Topic finding area and perimeter of a triangle: Understanding how to find the area and perimeter of a triangle is essential for solving various mathematical problems and real-life applications. This comprehensive guide will explore different methods and formulas to calculate the area and perimeter of triangles, making the learning process both easy and engaging.
Table of Content
- Finding Area and Perimeter of a Triangle
- Introduction
- Understanding Triangles
- Basics of Area and Perimeter
- Finding the Area of a Triangle
- Finding the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Practical Applications
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách tính diện tích và chu vi của một tam giác với Mr. J trong video này. Video này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn qua các bước đơn giản và dễ hiểu.
Finding Area and Perimeter of a Triangle
Understanding how to find the area and perimeter of a triangle is fundamental in geometry. Below are detailed explanations and examples of how to calculate both.
Area of a Triangle
The area \(A\) of a triangle can be found using the formula:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \]
Where the base is the length of one side of the triangle, and the height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex.
Example
- Base \(b = 10\) units
- Height \(h = 5\) units
Using the formula:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times 5 = 25 \, \text{square units} \]
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter \(P\) of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its sides. For a triangle with sides \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), the formula is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Example
- Side \(a = 5\) units
- Side \(b = 10\) units
- Side \(c = 7\) units
Using the formula:
\[ P = 5 + 10 + 7 = 22 \, \text{units} \]
Special Cases
Equilateral Triangle
For an equilateral triangle (all sides are equal), if each side is \(s\), the formulas simplify to:
Area:
\[ A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} s^2 \]
Perimeter:
\[ P = 3s \]
Example
- Side \(s = 6\) units
Using the formulas:
\[ A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 6^2 = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times 36 = 9\sqrt{3} \, \text{square units} \]
\[ P = 3 \times 6 = 18 \, \text{units} \]
Right Triangle
For a right triangle (one angle is 90 degrees), with legs \(a\) and \(b\), and hypotenuse \(c\), the formulas are:
Area:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} ab \]
Perimeter:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Using the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse:
\[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \]
Example
- Leg \(a = 3\) units
- Leg \(b = 4\) units
Using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[ c = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \, \text{units} \]
Area:
\[ A = \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6 \, \text{square units} \]
Perimeter:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{units} \]

READ MORE:
Introduction
Understanding the area and perimeter of a triangle is fundamental in geometry. This knowledge is applicable in various fields, from construction to art. The area of a triangle is the measure of the region enclosed by the triangle, while the perimeter is the total length of its sides. This section will explore the formulas and steps to calculate the area and perimeter of different types of triangles.
- Definition of a Triangle
- Types of Triangles
- Equilateral Triangle
- Isosceles Triangle
- Scalene Triangle
- Formulas for Area and Perimeter
- Area Formula: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Perimeter Formula: \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \) where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides.
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identifying the Base and Height
- Applying the Area Formula
- Summing the Side Lengths for Perimeter
- Examples and Practice Problems
By following these steps, you will be able to accurately determine the area and perimeter of any triangle, enhancing your understanding and application of geometric principles.
Understanding Triangles
Triangles are fundamental shapes in geometry, characterized by three sides and three angles. Understanding their properties is crucial for various calculations, including area and perimeter. This section will explore the different types of triangles and the basic formulas used to find their area and perimeter.
A triangle can be classified based on its sides and angles:
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal, and all three angles are 60 degrees.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are of equal length, and the angles opposite these sides are equal.
- Scalene Triangle: All three sides and angles are different.
- Right Triangle: One of the angles is 90 degrees.
To understand triangles better, let’s delve into the key formulas:
Area of a Triangle
- Using Base and Height: \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Using Heron's Formula (for sides \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\)):
- First, calculate the semi-perimeter \( s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \)
- Then, \( \text{Area} = \sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} \)
- Using Trigonometry (for two sides \(a\), \(b\) and included angle \(\gamma\)): \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times a \times b \times \sin(\gamma) \)
Perimeter of a Triangle
- For all three sides \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\): \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \)
- For two sides \(a\), \(b\) and the included angle \(\gamma\) (using the law of cosines to find the third side): \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\gamma)} \)
With these formulas, you can determine the area and perimeter of any triangle given sufficient information. Understanding these concepts is essential for solving various geometric problems.
