \text{m} \times 4 \, \text{m} = 24 \, \text{m}^2 \)
\( \text{Tile Area} = 0.5 \, \text{m} \times 0.5 \, \text{m} = 0.25 \, \text{m}^2 \)
\( \text{Number of Tiles} = \frac{\text{Floor Area}}{\text{Tile Area}} = \frac{24 \, \text{m}^2}{0.25 \, \text{m}^2} = 96 \).
Perimeter: Calculate the perimeter of the kitchen floor.
\( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) = 2 \times (6 \, \text{m} + 4 \, \text{m}) = 20 \, \text{m} \). -
4. Building a Fence
You have a rectangular playground that is 15 meters long and 10 meters wide. You want to build a fence around it and install a gate.
- Calculate the length of fencing required.
- Determine the area of the playground.
Solution:
Length of Fencing: The perimeter is needed for the fence.
\( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) = 2 \times (15 \, \text{m} + 10 \, \text{m}) = 50 \, \text{m} \).
Area: Calculate the area.
\( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 15 \, \text{m} \times 10 \, \text{m} = 150 \, \text{m}^2 \).

Interactive Activities and Games
Learning area and perimeter can be fun and engaging through various interactive activities and games. Here are some activities designed to help 4th graders grasp these concepts:
-
1. Virtual Shape Explorer
In this game, students use an interactive tool to draw different shapes on a grid. They calculate the area and perimeter of each shape they create.
- Draw a shape on the grid by clicking and dragging.
- Calculate the area by counting the number of square units inside the shape.
- Determine the perimeter by counting the units around the edge of the shape.
- Check your answers using the tool's built-in calculator.
-
2. Perimeter Puzzle Game
In this puzzle, students are given shapes with missing sides and must determine the unknown side lengths to achieve a specific perimeter.
- Each puzzle presents a shape with one or more missing side lengths.
- The total perimeter of the shape is given.
- Calculate the missing side lengths using the formula:
\( \text{Perimeter} = \text{sum of all side lengths} \) - Drag and drop numbers to fill in the missing sides and match the given perimeter.
-
3. Area Maze Challenge
Students navigate through a maze where they need to solve area problems to unlock the correct path.
- Navigate through the maze by solving area problems at each intersection.
- Calculate the area of different rectangles or irregular shapes to determine the right direction.
- Collect points and unlock rewards by choosing the correct path.
-
4. Area and Perimeter Jeopardy
This classroom activity is a team-based quiz game where students answer questions about area and perimeter.
- Form teams and choose questions from different categories related to area and perimeter.
- Answer correctly to earn points for your team.
- The team with the most points at the end wins the game.
-
5. Interactive Area Builder
Students use an online tool to build and compare areas of different shapes.
- Select a shape and adjust its dimensions using sliders.
- Observe how changes in dimensions affect the area.
- Compare areas of different shapes by overlaying them.
- Use the tool to visualize and understand the relationship between dimensions and area.
-
6. Perimeter Relay Race
A physical game where students measure and calculate perimeters in a relay race format.
- Set up stations with different shapes drawn on the ground or on paper.
- Each team calculates the perimeter of the shape at their station.
- Run to the next station after getting the correct answer.
- The team that completes all stations first wins.
Word Problems and Scenarios
Applying area and perimeter concepts to real-world scenarios helps solidify understanding. Here are detailed word problems and scenarios designed for 4th graders:
-
1. Rectangular Playground
A school is designing a rectangular playground that is 20 meters long and 15 meters wide.
- Problem: Calculate the area of the playground.
- Problem: Determine the perimeter to find out how much fencing is needed around the playground.
- Solution:
-
Area:
\( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 20 \, \text{m} \times 15 \, \text{m} = 300 \, \text{m}^2 \). -
Perimeter:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) = 2 \times (20 \, \text{m} + 15 \, \text{m}) = 70 \, \text{m} \).
-
2. Carpet for a Room
A room measures 12 feet by 10 feet, and you want to cover the floor with carpet.
- Problem: Calculate the area of the room to determine how much carpet is needed.
