Topic find perimeter of a semicircle: Discover how to find the perimeter of a semicircle with our simple and easy-to-follow guide. Whether you're a student or just curious about geometry, this article will help you understand the concept and calculations involved. Unlock the secrets of semicircles and master the formula for finding their perimeter in no time!
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Introduction to Semicircles
- Understanding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Basic Geometry of a Semicircle
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
- Examples of Perimeter Calculations
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Applications of Semicircle Perimeter in Real Life
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- FAQs on Semicircle Perimeter
- Conclusion and Recap
- YOUTUBE: Xem video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của một nửa hình tròn từ Corbettmaths, bài giảng rõ ràng và dễ hiểu.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle can be calculated using the radius or diameter of the semicircle. The formula incorporates both the curved part and the straight edge (diameter) of the semicircle.
Formula for Perimeter of a Semicircle
The formula to find the perimeter (P) of a semicircle with radius (r) is:
Or, using the diameter (d):
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Measure the radius (r) or diameter (d) of the semicircle.
- If you have the diameter, divide it by 2 to get the radius:
- Use the formula to find the perimeter:
- Using radius: $$P = \pi r + 2r$$
- Using diameter: $$P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d$$
- Substitute the value of radius or diameter into the formula.
- Calculate the value to get the perimeter.
$$r = \frac{d}{2}$$
Examples
Here are a few examples to illustrate how to find the perimeter of a semicircle:
| Example | Radius (r) | Diameter (d) | Perimeter Calculation | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example 1 | 7 cm | 14 cm | $$P = \pi \times 7 + 2 \times 7$$ | $$P \approx 43.98 \text{ cm}$$ |
| Example 2 | 10 cm | 20 cm | $$P = \pi \times 10 + 2 \times 10$$ | $$P \approx 51.42 \text{ cm}$$ |
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 5 cm.
- Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 12 cm.
- A semicircle has a perimeter of 31.4 cm. What is the radius?
Conclusion
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle is straightforward once you know the radius or diameter. By using the formula and substituting the values, you can easily determine the perimeter.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Semicircles
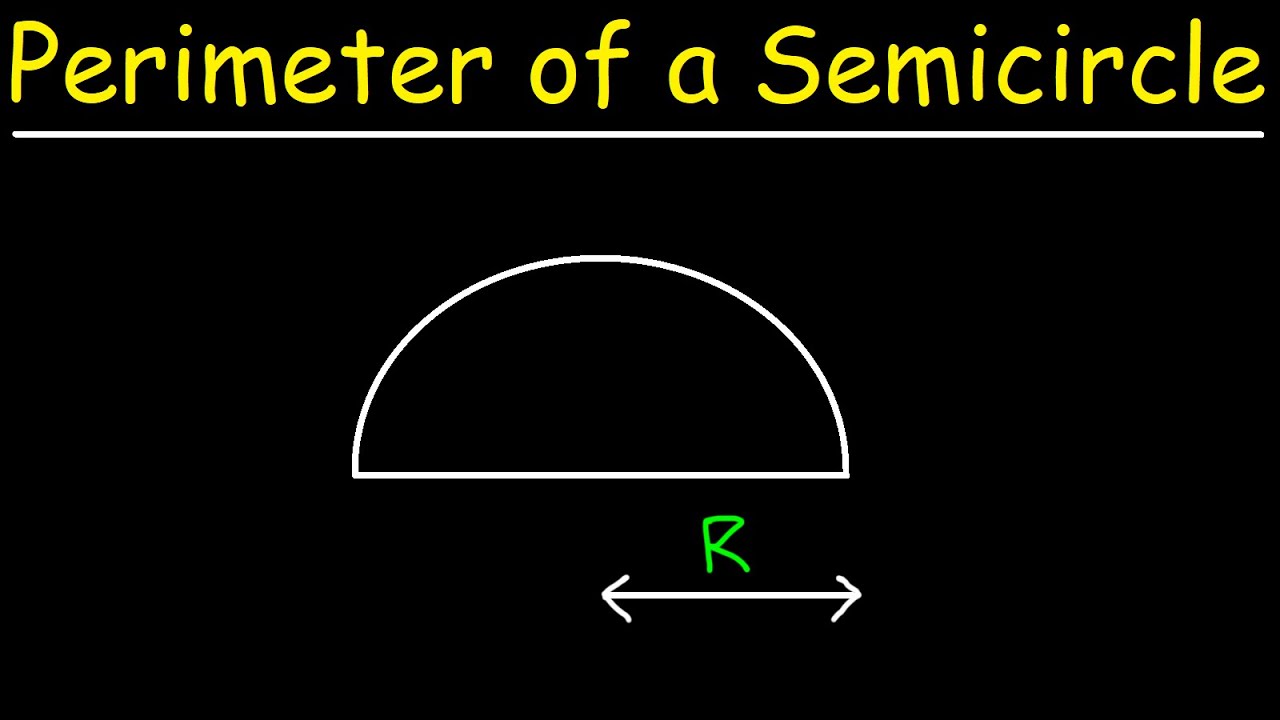
A semicircle is a two-dimensional geometric shape that represents half of a circle. It is formed by cutting a whole circle along its diameter, resulting in a curved edge and a straight edge. The key components of a semicircle include the radius, diameter, and the curved part known as the arc.