Basics of Area and Perimeter
Understanding the basics of area and perimeter is essential when studying geometry, especially triangles. This section will cover fundamental concepts and formulas to help you calculate these properties effectively.
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the shape. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
- Example: For a triangle with sides 5 cm, 7 cm, and 10 cm, the perimeter is \( 5 + 7 + 10 = 22 \) cm.
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle is the region enclosed by its three sides. The most common formula used to find the area of a triangle is:
A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}
Here, the base and height must be perpendicular to each other. For example, if the base is 5 cm and the height is 4 cm, the area is:
A = \frac{1}{2} \times 5 \, \text{cm} \times 4 \, \text{cm} = 10 \, \text{cm}^2
Heron's Formula
When you know the lengths of all three sides of a triangle, Heron's formula is useful for calculating the area:
s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} (semi-perimeter)A = \sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}
For example, for a triangle with sides 7 cm, 8 cm, and 9 cm:
s = \frac{7 + 8 + 9}{2} = 12 \, \text{cm} A = \sqrt{12(12-7)(12-8)(12-9)} = \sqrt{12 \times 5 \times 4 \times 3} = \sqrt{720} \approx 26.83 \, \text{cm}^2
Special Triangles
Different types of triangles have specific formulas for area:
- Equilateral Triangle:
A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times \text{side}^2 - Right Triangle:
A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{leg}_1 \times \text{leg}_2 - Isosceles Triangle:
A = \frac{1}{4} \times \text{base} \times \sqrt{4 \times \text{side}^2 - \text{base}^2}
By mastering these basic formulas, you can solve a wide variety of problems involving the area and perimeter of triangles.
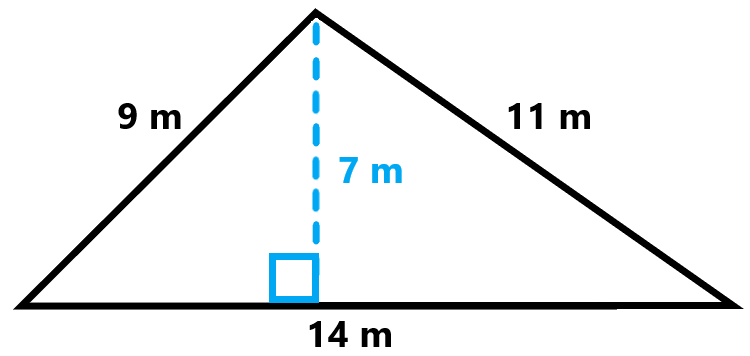
Finding the Area of a Triangle
Calculating the area of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry. The area can be determined using different methods based on the information available. Below are various methods to find the area of a triangle:
Using Base and Height
The most straightforward way to calculate the area of a triangle is by using its base and height. The formula is:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}
\]
- Step 1: Measure the base of the triangle.
- Step 2: Measure the perpendicular height from the base to the opposite vertex.
- Step 3: Substitute the base and height into the formula.
- Step 4: Calculate the area.
Using Heron's Formula
Heron's Formula is useful when you know all three sides of the triangle. It is expressed as:
\[
\text{Area} = \sqrt{s \times (s - a) \times (s - b) \times (s - c)}
\]
where \( s \) is the semi-perimeter of the triangle, and \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Step 1: Measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Step 2: Calculate the semi-perimeter: \[ s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \]
- Step 3: Substitute \( s \), \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) into Heron's formula.
- Step 4: Calculate the area by solving the formula.
Special Cases
Special triangles have simpler methods for finding their areas:
Right Triangles
For right triangles, the area can be calculated as:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{leg}_1 \times \text{leg}_2
\]
- The legs are the two sides that form the right angle.
Equilateral Triangles
For equilateral triangles (all sides are equal), the formula is:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} \times \text{side}^2
\]
- Only the length of one side is needed to use this formula.
