Topic what's the square root of 36: Have you ever wondered, "What's the square root of 36?" In this article, we will not only reveal the answer but also delve into its significance, methods to calculate it, and real-world applications. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of square roots and uncover why the square root of 36 is more than just a number.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 36
- Introduction to Square Roots
- What is the Square Root of 36?
- Mathematical Definition and Properties
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 36
- Historical Context and Significance
- Common Misconceptions and Errors
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Summary and Key Takeaways
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu về căn bậc hai của 36 trong video này để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm toán học quan trọng này.
Square Root of 36
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 36 can be represented as:
Steps to Find the Square Root of 36
- Identify the number you want to find the square root of, which is 36.
- Find a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 36.
- Since \(6 \times 6 = 36\), the square root of 36 is 6.
Properties of the Square Root of 36
- The square root of 36 is a rational number.
- It is also an integer.
- The square root function is the inverse of squaring a number.
Mathematical Representation
The square root of 36 can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{36} = 6
\]
Applications of the Square Root of 36
Understanding the square root of 36 is useful in various mathematical contexts, including:
- Geometry, for finding the side length of a square with area 36 square units.
- Algebra, in solving quadratic equations.
- Real-world measurements, such as calculating distances.
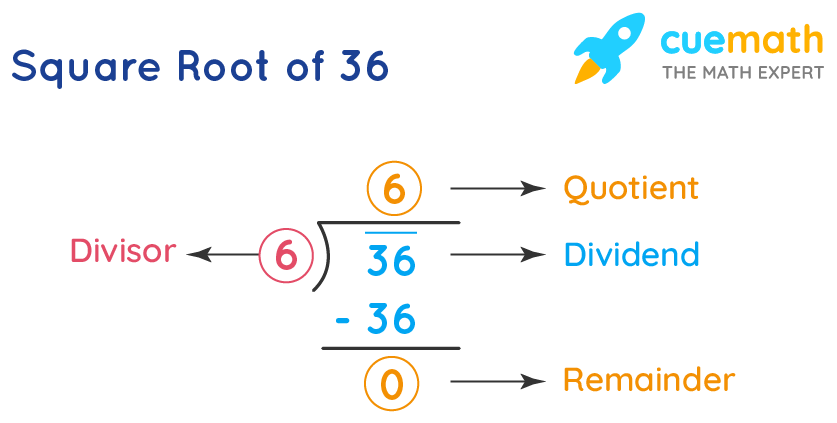
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Understanding square roots is fundamental in mathematics, as they play a crucial role in various mathematical concepts and real-world applications.
Here are some key points to understand about square roots:
- The square root of a number x is denoted as \( \sqrt{x} \).
- Square roots are the inverse operation of squaring a number.
- Every positive number has two square roots: a positive and a negative root. For example, the square roots of 36 are 6 and -6, since \( 6^2 = 36 \) and \( (-6)^2 = 36 \).
- The principal (or positive) square root is usually considered the primary root.
Let's take a closer look at how to calculate and understand square roots step by step:
- Identify the number you want to find the square root of, known as the radicand.
- Determine which number, when multiplied by itself, equals the radicand. This number is the square root.
- If the radicand is a perfect square (like 36), its square root is an integer.
- If the radicand is not a perfect square, the square root will be an irrational number, which can be approximated using various methods.
Square roots are widely used in different areas such as geometry, algebra, and even in real-life situations like measuring distances or areas. By mastering the concept of square roots, you can enhance your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities.
What is the Square Root of 36?
The square root of 36 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 36. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
\[
\sqrt{36} = 6
\]
Here's a step-by-step explanation of how we arrive at this value:
- Understand the Concept: The square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y \times y = x \). For 36, we are looking for a number that, when squared, equals 36.
- Identify Perfect Squares: 36 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. \( 6 \times 6 = 36 \).
