Topic finding perimeter of semicircle: Finding the perimeter of a semicircle is an essential skill in geometry, blending the concepts of circumference and linear measurement. In this guide, we'll explore step-by-step methods, practical examples, and real-world applications to help you master this calculation with ease and confidence.
Table of Content
- Finding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Introduction to Semicircles
- Understanding Perimeter and Circumference
- Formula for Perimeter of a Semicircle
- Step-by-Step Calculation Methods
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applications in Real Life
- Related Geometric Concepts
- Interactive Tools and Calculators
- Further Reading and Resources
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi nửa hình tròn một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết. Hãy khám phá cách thực hiện bài toán này cùng chúng tôi!
Finding the Perimeter of a Semicircle
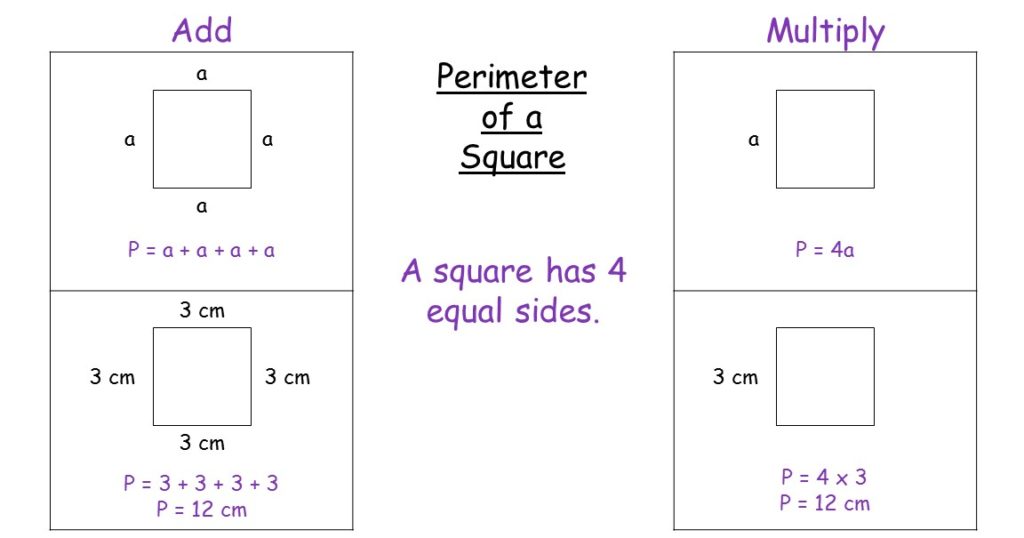
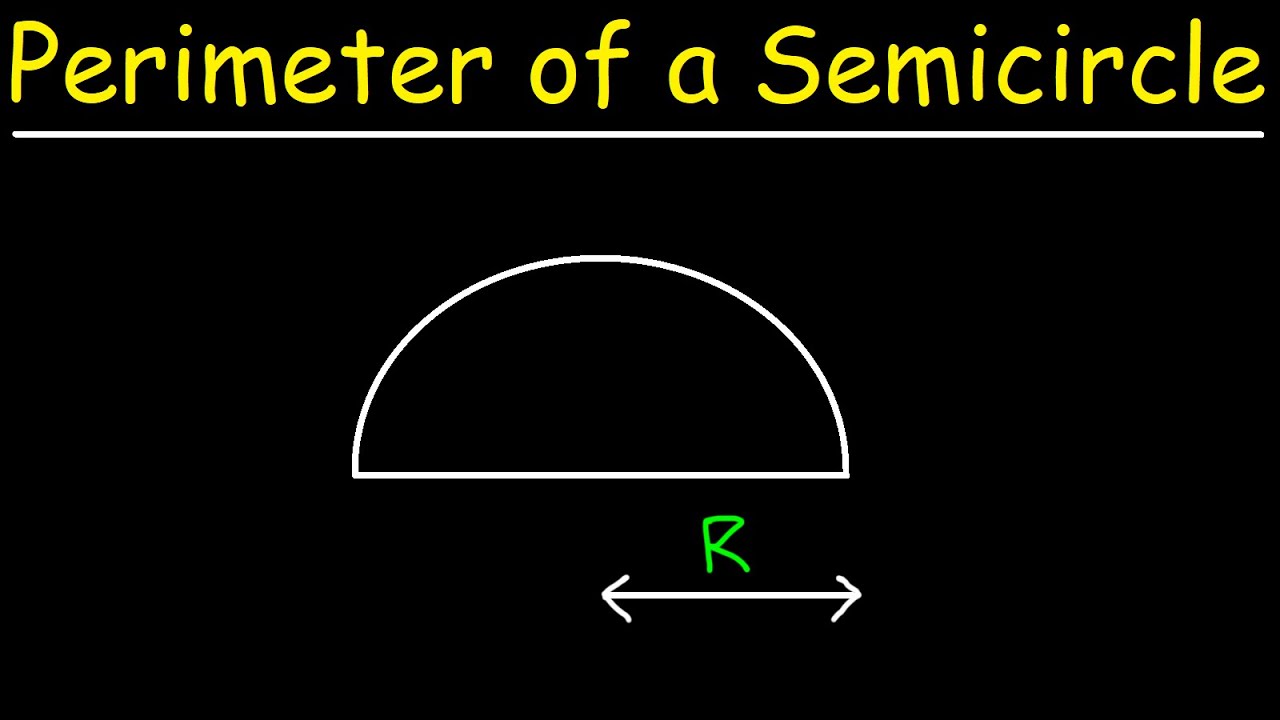
A semicircle is a half of a circle formed by cutting a whole circle along its diameter. The perimeter (or circumference) of a semicircle includes the curved part of the semicircle and the diameter.
Formulas to Calculate the Perimeter of a Semicircle
The formula for the perimeter of a semicircle depends on whether the radius or the diameter is given:
- If the diameter (d) is given, use the formula:
\( P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \) - If the radius (r) is given, use the formula:
\( P = r (\pi + 2) \)
Example Problems
Example 1: Perimeter with Diameter Given
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 10 units.
- Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \)
- Use the formula \( P = \frac{\pi d}{2} + d \):
\( P = \frac{3.14 \times 10}{2} + 10 = 15.7 + 10 = 25.7 \) units
Example 2: Perimeter with Radius Given
Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 8 units.
- Use the formula \( P = r (\pi + 2) \):
\( P = 8 (3.14 + 2) = 8 \times 5.14 = 41.12 \) units
Additional Notes
The perimeter of a semicircle is the sum of half the circumference of the full circle and the diameter. This includes the curved part (half the circumference) and the straight part (the diameter).
| Parameter | Formula |