The radius (r) is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. The diameter (d) is twice the radius, spanning from one end of the semicircle to the other through the center. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
$$d = 2r$$
Understanding the properties of a semicircle is crucial for various geometric calculations, including finding its perimeter. The perimeter of a semicircle consists of the straight edge (the diameter) and the curved edge (the arc). To calculate the arc length, we use the formula for the circumference of a circle and take half of it:
$$\text{Circumference of a full circle} = 2\pi r$$
$$\text{Arc length of a semicircle} = \pi r$$
The perimeter of the semicircle is the sum of the diameter and the arc length:
$$\text{Perimeter of a semicircle} = \pi r + d$$
Substituting \(d\) with \(2r\), we get:
$$\text{Perimeter of a semicircle} = \pi r + 2r$$
Let's summarize these steps in an easy-to-follow format:
- Identify the radius (r) of the semicircle.
- Calculate the diameter (d) using \(d = 2r\).
- Find the arc length using \(\pi r\).
- Sum the diameter and the arc length to get the perimeter: \(\pi r + 2r\).
This foundational understanding will help you confidently tackle problems involving semicircles and their perimeters.
Understanding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is the distance around the curved edge of the semicircle plus the diameter of the semicircle. Understanding this concept requires a basic knowledge of the properties of a circle and the relationship between a circle and a semicircle.
A semicircle is essentially half of a circle, which means it consists of the curved part (the arc) and the straight part (the diameter). To find the perimeter of a semicircle, we need to calculate both these parts and add them together.
Key Components of a Semicircle:
- Radius (r): The distance from the center of the semicircle to any point on the curved edge. It is half the diameter.
- Diameter (d): The straight line passing from one side of the semicircle to the other, through the center. It is twice the radius.
- Arc Length: The curved part of the semicircle. It is half the circumference of a full circle.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Semicircle:
The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a semicircle is given by:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
Here, \( \pi r \) represents the length of the curved part (half the circumference of the full circle), and \( 2r \) is the length of the diameter.
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Find the radius (r): Measure or obtain the radius of the semicircle.
- Calculate the arc length: Use the formula \( \pi r \) to find the length of the curved part.
- Determine the diameter: Multiply the radius by 2 to get the diameter (2r).
- Add the arc length and the diameter: The perimeter is the sum of the arc length and the diameter, \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
Example Calculation:
Consider a semicircle with a radius of 4 cm:
- Radius \( r = 4 \, \text{cm} \)
- Arc Length \( = \pi \times 4 = 4\pi \, \text{cm} \)
- Diameter \( = 2 \times 4 = 8 \, \text{cm} \)
- Perimeter \( = 4\pi + 8 \, \text{cm} \)
Thus, the perimeter of the semicircle is \( 4\pi + 8 \, \text{cm} \) (approximately 20.57 cm).
Summary:
Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle involves recognizing that it consists of both the curved edge and the diameter. Using the formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \), we can accurately calculate the perimeter by finding the radius, calculating the arc length, determining the diameter, and summing these values. This knowledge is foundational for solving geometry problems involving semicircles.
