Topic what is the square root of 27: Discover the fascinating world of mathematics as we explore what the square root of 27 is. In this article, we simplify the concept, provide exact and decimal forms, and explain practical applications. Join us on this educational journey to deepen your understanding of √27.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 27
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Concept of Square Roots
- The Square Root of 27 Explained
- Mathematical Derivation of Square Root of 27
- Simplifying Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method
- Square Root of 27 in Decimal Form
- Visualization of the Square Root of 27
- Applications of Square Root of 27
- FAQs on Square Root of 27
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
Square Root of 27
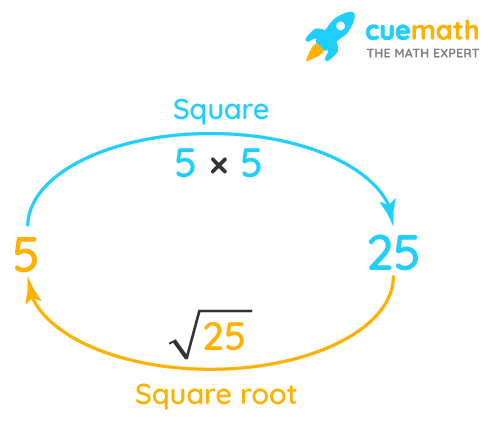
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In this case, we are looking for the square root of 27.
Exact Form
The square root of 27 in its simplest radical form is:
\(\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{9 \cdot 3} = \sqrt{9} \cdot \sqrt{3} = 3\sqrt{3}\)
Decimal Form
The square root of 27 in decimal form is approximately:
\(\sqrt{27} \approx 5.196152422706632\)
Steps to Simplify
- Find the prime factorization of 27: \(27 = 3 \times 3 \times 3 = 3^3\)
- Group the factors in pairs: \(27 = (3 \times 3) \times 3 = 9 \times 3\)
- Take the square root of each group: \(\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{9 \times 3} = \sqrt{9} \cdot \sqrt{3}\)
- Simplify: \(\sqrt{9} = 3\), so \(\sqrt{27} = 3\sqrt{3}\)
Visual Representation
Here's a visual representation of the square root of 27:
| Value | Approximation |
| \(\sqrt{27}\) | 5.196152422706632 |
| Exact Form | 3\(\sqrt{3}\) |
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3, because \(3 \times 3 = 9\).
Square roots are denoted by the radical symbol (√). The number under the radical sign is called the radicand. In this context, 27 is the radicand, and we seek its square root.
Understanding square roots involves several key steps:
- Identify the radicand.
- Determine if the radicand is a perfect square or can be simplified.
- Apply simplification techniques if necessary, such as prime factorization.
- Express the simplified form, if applicable, in both exact and decimal formats.
Let's delve deeper into these steps to comprehend the square root of 27.
1. Identify the radicand:
- In this case, the radicand is 27.
2. Determine if the radicand is a perfect square:
- 27 is not a perfect square, as there is no integer that, when multiplied by itself, equals 27.
3. Apply simplification techniques:
- We can use prime factorization to simplify √27.
Prime factorization of 27:
- 27 = 3 × 3 × 3 = 33
Simplifying the square root:
- \(\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{3^3} = \sqrt{9 \times 3} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{3} = 3\sqrt{3}\)
4. Express the simplified form:
- Exact form: 3√3
- Decimal form: \(\sqrt{27} \approx 5.196\)
With this understanding, you can now appreciate the process of finding and simplifying square roots, using 27 as an illustrative example.
Understanding the Concept of Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. This operation is the inverse of squaring a number.
The notation for square roots involves the radical symbol (√). For instance, \(\sqrt{25} = 5\) because \(5 \times 5 = 25\). In general, for any non-negative number \(x\), the square root is denoted as \(\sqrt{x}\).
Key points to understand about square roots include:
- Radicand: The number inside the radical sign is called the radicand. For example, in \(\sqrt{27}\), 27 is the radicand.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because their square roots are integers (e.g., \(\sqrt{16} = 4\)).
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that do not have integer square roots. For example, 27 is not a perfect square because there is no integer that multiplied by itself equals 27.
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. However, the principal square root (the non-negative root) is typically the focus. For example, the square roots of 25 are 5 and -5, but \(\sqrt{25}\) refers to 5.
- Real and Imaginary Roots: For non-negative radicands, square roots are real numbers. For negative radicands, square roots involve imaginary numbers (e.g., \(\sqrt{-1} = i\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit).