|---|---|
| Area | \(\frac{\pi r^2}{2}\) |
| Perimeter (using diameter) | \(\frac{\pi d}{2} + d\) |
| Perimeter (using radius) | \(r (\pi + 2)\) |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Semicircles
A semicircle is a geometric shape that represents half of a circle. It is formed by cutting a whole circle along its diameter, resulting in a shape that includes a straight edge (the diameter) and a curved edge (the arc).
The properties of a semicircle are important to understand as they lay the foundation for various calculations, including perimeter and area. Here are some key characteristics:
- Diameter (d): The straight line that passes through the center of the semicircle and connects two points on the boundary.
- Radius (r): Half of the diameter, the radius is the distance from the center of the semicircle to any point on the curved edge.
- Arc: The curved part of the boundary of the semicircle.
- Center: The midpoint of the diameter and the point from which the radius extends to the arc.
The perimeter (or circumference) of a semicircle is the sum of the length of the diameter and the length of the arc. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter requires knowledge of both the diameter and the properties of the circle.
In mathematical terms, the length of the arc of a semicircle is half the circumference of a full circle. The circumference (C) of a full circle is given by the formula:
\( C = 2 \pi r \)
Since the arc of a semicircle is half of the full circle's circumference, the length of the arc is:
\( \text{Arc length} = \pi r \)
Therefore, the perimeter (P) of a semicircle, including the diameter, is calculated as:
\( P = \pi r + 2r \)
where \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle. This formula is fundamental in understanding and solving problems related to the perimeter of a semicircle.
Understanding Perimeter and Circumference
When studying semicircles, it's essential to understand the concepts of perimeter and circumference, as they are fundamental to many geometric calculations.
Perimeter of a Semicircle: The perimeter of a semicircle is the total length around its boundary. Unlike a full circle, the semicircle has a straight edge along its diameter, which must be included in the perimeter calculation.
