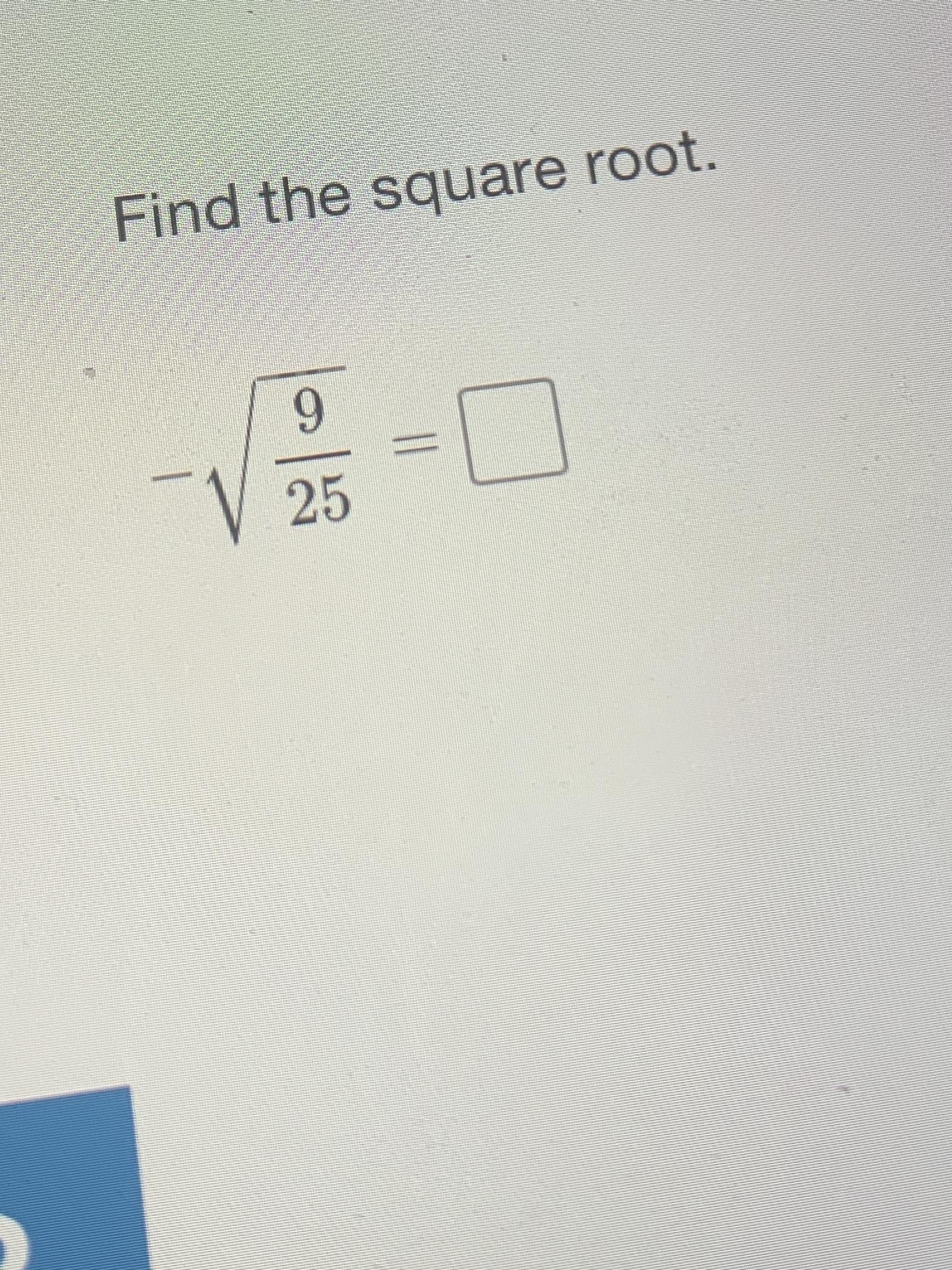
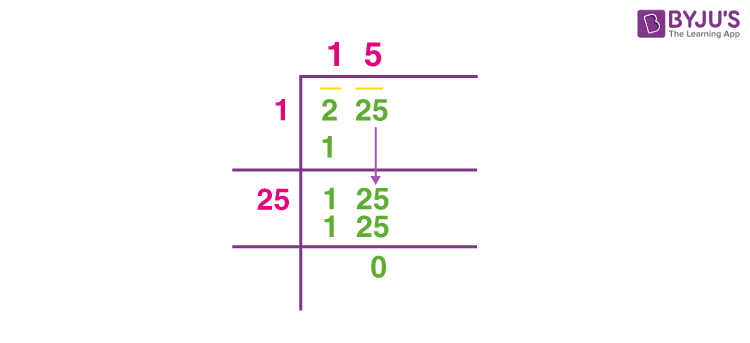Topic what is the square root 256: The square root of 256 is a fundamental concept in mathematics, often explored in both basic and advanced studies. In this article, we will delve into what the square root of 256 is, how to calculate it, and its significance in various mathematical contexts. Whether you're a student or just curious, this guide will provide clear insights.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 256
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 256
- Calculating the Square Root of 256
- Mathematical Explanation
- Positive and Negative Roots
- Perfect Square Concept
- Applications of Square Roots
- Visual Representation
- Common Questions and Misconceptions
- Historical Context
- Real-Life Examples
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về căn bậc hai của số 256 để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này và các ứng dụng trong thực tế.