- Problem: If the carpet costs $5 per square foot, calculate the total cost.
- Solution:
-
Area:
\( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 12 \, \text{ft} \times 10 \, \text{ft} = 120 \, \text{ft}^2 \). -
Total Cost:
\( \text{Total Cost} = \text{Area} \times \text{Cost per Square Foot} = 120 \, \text{ft}^2 \times \$5/\text{ft}^2 = \$600 \).
-
3. Painting a Fence
You need to paint a rectangular fence that surrounds a garden. The fence is 18 meters long and 12 meters wide.
- Problem: Calculate the perimeter to determine the length of the fence that needs painting.
- Problem: If one can of paint covers 25 meters, how many cans are needed?
- Solution:
-
Perimeter:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) = 2 \times (18 \, \text{m} + 12 \, \text{m}) = 60 \, \text{m} \). -
Cans of Paint:
\( \text{Cans Needed} = \frac{\text{Perimeter}}{\text{Coverage per Can}} = \frac{60 \, \text{m}}{25 \, \text{m}/\text{can}} = 2.4 \).
Since you can't buy a fraction of a can, you will need 3 cans.
-
4. Tiling a Bathroom Floor
You are tiling a rectangular bathroom floor that is 4 meters long and 3 meters wide. Each tile covers an area of 0.25 square meters.
- Problem: Calculate the total number of tiles needed.
- Problem: Determine the cost if each tile costs $2.
- Solution:
-
Total Number of Tiles:
\( \text{Floor Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} = 4 \, \text{m} \times 3 \, \text{m} = 12 \, \text{m}^2 \).
\( \text{Number of Tiles} = \frac{\text{Floor Area}}{\text{Tile Area}} = \frac{12 \, \text{m}^2}{0.25 \, \text{m}^2} = 48 \). -
Total Cost:
\( \text{Total Cost} = \text{Number of Tiles} \times \text{Cost per Tile} = 48 \times \$2 = \$96 \).
-
5. Making a Rectangle from Squares
You have 24 square tiles, each with a side length of 1 foot. You need to arrange them into a rectangle.
- Problem: What are the possible dimensions of the rectangle?
- Problem: Calculate the perimeter for each possible arrangement.
- Solution:
-
Possible Dimensions: The factors of 24 are: (1, 24), (2, 12), (3, 8), (4, 6).
Therefore, possible rectangles are: 1 ft x 24 ft, 2 ft x 12 ft, 3 ft x 8 ft, and 4 ft x 6 ft. -
Perimeter:
\( \text{Perimeter of 1 ft x 24 ft} = 2 \times (1 + 24) = 50 \, \text{ft} \) \( \text{Perimeter of 2 ft x 12 ft} = 2 \times (2 + 12) = 28 \, \text{ft} \) \( \text{Perimeter of 3 ft x 8 ft} = 2 \times (3 + 8) = 22 \, \text{ft} \) \( \text{Perimeter of 4 ft x 6 ft} = 2 \times (4 + 6) = 20 \, \text{ft} \)
Tips and Tricks for Understanding Area and Perimeter
Mastering the concepts of area and perimeter can be easier with some helpful tips and tricks. Here are effective strategies to enhance your understanding:
-
1. Visualize with Grid Paper
Using grid paper can help visualize how area and perimeter work. Here’s how:
- Draw shapes on grid paper.
- Count the squares inside the shape for the area.
- Count the squares along the edges for the perimeter.
-
2. Break Down Complex Shapes
For irregular shapes, breaking them into smaller, regular shapes (rectangles or squares) makes it easier to calculate area and perimeter.
- Divide the complex shape into smaller rectangles or squares.
- Calculate the area and perimeter of each smaller shape.
- Sum the areas for the total area, and add up the outer sides for the perimeter.
-
3. Remember Key Formulas
Memorize these essential formulas for quick calculations:
- Area of a Rectangle:
\( \text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{width} \) - Perimeter of a Rectangle:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \) - Area of a Square:
\( \text{Area} = \text{side} \times \text{side} \) - Perimeter of a Square:
\( \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \)
- Area of a Rectangle:
-
4. Use Real-Life Objects
Apply area and perimeter to real-life objects around you:
- Measure the length and width of books, tables, or picture frames.