Basic Geometry of a Semicircle
A semicircle is formed when a circle is cut into two equal halves along its diameter. Understanding the basic geometry of a semicircle involves familiarizing yourself with key components and properties.
- Circle: A round plane figure whose boundary (circumference) is equidistant from a fixed point known as the center.
- Diameter: A straight line passing through the center of the circle and touching both sides of the circumference. The diameter divides the circle into two equal semicircles.
- Radius: A line segment from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. The radius is half of the diameter.
In a semicircle:
- The arc represents half of the circle's circumference.
- The straight edge (base) is the diameter of the circle.
To summarize, a semicircle combines these two segments: the curved arc, which is half the circumference of the original circle, and the straight diameter.
The formula for the area of a semicircle is derived from the area of a full circle:
where r is the radius of the circle.
The formula for the perimeter (or circumference) of a semicircle includes both the arc and the diameter:
In this formula, r is the radius, π (pi) is approximately 3.14159, and the term 2r accounts for the diameter.
Formula for the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is the total length around the boundary of the semicircle, which includes half of the circumference of a full circle plus the diameter. To understand this better, let's break down the formula.
The formula for the perimeter (P) of a semicircle is:
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]
Where:
- r is the radius of the semicircle
- \(\pi\) (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159
This formula can be understood in two parts:
- Half the Circumference of the Circle: The circumference of a full circle is \(2\pi r\). Since a semicircle is half of a circle, its curved boundary is half of the full circle's circumference, which is \(\pi r\).
- The Diameter: The straight edge of the semicircle is the diameter of the original circle, which is \(2r\).
By adding these two components together, we get the total perimeter of the semicircle:
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]
For a more simplified representation, we can factor out the radius \(r\):
\[
P = r (\pi + 2)
\]
Let's look at an example to clarify:
Example: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 5 cm.
- First, calculate the curved part: \(\pi \times 5 = 15.707 \) cm
- Then, add the diameter: \(2 \times 5 = 10 \) cm
- Therefore, the total perimeter is: \(15.707 + 10 = 25.707 \) cm
In another example, if the radius is given as 8 cm:
- Curved part: \(\pi \times 8 = 25.133 \) cm
- Diameter: \(2 \times 8 = 16 \) cm
- Total perimeter: \(25.133 + 16 = 41.133 \) cm
Understanding this formula is crucial for solving problems related to the perimeter of semicircles in various applications, such as architecture, engineering, and everyday situations.

Step-by-Step Calculation of the Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle involves a few straightforward steps. Below is a detailed guide to help you understand and compute the perimeter accurately.
-
Identify the radius of the semicircle:
The radius (r) is half of the diameter. If the diameter is given, use the formula:
\[
r = \frac{d}{2}
\]For example, if the diameter \(d\) is 10 units, the radius \(r\) will be:
\[
r = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \text{ units}
\] -
Calculate the curved part of the perimeter:
The curved part of the semicircle is half of the circumference of a full circle. The formula for the circumference of a full circle is \(2 \pi r\). Thus, the curved part is:
\[
\text{Curved part} = \pi r
\]Using our example where \(r = 5\) units, the curved part would be:
\[
\pi \times 5 \approx 15.71 \text{ units}
\] -
Calculate the straight part of the perimeter:
The straight part of the perimeter is simply the diameter of the semicircle:
\[
\text{Straight part} = 2r
\]Using our example where \(r = 5\) units, the straight part would be:
\[
2 \times 5 = 10 \text{ units}
\] -
Add the curved and straight parts together:
The total perimeter \(P\) of the semicircle is the sum of the curved part and the straight part:
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]Using our example, the total perimeter would be:
\[
P = 15.71 + 10 = 25.71 \text{ units}
\]
Thus, the perimeter of a semicircle can be calculated using the simplified formula:
\[
P = r (\pi + 2)
\]
Where \(r\) is the radius of the semicircle. For a radius of 5 units, this can be verified as:
\[
P = 5 (\pi + 2) \approx 5 \times 5.14 = 25.71 \text{ units}
\]
Examples of Perimeter Calculations
Understanding the calculation of the perimeter of a semicircle can be made clearer through practical examples. Let's explore a few scenarios:
Example 1: Perimeter of a Semicircle with Given Radius
Problem: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 cm.
