Topic what is the perimeter of the octagon below: Understanding the perimeter of an octagon is crucial for various geometric calculations and practical applications. The perimeter is simply the total length of all the sides of the octagon. For a regular octagon, this can be easily calculated using the formula \( P = 8a \), where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of an Octagon
- Area of a Regular Octagon
- Area of a Regular Octagon
- Definition of an Octagon
- Properties of an Octagon
- Formulas for Octagons
- Types of Octagons
- Real Life Examples of Octagons
- How to Calculate the Perimeter of an Octagon
- How to Calculate the Area of an Octagon
- Using an Octagon Calculator
- Examples and Practice Problems
- YOUTUBE:
Perimeter of an Octagon
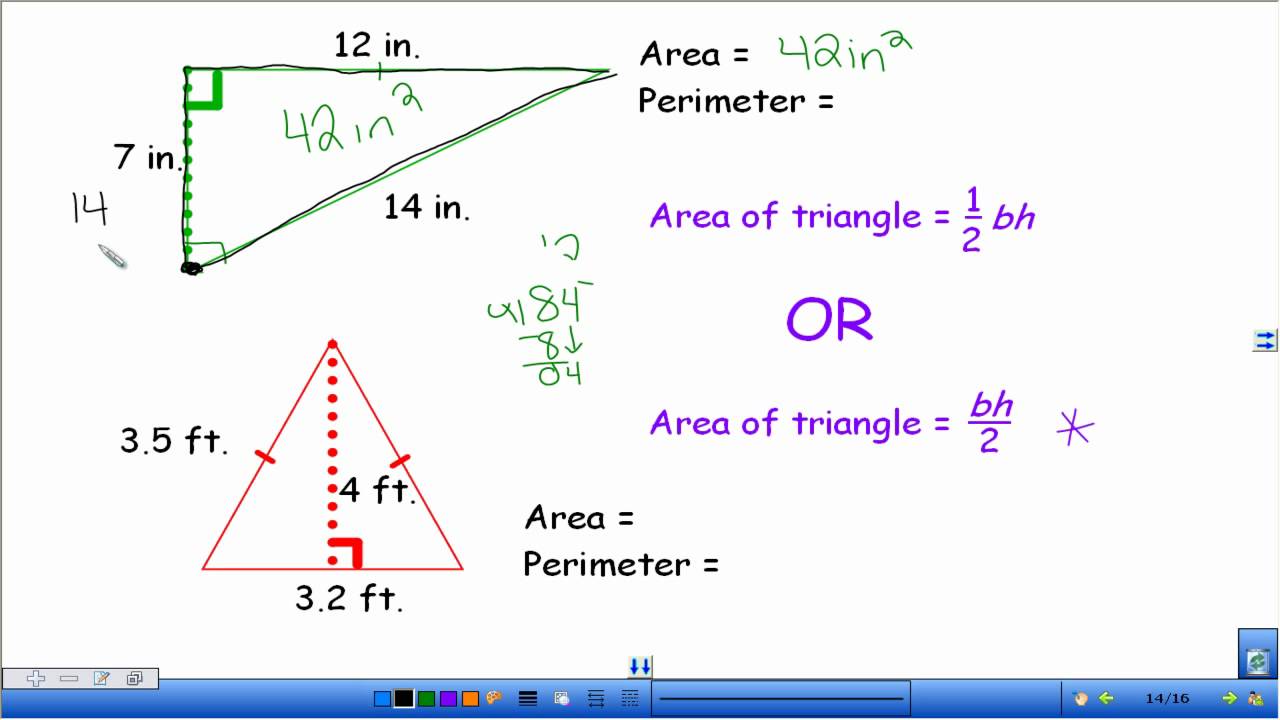
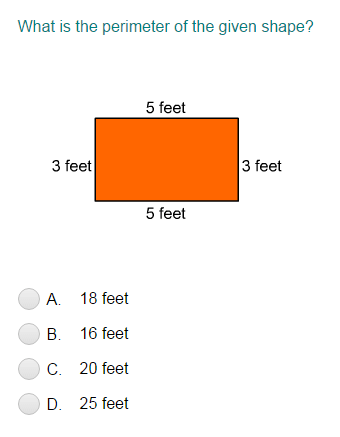
An octagon is a polygon with 8 sides and 8 angles. Below are the steps and formulas used to find the perimeter of an octagon.