Understanding the Square Root of 256
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In this guide, we will explore the square root of 256 in detail.
What is the Square Root of 256?
The square root of 256 is 16.
This can be represented mathematically as:
\[
\sqrt{256} = 16
\]
How to Determine the Square Root of 256
To understand why 16 is the square root of 256, we need to find a number that, when squared, equals 256.
\[
16 \times 16 = 256
\]
Thus, \(\sqrt{256} = 16\).
Properties of the Square Root of 256
- Positive and Negative Roots: While the principal (positive) square root of 256 is 16, it is important to remember that every positive number has two square roots. The negative square root of 256 is -16. Therefore, \(\sqrt{256} = \pm 16\).
- Perfect Square: 256 is a perfect square because it is the square of an integer (16).
- Even Number: The square root of 256 is an even number (16).
Visualizing the Square Root of 256
Visual aids can help in understanding the concept of square roots. Imagine a square with an area of 256 square units. Each side of this square would measure 16 units.
\[
\text{Area} = \text{side length}^2 \\
256 = 16^2
\]
Applications of the Square Root of 256
The concept of square roots is widely used in various fields, including mathematics, engineering, and physics. For instance, calculating the side length of a square when its area is known, understanding wave functions in quantum mechanics, and solving quadratic equations are some applications.
Conclusion
The square root of 256 is an integral part of mathematical concepts and has practical applications in various fields. Understanding how to find and use the square root of 256 can enhance problem-solving skills and mathematical knowledge.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental concepts in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. The symbol for the square root is √, and the number under the square root symbol is called the radicand. For instance, the square root of 256 is denoted as √256.
Square roots can be positive or negative because a negative number squared also gives a positive result. Therefore, the square root of 256 is ±16 since both 16 and -16 satisfy the equation 16² = 256 and (-16)² = 256.
There are various methods to find square roots, such as the prime factorization method, the long division method, and the method of repeated subtraction. Each method offers a step-by-step approach to simplifying and understanding square roots.
-
Prime Factorization Method:
This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors. For 256, the prime factors are:
256 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
Grouping the prime factors in pairs gives:
√256 = √((2 × 2) × (2 × 2) × (2 × 2) × (2 × 2)) = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 16 -
Long Division Method:
The long division method involves grouping the digits of the number in pairs, starting from the decimal point and working both left and right. It provides a systematic approach to finding the square root.
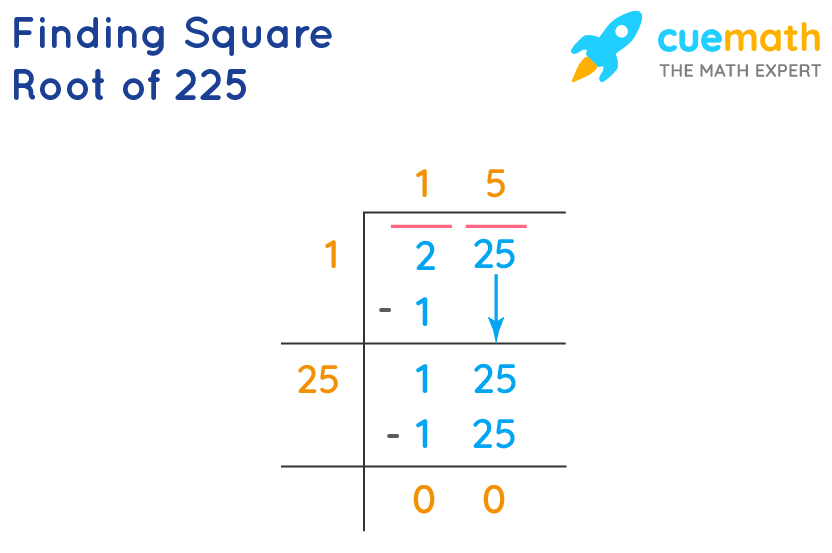
For example, to find √256:- Pair the digits: 2 and 56.
