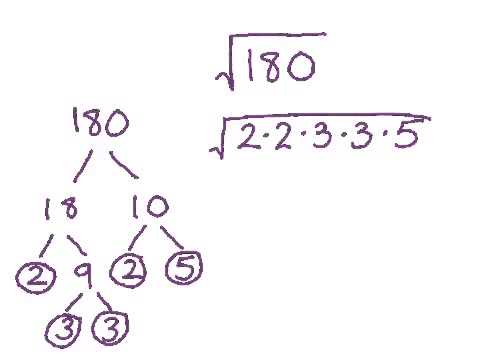Topic 24 square root simplified: Understanding the simplified square root of 24 is essential for various mathematical applications. The square root of 24, expressed as 2√6, is derived using prime factorization and can be approximated as 4.898 in decimal form. This guide will walk you through the process of simplifying √24 and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Table of Content
- Simplifying the Square Root of 24
- Introduction
- Understanding Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method
- Exact and Decimal Forms
- Why the Square Root of 24 is an Irrational Number
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 24: Căn(24). Video này giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách thực hiện từng bước để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 24.
Simplifying the Square Root of 24
The square root of 24 can be simplified by following a step-by-step process to find its simplest radical form. Here is a detailed explanation:
Step-by-Step Simplification
- Factor the number 24 into its prime factors: \(24 = 2^3 \times 3\).
- Group the factors into pairs of squares: \(24 = (2^2) \times 6\).
- Rewrite the expression using the square root: \(\sqrt{24} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 6}\).
- Take the square root of the square number: \(\sqrt{2^2} = 2\).
- Multiply the result by the remaining factor inside the square root: \(2\sqrt{6}\).
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 24 is:
\(\sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6}\)
Decimal Form
In decimal form, the square root of 24 is approximately:
\(\sqrt{24} \approx 4.89898\)
Additional Information
- The square root of 24 is an irrational number.
- 24 is not a perfect square, hence its square root is not a whole number.
- The simplified radical form provides an exact representation of the square root.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 24 can be simplified to \(2\sqrt{6}\). Simplifying square roots involves finding the prime factors of the number and then simplifying them under the radical sign. In this case, the prime factorization of 24 is \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3\), which can be written as \(2^2 \times 6\). Taking the square root of \(2^2\) gives us 2, leaving us with \(2\sqrt{6}\). This process helps to simplify the square root to its simplest radical form.
-
Step-by-Step Simplification:
- Identify the prime factors of 24: \(24 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3\).
- Group the prime factors: \(24 = 2^2 \times 6\).
- Simplify under the square root: \(\sqrt{24} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 6}\).
- Take the square root of the square number: \(2\sqrt{6}\).
Properties of the Square Root of 24:
- The square root of 24 is an irrational number.
- In decimal form, it is approximately 4.899.
- It is not a perfect square, as 24 does not have an integer square root.
Understanding Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 24 is represented as √24. This means that if you multiply √24 by itself, you get 24.
Mathematically, the square root of 24 can be simplified. The number 24 can be factored into its prime factors: 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3. Using these factors, the square root can be rewritten:
- First, write 24 as a product of its prime factors: \( 24 = 2^2 \times 2 \times 3 \)
- Next, separate the perfect square from the non-perfect square: \( \sqrt{24} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 6} \)
- Then, take the square root of the perfect square out of the radical: \( \sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6} \)
This gives us the simplified form of the square root of 24 as \( 2\sqrt{6} \). In decimal form, this is approximately equal to 4.898979485.
Understanding the concept of square roots helps in various mathematical applications, including solving equations and understanding geometric properties.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a systematic way to simplify the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. Here's a step-by-step guide to simplify the square root of 24 using this method:
- Find the prime factors of 24:
- 24 can be factored into 2 × 2 × 2 × 3.
- Express the number under the square root using its prime factors:
- \(\sqrt{24} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3}\)
- Group the prime factors into pairs:
- \(\sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 3}\)
- Simplify by taking out the pairs from under the square root:
- \(\sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{6} = 2\sqrt{6}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{24}\) is \(2\sqrt{6}\). This method not only helps in simplifying the square root but also provides a clear understanding of the factorization process involved.
Exact and Decimal Forms
The square root of 24 can be expressed in both exact and decimal forms. Understanding these forms helps in various mathematical calculations and practical applications.