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a semicircle is derived by adding the length of the diameter to half the circumference of the full circle:
Perimeter \( P \) of a semicircle with radius \( r \) is given by:
\[
P = \pi r + 2r
\]
Alternatively, if the diameter \( d \) is known, the formula is:
\[
P = \frac{1}{2} \pi d + d
\]
Here, \( \pi \) (pi) is approximately 3.14.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Semicircle:
- Identify the radius or diameter: Determine whether you are given the radius or the diameter of the semicircle. Remember that the diameter is twice the radius (\( d = 2r \)).
- Use the appropriate formula:
- If you have the radius: \( P = \pi r + 2r \)
- If you have the diameter: \( P = \frac{1}{2} \pi d + d \)
- Perform the calculation: Substitute the known values into the formula and calculate the perimeter. Ensure to use the value of \( \pi \) as 3.14 or use a calculator for more precision.
Example Problems:
- Example 1: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 10 units.
- Calculate the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \)
- Substitute into the formula: \( P = \pi \cdot 5 + 2 \cdot 5 = 3.14 \cdot 5 + 10 = 25.7 \) units
- Example 2: Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 7 cm.
- Use the formula: \( P = \pi \cdot 7 + 2 \cdot 7 = 3.14 \cdot 7 + 14 = 35.98 \) cm
Understanding these concepts allows you to solve various geometric problems involving semicircles efficiently.
Formula for Perimeter of a Semicircle
The perimeter of a semicircle is a combination of the curved edge (half of the circumference of a full circle) and the straight edge (the diameter). To calculate the perimeter of a semicircle, you can use the following formula:
Formula:
\[ P = r(\pi + 2) \]
Where:
- \( P \) is the perimeter of the semicircle
- \( r \) is the radius of the semicircle
- \( \pi \) (pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159
The formula can also be expressed in terms of the diameter \( d \) (since \( d = 2r \)):
\[ P = \frac{1}{2} \pi d + d \]
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- Determine the radius (r) or diameter (d) of the semicircle.
- Calculate the curved part of the perimeter, which is half of the circumference of the full circle: \( \frac{1}{2} \pi d \) or \( \pi r \).
- Add the length of the diameter to the curved part: \( \frac{1}{2} \pi d + d \) or \( \pi r + 2r \).
- Simplify the expression to get the final perimeter: \( P = r(\pi + 2) \).
Example Problems:
1. Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a diameter of 10 units.
- First, find the radius: \( r = \frac{d}{2} = \frac{10}{2} = 5 \).
- Plug the radius into the formula: \( P = 5(\pi + 2) \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 5(3.14159 + 2) = 5(5.14159) = 25.70795 \).
2. Find the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 8 units.
- Plug the radius directly into the formula: \( P = 8(\pi + 2) \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 8(3.14159 + 2) = 8(5.14159) = 41.13272 \).
3. A semicircle has a perimeter of 27 units. What is the radius?
- Use the formula \( P = r(\pi + 2) \) and solve for r: \( 27 = r(3.14159 + 2) \).
- Rearrange to find \( r \): \( r = \frac{27}{3.14159 + 2} = \frac{27}{5.14159} = 5.251 \).
Understanding these formulas and steps helps in calculating the perimeter of a semicircle accurately for various applications.
Step-by-Step Calculation Methods
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle involves understanding both the linear and curved components of the shape. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
-
Understand the Components: The perimeter of a semicircle consists of the straight edge (diameter) and the curved edge (half of the circumference).
-
Identify the Radius: Determine the radius (R) of the semicircle. If you have the diameter (D), remember that the radius is half of the diameter.
R = \frac{D}{2} -
Calculate the Diameter: Multiply the radius by 2 to get the diameter.
D = 2R -
Calculate the Curved Edge: Find the circumference of the full circle and then take half of it to get the length of the curved edge.
The circumference of a full circle is
C = 2\pi R, so the curved edge of the semicircle is\frac{2\pi R}{2} = \pi R. -
Sum the Components: Add the diameter and the length of the curved edge to get the total perimeter of the semicircle.
Perimeter = \pi R + 2R -
Factor for Simplification: Combine like terms to simplify the formula.