- Find the largest square number less than or equal to the first pair (2): 1.
- Subtract the square of this number (1) from the first pair (2), bring down the next pair (56).
- Double the result (1) and use it as the divisor for the next steps. Continue this process until all pairs are used.
-
Repeated Subtraction Method:
This method involves subtracting successive odd numbers from the radicand until zero is reached. The number of subtractions performed will be the square root of the number.
For 256, you subtract:
256 - 1 = 255
255 - 3 = 252
252 - 5 = 247
... and so on, until the result is 0.
Understanding these methods and concepts helps in grasping the broader applications of square roots in various fields of science, engineering, and everyday problem-solving.
Understanding the Square Root of 256
The square root of 256 is a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 256. This value is crucial in various mathematical calculations and applications. Let's delve into the details of understanding the square root of 256 step by step.
Firstly, the square root of 256 is 16, as 16 multiplied by 16 gives 256. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
\[\sqrt{256} = 16\]
Steps to Calculate the Square Root of 256
Prime Factorization Method: Break down 256 into its prime factors.
- \[256 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 2^8\]
- Pair the prime factors: \[(2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) = 4 \times 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 16\]
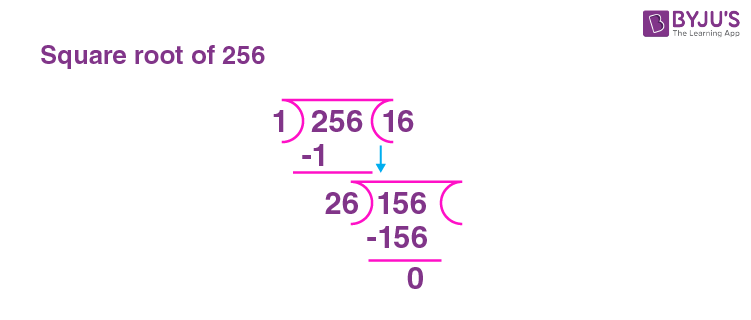
Long Division Method: Use the long division method for finding the square root.
- Pair the digits from right to left: 256 is paired as (2)(56).
- Find a number that, when squared, is less than or equal to 2 (in this case, 1).
- Double the quotient and use it as the new divisor for the next pair of digits.
- Continue the process until all pairs of digits are used, resulting in a quotient of 16.
Properties of the Square Root of 256
- Rational Number: The square root of 256 is a rational number because it can be expressed as a simple fraction (16/1).
- Perfect Square: 256 is a perfect square, meaning its square root is an integer.
- Positive and Negative Roots: While the principal square root of 256 is 16, it also has a negative counterpart: \[-16\], because \((-16) \times (-16) = 256\].
Understanding these methods and properties helps in recognizing the significance of square roots in both theoretical and practical mathematical problems.
Calculating the Square Root of 256
Calculating the square root of a number involves finding a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 256, the steps are straightforward because 256 is a perfect square. Here is a step-by-step guide to calculating the square root of 256:
- Recognize that 256 is a perfect square.
- List the factors of 256 to identify pairs of numbers that multiply to 256:
- 1 × 256
- 2 × 128
- 4 × 64
- 8 × 32
- 16 × 16
- Notice that 16 × 16 = 256, which indicates that the square root of 256 is 16.
To verify this calculation, you can use the square root function:
\[ \sqrt{256} = 16 \]
Let's break it down further with a simple algorithm:
- Estimate: Start with a rough estimate close to the possible square root. For 256, since we know 16 × 16 is close, we start with 16.
- Divide: Divide 256 by your estimate. \[ \frac{256}{16} = 16 \]
- Average: Take the average of the result and the original estimate. \[ \frac{16 + 16}{2} = 16 \]
- Repeat: Since the average is the same as the previous estimate, the calculation is complete.
In conclusion, the square root of 256 is:
\[ \sqrt{256} = 16 \]
Mathematical Explanation
The square root of 256 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 256. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{256} = x \quad \text{such that} \quad x^2 = 256
\]
To find the square root of 256, we consider the following steps:
- Identify that 256 is a perfect square.