- Exact Form:
The exact form of the square root of 24 is derived using prime factorization. Breaking down 24, we have:
- 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
We can pair the twos and take one out of the radical:
√24 = √(22 × 6) = 2√6
- Decimal Form:
The decimal form is obtained using a calculator or long division method. The square root of 24 is approximately:
√24 ≈ 4.899
This form is useful in practical scenarios where an approximate value is sufficient.
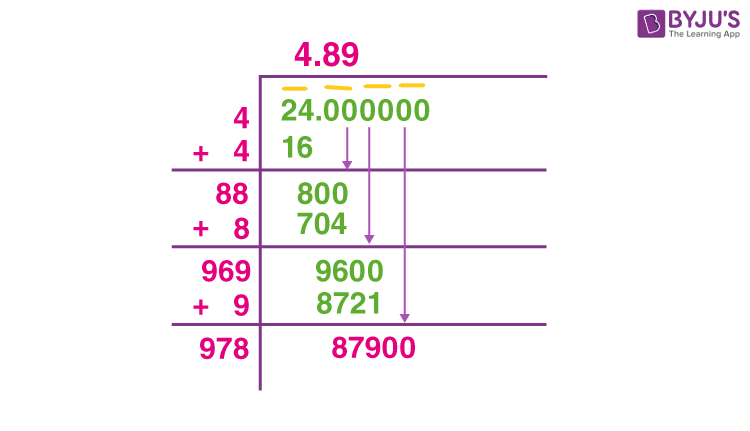
Why the Square Root of 24 is an Irrational Number
To understand why the square root of 24 is an irrational number, we need to delve into the nature of square roots and the definition of irrational numbers.
An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, i.e., it cannot be written as a/b where a and b are integers and b is not zero. Irrational numbers have non-terminating and non-repeating decimal expansions.
Let's examine the square root of 24:
-
Prime Factorization Method:
We start by finding the prime factorization of 24:
\(24 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3\)
Grouping the prime factors into pairs gives us:
\(24 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 3 = 2^2 \times 2 \times 3\)
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
\(\sqrt{24} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 3}\)
This simplifies to:
\(\sqrt{24} = 2 \sqrt{6}\)
-
Nature of the Square Root of 6:
Next, we need to understand \(\sqrt{6}\). The number 6 is not a perfect square, and its square root is known to be an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed exactly as a fraction and has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion.
Since \(\sqrt{6}\) is irrational, multiplying it by 2 does not change its irrational nature:
\(2 \sqrt{6}\) is also irrational.
-
Decimal Representation:
The decimal representation of \(\sqrt{24}\) further confirms its irrationality:
\(\sqrt{24} \approx 4.898979485\ldots\)
This decimal is non-terminating and non-repeating, which is a key characteristic of irrational numbers.
Therefore, because \(\sqrt{6}\) is irrational and the decimal expansion of \(\sqrt{24}\) is non-terminating and non-repeating, we conclude that the square root of 24 is an irrational number.
Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding how to simplify the square root of 24 can be solidified through various examples and practice problems. Below are detailed examples and practice problems to help you master this concept.
Examples
-
Example 1: Simplify the square root of 24.
Solution:
- Factor 24 into its prime factors: \(24 = 2^3 \times 3\).
- Group the factors into pairs: \(\sqrt{24} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 6}\).
- Simplify the expression: \(\sqrt{2^2 \times 6} = 2\sqrt{6}\).
- Thus, the simplified form is \(2\sqrt{6}\).
-
Example 2: Find the value of \(7 \times \sqrt{24}\).
Solution:
- First, simplify \(\sqrt{24}\): \(2\sqrt{6}\).
- Multiply: \(7 \times 2\sqrt{6} = 14\sqrt{6}\).
- Thus, the value is \(14\sqrt{6}\).
-
Example 3: Calculate the length of a side of a square with an area of 24 square centimeters.
Solution:
- Given the area \(A = 24 \, \text{cm}^2\).
- The length of a side is the square root of the area: \(\text{Side} = \sqrt{24}\).
- Simplify \(\sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6}\).
- Thus, the length of the side is \(2\sqrt{6}\) cm.
-
Example 4: Simplify \((\sqrt{24})^3\).
Solution:
- First, simplify \(\sqrt{24} = 2\sqrt{6}\).