- Calculate their area and perimeter using the formulas.
- Compare your results with the actual dimensions to check accuracy.
-
5. Practice with Perimeter Patterns
Observe patterns in perimeters of similar shapes:
- Compare the perimeters of rectangles with the same area but different dimensions.
- Notice how changing length and width while keeping the same area affects the perimeter.
- Explore why longer, narrower shapes have larger perimeters than more square-like shapes.
-
6. Area and Perimeter Relationship
Understand the difference between area and perimeter:
- Area measures the space inside a shape.
- Perimeter measures the distance around the shape.
- Recognize that two shapes can have the same perimeter but different areas, and vice versa.
-
7. Check Your Work
Double-checking your calculations helps avoid mistakes:
- Recalculate both area and perimeter to ensure consistency.
- Use estimation to verify that your answers are reasonable.
- If possible, use another method to cross-check your results.
-
8. Interactive Tools
Leverage online tools and apps for practice:
- Use interactive area and perimeter calculators to test various shapes.
- Participate in online quizzes and games focused on these concepts.
- Utilize virtual manipulatives to experiment with different shapes and their properties.
-
9. Mnemonics and Rhymes
Remember formulas and concepts with catchy phrases:
- Create simple rhymes or phrases to recall area and perimeter formulas.
- For example, "Length times Width for Area's might, Add all sides for Perimeter's flight."
- Use these mnemonics during tests and exercises for quick recall.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When dealing with area and perimeter problems, it's essential to be mindful of common mistakes that students often make. By being aware of these pitfalls, you can improve your understanding and accuracy in these mathematical concepts.
- Misinterpreting Units: One common mistake is misinterpreting the units given in the problem. Always double-check whether the units are in inches, feet, meters, etc., and ensure that your final answer reflects the appropriate unit.
- Forgetting to Include All Sides: When calculating perimeter, it's crucial to include all sides of the shape. Sometimes, students overlook a side or count it multiple times, leading to incorrect results. Take your time to identify and measure each side accurately.
- Confusing Area and Perimeter: Area and perimeter are distinct mathematical concepts, but they are often confused. Remember, perimeter refers to the distance around the outside of a shape, while area measures the space enclosed within the shape. Be clear on which concept the problem is asking for.
- Incorrect Application of Formulas: Using the wrong formula for calculating area or perimeter can result in errors. Make sure you understand the formulas properly and apply them correctly to the given shapes. Practice using different formulas to reinforce your understanding.
- Ignoring the Shape's Characteristics: Each shape has unique characteristics that affect its area and perimeter calculations. Ignoring these characteristics or assuming that all shapes are similar can lead to inaccurate solutions. Pay attention to the specific attributes of the shape in the problem.
- Rounding Errors: Rounding numbers during calculations can introduce errors, especially when dealing with decimals. Keep track of significant digits and only round your final answer to the appropriate precision specified in the problem.
- Skipping the Visualization Step: Visualizing the shape and its dimensions before solving the problem can help you avoid mistakes. Take the time to sketch the shape and label its sides, angles, and measurements before diving into the calculations.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and practicing regularly, you can enhance your proficiency in solving area and perimeter problems with confidence.