Perimeter = R(\pi + 2)
Example Calculation:
Let's calculate the perimeter of a semicircle with a radius of 5 units:
- Identify the radius (R):
R = 5units. - Calculate the diameter (D):
D = 2 \times 5 = 10units. - Calculate the curved edge:
\pi R = \pi \times 5 = 15.71units (using \(\pi \approx 3.14\)). - Add the diameter and the curved edge:
Perimeter = 15.71 + 10 = 25.71units.
Therefore, the perimeter of the semicircle is approximately 25.71 units.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
- Confusing radius with diameter. Remember, the radius is half the diameter.
- Forgetting to add the diameter to the curved part when calculating the perimeter.
- Using incorrect values for \(\pi\). For better accuracy, use more precise values or the \(\pi\) function on a calculator.
- Mixing up units. Ensure consistency in the units of measurement throughout the calculation.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle is a straightforward process, but certain common mistakes can lead to errors. Here are some key pitfalls to watch out for:
- Omitting the Diameter: Remember that the perimeter of a semicircle includes both the curved part and the straight diameter. The formula is \( P = r(\pi + 2) \). Forgetting to add the diameter can lead to incorrect results.
- Confusing Radius and Diameter: Ensure you are using the correct measurement in the formula. The radius is half the diameter, so double-check that you are substituting the right value.
- Incorrect Value of π: While 3.14 is a common approximation for π, using a more precise value (like 3.14159) can improve accuracy. Be consistent with the level of precision required for your calculation.
- Unit Conversion Errors: Make sure all measurements are in the same unit system. Converting units incorrectly can significantly affect the final answer.
- Rounding Errors: Be careful with rounding during intermediate steps. Consistently rounding can help maintain accuracy, but over-rounding can distort the result.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, you can improve your accuracy and confidence when calculating the perimeter of a semicircle.
Applications in Real Life
The concept of the perimeter, including that of a semicircle, finds various applications in everyday life. Here are some practical scenarios where calculating the perimeter is essential:
-
Architecture and Construction:
In construction projects, knowing the perimeter is crucial for determining the amount of materials needed. For example, when designing a semicircular garden bed or a decorative archway, the perimeter helps in calculating the length of the border material required.
-
Gardening:
When creating garden plots with semicircular shapes, understanding the perimeter is necessary to purchase the correct amount of fencing or edging materials to enclose the area.
-
Urban Planning:
In urban planning and landscape design, semicircular pathways or water features often require perimeter calculations to estimate the length of paving materials or the borders for these structures.
-
Sports and Recreation:
Many sports fields and recreational areas use semicircular designs. For instance, the arc of a basketball court's three-point line or the curved edges of a running track involve calculating the perimeter to ensure proper measurements and material usage.
-
Art and Design:
Artists and designers frequently use semicircles in their work, from sculptures to installation art. Knowing the perimeter helps in creating accurate and proportionate pieces.
-
Land Surveying:
Surveyors often encounter semicircular plots of land or property boundaries. Calculating the perimeter is essential for determining property lines and planning land use efficiently.
-
Event Planning:
In event planning, particularly for outdoor events, semicircular seating arrangements or stage designs require perimeter calculations to ensure enough seating and structural support materials.
-
Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, especially for products with curved edges or semicircular components, calculating the perimeter helps in material estimation and cutting precision.
These applications demonstrate the importance of understanding and accurately calculating the perimeter of semicircles in various fields, ensuring efficiency and precision in both planning and execution.
Related Geometric Concepts
Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle involves familiarity with several related geometric concepts. Here, we will explore these concepts to provide a comprehensive understanding.
- Circle: A circle is a simple closed shape where all points are an equal distance from the center. Key properties include the radius, diameter, and circumference.
- Radius and Diameter: The radius of a circle is the distance from the center to any point on the circle. The diameter is twice the radius and spans from one point on the circle through the center to another point on the circle.
- Perimeter (Circumference): The circumference of a circle is the distance around the circle. The formula is \( C = 2\pi r \), where \( r \) is the radius.
- Semicircle: A semicircle is half of a circle, formed by dividing the circle along the diameter. The perimeter of a semicircle includes half the circumference of the circle plus the diameter, given by \( \pi r + 2r \).
- Arc: An arc is any part of the circumference of a circle. In a semicircle, the arc represents half of the circle's circumference.