- Verification: To verify, we can calculate:
\[
6^2 = 36
\]
\[
(-6)^2 = 36
\]Therefore, both 6 and -6 are square roots of 36. However, the principal square root is 6.
- Properties of the Square Root:
- The square root of a positive number has both a positive and a negative root.
- The principal square root is the positive root, denoted by \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \).
- The negative square root is written as \( -\sqrt{36} = -6 \).
In summary, the square root of 36 is 6, and this value is significant in various mathematical calculations and real-world applications.
Mathematical Definition and Properties
The square root of a number is a fundamental concept in mathematics, denoted by the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \). It represents a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. Let's delve into the mathematical definition and properties of the square root of 36.
Mathematical Definition:
The square root of 36 is expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{36} = 6
\]
This means that 6 is the number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 36:
\[
6 \times 6 = 36
\]
Properties of Square Roots:
- Non-negative Principal Root: The principal square root of a non-negative number is always non-negative. For 36, the principal square root is 6.
- Negative Square Root: Every positive number also has a negative square root. Thus, -6 is also a square root of 36:
\[
(-6) \times (-6) = 36
\] - Perfect Squares: 36 is a perfect square because it is the product of an integer (6) multiplied by itself.
- Inverse Operation: Squaring is the inverse operation of finding a square root. This relationship is expressed as:
For example:
\[
(\sqrt{x})^2 = x
\]
\[
(\sqrt{36})^2 = 36
\] - Rational Number: The square root of 36 is a rational number because it can be expressed as a simple fraction (6/1).
- Positive and Negative Roots: For any positive number \( x \), the equation \( y^2 = x \) has two solutions: \( y = \sqrt{x} \) and \( y = -\sqrt{x} \). Therefore, the square roots of 36 are 6 and -6.
Applications:
Understanding the square root of 36 is important for various mathematical and real-world applications, such as:
- Calculating areas and side lengths in geometry.
- Solving quadratic equations in algebra.
- Performing operations in engineering and physics where square roots frequently appear.
In conclusion, the square root of 36, represented as \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \), is a crucial concept with various mathematical properties and practical applications.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 36
Calculating the square root of 36 can be approached in several ways. Here, we will discuss three common methods: using prime factorization, the long division method, and estimation. Each method offers a unique approach to finding the square root.
1. Prime Factorization Method
- Start with the number 36 and express it as a product of its prime factors:
\[
36 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 = 2^2 \times 3^2
\] - Group the prime factors into pairs:
\[
(2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3)
\] - Take one factor from each pair and multiply them together to get the square root:
\[
2 \times 3 = 6
\]Therefore, the square root of 36 is 6.
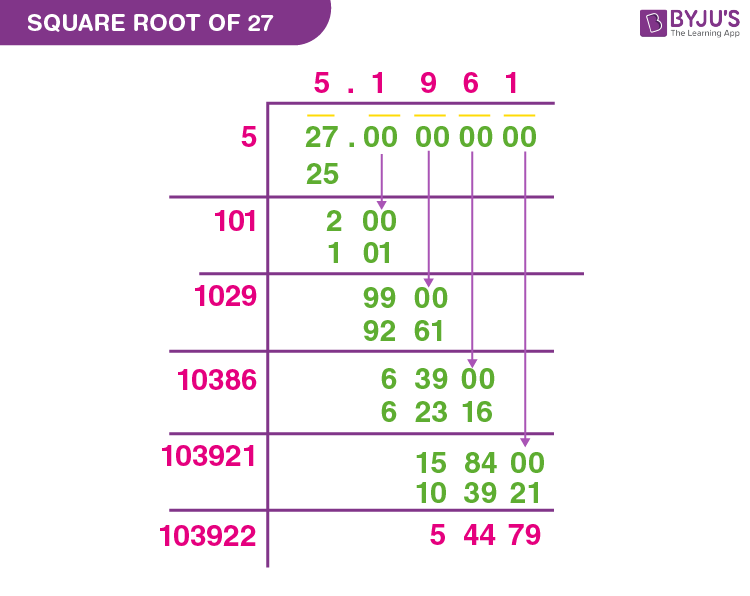
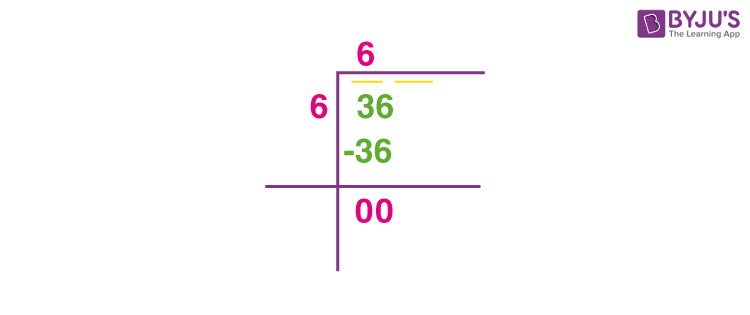
2. Long Division Method
- Write 36 as 36.000000 to prepare for long division.