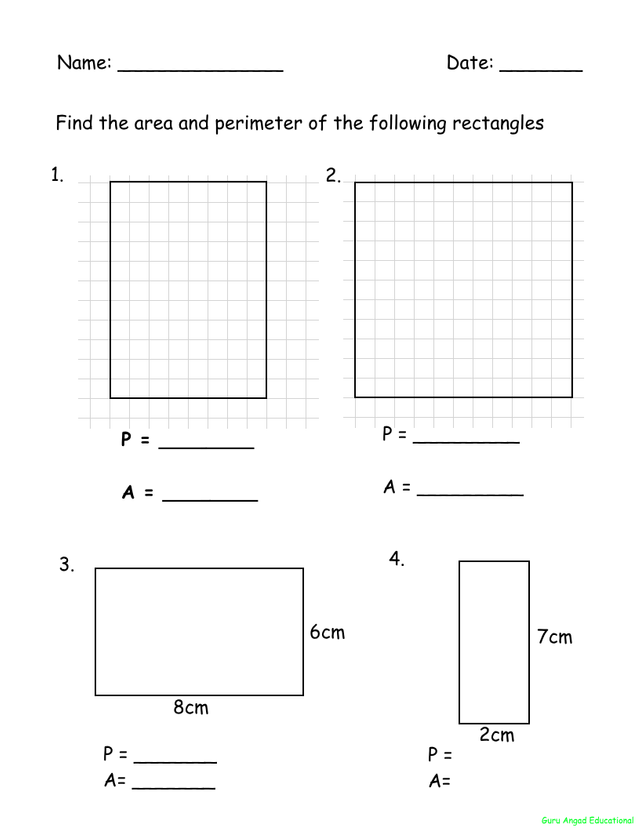
Answer Keys and Explanations
Access to answer keys and explanations is crucial for reinforcing learning and understanding concepts effectively. Here's a breakdown of what you can expect:
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Detailed explanations accompany each answer, providing a step-by-step breakdown of the solution process. This helps students understand the logic behind each calculation and reinforces problem-solving skills.
- Clear Diagrams and Visual Aids: Visual aids such as diagrams and illustrations are often included to enhance comprehension. These visual representations help students visualize the problem and better understand geometric concepts.
- Highlighted Key Concepts: Answer keys typically highlight key concepts and formulas used in each problem. This reinforcement of fundamental principles helps solidify understanding and prepares students for more complex problems.
- Common Errors: In addition to providing correct answers, answer keys may also address common mistakes and errors that students make. Understanding these errors helps students identify misconceptions and avoid similar mistakes in the future.
- Alternative Approaches: Sometimes, there may be multiple ways to solve a problem. Answer keys may present alternative approaches or methods, encouraging students to think flexibly and creatively when tackling mathematical problems.
By utilizing answer keys and explanations effectively, students can gain confidence in their problem-solving abilities and develop a deeper understanding of area and perimeter concepts.
Additional Resources and Practice Sheets
Accessing additional resources and practice sheets can greatly enhance your understanding and proficiency in area and perimeter concepts. Here's what you can expect from these supplementary materials:
- Varied Levels of Difficulty: Practice sheets often offer problems of varying difficulty levels, allowing students to gradually build their skills and confidence.
- Topic-Specific Practice: Resources may focus on specific topics within area and perimeter, such as calculating area of rectangles, finding perimeter of irregular shapes, or solving word problems.
- Interactive Activities: Some resources may include interactive activities and games that engage students while reinforcing key concepts. These activities make learning enjoyable and encourage active participation.
- Real-Life Applications: Practice sheets may include problems that relate to real-life scenarios, helping students understand the practical significance of area and perimeter in everyday situations.
- Answer Keys for Self-Assessment: Many practice sheets come with answer keys, allowing students to check their answers independently and track their progress. This self-assessment helps identify areas for improvement.
- Online and Printable Options: Resources may be available in both online and printable formats, offering flexibility in how students access and complete the practice materials.
- Additional Learning Materials: In addition to practice sheets, supplementary resources such as instructional videos, tutorials, and explanatory guides may also be available to further support learning.
By utilizing these additional resources and practice sheets effectively, students can reinforce their understanding of area and perimeter concepts and build confidence in their mathematical abilities.
Xem bài hát về diện tích và chu vi này để giúp trẻ em lớp 3 - lớp 4 học về các khái niệm toán học một cách vui nhộn và dễ hiểu.
Bài hát về Diện tích và Chu vi cho Trẻ em | Lớp 3 - Lớp 4
Xem video về diện tích và chu vi này để giúp học sinh lớp 4 và tiểu học cao cấp hiểu về các khái niệm toán học một cách chi tiết và thú vị.
Diện tích và Chu vi cho Lớp 4 và Tiểu học cao cấp - Đo lường