- First, calculate the curved part of the semicircle (half the circumference of the full circle): \[ \text{Curved part} = \pi r = \pi \times 7 \] Using \(\pi \approx 3.14\): \[ \text{Curved part} \approx 3.14 \times 7 = 21.98 \, \text{cm} \]
- Next, add the diameter of the semicircle: \[ \text{Diameter} = 2r = 2 \times 7 = 14 \, \text{cm} \]
- Combine both parts to get the total perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \approx 21.98 + 14 = 35.98 \, \text{cm} \]
Answer: The perimeter of the semicircle is approximately 35.98 cm.
Example 2: Perimeter of a Semicircle with Given Diameter
Problem: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 12 inches.
- First, determine the radius: \[ r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{12}{2} = 6 \, \text{inches} \]
- Calculate the curved part of the semicircle: \[ \text{Curved part} = \pi r = \pi \times 6 \approx 3.14 \times 6 = 18.84 \, \text{inches} \]
- Add the diameter to get the total perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + d = 18.84 + 12 = 30.84 \, \text{inches} \]
Answer: The perimeter of the semicircle is approximately 30.84 inches.
Example 3: Finding the Radius from the Perimeter
Problem: A semicircle has a perimeter of 31.4 cm. Find its radius.
- Use the perimeter formula \( P = \pi r + 2r \) and solve for \( r \): \[ 31.4 = r(\pi + 2) \]
- Substitute \(\pi \approx 3.14\): \[ 31.4 = r(3.14 + 2) = r \times 5.14 \]
- Solve for \( r \): \[ r = \frac{31.4}{5.14} \approx 6.11 \, \text{cm} \]
Answer: The radius of the semicircle is approximately 6.11 cm.
Example 4: Perimeter of a Semicircle with Given Area
Problem: Find the perimeter of a semicircle if its area is 50 square units.
- First, find the radius using the area formula \( \text{Area} = \frac{\pi r^2}{2} \): \[ 50 = \frac{\pi r^2}{2} \]
- Solving for \( r^2 \): \[ \pi r^2 = 100 \implies r^2 = \frac{100}{\pi} \approx \frac{100}{3.14} \approx 31.85 \implies r \approx \sqrt{31.85} \approx 5.64 \]
- Calculate the curved part: \[ \text{Curved part} = \pi r \approx 3.14 \times 5.64 \approx 17.71 \]
- Add the diameter: \[ \text{Diameter} = 2r \approx 2 \times 5.64 = 11.28 \]
- Find the total perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \approx 17.71 + 11.28 = 28.99 \, \text{units} \]
Answer: The perimeter of the semicircle is approximately 28.99 units.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle involves more than just applying formulas. It's essential to grasp common pitfalls and misconceptions to ensure accuracy in your calculations.
- Ignoring the Diameter: Many forget to add the diameter when calculating the perimeter of a semicircle. Remember, the perimeter includes both the curved edge and the straight edge (diameter).
- Confusing Radius and Diameter: A frequent error is using the diameter in place of the radius or vice versa in the formula. The radius is half the diameter, which is crucial for calculating the curved part of the perimeter.
- Misapplying the Formula: Mistakes often occur in the application of the formula, such as incorrect placement of π (pi) or misunderstanding its value. Ensure you use π ≈ 3.14 or a more precise value for accurate results.
- Unit Inconsistency: Mixing units (e.g., centimeters and meters) can lead to incorrect results. Ensure all measurements are in the same unit before starting your calculation.
- Approximation Errors: While approximating π is common, using a value that is too simplified can lead to significant inaccuracies in the perimeter. Use a standard value of π for more precise calculations.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and misconceptions, you can improve the accuracy of your perimeter calculations and enhance your understanding of geometry principles.
Applications of Semicircle Perimeter in Real Life
The concept of the perimeter of a semicircle has numerous practical applications in real life. Here are some notable examples:
- Architecture and Construction: Semicircular designs are prevalent in architecture, such as archways, windows, and tunnels. Calculating the perimeter is essential for determining the length of materials needed to create these structures.