Regular Octagon
A regular octagon has all sides of equal length. The perimeter (P) of a regular octagon is calculated using the formula:
\( P = 8a \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side of the octagon.
Example: If each side of a regular octagon is 12 meters, the perimeter is:
\( P = 8 \times 12 = 96 \, \text{meters} \)
Irregular Octagon
An irregular octagon has sides of different lengths. The perimeter of an irregular octagon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. The formula is:
\( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 + s_7 + s_8 \)
where \( s_1, s_2, \ldots, s_8 \) are the lengths of the sides.
Example: If the side lengths of an irregular octagon are 3 cm, 3 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, 6 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 4 cm, the perimeter is:
\( P = 3 + 3 + 3 + 4 + 6 + 5 + 6 + 4 = 34 \, \text{centimeters} \)

READ MORE:
Area of a Regular Octagon
The area of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula:
\( A = 2(1 + \sqrt{2})a^2 \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Example: For a regular octagon with each side of length 9 feet, the area is:
\( A = 2(1 + \sqrt{2}) \times 9^2 \approx 391.10 \, \text{square feet} \)
Summary of Properties
- An octagon has 8 sides, 8 angles, and 8 vertices.
- The sum of the interior angles is 1080°.
- The sum of the exterior angles is 360°.
- A regular octagon has all sides and all interior angles equal, with each interior angle measuring 135°.
Area of a Regular Octagon
The area of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula:
\( A = 2(1 + \sqrt{2})a^2 \)
where \( a \) is the length of one side.
Example: For a regular octagon with each side of length 9 feet, the area is:
\( A = 2(1 + \sqrt{2}) \times 9^2 \approx 391.10 \, \text{square feet} \)
Summary of Properties
- An octagon has 8 sides, 8 angles, and 8 vertices.
- The sum of the interior angles is 1080°.
- The sum of the exterior angles is 360°.
- A regular octagon has all sides and all interior angles equal, with each interior angle measuring 135°.
Definition of an Octagon
An octagon is a polygon with eight sides, eight angles, and eight vertices. The term "octagon" comes from the Greek words "okta" meaning eight and "gon" meaning angle. Octagons can be regular or irregular. In a regular octagon, all sides and angles are equal, while in an irregular octagon, they are not. The sum of the interior angles of an octagon is 1080 degrees, and the sum of the exterior angles is always 360 degrees.
- An octagon has 8 sides.
- It has 8 interior and 8 exterior angles.
- The sum of the interior angles is 1080 degrees.
- Each interior angle of a regular octagon measures 135 degrees.
- Each exterior angle of a regular octagon measures 45 degrees.
- A regular octagon can be divided into 8 isosceles triangles.
In geometry, the perimeter of a regular octagon is calculated by the formula:
\[ P = 8a \]
where \(a\) is the length of one side. The area of a regular octagon is given by:
\[ A = 2a^2(1 + \sqrt{2}) \]
where \(a\) is the length of one side. These properties and formulas help in various geometrical calculations and have practical applications in design and architecture.
Properties of an Octagon
An octagon is a polygon with eight sides and eight angles. Here are some key properties of an octagon:
- An octagon has eight sides of equal length (if it is a regular octagon).
- It has eight interior angles.
- The sum of the interior angles of an octagon is \(1080^\circ\).
- Each interior angle in a regular octagon measures \(135^\circ\).
- An octagon has eight exterior angles, and the sum of the exterior angles is \(360^\circ\).
- Each exterior angle in a regular octagon measures \(45^\circ\).
- An octagon can be divided into 6 triangles.
- A regular octagon can be inscribed in a circle, with all vertices lying on the circumference.
- The area \(A\) of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula: \[ A = 2(1 + \sqrt{2})a^2 \] where \(a\) is the length of a side.
- The perimeter \(P\) of a regular octagon is: \[ P = 8a \] where \(a\) is the length of a side.
Octagons can be regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles are not equal).
Here is a summary of the properties of a regular octagon in a table:
| Number of sides | 8 |
| Sum of interior angles | 1080° |
| Each interior angle | 135° |
| Sum of exterior angles | 360° |
| Each exterior angle | 45° |
| Number of triangles formed | 6 |
| Area | \(2(1 + \sqrt{2})a^2\) |
| Perimeter | 8a |

Formulas for Octagons
The formulas for calculating the perimeter and area of a regular octagon are essential for understanding its geometric properties. A regular octagon has eight equal sides and eight equal angles. Here are the key formulas:
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula:
\[ P = 8a \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( a \) is the length of one side.