Let's explore the square root of 27 in detail:
- Identify the radicand: The radicand here is 27.
- Simplify using prime factorization: 27 can be expressed as \(3 \times 3 \times 3 = 3^3\).
- Group the factors: Pairing the factors gives us \( \sqrt{3^3} = \sqrt{9 \times 3} = \sqrt{9} \cdot \sqrt{3} \).
- Calculate the simplified form: \(\sqrt{9} = 3\), so \(\sqrt{27} = 3\sqrt{3}\).
Thus, the square root of 27 is simplified to \(3\sqrt{3}\) in exact form. For practical applications, it is often useful to express it in decimal form: \(\sqrt{27} \approx 5.196\).
Understanding square roots helps in various mathematical operations and real-world applications, making it a vital concept in both basic and advanced mathematics.
The Square Root of 27 Explained
The square root of 27 is a mathematical concept that involves finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 27. This value is represented as √27.
To express the square root of 27 in its simplest radical form, we can break it down into prime factors. The prime factorization of 27 is:
- 27 = 3 × 3 × 3
Using this, we can simplify √27:
\[
\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{3 \times 3 \times 3} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 3} = 3\sqrt{3}
\]
Thus, the simplest form of √27 is 3√3.
In decimal form, the square root of 27 is approximately 5.196, since:
\[
3 \sqrt{3} \approx 3 \times 1.732 = 5.196
\]
We can also determine the square root of 27 using the long division method. Here's a step-by-step outline:
- Group the digits of 27 and place them inside the division symbol.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 27, which is 5 (since 5×5 = 25).
- Use this number as the divisor and continue the process with decimal places.
- Stop the process after a few iterations to get an approximate value.
The exact decimal value obtained through long division is again approximately 5.196.
Understanding the concept of square roots, especially of non-perfect squares like 27, is fundamental in various fields of mathematics and its applications. The square root of 27, represented as 3√3 in radical form and approximately 5.196 in decimal form, illustrates this well.
Mathematical Derivation of Square Root of 27
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. To derive the square root of 27, we use a methodical approach involving prime factorization and simplification.
Here is the step-by-step mathematical derivation:
- Prime Factorization:
First, we break down 27 into its prime factors:
- 27 = 3 × 3 × 3
- This can be written as \(27 = 3^3\).
- Simplify the Radical Expression:
Using the property of square roots that \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\), we simplify:
- \(\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{3^3}\)
- \(\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 3} = \sqrt{3^2} \times \sqrt{3} = 3\sqrt{3}\)
Thus, the simplest form of \(\sqrt{27}\) is \(3\sqrt{3}\).
- Decimal Approximation:
We know that the square root of 3 (\(\sqrt{3}\)) is approximately 1.732. Therefore:
- \(3\sqrt{3} \approx 3 \times 1.732 = 5.196\)
So, \(\sqrt{27} \approx 5.196\).
- Verification:
To verify, we square the decimal approximation:
- \((5.196)^2 \approx 27\)
This step-by-step derivation helps in understanding the process of finding the square root of a number using prime factorization and simplification. The exact form of the square root of 27 is \(3\sqrt{3}\), and the approximate decimal form is 5.196.

Simplifying Square Roots
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down the number under the square root into its prime factors. For the square root of 27, we start by expressing 27 as a product of its prime factors.
The prime factorization of 27 is:
- 27 = 3 × 3 × 3
To simplify the square root, we use the property of square roots that states \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \). We can group the prime factors in pairs:
\( \sqrt{27} = \sqrt{3 \times 3 \times 3} \)
Grouping the pairs, we get:
\( \sqrt{27} = \sqrt{(3 \times 3) \times 3} \)
Since the square root of \(3 \times 3\) is 3, we can simplify this to:
\( \sqrt{27} = 3 \times \sqrt{3} \)
Therefore, the simplest form of the square root of 27 is:
\( 3\sqrt{3} \)
This simplification process helps us to express the square root in a more manageable form, making calculations easier.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a useful approach to simplify square roots by breaking down the number into its prime factors. Let's go through the steps to find the square root of 27 using this method.