Isosceles Triangles
For isosceles triangles (two sides are equal), you can use the base and height method or, if the height is not given, use the following:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \sqrt{\text{side}^2 - \left(\frac{\text{base}}{2}\right)^2}
\]
- This formula uses the Pythagorean Theorem to determine the height if it is not directly available.
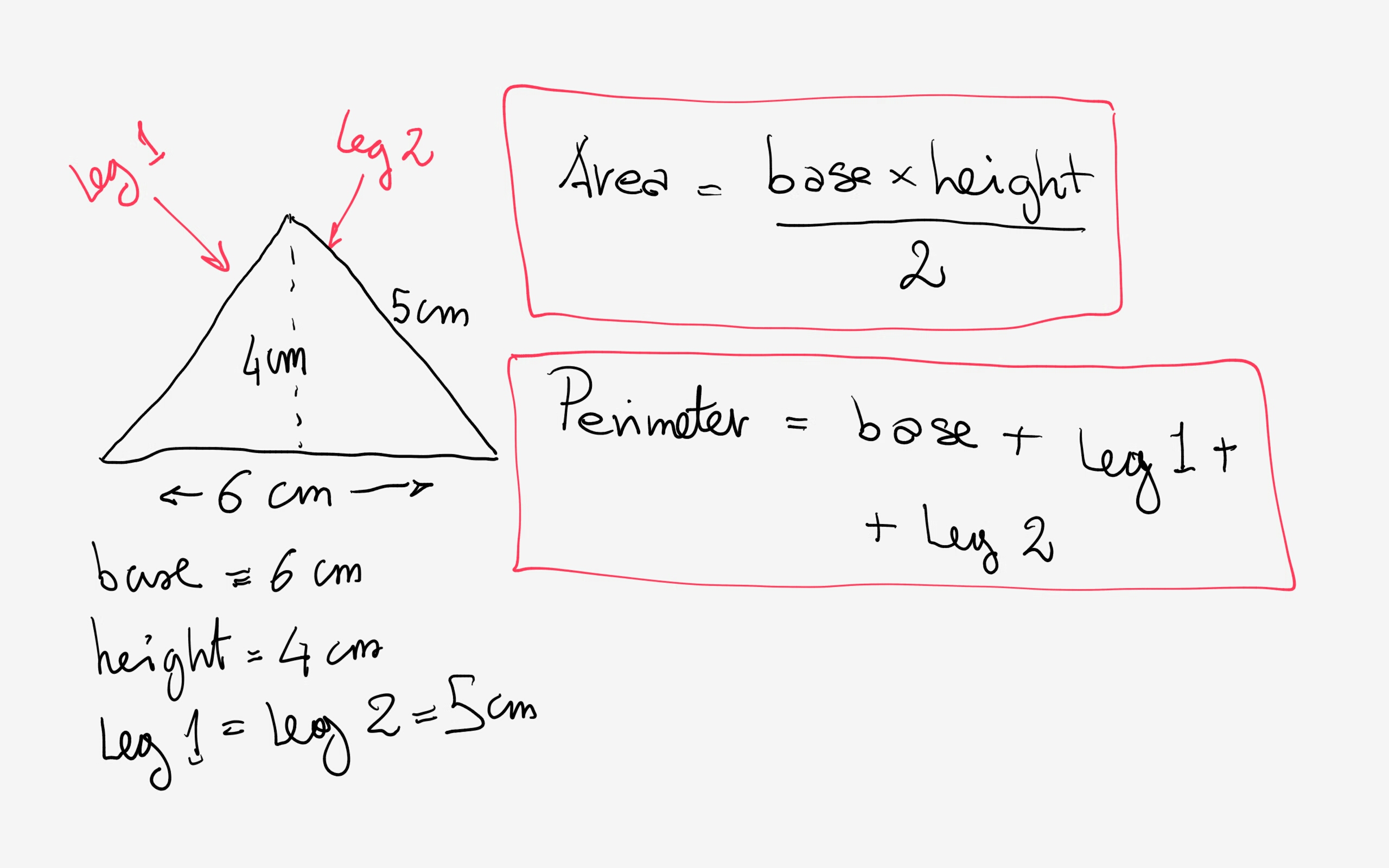
Finding the Perimeter of a Triangle
To find the perimeter of a triangle, you need to add the lengths of all its three sides.