- Use the prime factorization method:
- Since the exponent is even, we take half of it:
\[
256 = 2^8
\]
\[
\sqrt{256} = 2^{\frac{8}{2}} = 2^4 = 16
\]
Therefore, the positive square root of 256 is 16. Mathematically, we express this as:
\[
\sqrt{256} = 16
\]
However, considering both positive and negative roots, we have:
\[
\sqrt{256} = \pm 16
\]
This indicates that 256 has two square roots: 16 and -16.
Positive and Negative Roots
When discussing the square root of a number, it's important to understand that there are both positive and negative roots. This concept arises from the definition of the square root, which is a number that, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number.
For the number 256, its square roots can be denoted as:
\[
\sqrt{256} = 16 \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{256} = -16
\]
Here's a step-by-step explanation of why there are both positive and negative roots:
- Definition: By definition, the square root of 256 is a number which, when squared, equals 256.
- Positive Root: The positive square root of 256 is 16 because \(16 \times 16 = 256\).
- Negative Root: Similarly, the negative square root of 256 is -16 because \((-16) \times (-16) = 256\).
This can be summarized mathematically as:
\[
\sqrt{256} = \pm 16
\]
In general, for any positive number \(a\), the equation:
\[
x^2 = a
\]
has two solutions: \(x = \sqrt{a}\) and \(x = -\sqrt{a}\).
To illustrate this with 256:
\[
x^2 = 256
\]
Solving for \(x\) gives:
\[
x = \pm \sqrt{256} = \pm 16
\]
It’s crucial to note that while both 16 and -16 are valid square roots of 256, the principal square root refers specifically to the positive root, which is 16 in this case.
Perfect Square Concept
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. In other words, a number \( n \) is a perfect square if there exists an integer \( m \) such that:
\[
n = m^2
\]
For example, the number 256 is a perfect square because it can be written as:
\[
256 = 16^2
\]
This means that 256 is the product of 16 multiplied by 16. Here are some properties and steps to identify a perfect square:
- Integer Result: The square root of a perfect square is always an integer. In the case of 256, the square root is 16.
- Non-negative: Perfect squares are always non-negative because squaring a positive or negative number results in a positive value.
- Factors: A perfect square has an odd number of total factors. For 256, the factors are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256.
To further understand perfect squares, consider these additional examples:
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
Each of these numbers can be expressed as the square of an integer, confirming their status as perfect squares.
Understanding the concept of perfect squares is crucial in various mathematical applications, including solving quadratic equations and simplifying radical expressions.
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots are widely used in various fields and real-life applications. Below are some of the key areas where square roots play a crucial role:
- Geometry:
In geometry, square roots are essential for calculating distances and lengths, especially when applying the Pythagorean theorem. For instance, in a right-angled triangle, the length of the hypotenuse can be found using the square root of the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
- Physics:
Square roots are used to determine physical quantities such as the velocity of an object under uniform acceleration. The formula \( v = \sqrt{2gh} \) (where \( v \) is velocity, \( g \) is acceleration due to gravity, and \( h \) is height) is an example of such application.
- Statistics:
In statistics, the standard deviation is calculated using the square root of the variance. This measure helps to understand the spread or dispersion of a set of data points from the mean.
- Finance:
In finance, square roots are used to calculate volatility, which measures the variation in the price of a financial instrument over time. The standard deviation of returns, often used to assess risk, involves taking the square root of the variance.
- Engineering:
Engineers use square roots to calculate various structural properties, such as the natural frequency of a bridge or building. This is crucial for ensuring the stability and safety of structures under different load conditions.
- Computer Science:
In computer science, square roots are used in algorithms related to graphics and cryptography. For example, calculating the distance between points in 2D or 3D space often involves the square root function.
- Navigation:
Square roots are used in navigation to compute the shortest path or distance between two points. This is particularly important for GPS technology and mapping applications.
Visual Representation
Visualizing the square root of 256 can be quite helpful in understanding its properties and applications. Below are different ways to represent this concept graphically and numerically.