- Raise to the power of 3: \((2\sqrt{6})^3 = 2^3 \times (\sqrt{6})^3 = 8 \times 6\sqrt{6}\).
- Thus, the simplified form is \(48\sqrt{6}\).
Practice Problems
Try solving the following problems to test your understanding. Check your answers to verify your solutions.
- What is the simplified form of \(\sqrt{50}\)?
- Find the value of \(5 \times \sqrt{24}\).
- Calculate the length of a side of a square with an area of 50 square centimeters.
- Simplify \((\sqrt{32})^2\).
- Find the value of \(3 \times (\sqrt{24})^2\).
These examples and problems provide a comprehensive way to practice simplifying square roots and understanding their applications. By solving these problems, you'll enhance your skills and confidence in working with square roots.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When simplifying the square root of 24, several common mistakes can occur. Being aware of these can help you avoid errors and ensure accurate results.
-
Incorrect Factorization:
One frequent mistake is not breaking down the number 24 into its correct prime factors. The prime factorization of 24 is \(2^3 \times 3\), not just 2 and 12.
-
Adding Square Roots Incorrectly:
Another common error is assuming that the square root of a sum is equal to the sum of the square roots, which is incorrect. For instance, \(\sqrt{24}\) is not equal to \(\sqrt{4 + 20}\) or \(\sqrt{16 + 8}\).
Remember, \(\sqrt{a + b} \neq \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}\).
-
Improper Distribution:
Ensure you distribute multiplication across addition correctly when dealing with square roots. For example, \(2(\sqrt{6} + \sqrt{4}) = 2\sqrt{6} + 2\sqrt{4}\), not \(2\sqrt{10}\).
-
Misapplying Simplification Rules:
Some students mistakenly simplify square roots without considering perfect squares. For instance, \(\sqrt{24} = \sqrt{4 \times 6} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{6} = 2\sqrt{6}\).
-
Incorrectly Canceling Terms:
Be cautious when canceling terms in fractions. You can only cancel terms if they appear in every term of the numerator and the denominator. For example, \(\frac{\sqrt{24}}{2} \neq \sqrt{12}\). Instead, it simplifies to \(\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{2} = \sqrt{6}\).
-
Forgetting to Rationalize the Denominator:
When dealing with fractions involving square roots, always remember to rationalize the denominator. For example, \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{24}}\) should be rationalized to \(\frac{\sqrt{24}}{24}\) and further simplified to \(\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{24} = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{12}\).
By keeping these common mistakes in mind, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and simplify the square root of 24 accurately.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the value of \(\sqrt{24}\) times \(\sqrt{24}\)?
The value of \(\sqrt{24} \times \sqrt{24} = 24\).
-
Is 24 a perfect square root?
No, 24 is not a perfect square. There is no natural number that can be squared to result in 24.
-
What are the square roots of -24?
The square roots of negative numbers are imaginary. For -24, these are expressed as \(\sqrt{-24} = \pm 2\sqrt{6}i\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit.
-
Is the square root of 24 a rational number?
No, the square root of 24 is not a rational number. It is an irrational number because its decimal representation is non-terminating and cannot be expressed as a fraction.
-
Can we find the square root of 24 by the repeated subtraction method?
No, the repeated subtraction method only works for perfect squares, and 24 is not a perfect square.

Conclusion
The process of simplifying the square root of 24 helps us understand fundamental concepts in mathematics such as prime factorization and properties of irrational numbers. The simplified form of the square root of 24 is \( 2\sqrt{6} \), which offers both an exact and a decimal approximation (approximately 4.899).
By learning how to simplify square roots, we can make complex calculations more manageable and enhance our problem-solving skills. Remember, while 24 is not a perfect square, its square root can still be expressed in a simplified radical form. This understanding is crucial for higher-level math and various practical applications in fields such as geometry, engineering, and physics.
Whether using the prime factorization method, estimation, or calculators, knowing multiple approaches to finding square roots broadens our mathematical toolkit. Always double-check your work to avoid common mistakes and reinforce your learning through practice problems.
Overall, mastering the simplification of square roots, including those of non-perfect squares like 24, is an essential step in advancing your mathematical proficiency and confidence.
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 24: Căn(24). Video này giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách thực hiện từng bước để đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 24.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Của 24: Căn(24)
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 24 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 24