- Group the digits in pairs, starting from the decimal point and moving to the left and right.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (36). In this case, 6:
\[
6 \times 6 = 36
\]Write 6 as the first digit of the square root.
- Subtract 36 from 36 to get 0. Bring down the next pair of zeros.
- Since there are no more digits left to bring down, the process ends here. The square root of 36 is 6.
3. Estimation Method
- Identify two perfect squares between which 36 lies. These are 25 (52) and 49 (72).
- Since 36 is closer to 36 (62), we can estimate the square root to be closer to 6.
- By confirming:
\[
6 \times 6 = 36
\]We find that the square root of 36 is exactly 6.
These methods offer a thorough understanding of how to calculate the square root of 36. Whether using prime factorization, long division, or estimation, each technique confirms that the square root of 36 is indeed 6.
Historical Context and Significance
The concept of square roots has a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations. The square root of 36, being a simple and perfect square, has played a role in various mathematical developments and applications throughout history.
Ancient Civilizations:
Ancient Babylonians and Egyptians were among the first to explore square roots. They used geometric methods to approximate square roots, applying these techniques in architecture and astronomy. The square root of 36, for example, would have been significant in calculating areas and constructing square-based structures.
Greek Contributions:
The Greeks, particularly Pythagoras and his followers, further developed the concept of square roots. The Pythagorean Theorem, which relates the sides of a right triangle, inherently involves the calculation of square roots. For instance, in a right triangle with sides 6 and 6, the hypotenuse would be:
\[
\sqrt{6^2 + 6^2} = \sqrt{36 + 36} = \sqrt{72}
\]
This illustrates the importance of understanding square roots in Greek mathematics.
Medieval and Renaissance Periods:
During the medieval period, Islamic mathematicians preserved and expanded upon Greek mathematical knowledge. They introduced algebraic methods to calculate square roots more efficiently. The square root of 36, being an easy and perfect square, served as a fundamental example in teaching these methods.
In the Renaissance, European mathematicians like Leonardo Fibonacci adopted and further developed these methods. Fibonacci’s work, especially in his book "Liber Abaci," helped standardize the notation and methods for calculating square roots.
Modern Significance:
Today, the square root of 36 continues to be a basic yet essential element in education. It serves as an introductory example in teaching the concept of square roots and the methods to calculate them. Understanding perfect squares like 36 helps students grasp more complex mathematical ideas and develop problem-solving skills.
Applications in Various Fields:
- Geometry: Square roots are used to determine side lengths, areas, and distances. For example, a square with an area of 36 square units has a side length of:
\[
\sqrt{36} = 6
\] - Engineering: Square roots are crucial in calculations involving physical dimensions, such as finding the diagonal of a square or the resultant force in mechanics.
- Science: Square roots appear in formulas and equations in physics and chemistry, such as calculating the root mean square speed of gas particles.