- First, find the prime factors of 27. The prime factorization of 27 is:
- 27 ÷ 3 = 9
- 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- 3 ÷ 3 = 1
- Write 27 as a product of its prime factors:
27 = 3 × 3 × 3 = 33
- Group the prime factors in pairs to simplify the square root. Since 27 is written as 33, we can group the factors as follows:
(3 × 3) × 3 = 9 × 3
- Take the square root of each group of prime factors:
\(\sqrt{27} = \sqrt{9 \times 3} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{3}\)
- Simplify the square roots:
\(\sqrt{9} = 3\)
- Combine the results to get the simplified form of the square root of 27:
\(\sqrt{27} = 3\sqrt{3}\)
Thus, using the prime factorization method, the square root of 27 can be simplified to \(3\sqrt{3}\).
Square Root of 27 in Decimal Form
The square root of 27 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansion. To find the square root of 27 in decimal form, we can use several methods, including approximation techniques or calculator functions.
Using a calculator, the square root of 27 is approximately:
\[\sqrt{27} \approx 5.1961524227\]
This value is obtained by finding the number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the product of 27.
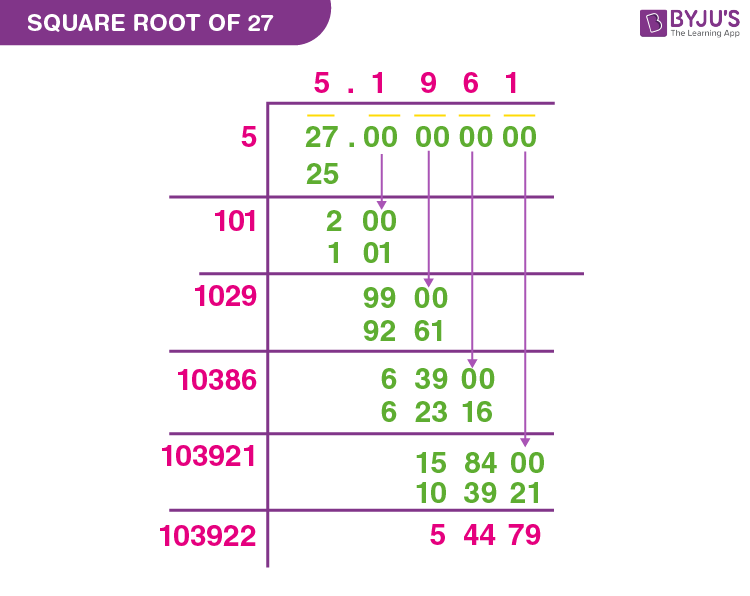
Here is a step-by-step explanation of the long division method to approximate the square root of 27:
- Group the Digits: Since 27 is a two-digit number, consider 27 as it is.
- Find the Starting Number: Identify the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 27. The largest such number is 5, because \(5^2 = 25\).
- Subtract and Bring Down: Subtract 25 from 27, resulting in 2. Bring down a pair of zeros to the right of 2, making it 200.
- Find the Next Digit: Double the current quotient (5) to get 10. Determine the largest digit (x) such that \(10x \cdot x \leq 200\). The appropriate digit is 1, as \(101 \cdot 1 = 101\).
- Subtract Again: Subtract 101 from 200, leaving 99. Bring down another pair of zeros to make it 9900.
- Continue the Process: Repeat the steps with the new value, continuing the division process to obtain more decimal places if needed.
After a few iterations, the approximate value of the square root of 27 up to ten decimal places is:
\[\sqrt{27} \approx 5.1961524227\]
Using software tools like Excel or Google Sheets, you can find the square root by simply using the function:
=SQRT(27)This will directly give the result of approximately 5.196152423.
For practical applications, this value can be rounded to 5.2 for simplicity.
The square root of 27 can also be expressed in its simplest radical form:
\[\sqrt{27} = 3\sqrt{3}\]
Visualization of the Square Root of 27
Visualizing the square root of 27 can be achieved through several methods, including graphical representations and geometric interpretations. Here, we'll explore a few approaches to help understand this concept better.
Graphical Representation
One effective way to visualize the square root of 27 is to plot it on a number line or a coordinate plane. The square root of 27 is approximately 5.196. On a number line, you can locate this value between 5 and 6, closer to 5.2.
Geometric Interpretation
To geometrically interpret the square root of 27, consider a square with an area of 27 square units. The side length of this square would be the square root of 27. By comparing it to a known square, such as one with an area of 25 square units (side length of 5), you can see that the side length of our square is slightly more than 5 units.
Using a visual aid, you can place a smaller square (area of 25) inside the larger square (area of 27) and see that there is an extra area that needs to be filled. This extra area can be visualized as small squares or strips that fill the gap.