Let's denote the lengths of the three sides of the triangle as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
Therefore, the perimeter (\( P \)) of the triangle is given by:
Here are the steps to find the perimeter of a triangle:
- Determine the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Add the lengths of the three sides together.
- The sum obtained in step 2 is the perimeter of the triangle.
It's important to remember that the units of measurement for the sides should be the same, whether it's in centimeters, inches, or any other unit.
Now, let's explore some special cases when finding the perimeter of certain types of triangles:
- Right Triangles: In a right triangle, one of the angles measures 90 degrees. The perimeter can be found using the Pythagorean theorem or by simply adding the lengths of the three sides.
- Equilateral Triangles: In an equilateral triangle, all three sides are of equal length. So, the perimeter is three times the length of one side (\( P = 3 \times a \)).
- Isosceles Triangles: In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of equal length. To find the perimeter, add the lengths of the two equal sides and the length of the remaining side.
These methods should help you accurately calculate the perimeter of any triangle, whether it's a standard triangle or a special case.
Practical Applications
The concepts of finding the area and perimeter of a triangle have numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some examples:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects and construction workers often need to calculate the area of triangular surfaces, such as roofs, to estimate materials required for construction.
- Landscaping: Landscape designers use triangle area calculations to plan garden layouts, measure turf or gravel needed for pathways, and estimate the size of flower beds or lawns.
- Surveying: Surveyors use the principles of triangle area and perimeter to measure land parcels, determine property boundaries, and create topographic maps.
- Engineering: Engineers utilize triangle area and perimeter calculations in various applications, including structural analysis, fluid dynamics, and heat transfer calculations.
- Computer Graphics: Graphics designers and game developers use triangle geometry extensively to render 3D models, calculate surface areas, and simulate physical interactions.
- Navigation: Pilots, sailors, and navigators use triangle trigonometry to calculate distances, angles, and positions, essential for navigation and route planning.
- Finance and Economics: Analysts and economists apply triangle area and perimeter concepts in financial modeling, risk assessment, and market analysis.
These practical applications highlight the importance of understanding and applying the principles of triangle geometry in various real-world scenarios, demonstrating the relevance and versatility of these mathematical concepts.
Conclusion
Understanding the area and perimeter of a triangle is crucial for various applications in mathematics, science, and engineering. In this guide, we have covered the fundamental concepts and methods used to calculate these important geometric properties. Let's summarize the key points and provide additional resources for further learning.
Summary of Key Points
- Types of Triangles: We discussed different types of triangles including right, equilateral, and isosceles triangles, and how their properties affect the calculation of area and perimeter.
- Properties of Triangles: We explored the basic properties of triangles such as the sum of interior angles and the relationship between side lengths.
- Definition of Area and Perimeter: We defined what area and perimeter mean in the context of triangles and the formulas used to calculate them.
- Calculating Area: Methods such as using the base and height, Heron's formula, and special cases for right, equilateral, and isosceles triangles were covered.
- Calculating Perimeter: We learned how to calculate the perimeter by summing the side lengths and considered special cases for different types of triangles.
- Practical Applications: We looked at real-life examples and geometry problems to understand the practical applications of calculating area and perimeter.
Further Reading and Resources
For those interested in diving deeper into the topic, here are some recommended resources:
We hope this guide has been helpful in enhancing your understanding of how to find the area and perimeter of triangles. Keep practicing with different problems and utilize the resources provided to deepen your knowledge.
Tìm hiểu cách tính diện tích và chu vi của một tam giác với Mr. J trong video này. Video này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn qua các bước đơn giản và dễ hiểu.
Làm Thế Nào Để Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi Của Một Tam Giác | Toán Học Với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tính diện tích và chu vi của một tam giác trong video này. Video này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn từng bước đơn giản và dễ hiểu.
Làm Thế Nào Để Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi Của Một Tam Giác