In summary, the square root of 36, while simple, has significant historical and educational value. Its role in ancient mathematics, its preservation through the ages, and its continued application in modern science and education highlight its enduring importance.
Common Misconceptions and Errors
Understanding the square root of 36 can sometimes lead to misconceptions and errors. Here are some of the most common ones and explanations to help clarify these points:
-
Misconception: The square root of 36 is always a positive number.
While the principal square root of 36 is 6, it's important to remember that there are two square roots: 6 and -6. Both 62 and (-6)2 equal 36.
-
Misconception: The square root of 36 is not an integer.
Some might think that the square root of a number is always a fraction or an irrational number. However, the square root of 36 is an integer (6 and -6) because 36 is a perfect square.
-
Misconception: The square root function is linear.
It is incorrect to assume that the square root function behaves linearly. For instance, the square root of a sum is not equal to the sum of the square roots: . Instead, √(36 + 16) = √52, which is not equal to 6 + 4 = 10.
-
Misconception: Simplifying square roots can be ignored.
Sometimes, people forget to simplify square roots when they can. For example, simplifying √36 to 6 makes calculations much easier and clearer.
-
Misconception: The square root of a negative number is always undefined.
While it is true in the context of real numbers, the square root of a negative number is defined in the context of complex numbers. For example, , where is the imaginary unit.
By addressing these common misconceptions, you can have a clearer understanding of the properties and calculations related to the square root of 36.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the square root of 36?
The square root of 36 is 6. This is because 6 multiplied by itself (6 × 6) equals 36.
-
Is the square root of 36 always positive?
No, the square root of 36 has two values: 6 and -6. Both 6 × 6 and (-6) × (-6) equal 36.
-
How do you calculate the square root of 36 manually?
To calculate the square root of 36 manually, you can use the factorization method. Since 36 is a perfect square, you can find its factors: 36 = 6 × 6. Therefore, the square root of 36 is 6.
-
Is the square root of 36 an integer?
Yes, the square root of 36 is an integer. It is 6 (or -6), both of which are whole numbers.
-
Can the square root of 36 be a negative number?
Yes, in addition to the positive square root (6), there is also a negative square root (-6). Both are valid square roots of 36.
-
Why is the square root of 36 important?
The square root of 36 is important in various mathematical applications, including solving quadratic equations, geometry, and understanding the properties of perfect squares.
Summary and Key Takeaways
The square root of 36, denoted as \(\sqrt{36}\), is a fundamental mathematical concept with several key properties and applications. Here are the main points to remember:
- Value: The square root of 36 is 6, expressed as
\(\sqrt{36} = 6\)or6^2 = 36. - Positive and Negative Roots: While the principal square root is 6, the equation
\(x^2 = 36\)has two solutions: \(x = 6\) and \(x = -6\). - Rational Number: The square root of 36 is a rational number because it can be expressed as a fraction
\(\frac{6}{1}\), indicating it is a whole number. - Methods of Calculation: The square root can be determined using various methods such as prime factorization, long division, and using a calculator. For example, the prime factorization method involves breaking down 36 into
2^2 \times 3^2and then simplifying to get the square root. - Applications: Understanding square roots is essential in solving quadratic equations, understanding geometric principles (such as the side length of a square), and various real-world applications like calculating areas and volumes.
- Historical Context: The concept of square roots has been explored since ancient times, with significant contributions from Greek mathematicians like Pythagoras and Euclid.
By grasping these key points, you can appreciate the importance and utility of square roots in both mathematical theory and practical applications. The simplicity of the square root of 36 makes it a great example to illustrate broader mathematical principles.
Tìm hiểu về căn bậc hai của 36 trong video này để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm toán học quan trọng này.
Căn bậc hai của 36
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 36 trong video này. Tìm hiểu các bước cụ thể để hiểu rõ hơn về sqrt(36).
Cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 36: sqrt(36)