- Urban Planning: In landscaping and urban design, semicircular layouts are used for gardens, fountains, and pathways. Knowing the perimeter helps in planning and resource allocation.
- Furniture Design: Items like round tables with semicircular extensions, or semicircular benches, require precise perimeter calculations for manufacturing and material estimation.
- Education Tools: Instruments like protractors, which are semicircular, rely on accurate perimeter measurements for precise angle calculations.
- Everyday Objects: Many common items such as napkin holders, doormats, and certain kitchenware have semicircular shapes where knowing the perimeter is useful for design and production.
Here are some specific examples:
- Protractors: Used in geometry to measure angles, typically designed as a semicircle.
- Japanese Fans: Often semicircular, combining aesthetic appeal with functionality.
- Speedometers: Many analogue speedometers in vehicles are designed as semicircles, making it easier to read the gauge.
- Windows: Semicircular windows add a decorative touch to buildings and require precise perimeter calculations for fitting and installation.
- Tunnels: The curved structure of tunnels often follows a semicircular shape, crucial for stability and aesthetics.
- Tacos: A taco, when viewed from the side, forms a semicircular shape, highlighting the use of semicircles in culinary presentation.
- Napkin Holders: Often designed with semicircular ends, combining functionality with a pleasing shape.
- Doormats: Many doormats are semicircular, fitting neatly against doorways and enhancing the entrance area.
- Pizzas: A pizza cut in half creates two semicircles, a simple yet delicious example of semicircular geometry.
- The Moon: The moon in its first or last quarter phase forms a semicircular shape, a natural example observed in the sky.
Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle is crucial in these applications, ensuring accurate measurements and efficient use of materials.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Here are some practice problems to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle. Each problem is followed by a detailed solution.
Problem 1
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 cm.
- First, find the circumference of the full circle: \[ C = 2\pi r = 2 \times \pi \times 7 \] \[ C = 14\pi \]
- Calculate half of the circumference: \[ \text{Half of the circumference} = \frac{14\pi}{2} = 7\pi \]
- Add the diameter to half of the circumference: \[ \text{Diameter} = 2r = 2 \times 7 = 14 \] \[ \text{Perimeter of the semicircle} = 7\pi + 14 \] \[ \approx 21.99 + 14 \] \[ \approx 35.99 \, \text{cm} \]
Problem 2
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 10 cm.
- First, calculate the radius: \[ r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \, \text{cm} \]
- Find the circumference of the full circle: \[ C = 2\pi r = 2 \times \pi \times 5 = 10\pi \]
- Calculate half of the circumference: \[ \text{Half of the circumference} = \frac{10\pi}{2} = 5\pi \]
- Add the diameter to half of the circumference: \[ \text{Diameter} = 10 \] \[ \text{Perimeter of the semicircle} = 5\pi + 10 \] \[ \approx 15.71 + 10 \] \[ \approx 25.71 \, \text{cm} \]
Problem 3
If the perimeter of a semicircle is 36 units, find the radius.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \] Given \( P = 36 \): \[ 36 = \pi r + 2r \]
- Factor out the radius \( r \): \[ 36 = r(\pi + 2) \]
- Solve for \( r \): \[ r = \frac{36}{\pi + 2} \] \[ \approx \frac{36}{3.14 + 2} \] \[ \approx \frac{36}{5.14} \] \[ \approx 7 \, \text{units} \]
Problem 4
Find the circumference and area of a semicircle whose diameter is 21 cm.
- Calculate the radius: \[ r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{21}{2} = 10.5 \, \text{cm} \]
- Find the circumference of the semicircle: \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi r + 2r \] \[ \text{Perimeter} = \pi \times 10.5 + 2 \times 10.5 \] \[ \approx 3.14 \times 10.5 + 21 \] \[ \approx 32.97 + 21 \] \[ \approx 53.97 \, \text{cm} \]
- Calculate the area of the semicircle: \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2}\pi r^2 \] \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 3.14 \times (10.5)^2 \] \[ \text{Area} \approx \frac{1}{2} \times 3.14 \times 110.25 \] \[ \text{Area} \approx \frac{1}{2} \times 346.39 \] \[ \text{Area} \approx 173.2 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
Problem 5
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 15 cm.