Number Line Representation
On a number line, the square root of 256 is represented by marking the point at 16, as shown below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| -16 | -14 | -12 | -10 | -8 | -6 | -4 | -2 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
Geometric Representation
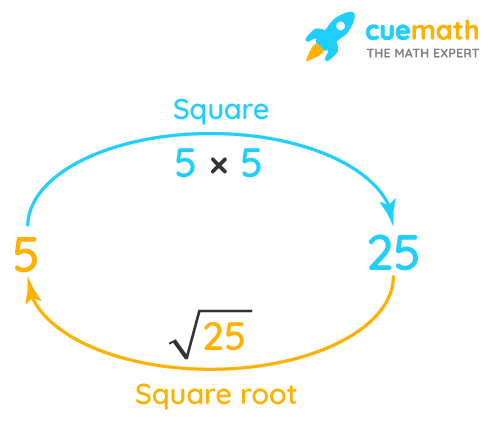
The square root of 256 can be visualized as the side length of a square whose area is 256 square units. Below is an illustration:
Each side of the square above is 16 units long, demonstrating that the area (16 * 16) equals 256 square units.
Graphical Representation
A graphical method to represent the square root of 256 is to plot the function \( y = \sqrt{x} \) and mark the point where \( x = 256 \).
In the graph below, the point (256, 16) is highlighted:
| x | y |
| 256 | 16 |
These visual tools help reinforce the understanding that the square root of 256 is 16.

Common Questions and Misconceptions
When discussing the square root of 256, several common questions and misconceptions often arise. Let's address some of these to clarify any confusion.
- Is 256 a Perfect Square?
Yes, 256 is a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. In this case, \( 16 \times 16 = 256 \), so the square root of 256 is 16.
- Is the Square Root of 256 Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 256 is rational. A rational number is a number that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Since 16 is an integer, and the square root of 256 is 16, it is rational.
- Can the Square Root of 256 Be Negative?
While the principal (commonly referred to) square root of 256 is 16, the equation \( x^2 = 256 \) has two solutions: \( x = 16 \) and \( x = -16 \). Therefore, both positive and negative roots are possible mathematically.
- What Are Some Practical Applications of Knowing the Square Root of 256?
- In geometry, the square root is useful in finding the side length of a square given its area.
- In computer science, perfect squares are used in algorithms and data structure designs.
- In everyday calculations, understanding square roots can help in diverse fields such as engineering, physics, and finance.
- Why Do We Need to Learn About Square Roots?
Square roots are fundamental in various branches of mathematics and are crucial for solving quadratic equations, analyzing geometric shapes, and understanding algebraic concepts. They also have practical applications in science and engineering fields.
Historical Context
The concept of square roots dates back to ancient civilizations such as the Babylonians and Egyptians, who used basic methods to approximate square roots. However, it was the ancient Greeks, particularly mathematicians like Euclid and Pythagoras, who formalized the understanding of square roots within the context of geometry and number theory.
During the Renaissance period, interest in mathematics and its applications surged, leading to advancements in algebraic methods for calculating square roots. The development of symbolic algebra by mathematicians like Descartes and Fermat further refined these techniques.
In the 18th and 19th centuries, mathematicians delved deeper into the properties of square roots as part of broader investigations into real and complex numbers. The advent of calculus and the rigorous development of mathematical analysis provided new insights into the nature of square roots and their applications in various scientific disciplines.
Today, the square root of 256 is a fundamental concept taught in elementary mathematics, symbolizing the principal (positive) square root of the number 256. This foundational knowledge continues to underpin more advanced mathematical theories and practical applications in fields such as physics, engineering, and computer science.
Real-Life Examples
In real-world applications, understanding the square root of 256 is crucial in various scenarios:
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots extensively in calculations involving areas, volumes, and structural stability. For instance, in construction, knowing the dimensions derived from square roots ensures precise designs and material estimations.
- Finance: Financial analysts utilize square roots in risk assessment models and financial forecasting. The square root of 256 can represent the standard deviation in statistical analysis, helping to gauge the volatility of investments.
- Technology: In computer science, algorithms often require the use of square roots for tasks such as image processing, cryptography, and data compression. Knowing the square root of 256 aids in efficient computation and data manipulation.
- Physics: Physicists apply square roots in formulas related to energy, force, and wave propagation. Understanding the mathematical underpinnings of the square root of 256 assists in modeling physical phenomena accurately.
Xem video về căn bậc hai của số 256 để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này và các ứng dụng trong thực tế.
Video về "Căn bậc hai của 256"
READ MORE:
Xem video hướng dẫn cách tìm căn bậc hai của số 256 bằng phân tích thừa số nguyên tố để hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này và cách áp dụng trong thực tế.
Video về "Cách Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 256 bằng Phân Tích Thừa Số Nguyên Tố / Căn Bậc Hai của 256 / 256 Căn Bậc Hai"