Using Manipulatives
Manipulatives like algebra tiles can also be used to visualize square roots. By arranging tiles to form a square, you can demonstrate how the side length relates to the area. This hands-on approach makes abstract concepts more concrete, especially for students learning about square roots for the first time.
Interactive Tools
There are several online tools and software, such as GeoGebra and Wolfram Demonstrations, that allow interactive exploration of square roots. These tools can show how the square root function distorts a graph and provide a visual understanding of irrational numbers like the square root of 27.
For example, using GeoGebra, you can create dynamic models that illustrate the iterative process of approximating square roots and demonstrate why the square root of 27 is irrational.
Conclusion
Visualizing the square root of 27 through different methods helps in understanding its value and properties. Whether using a number line, geometric shapes, manipulatives, or interactive software, these techniques provide a comprehensive grasp of what the square root of 27 represents.

Applications of Square Root of 27
The square root of 27 has several practical applications across various fields. Here are some detailed examples:
1. Geometry and Trigonometry
In geometry, the square root of 27 can be used to solve problems involving right triangles and other polygons. For example, using the Pythagorean theorem, if one side of a right triangle is √27, it can help in determining the lengths of other sides or the hypotenuse.
2. Physics and Engineering
In physics, the square root of 27 might be used in formulas to calculate distances, speeds, or areas under specific conditions. For instance, determining the natural frequency of structures like bridges involves square root calculations to predict how they will react to various forces.
3. Statistics
Square roots are fundamental in statistical analysis, particularly in calculating standard deviation, which is the square root of the variance. This helps statisticians understand the spread of data points in a dataset.
4. Computer Science and Cryptography
In computer science, square roots are used in algorithms related to graphics, cryptography, and data security. For example, encryption algorithms often use modular arithmetic involving square roots to generate secure keys for data transmission.
5. Finance
In finance, square roots are used to calculate the volatility of stock prices. The standard deviation, a measure of volatility, is derived from the square root of the variance of stock returns, helping investors assess the risk of investments.
6. Navigation
Navigation systems use square roots to compute distances between points on a map using the distance formula derived from the Pythagorean theorem. This is essential for pilots, sailors, and even for GPS technology to provide accurate positioning and routing information.
These applications show how the mathematical concept of the square root of 27 can be utilized in practical and theoretical scenarios across different disciplines, highlighting its importance and versatility.
FAQs on Square Root of 27
-
What is the square root of 27?
The square root of 27 is approximately 5.1961524227. This value can be written as
\(\sqrt{27} \approx 5.196\)when rounded to three decimal places. -
Is the square root of 27 a rational or irrational number?
The square root of 27 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating.
-
How can the square root of 27 be simplified?
The square root of 27 can be simplified using prime factorization. Since 27 = 33, the square root can be simplified to
\(3\sqrt{3}\). -
What are the methods to find the square root of 27?
There are several methods to find the square root of 27, including:
- Prime Factorization Method
- Long Division Method
- Using a Calculator
- Newton's Method
- Approximation Methods
-
Can the square root of 27 be expressed in exponential form?
Yes, the square root of 27 can be expressed in exponential form as \(27^{1/2}\) or \(27^{0.5}\).
-
What is the radical form of the square root of 27?
The radical form of the square root of 27 is
\(3\sqrt{3}\). -
Why is the square root of 27 not a natural number?
The square root of 27 is not a natural number because natural numbers are positive integers starting from 1, and the square root of 27 is an irrational number.
Conclusion
The square root of 27 is an intriguing mathematical concept with various applications and methods to determine its value. By employing the prime factorization method, we identify that the square root of 27 is represented in its simplest radical form as \(3\sqrt{3}\). In decimal form, this value is approximately 5.196.
Understanding the square root of 27 involves not only recognizing its value but also appreciating the processes used to derive it, such as the long division method and prime factorization. These methods provide a comprehensive view of how non-perfect squares like 27 can be broken down and calculated.
The practical applications of the square root of 27 extend into various fields, including geometry, physics, and engineering, where precise calculations are necessary. Whether used for theoretical exploration or practical problem-solving, the square root of 27 exemplifies the elegance and utility of mathematical concepts.
In summary, the square root of 27, whether viewed in its radical form \(3\sqrt{3}\) or its decimal approximation 5.196, highlights the importance of mathematical operations and their relevance to real-world scenarios. This exploration underscores the beauty of mathematics in uncovering the hidden relationships within numbers.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Của 27: sqrt(27)