- Quadrants and Sectors: A quadrant is one-fourth of a circle, while a sector is a portion of a circle defined by two radii and the connecting arc.
These concepts are fundamental in geometry and are interconnected. For instance, understanding the radius and diameter is essential for calculating the circumference of a circle, which in turn helps in finding the perimeter of a semicircle. Additionally, the idea of arcs and sectors extends to more complex geometric shapes and problems.
| Concept | Definition | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Circle | A shape with all points equidistant from the center | \( C = 2\pi r \) |
| Radius | Distance from the center to the circle | \( r \) |
| Diameter | Twice the radius | \( d = 2r \) |
| Semicircle | Half of a circle | \( \pi r + 2r \) |
| Arc | Part of the circumference | \( \text{Length} = \theta r \) (for angle \( \theta \) in radians) |
| Sector | Portion of a circle defined by two radii and an arc | \( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} r^2 \theta \) (for angle \( \theta \) in radians) |
Interactive Tools and Calculators
Calculating the perimeter of a semicircle can be streamlined using various interactive tools and calculators available online. These tools provide a user-friendly interface to quickly compute the perimeter by simply entering the required parameters. Below are a few notable examples:
-
Semicircle Perimeter Calculator by Savvy Calculator
This tool allows users to enter the radius of the semicircle to instantly calculate the perimeter. The formula used is \( P = \pi \cdot r + 2 \cdot r \). Simply input the radius value, and the calculator will provide the result.
-
Areavolumecalculator.com
This website provides a detailed semicircle perimeter calculator that not only performs the calculation but also explains the steps involved. Users can enter the radius, and the tool uses the formula \( P = (\pi + 2) \cdot r \) to compute the perimeter. The platform also offers manual calculation methods and example problems for better understanding.
-
Swiftutors.com
Swiftutors offers an easy-to-use semicircle perimeter calculator. Users need to enter the radius, and the tool quickly calculates the perimeter using the formula \( P = \pi \cdot r + 2 \cdot r \). This tool is particularly useful for quick computations and educational purposes.
These tools are designed to simplify the process of finding the perimeter of a semicircle, making them ideal for students, teachers, and professionals who need accurate and fast results. The calculators typically require only the radius as input and provide immediate outputs, reducing the chances of manual calculation errors.
In addition to calculators, many of these platforms offer supplementary educational resources such as example problems, step-by-step solutions, and explanations of the underlying mathematical concepts. These resources can enhance learning and provide deeper insights into geometric calculations.
Further Reading and Resources
Understanding the perimeter of a semicircle is just one aspect of geometry. To deepen your knowledge and explore related concepts, here are some valuable resources and tools:
- Textbooks and Guides
Geometry: A Comprehensive Course - This textbook covers all fundamental aspects of geometry, including circles and semicircles. It provides in-depth explanations and numerous practice problems.
The Art of Problem Solving: Geometry - Aimed at students preparing for math competitions, this book delves into more complex geometric concepts with a focus on problem-solving techniques.
- Online Courses and Tutorials
- Offers free, comprehensive lessons on various geometric topics, including semicircles, with interactive exercises and instructional videos.
- A selection of courses from top universities that cover both basic and advanced geometric concepts, available for free or with a paid certificate.
- Interactive Tools and Calculators
- An online tool for graphing and exploring geometric shapes, including semicircles. It helps visualize the relationship between different geometric properties.
- A dynamic mathematics software that combines geometry, algebra, and calculus, allowing you to construct and analyze geometric figures interactively.
- Practice Problems and Worksheets
- Offers a variety of printable worksheets for practicing geometry problems, including calculating the perimeter and area of semicircles.
- Provides engaging worksheets for different grade levels, designed to reinforce geometric concepts through practice.
- Academic Articles and Papers
- Access a vast library of academic papers and articles on various geometric topics. Search for specific studies on semicircles and their properties.
- A freely accessible web search engine that indexes scholarly articles across various disciplines, including geometry. Find research papers on the mathematical properties of semicircles.
Hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi nửa hình tròn một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết. Hãy khám phá cách thực hiện bài toán này cùng chúng tôi!
Cách Tính Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn tính chu vi nửa hình tròn từ Corbettmaths. Hãy học cách thực hiện phép tính này một cách chính xác và dễ hiểu!
Chu Vi Nửa Hình Tròn - Corbettmaths