Example: For a side length of 20 cm, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = 8 \times 20 = 160 \text{ cm} \] - Area: The area of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula:
\[ A = 2a^2 (1 + \sqrt{2}) \]
where \( A \) is the area and \( a \) is the length of one side.
Example: For a side length of 12 cm, the area \( A \) is:
\[ A = 2 \times 12^2 \times (1 + \sqrt{2}) \]
\[ A = 2 \times 144 \times (1 + \sqrt{2}) \]
\[ A = 288 \times (1 + \sqrt{2}) \approx 695.4 \text{ cm}^2 \]
These formulas provide a straightforward way to determine the perimeter and area of regular octagons, making it easier to solve geometric problems involving this shape.
Types of Octagons
Octagons can be classified into different types based on their side lengths and angle measures. Below are the main types of octagons:
- Regular Octagon: All sides and all angles are equal. Each interior angle in a regular octagon is 135°, and each exterior angle is 45°. Regular octagons are symmetrical and have eight lines of symmetry.
- Irregular Octagon: The sides and angles are not equal. Irregular octagons lack the symmetry found in regular octagons and do not have equal-length sides or equal-measure angles.
- Convex Octagon: All interior angles are less than 180°, and no angles point inward. This means all vertices "point outwards" relative to the center of the octagon.
- Concave Octagon: One or more interior angles are greater than 180°, causing some vertices to "point inward" towards the center of the shape.
Here is a table summarizing the properties of regular and irregular octagons:
| Type | Side Lengths | Angles | Symmetry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regular Octagon | Equal | 135° (each) | 8 lines of symmetry |
| Irregular Octagon | Unequal | Varies | No lines of symmetry |
Convex and concave octagons can be either regular or irregular, but their defining characteristic is whether their interior angles point outwards or inwards:
- Convex Octagon:

- Concave Octagon:

Real Life Examples of Octagons
Octagons are a fascinating geometric shape with eight sides and eight angles, commonly found in various real-life objects and structures. Here are some prominent examples:
- Stop Signs: One of the most recognizable examples of an octagon is the stop sign used in traffic control. It is a red, regular octagon with white lettering, ensuring it is highly visible to drivers.
- Architecture: Many buildings and architectural elements incorporate octagonal designs. For instance, some gazebos and pavilions feature octagonal floors or roofs, adding aesthetic appeal and structural integrity.
- Coins: Certain coins, such as the one-dollar coin in Hong Kong, have an octagonal shape. This unique design helps in easy identification and adds a distinctive look.
- Tables: Octagonal tables are popular in furniture design. These tables provide ample surface area and a unique style, often seen in dining rooms or as patio furniture.
- Tiles: Octagonal tiles are used in flooring and wall designs. They create interesting patterns and are often combined with square or rectangular tiles for a decorative effect.
- Umbrellas: Some umbrellas are designed with an octagonal canopy. This shape can provide better coverage and a stylish look.
- Fountains: Octagonal shapes are also used in the design of fountains, especially in historical and ornamental gardens, adding symmetry and elegance to the landscape.
- Sports Arenas: The octagonal shape is used in the design of some sports arenas, such as the UFC fighting ring, known as "The Octagon," providing a unique and recognizable setting for competitions.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and aesthetic appeal of octagons in various fields, from traffic management to design and architecture.
How to Calculate the Perimeter of an Octagon
Calculating the perimeter of an octagon is a straightforward process, especially if it is a regular octagon, where all sides are of equal length. Here are the steps to calculate the perimeter:
-
Identify the length of one side of the octagon. Let this length be denoted as a.
-
Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular octagon:
This formula simply multiplies the length of one side by 8, since an octagon has eight sides.
-
Substitute the length of the side into the formula. For example, if the side length a is 5 units:
Calculating this gives:
Thus, the perimeter of the octagon is 40 units.
Here is a quick reference table for different side lengths:
| Side Length (a) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 2 | 16 |
| 3 | 24 |
| 4 | 32 |
| 5 | 40 |
| 6 | 48 |
Using this method, you can calculate the perimeter for any given side length of a regular octagon.