- First, find the circumference of the full circle: \[ C = 2\pi r = 2 \times \pi \times 15 = 30\pi \]
- Calculate half of the circumference: \[ \text{Half of the circumference} = \frac{30\pi}{2} = 15\pi \]
- Add the diameter to half of the circumference: \[ \text{Diameter} = 2r = 2 \times 15 = 30 \] \[ \text{Perimeter of the semicircle} = 15\pi + 30 \] \[ \approx 47.12 + 30 \] \[ \approx 77.12 \, \text{cm} \]
FAQs on Semicircle Perimeter
Here are some frequently asked questions about finding the perimeter of a semicircle, along with detailed answers to help you understand the concept better:
- Q1: What is the perimeter of a semicircle?
- Q2: How do you calculate the perimeter of a semicircle?
- Measure the radius \( r \) of the semicircle.
- Calculate the curved part using \( \pi r \).
- Add the diameter \( 2r \) to the curved part.
- Combine these to get the perimeter: \( P = \pi r + 2r \).
- Q3: What if I only know the diameter?
- Q4: Is the perimeter of a semicircle the same as the circumference of a semicircle?
- Q5: Can the formula for the perimeter of a semicircle be used for a quarter circle?
- Q6: Why is it important to know the perimeter of a semicircle?
The perimeter of a semicircle is the sum of the straight edge (diameter) and the curved edge (half the circumference of the circle). The formula is: \( P = \pi r + 2r \) where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle.
To calculate the perimeter of a semicircle:
If you know the diameter \( d \), you can still find the perimeter by using the relationship \( d = 2r \). So the formula becomes: \( P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \).
No, the circumference of a semicircle refers only to the curved part, which is \( \pi r \). The perimeter includes the diameter as well, making it \( \pi r + 2r \).
No, the formula for a quarter circle is different because it involves a quarter of the circumference plus two radii. For a quarter circle, the perimeter is: \( P = \frac{\pi r}{2} + 2r \).
Knowing the perimeter of a semicircle is essential in various applications such as architecture, engineering, and even everyday tasks like crafting and construction where precise measurements are needed.
Conclusion and Recap
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a semicircle is a fundamental skill in geometry that has practical applications in various fields. Here's a summary of the key points covered in this guide:
- Definition: A semicircle is half of a circle, bounded by a diameter and the corresponding arc.
- Formula: The formula for the perimeter of a semicircle is: \[ P = \pi r + 2r \] where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle. Alternatively, if the diameter \( d \) is known, the formula can be written as: \[ P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \]
- Steps to Calculate:
- Measure or identify the radius \( r \) or diameter \( d \) of the semicircle.
- Calculate the curved part of the perimeter using \( \pi r \) if you have the radius, or \( \frac{\pi d}{2} \) if you have the diameter.
- Add the length of the diameter \( 2r \) if you have the radius, or simply the diameter \( d \).
- Combine these parts to get the total perimeter.
- Example: For a semicircle with a radius of 5 units:
- Curved part: \( \pi \times 5 = 15.7 \) units (using \( \pi \approx 3.14 \))
- Straight part (diameter): \( 2 \times 5 = 10 \) units
- Total perimeter: \( 15.7 + 10 = 25.7 \) units
- Common Mistakes: Ensure not to confuse the perimeter with the circumference. Remember, the perimeter of a semicircle includes both the curved edge and the straight edge (diameter).
- Applications: Knowing how to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle is useful in real-world contexts such as construction, landscaping, design, and various engineering tasks.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently calculate the perimeter of any semicircle. Practice with different examples to solidify your understanding and avoid common errors.
Xem video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của một nửa hình tròn từ Corbettmaths, bài giảng rõ ràng và dễ hiểu.
Chu vi của một nửa hình tròn - Corbettmaths
READ MORE:
Xem video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của một nửa hình tròn, bài giảng rõ ràng và dễ hiểu.
Chu vi của một nửa hình tròn