How to Calculate the Area of an Octagon
To calculate the area of a regular octagon, you can use the following formula:
\[ \text{Area} = 2s^2 (1 + \sqrt{2}) \]
Where \( s \) is the length of a side of the octagon.
Step-by-Step Calculation
-
Measure the length of one side of the octagon.
-
Square the side length:
\( s^2 \)
-
Multiply the squared side length by 2:
\( 2s^2 \)
-
Calculate \( 1 + \sqrt{2} \):
\( 1 + \sqrt{2} \approx 2.414 \)
-
Multiply the result from step 3 by the result from step 4:
\( 2s^2 \times (1 + \sqrt{2}) \)
-
The resulting value is the area of the octagon.
Example Calculation
Let's find the area of a regular octagon with a side length of 4 cm.
-
Square the side length:
\( 4^2 = 16 \)
-
Multiply by 2:
\( 2 \times 16 = 32 \)
-
Calculate \( 1 + \sqrt{2} \):
\( 1 + \sqrt{2} \approx 2.414 \)
-
Multiply the results from steps 2 and 3:
\( 32 \times 2.414 \approx 77.25 \)
-
The area of the octagon is approximately 77.25 square cm.
Using an Octagon Calculator
For quick calculations, you can use an octagon calculator. Enter the side length, and the calculator will automatically apply the formula to provide the area. This can be especially useful for verifying your manual calculations or when dealing with complex problems.
Using an Octagon Calculator
Using an octagon calculator simplifies the process of determining various properties of an octagon, such as its area, perimeter, and side length. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use an octagon calculator effectively:
-
Select the Calculation Type: First, decide what you need to calculate – the area, the perimeter, or the side length of the octagon. Choose the appropriate option from the calculator’s dropdown menu.
-
Enter the Given Information: Depending on the calculation type, input the known value. For instance, if calculating the area and you know the side length, enter the side length.
-
Perform the Calculation: Click on the calculate button. The calculator will use the relevant formulas to provide the result. For example:
-
Area Calculation: If you enter the side length \( s \), the calculator will use the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = 2s^2 (1 + \sqrt{2})
\] -
Perimeter Calculation: If you enter the side length \( s \), the calculator will use the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 8s
\]
-
-
Review the Results: The calculator will display the result along with the formula used and the steps involved in the calculation. This not only helps verify the answer but also enhances understanding of the concepts.
Here is an example of calculating the area of a regular octagon with a side length of 4 cm using an octagon calculator:
- Select "Area" from the calculation type dropdown.
- Choose "Side" as the given information and enter 4 cm.
- Click on "Calculate".
- The calculator will show the result:
\[
\text{Area} = 2(4)^2 (1 + \sqrt{2}) = 38.18 \text{ square cm}
\]
Using an octagon calculator is a quick and efficient way to handle these geometric calculations without manual computation.
Examples and Practice Problems
Below are some examples and practice problems to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter and area of an octagon.
Example 1: Calculating the Perimeter of a Regular Octagon
Given a regular octagon with each side measuring 6 cm, find the perimeter.
Solution:
- Identify the formula for the perimeter of a regular octagon: P = 8a, where a is the side length.
- Substitute the given side length into the formula: P = 8 × 6.
- Calculate the result: P = 48 cm.
Example 2: Calculating the Area of a Regular Octagon
Given a regular octagon with each side measuring 4 cm, find the area.
Solution:
- Identify the formula for the area of a regular octagon: A = 2a2(1 + √2), where a is the side length.
- Substitute the given side length into the formula: A = 2(4)2(1 + √2).
- Calculate the result: A = 2 × 16 × (1 + √2) ≈ 77.25 cm2.
Practice Problems
-
Problem 1: A regular octagon has a side length of 7 cm. Calculate its perimeter.
Solution:
- Use the perimeter formula: P = 8a.
- Substitute a = 7: P = 8 × 7 = 56 cm.
-
Problem 2: Calculate the area of a regular octagon with each side measuring 3 cm.
Solution:
- Use the area formula: A = 2a2(1 + √2).
- Substitute a = 3: A = 2(3)2(1 + √2) ≈ 43.45 cm2.
-
Problem 3: An irregular octagon has sides measuring 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm. Find its perimeter.
Solution:
- Add the lengths of all sides: P = 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 44 cm.
HÌNH BÁT GIÁC ĐỀU: DIỆN TÍCH & CHU VI
READ MORE:
Làm thế nào: Tính chu vi của các đa giác